The phenomenon of reduced audio clarity experienced when utilizing Apple AirPods with a personal computer presents a common user frustration. This issue often manifests as a loss of high-frequency detail, a reduction in overall volume, and a perceived lack of richness in the audio output. For example, music may sound flat, and voice communications may lack clarity, hindering effective communication.
Addressing this auditory degradation is important for maintaining a productive workflow and an enjoyable entertainment experience. Clear audio facilitates effective communication during virtual meetings, enhances the appreciation of multimedia content, and reduces listener fatigue. Historically, discrepancies in Bluetooth codec support and driver compatibility between Apple devices and Windows-based systems have contributed to this recurring problem.
The subsequent discussion will delve into the underlying causes of this diminished audio fidelity, explore potential solutions including Bluetooth configuration adjustments, driver updates, and codec selection, and provide practical steps for optimizing the audio output of AirPods when used with a computer.
Optimizing AirPods Audio on PC
The following tips address the issue of degraded audio quality encountered when using AirPods with a personal computer. Implementing these strategies can significantly improve the auditory experience.
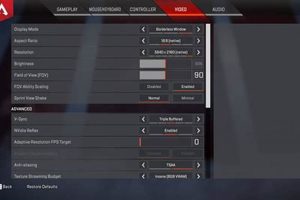
Tip 1: Verify the Active Bluetooth Profile. Ensure that the active Bluetooth profile is set to stereo output rather than the hands-free profile. The hands-free profile, optimized for voice calls, often sacrifices audio fidelity for microphone functionality. Navigate to the sound settings within the operating system to confirm the selected profile.
Tip 2: Update Bluetooth Drivers. Outdated or corrupted Bluetooth drivers can lead to compatibility issues and suboptimal audio transmission. Visit the computer manufacturer’s website or utilize the device manager to identify and install the latest drivers specific to the Bluetooth adapter.
Tip 3: Disable Audio Enhancements. Certain audio enhancements, such as loudness equalization or virtual surround sound, can negatively impact the clarity of the audio signal when using AirPods. These enhancements, often found within the sound control panel, should be disabled to achieve a more neutral and accurate sound reproduction.
Tip 4: Adjust the Default Format. In the sound settings, experiment with different default formats (e.g., 16 bit, 44100 Hz (CD Quality) or 24 bit, 48000 Hz (Studio Quality)). Selecting a higher bit depth and sample rate can potentially improve the overall audio resolution and reduce the perceived muffled effect.
Tip 5: Investigate Codec Support. The specific Bluetooth codec used for audio transmission can significantly influence sound quality. While AirPods primarily utilize AAC, some computers may default to SBC, a lower-quality codec. Tools may be available to force AAC encoding, contingent upon hardware compatibility.
Tip 6: Proximity and Interference. Bluetooth signals are susceptible to interference from other electronic devices and physical obstructions. Ensure that the computer and AirPods are in close proximity and free from potential sources of signal disruption such as microwaves or other Bluetooth devices operating on the same frequency.
By systematically addressing these potential causes of reduced audio quality, users can often achieve a noticeable improvement in the sound experienced when using AirPods with a computer. Consistent audio fidelity is essential for both professional and leisure activities.
The next section will outline advanced troubleshooting steps for persistent issues, including external hardware solutions and software-based modifications.
1. Bluetooth Profile Selection
Incorrect Bluetooth profile selection represents a primary cause of diminished audio clarity experienced when utilizing AirPods with a personal computer. The Bluetooth protocol incorporates multiple profiles, each designed for specific functions. AirPods typically support two primary profiles: A2DP (Advanced Audio Distribution Profile) for high-quality stereo audio output and HFP/HSP (Hands-Free Profile/Headset Profile) for voice communication. If the computer erroneously selects the HFP/HSP profile, designed for microphone use and lower-bandwidth audio, the resulting sound quality will be significantly degraded. This manifests as a “muffled” sound due to the profile’s emphasis on voice frequencies and reduced bandwidth for richer audio.
The operating system’s sound control panel governs Bluetooth profile selection. For instance, after connecting AirPods, the sound settings may default to “AirPods Hands-Free AG Audio” instead of “AirPods Stereo.” Manually switching to the “Stereo” option corrects this issue, enabling A2DP and restoring high-fidelity audio. A practical example of this problem is occurring when joining a video conference; the system automatically switches to the HFP/HSP profile for microphone access, and sometimes it fails to revert to A2DP after the call concludes, necessitating manual adjustment. Understanding this distinction and the ability to manually select the appropriate profile is critical for optimal audio performance.
Effective Bluetooth profile management, therefore, requires vigilance. The operating system does not always reliably choose the ideal profile. Persistent muffled audio from AirPods on a computer often signals an incorrect profile assignment. Regular verification of the active Bluetooth profile within the sound settings and manual correction when necessary represents a vital step in troubleshooting and resolving such audio degradation. The correct profile ensures AirPods operate according to their intended capabilities, delivering a clear and balanced sound output.
2. Driver Compatibility Status
The operating system’s ability to correctly interface with Bluetooth devices like AirPods is largely determined by the installed drivers. Incompatible, outdated, or corrupted Bluetooth drivers can directly lead to audio degradation, manifesting as muffled sound. The driver acts as a translator between the hardware (Bluetooth adapter) and the operating system, enabling proper communication and audio signal processing. When driver compatibility is compromised, the system may fail to utilize the correct audio codecs, negotiate optimal bitrates, or manage the connection stability, resulting in subpar audio output.
Real-life examples are pervasive. Consider a scenario where a recent Windows update introduces incompatibilities with the existing Bluetooth drivers. Users might suddenly experience muffled audio with their AirPods, despite having previously enjoyed clear sound. Updating to the latest drivers provided by the computer manufacturer or directly from the Bluetooth adapter vendor often resolves this issue. Similarly, generic drivers provided by the operating system may lack the specific optimizations required for AirPods, leading to reduced performance. Practical significance lies in proactive driver management; regularly checking for and installing the latest compatible drivers can prevent or address audio degradation problems.
In summary, the status of Bluetooth drivers is critically linked to audio quality when using AirPods with a computer. Incompatibility and outdated drivers hinder proper audio processing, often leading to muffled sound. Regular driver updates and verification of compatibility ensure optimal communication between the operating system and the Bluetooth adapter, mitigating audio degradation and maximizing the AirPods’ audio potential. Maintaining driver compatibility is essential for ensuring that AirPods function correctly on a computer and deliver their intended audio performance.
3. Codec Negotiation Issues
Codec negotiation failures between a personal computer and Apple AirPods represent a significant factor contributing to compromised audio quality. When devices fail to agree on a suitable codec, the resulting audio can exhibit characteristics of muffled sound, reduced fidelity, and an overall degraded listening experience. This results from utilizing a less efficient codec, or one unsuited to the AirPods capabilities.
- Bluetooth Codec Hierarchy
Bluetooth audio codecs operate within a hierarchy of quality and complexity. AirPods primarily support AAC (Advanced Audio Coding), a codec known for its efficient compression and reasonable audio fidelity. However, a computer may default to SBC (Subband Codec), a mandatory but less efficient codec present in all Bluetooth devices, if AAC support is absent or improperly negotiated. SBC has a lower bitrate and a simpler compression algorithm, resulting in reduced audio quality. The shift to SBC would explain the compromised sound that becomes evident.
- Operating System Limitations
Operating systems handle Bluetooth codec selection differently. Some Windows versions may not prioritize AAC or may have limitations in their Bluetooth stack that hinder proper AAC negotiation. This can force the use of SBC even when the hardware is capable of AAC transmission. A typical scenario involves a Windows computer connecting to AirPods and defaulting to SBC without providing an option to switch to AAC within the system settings. Third-party software or registry tweaks are sometimes required to address such operating system limitations.
- Driver Influence on Codec Selection
Bluetooth drivers play a crucial role in codec negotiation. Outdated or incorrectly configured drivers may fail to properly advertise the computer’s AAC capabilities to the AirPods, resulting in the selection of SBC. Conversely, updated drivers optimized for Bluetooth audio can facilitate correct codec negotiation. For example, installing the latest Bluetooth drivers from the computer manufacturer’s website can sometimes resolve codec negotiation issues and improve audio quality by enabling AAC.
- Hardware Compatibility Constraints
While AirPods and most modern computers support AAC, older or less capable Bluetooth adapters may lack the necessary hardware to efficiently encode and decode AAC audio. In such cases, the system may revert to SBC to ensure stable audio transmission, sacrificing sound quality. This limitation highlights the importance of ensuring that the computers Bluetooth hardware meets the minimum specifications for high-quality audio streaming. An older computer might negotiate SBC due to these limitations, even though the AirPods themselves are fully capable of AAC.
In conclusion, codec negotiation issues form a complex interaction between the AirPods, the computers operating system, Bluetooth drivers, and hardware capabilities. When these components fail to correctly negotiate and utilize AAC, the resulting audio quality can suffer noticeably. Resolving this issue often requires a multifaceted approach that includes driver updates, operating system adjustments, and hardware verification, all aimed at ensuring the proper utilization of the higher-quality AAC codec for optimal audio transmission.
4. Interference Sources Nearby
Electromagnetic interference from surrounding devices can significantly contribute to the perceived degradation of audio quality when using AirPods with a computer, often manifesting as muffled sound. Bluetooth, the wireless technology facilitating audio transmission between the AirPods and the computer, operates within a specific frequency range susceptible to disruption from various electronic sources. These interference sources compromise the integrity of the wireless signal, leading to data loss, reduced bandwidth, and subsequently, diminished audio fidelity. The proximity of devices emitting radio frequencies, such as microwaves, Wi-Fi routers, cordless phones, and other Bluetooth-enabled devices, increases the likelihood of signal interference.
The impact of interference is practical and observable. For example, operating a microwave oven while simultaneously using AirPods can noticeably degrade audio quality, introducing static, dropouts, or a muffled sound. Similarly, a congested Wi-Fi environment with numerous devices transmitting data can create a “noisy” wireless landscape, impeding the clear transmission of audio data to the AirPods. Real-world scenarios such as working in a densely populated office environment with multiple wireless devices often reveal the tangible impact of interference. Addressing this involves identifying potential interference sources and increasing the physical separation between these sources and the computer or AirPods. Sometimes simply changing the orientation of the computer or relocating the Bluetooth receiver can reduce the issue.
In summary, understanding the role of interference sources in audio degradation is crucial for troubleshooting and optimizing AirPods performance. Recognizing potential sources of interference allows for proactive measures, such as minimizing proximity and mitigating competing wireless signals, to improve audio clarity. While other factors such as codec negotiation and driver compatibility are important, the often overlooked impact of environmental interference can be a significant contributor to the issue. Addressing interference is key to ensuring the stability and quality of Bluetooth audio transmission, and thus helps optimize the overall listening experience when using AirPods with a computer.
5. Audio Enhancement Settings
The configuration of audio enhancement settings within an operating system frequently influences the perceived audio quality when utilizing Apple AirPods with a personal computer. These software-based adjustments, designed to modify the audio output, can inadvertently introduce distortions or alterations that manifest as a “muffled” sound, impacting the intended fidelity of the AirPods.
- Loudness Equalization
Loudness equalization, an enhancement intended to normalize volume levels across different audio sources, often compresses the dynamic range of the audio signal. By reducing the difference between the quietest and loudest sounds, this feature can diminish subtle nuances and create a flattened, less detailed soundscape. When applied to AirPods, loudness equalization can eliminate the subtle details, resulting in a perceived lack of clarity and an overall “muffled” effect. For example, in music, the quiet details in the music become less audible, causing some of the frequencies to be less dominant, therefore, making them have diminished clarity and detail.
- Virtual Surround Sound
Virtual surround sound attempts to simulate a multi-channel audio environment using stereo headphones like AirPods. These algorithms often introduce artificial reverberation and phase shifts to create the illusion of spatial audio. However, these effects can also muddy the soundstage and obscure finer details, contributing to a “muffled” perception. In practice, activating virtual surround sound can add artificial spatial cues that compete with the AirPods’ natural sound reproduction, blurring the distinct separation of instruments or voices and diminishing overall clarity.
- Bass Boost/Treble Boost
Adjustments that emphasize either bass or treble frequencies can disproportionately alter the sound balance, leading to a perceived “muffled” quality. Excessive bass boost can overpower the higher frequencies, obscuring details in the midrange and treble regions. Conversely, exaggerated treble boost can introduce harshness and sibilance, masking other sonic elements. Applying such enhancements to AirPods can disrupt their intended frequency response, creating an unbalanced sound profile that listeners perceive as less clear or “muffled”.
- Room Correction
Some audio drivers include room correction features designed to compensate for acoustic imperfections in the listening environment. These algorithms analyze the sound output and apply filters to flatten the frequency response. However, if the room correction is not properly calibrated or is applied inappropriately, it can introduce unintended alterations that negatively impact audio clarity, leading to a “muffled” sound. For example, an attempt to correct for a non-existent acoustic issue can result in a distorted or unnatural sound profile.
In conclusion, audio enhancement settings, while intended to improve the listening experience, can paradoxically contribute to diminished audio quality when using AirPods with a computer. Features like loudness equalization, virtual surround sound, and frequency-specific boosts can alter the audio signal in ways that obscure detail and create a “muffled” effect. Disabling these enhancements often results in a clearer, more accurate sound reproduction that aligns with the inherent capabilities of the AirPods.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding the degraded audio experienced when using Apple AirPods with a personal computer.
Question 1: Why does the audio from AirPods sound muffled when connected to a PC compared to an iPhone?
The difference in audio quality often stems from codec negotiation and Bluetooth profile selection. PCs may default to the SBC codec or the Hands-Free Profile (HFP), while iPhones typically prioritize AAC and the A2DP stereo profile. This discrepancy results in reduced bandwidth and a diminished frequency response on the PC, leading to a muffled sound.
Question 2: How can Bluetooth drivers influence audio quality when using AirPods on a PC?
Bluetooth drivers serve as the intermediary between the operating system and the Bluetooth adapter. Outdated, incompatible, or corrupted drivers can hinder proper codec negotiation and introduce instability, resulting in a compromised audio signal. Regular driver updates are essential for optimal performance.
Question 3: Are audio enhancements in Windows responsible for the muffled sound in AirPods?
Audio enhancements such as loudness equalization, virtual surround sound, and bass boost can alter the audio signal in ways that negatively impact clarity. These enhancements can compress the dynamic range, introduce artificial reverberation, or distort the frequency response, contributing to a muffled perception. Disabling these enhancements is often advisable.
Question 4: Is there a connection between Bluetooth version and audio quality with AirPods on a PC?
The Bluetooth version can influence audio quality. Newer Bluetooth versions generally support higher bandwidth and more efficient codecs, potentially improving audio fidelity. However, the computers Bluetooth adapter and drivers must also be compatible with the latest standards to realize these benefits.
Question 5: Does the distance between the PC and AirPods affect the audio quality?
Yes, distance and obstructions can significantly impact Bluetooth signal strength and stability. Increased distance and physical barriers can weaken the signal, leading to data loss, dropouts, and a reduction in audio fidelity. Maintaining close proximity and minimizing obstructions can improve audio quality.
Question 6: How can interference from other devices cause AirPods audio to sound muffled on a PC?
Electromagnetic interference from devices such as microwaves, Wi-Fi routers, and other Bluetooth devices can disrupt the Bluetooth signal between the PC and AirPods. This interference can introduce static, dropouts, or a general degradation in audio quality, contributing to a muffled sound. Minimizing proximity to these devices is recommended.
In summary, achieving optimal audio quality with AirPods on a PC involves addressing codec selection, driver compatibility, audio enhancement settings, Bluetooth version, distance, and potential interference sources. A systematic approach to these factors is crucial for resolving muffled audio issues.
The following section provides a technical deep dive into advanced troubleshooting techniques for persistent audio quality problems.
Conclusion
The preceding analysis has thoroughly examined the multifaceted issue of degraded audio quality experienced when using AirPods with a personal computer. The investigations encompassed Bluetooth profile selection, driver compatibility status, codec negotiation failures, potential interference sources, and the impact of audio enhancement settings. It has been established that a confluence of these factors can result in the phenomenon whereby airpods sounds muffled on pc, hindering optimal audio experiences.
The successful mitigation of compromised audio requires diligent troubleshooting and a proactive approach to system configuration. As Bluetooth technology continues to evolve, sustained vigilance regarding driver updates and codec support will remain essential for maximizing the potential of wireless audio devices on computer platforms. Further research into optimizing Bluetooth audio transmission within diverse computing environments is warranted to ensure consistent and high-fidelity audio experiences across all devices.


![Fix: Adobe Audition Makes Sound Muffled [Solved!] Safem Fabrication - Precision Engineering & Custom Manufacturing Solutions Fix: Adobe Audition Makes Sound Muffled [Solved!] | Safem Fabrication - Precision Engineering & Custom Manufacturing Solutions](https://dnamufflers.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/th-559-300x200.jpg)
![Fix: Why Does My Phone Sound Muffled? [Easy Guide] Safem Fabrication - Precision Engineering & Custom Manufacturing Solutions Fix: Why Does My Phone Sound Muffled? [Easy Guide] | Safem Fabrication - Precision Engineering & Custom Manufacturing Solutions](https://dnamufflers.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/th-540-300x200.jpg)


