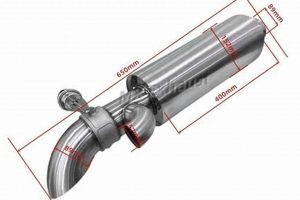
The source of an unusual noise emanating from a vehicle’s exhaust system, specifically a metallic vibrating sound occurring during operation, often stems from internal or external issues affecting the exhaust components. Such a sound indicates a potential problem within the system itself or with its connections to the vehicle. The sound’s characteristics and timing are crucial in identifying the underlying cause and guiding appropriate repair strategies.
Addressing abnormal exhaust noises is vital for maintaining vehicle performance, fuel efficiency, and environmental compliance. Undiagnosed issues can lead to more significant damage, increased repair costs, and potential safety hazards. Furthermore, a properly functioning exhaust system plays a crucial role in managing emissions and minimizing harmful pollutants released into the atmosphere. Timely identification and rectification of noise problems are therefore essential for responsible vehicle ownership.
Potential causes for such noises include loose or damaged heat shields, internal component failure within the silencer, compromised exhaust hangers, or contact between the exhaust system and other parts of the vehicle’s undercarriage. A thorough inspection of these areas will typically reveal the origin of the unwanted sound, enabling effective remediation.
Diagnostic and Remedial Guidance Regarding Exhaust System Rattling
The following guidelines provide a structured approach to identifying and resolving the causes of exhaust system noise issues. Careful adherence to these procedures will facilitate effective troubleshooting and repair.
Tip 1: Visual Examination of Exhaust Components: Begin with a comprehensive visual assessment of the entire exhaust system, from the manifold to the tailpipe. Observe the condition of pipes, welds, and connections for signs of rust, corrosion, or physical damage. Note any areas where components appear loose or detached.
Tip 2: Heat Shield Inspection: Pay particular attention to the heat shields surrounding the exhaust components. These shields are often thin and prone to corrosion, leading to detachment and subsequent rattling. Secure loose shields with appropriate fasteners or replace them if significantly damaged.
Tip 3: Exhaust Hanger Assessment: Inspect the rubber exhaust hangers that support the system. Deteriorated or broken hangers allow excessive movement, which can cause the exhaust system to contact other vehicle components, generating noise. Replace worn hangers to ensure proper support and isolation.
Tip 4: Internal Muffler Evaluation: If external components appear sound, the source of the sound may reside within the silencer itself. Internal baffles can become detached or corroded, resulting in a metallic vibration. Replacement of the silencer is typically the most effective solution in this scenario.
Tip 5: Clearance Verification: Ensure adequate clearance between the exhaust system and other undercarriage components, such as the chassis, suspension, and fuel lines. Insufficient clearance can result in contact and noise generation, particularly during vehicle movement or engine vibration. Adjust exhaust system positioning as needed.
Tip 6: Professional Diagnostic Assistance: If the source of the noise remains elusive, seek assistance from a qualified automotive technician. Specialized diagnostic equipment and expertise may be required to pinpoint the underlying cause and implement appropriate repairs.
Addressing exhaust system noise promptly prevents further damage and maintains optimal vehicle performance. Systematic troubleshooting, coupled with appropriate repair procedures, ensures the integrity and longevity of the exhaust system.
Following these diagnostic and remedial guidelines facilitates effective management of exhaust system noise problems. Continued maintenance practices will contribute to long-term vehicle reliability and environmental responsibility.
1. Corrosion.
Corrosion is a significant factor contributing to exhaust system malfunctions and subsequent noise generation. It weakens structural integrity and accelerates the deterioration of critical components, directly impacting the functionality and sound characteristics of the exhaust system.
- Heat Shield Degradation
Heat shields, typically constructed from thin metal, are particularly vulnerable to corrosion due to their exposure to extreme temperatures and road salts. As corrosion progresses, the heat shield’s mounting points weaken, leading to loosening and subsequent rattling against the exhaust pipe. This is a common source of unwanted noise.
- Muffler Body Perforation
The silencer, exposed to both external moisture and internal combustion byproducts, is susceptible to rust. Corrosion can weaken the silencer’s outer shell, eventually creating perforations. These holes alter the internal acoustics, causing abnormal sounds. Furthermore, internal components within the silencer may corrode and detach, generating rattling noises.
- Exhaust Pipe Weakening
Corrosion along exhaust pipes weakens their structural integrity, making them more prone to vibrations and potential failure. Severely corroded pipes may develop pinholes or cracks, which alter exhaust gas flow and create hissing or sputtering sounds, potentially accompanied by rattling from loose sections.
- Hanger Attachment Point Failure
The points where exhaust hangers attach to the system are prime locations for corrosion, especially at welds. As corrosion weakens these attachment points, the hangers become less effective in supporting the exhaust system. This increased movement amplifies vibrations and can result in the exhaust system striking other vehicle components, generating rattling noises.
The cumulative effect of corrosion across various exhaust system components directly contributes to unwanted noises. Regular inspection and preventative measures, such as rust inhibitors, can mitigate the detrimental effects of corrosion and prolong the lifespan of the exhaust system, thereby reducing the likelihood of problematic sounds.
2. Loose Heat Shields.
Detached or improperly secured thermal barriers surrounding exhaust components represent a significant contributor to unusual noises emanating from a vehicle’s undercarriage. These shields, designed to mitigate heat transfer, can become dislodged, resulting in vibrational sounds that are frequently misattributed to other exhaust system malfunctions.
- Vibrational Resonance
When a heat shield becomes detached or partially secured, it is free to vibrate against the exhaust pipe or adjacent vehicle components. The frequency of these vibrations often falls within an audible range, producing a metallic rattling or buzzing sound that is particularly noticeable during engine operation or when the vehicle is in motion. The sound’s intensity is influenced by the engine’s RPM and the vehicle’s speed.
- Material Degradation and Fastener Failure
Heat shields are typically fabricated from thin gauge aluminum or stainless steel, materials susceptible to corrosion, particularly in regions with road salt usage. Corrosion weakens the shield’s structural integrity, compromising the mounting points. Fasteners, such as bolts or clips, may also corrode or break, further contributing to the shield’s loosening and subsequent ability to vibrate.
- Acoustic Amplification
The shape and proximity of the heat shield to the exhaust pipe can amplify the vibrational sound. The shield acts as a resonant chamber, intensifying the perceived noise level. This amplification effect can make it challenging to pinpoint the source of the sound without a thorough inspection.
- Misdiagnosis and Delayed Repair
The location and nature of heat shield sounds often lead to misdiagnosis. Individuals may assume the sound originates from within the muffler or catalytic converter, resulting in unnecessary and costly repairs. A proper diagnosis involves a careful visual inspection of the heat shields and their attachment points to identify any looseness or damage.
In summary, compromised thermal barriers are frequent generators of distracting auditory disturbances within the exhaust system. Identifying and rectifying issues related to heat shields is a critical step in addressing unusual exhaust sounds, preventing misdiagnosis, and maintaining overall vehicle integrity.
3. Internal Baffle Damage.
Internal baffle damage within a muffler is a primary contributor to the presence of rattling sounds emanating from the exhaust system. The silencer contains a series of baffles designed to attenuate sound waves generated by the engine. These components redirect and diffuse sound energy, reducing the overall noise level emitted from the vehicle. When these baffles become detached, corroded, or otherwise compromised, their intended function is disrupted, leading to a characteristic rattling noise.
The cause-and-effect relationship is direct: compromised internal baffles are unable to effectively dampen sound. Instead, they vibrate freely within the muffler casing, producing metallic rattling sounds. This noise is particularly noticeable during engine idling, acceleration, and deceleration when exhaust gas flow fluctuates. The severity of the sound corresponds to the extent of the internal damage. For example, a single detached baffle may produce a faint rattle, while multiple damaged baffles can generate a pronounced and consistent noise. The location of the damage also influences the specific sound characteristics; baffles closer to the inlet pipe may produce a higher-pitched rattle, while those near the outlet may generate a deeper tone.
Understanding the connection between internal baffle damage and exhaust system noise is of practical significance for accurate diagnosis and repair. Technicians can use this knowledge to differentiate between rattling caused by internal silencer problems and issues originating from external sources, such as loose heat shields or exhaust hangers. The ability to accurately identify the root cause enables targeted repairs, avoiding unnecessary component replacements. When internal silencer damage is confirmed, replacement of the entire unit is typically the most effective solution, restoring proper exhaust system function and eliminating the unwanted noise.
4. Broken Exhaust Hangers.
Deteriorated or fractured exhaust hangers significantly contribute to exhaust system noise due to the loss of secure mounting. These hangers, typically constructed of rubber or metal with rubber insulators, are designed to isolate the exhaust system from the vehicle’s chassis, minimizing vibration transfer and preventing contact between the exhaust components and the vehicle body. When these hangers fail, the exhaust system’s movement is no longer adequately restricted, allowing it to vibrate excessively and potentially collide with other parts of the vehicle. This contact generates metallic rattling or banging noises, which are particularly noticeable during engine operation, acceleration, and when traversing uneven road surfaces. The compromised stability also places additional stress on other exhaust components, accelerating wear and potentially leading to further failures, such as cracked pipes or damaged welds. The sound produced is a direct result of the physical interaction between the unrestrained exhaust system and the vehicle’s undercarriage.
One common scenario illustrating the impact of failed exhaust hangers involves the silencer contacting the vehicle’s frame. The silencer, being a relatively large and heavy component, generates considerable force when vibrating. Without the proper support of functional hangers, the silencer may repeatedly strike the frame, producing a loud, resonant rattling noise. Similarly, the exhaust pipe itself can come into contact with suspension components or the vehicle’s floor pan, leading to similar auditory disturbances. Furthermore, broken hangers can cause the exhaust system to sag, reducing ground clearance and increasing the risk of damage from road debris. In regions with harsh winter conditions and road salting, corrosion accelerates the deterioration of exhaust hangers, increasing the likelihood of failure.
In summary, the structural integrity of exhaust hangers is essential for maintaining a quiet and properly functioning exhaust system. Neglecting to address damaged or broken hangers not only leads to unwanted noises but also increases the risk of further component damage and potential safety hazards. Regular inspection and timely replacement of worn exhaust hangers are therefore crucial maintenance practices for preserving the longevity and performance of the exhaust system and ensuring a comfortable driving experience.
5. Component Contact.
Physical interaction between elements of the exhaust system and other undercarriage components is a frequent cause of extraneous noises, including the specific rattling sound often associated with silencer issues. Insufficient clearance, compromised mounting, or structural deformation can lead to such contact, translating vibrations into audible disturbances.
- Chassis Interference
Exhaust system components, particularly the silencer and exhaust pipes, may come into contact with the vehicle’s chassis due to sagging supports or misalignment. Engine vibrations and road irregularities then transmit through these components to the chassis, generating a resonant rattling or knocking sound. The specific frequency and intensity of the noise vary depending on the contact point and the engine’s operating conditions. This issue is commonly observed after repairs where the exhaust system was not properly realigned.
- Suspension System Interaction
Proximity to suspension components creates opportunities for contact, especially during vehicle operation involving suspension articulation. The exhaust pipe can strike suspension arms, springs, or shock absorbers, producing a metallic clanging or rattling sound. This type of contact is often intermittent, occurring only during specific driving maneuvers or when the suspension is heavily loaded. The severity of the sound depends on the force of the impact and the materials involved.
- Heat Shield Proximity
While heat shields are intended to protect surrounding components, they can become a source of noise if they are bent, loose, or improperly positioned. Contact between a heat shield and the exhaust pipe or other undercarriage components generates a buzzing or rattling sound, particularly when the engine is at operating temperature. The thermal expansion of the exhaust system can exacerbate this issue, increasing the frequency and intensity of the sound. Corrosion can also contribute by weakening the shield’s mounting points, increasing the likelihood of contact.
- Fuel and Brake Line Interference
Although less common, direct contact between the exhaust system and fuel or brake lines poses a significant safety risk. The heat from the exhaust can damage these lines, potentially leading to fuel leaks or brake failure. Even without direct contact, proximity can cause excessive heat transfer, affecting the performance and longevity of these critical systems. Any unusual noises accompanied by a burning smell or noticeable changes in vehicle performance should be immediately investigated to rule out this type of interference.
Consequently, diagnosing rattling sounds necessitates a comprehensive inspection of the exhaust system’s routing and mounting, ensuring adequate clearance from surrounding components. Rectifying issues related to component contact prevents further damage, eliminates unwanted noises, and ensures the safe operation of the vehicle.
6. Weld Failures.
The structural integrity of an exhaust system relies heavily on the quality and durability of its welded joints. Weld failures directly contribute to noise generation, including rattling sounds, stemming from compromised connections between exhaust components. These failures disrupt the intended gas flow, create points of vibrational instability, and can ultimately lead to component separation. Considering the extreme operating conditions of an exhaust systemhigh temperatures, corrosive gases, and constant vibrationwelds represent a vulnerable point susceptible to fatigue and degradation over time.
A common example involves the welds connecting the silencer to the exhaust pipes. If these welds crack or fail completely, the silencer becomes partially or fully detached. This detachment introduces excessive movement, allowing the silencer to vibrate against the vehicle’s undercarriage or other exhaust components. The resulting metallic rattling noise is a direct consequence of the weld failure. Similarly, welds securing mounting brackets or heat shields can fail, leading to rattling as these components become loose and vibrate against the exhaust pipes. The location and severity of the weld failure will influence the characteristics of the noise, with larger cracks or complete separations producing louder and more consistent sounds.
Therefore, understanding the role of weld failures in the genesis of exhaust system noises is essential for accurate diagnosis and effective repair. A thorough inspection should include careful examination of all welded joints for signs of cracking, corrosion, or separation. Addressing weld failures promptly through re-welding or component replacement prevents further damage and eliminates the source of the unwanted noise, maintaining the exhaust system’s functionality and minimizing potential safety hazards.
7. Debris Impact.
Strike from foreign objects encountered during vehicle operation, constitutes a tangible threat to exhaust system integrity, potentially precipitating internal or external damage that results in the generation of rattling noises. The severity and nature of these noises are contingent on the size, mass, and velocity of the impacting object, as well as the specific location and vulnerability of the exhaust component affected. This impact can compromise structural integrity, leading to both immediate and latent auditory disturbances.
- Physical Deformation of Exhaust Pipes
Substantial impacts from road debris, such as rocks or large pieces of metal, can create dents or bends in exhaust pipes. These deformations disrupt the smooth flow of exhaust gases, potentially causing internal turbulence and generating rattling or whistling sounds. Furthermore, a bent pipe can contact other vehicle components, leading to secondary rattling due to vibration transfer.
- Compromised Heat Shield Integrity
Heat shields, typically constructed of thin metal, are particularly susceptible to damage from road debris. Direct impacts can bend or tear these shields, loosening their mounting points and allowing them to vibrate against the exhaust pipe. The resulting rattling noise is often described as a metallic buzzing or fluttering sound, particularly noticeable during acceleration.
- Internal Silencer Damage
While the silencer is designed to withstand internal pressure, external impacts can compromise its structural integrity. Impacts from debris can dent or puncture the silencer casing, potentially damaging internal baffles. Detached or damaged baffles will then rattle freely within the silencer, producing a distinct metallic rattling sound. This type of damage often necessitates complete silencer replacement.
- Catalytic Converter Substrate Fracturing
The catalytic converter contains a fragile ceramic substrate that can be fractured by significant impacts. While a fractured substrate may not immediately generate rattling noises, the resulting increase in exhaust backpressure and altered gas flow can cause vibrations in other exhaust components, eventually leading to rattling sounds. Moreover, the fractured substrate can disintegrate over time, creating loose particles that rattle within the converter housing.
Accordingly, the consequences of impact from detritus are diverse, ranging from superficial cosmetic damage to more severe structural compromise that directly contributes to unwanted auditory emissions. Consistent with prudent vehicle management, a thorough undercarriage assessment is advisable following encounters with road obstacles, enabling timely identification and rectification of induced anomalies, and thereby preventing escalating complications.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following section addresses common inquiries regarding noises stemming from a vehicle’s exhaust system. This information aims to provide clarity and guidance for vehicle owners and maintenance personnel.
Question 1: What signifies that metallic vibration originates from the exhaust system?
A metallic vibration, particularly noticeable during engine operation, acceleration, or deceleration, often suggests an exhaust system issue. Further inspection is necessary to pinpoint the exact source.
Question 2: What potential risks arise from disregarding noises within the exhaust framework?
Ignoring abnormal sounds can lead to escalating damage, reduced fuel efficiency, increased emissions, and potential safety hazards due to component failure.
Question 3: Can corrosion realistically trigger disturbances within the silencer structure?
Yes, corrosion weakens metal components, causing the degradation of thermal barriers, pipe structures, and internal baffle systems within the silencer, ultimately precipitating rattling occurrences.
Question 4: Where does failure typically manifest with support hardware and how does that promote an environment for disruptive sounds?
Failure usually appears at rubber insulators or metal fasteners. This loss facilitates unrestrained movement and potential impacts against chassis members, generating rattling disturbances.
Question 5: Is there utility in a regular inspection schedule focused on the exhaust assembly?
A regimen of systematic examination identifies latent fissures, decrepit hardware, or improper routing, enabling preemptive intervention against larger complications.
Question 6: Is repair for anomalies usually approachable via DIY methods or does this ordinarily necessitate third-party intervention by competent, trained professionals?
Minor repairs, such as heat shield tightening, may be DIY-approachable. Complex issues, however, necessitate the diagnostic precision and tooling of a qualified technician.
Prompt attention to exhaust system anomalies safeguards the health of a vehicular investment. Consistent management is an advantageous directive.
The following section addresses relevant terminologies.
Conclusion
Exhaust system noises, specifically a rattling sound, frequently originate from a confluence of factors ranging from corrosion and impact damage to component failure and inadequate mounting. The source can reside externally, such as with loose heat shields or damaged hangers, or internally, with degraded silencer components. Accurate diagnosis requires a systematic approach, encompassing visual inspection, component testing, and, when necessary, professional consultation. Identifying and addressing the root cause mitigates further system degradation and potential safety hazards.
Understanding the complex interplay of elements contributing to exhaust system rattling promotes responsible vehicle ownership and maintenance. Diligence in regular inspections and prompt attention to anomalous sounds ensures system longevity, efficient operation, and minimizes environmental impact. Continued vigilance remains paramount in preserving the integrity and performance of this critical automotive system.