
Best Mike's Muffler & Custom Exhaust Near You: Experts!
8 January 2026
0 comment
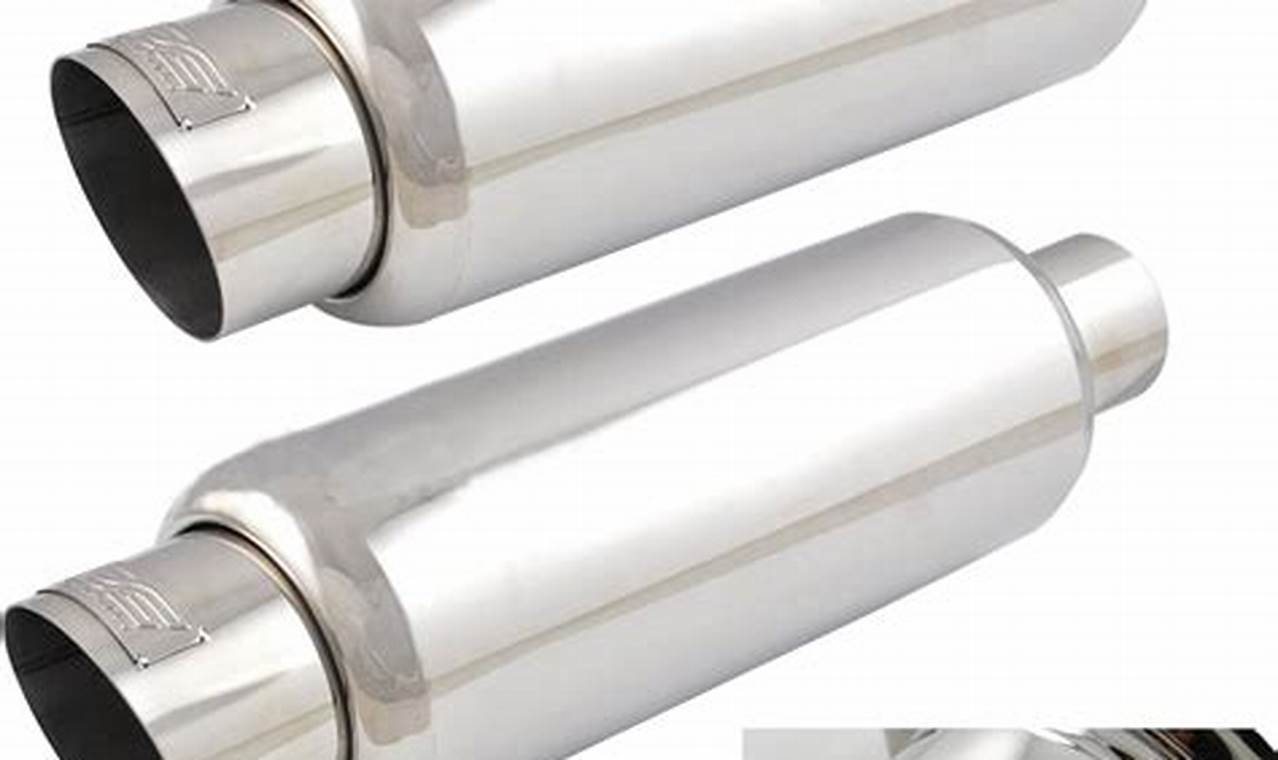

Maximize Your Ride: DC Sports Exhaust Muffler Power!
7 January 2026
0 comment

Exhaust vs. Muffler: Key Differences Explained + Tips
7 January 2026
0 comment

Walker Exhaust: SoundFX Muffler Upgrade | Deep Tone
5 January 2026
0 comment
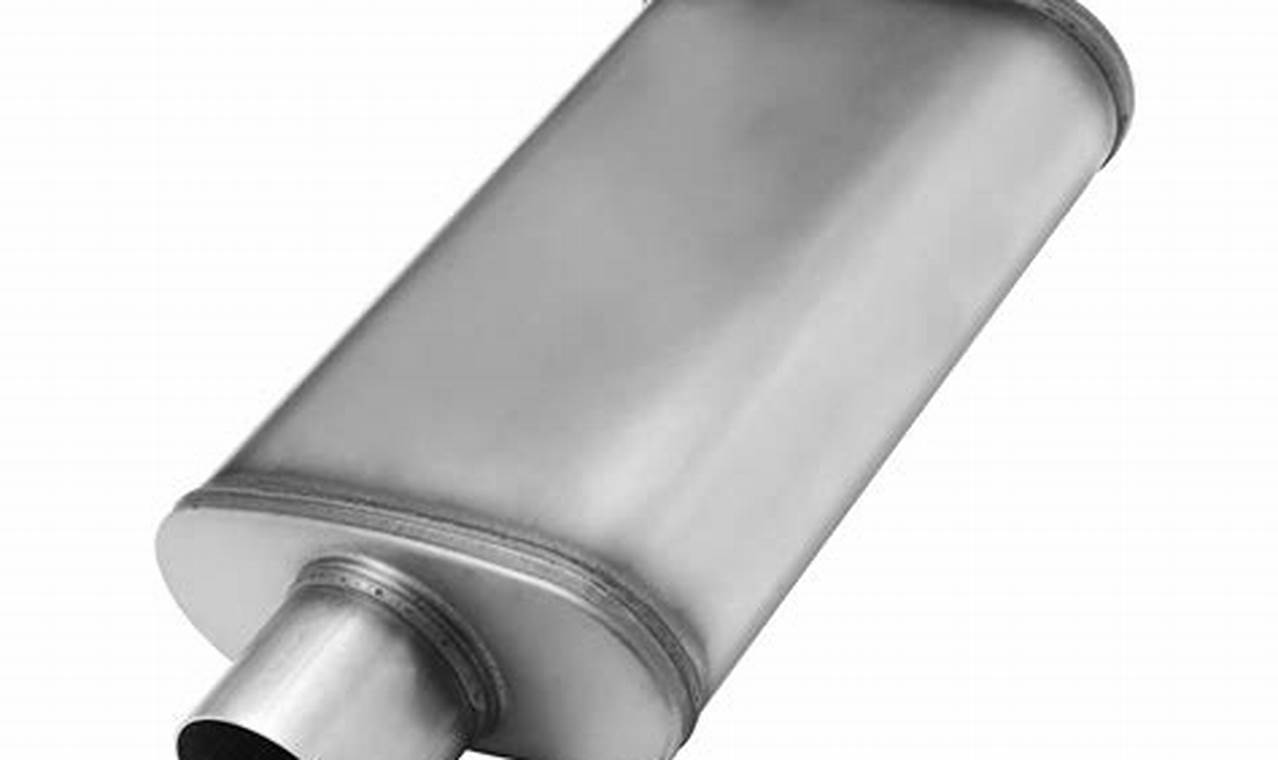

7 March 2026
0 comment
The components responsible for vehicle deceleration and exhaust noise reduction are critical systems for safe and compliant...

7 October 2025
0 comment
A specific automotive service location situated in a particular geographic area is the focal point. This entity...

Monro Muffler Carthage NY: Expert Car Care Nearby
6 October 2025
0 comment

Saranac Lake's Monro Muffler: Expert Exhaust & More!
4 October 2025
0 comment

Best TP Brake & Muffler Repair Near Rome NY: Experts!
4 October 2025
0 comment
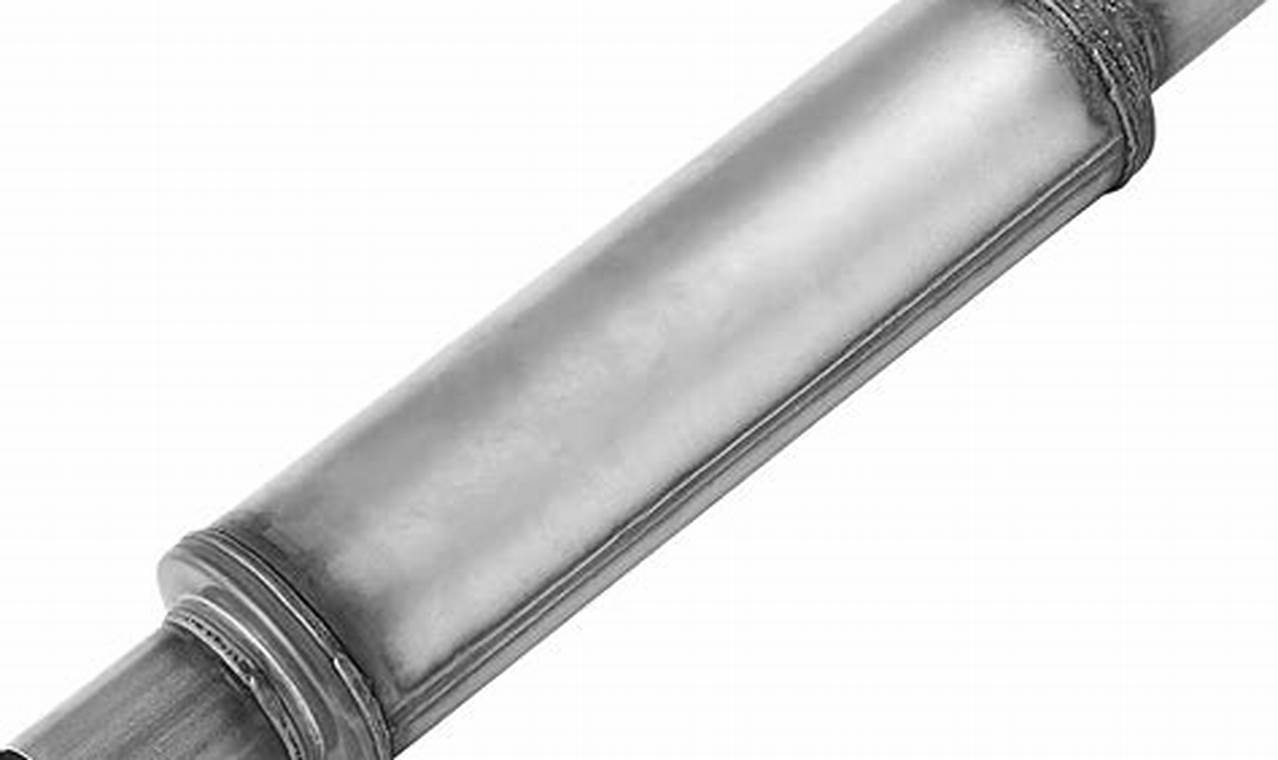

22 October 2025
0 comment
A cylindrical component, typically constructed from steel or aluminum, with a three-inch diameter, designed for integration into...

Kingsport's Jeff's Pipe & Muffler: Expert Exhaust
21 October 2025
0 comment

DIY Muffler Pipe Repair Tips: Extend Your Pipe Life!
21 October 2025
0 comment

Why Exhaust Pipe & Muffler Disconnected? Causes & Fixes
20 October 2025
0 comment
Help! Ear Ache & Muffled Hearing: Causes & Relief
22 October 2025
0 comment
Otalgia, often accompanied by a diminished capacity to perceive auditory stimuli clearly, can stem from various etiologies....

Quiet Ride: Honda Accord Muffler Excellence
8 March 2026
0 comment
An exhaust system component designed to reduce engine noise on a specific vehicle model. This part diminishes...
Fixing Muffled Mic Sound: Causes & Solutions
8 March 2026
0 comment

Quick Fix: How to Fix Muffled Earphones + Tips
4 March 2026
0 comment

Do Muffler Tips Change Sound? + Awesome Sound!
3 March 2026
0 comment





















![Rainbow Muffler Willoughby Hills OH: [Expert Repair] Best Mufflers for Cars & Trucks | Performance, Sound & Durability Upgrades Rainbow Muffler Willoughby Hills OH: [Expert Repair] | Best Mufflers for Cars & Trucks | Performance, Sound & Durability Upgrades](https://dnamufflers.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/03/th-136-300x200.jpg)