A component employed in exhaust systems, particularly those found in larger vehicles, serves to reduce noise levels generated by the engine’s combustion process. This device is not designed for complete sound dampening, but rather offers a balance between noise reduction and minimal backpressure, contributing to efficient engine operation. For example, in commercial trucks where strict regulations govern decibel limits, but engine performance is paramount, a device providing partial noise attenuation is frequently utilized.
The significance of such a component lies in its ability to mitigate noise pollution while maintaining optimal engine performance. Historical context reveals a continuous evolution driven by increasingly stringent noise regulations and a growing awareness of environmental impact. This balance enhances operator comfort, reduces community noise disturbances, and ensures compliance with legal requirements, leading to improved operational efficiency and environmental responsibility.
The subsequent sections will delve into the specific designs, applications, and performance characteristics of these noise reduction devices, providing a detailed examination of their role in modern vehicular technology and their implications for sound management practices. The different types and their use cases will be discussed.
Guidance on Partial Exhaust Sound Dampening Devices
The following recommendations offer insights into the selection, maintenance, and proper usage of components designed for partial exhaust sound reduction in vehicular applications. These tips are designed to maximize performance, longevity, and regulatory compliance.
Tip 1: Material Selection: Choose materials appropriate for the operating environment. Stainless steel or aluminized steel offers superior corrosion resistance, especially in regions with harsh weather conditions or exposure to road salts, thereby extending the component’s lifespan.
Tip 2: Proper Installation: Ensure correct installation according to manufacturer specifications. Improper installation can lead to leaks, reduced performance, and premature failure. Consult a qualified technician for complex installations.
Tip 3: Regular Inspection: Conduct periodic visual inspections for signs of damage, such as cracks, rust, or loose connections. Early detection of problems can prevent more significant and costly repairs down the line.
Tip 4: Performance Monitoring: Monitor engine performance and fuel efficiency. A decrease in either can indicate a problem with the exhaust system, including the partial sound dampening device, which could be causing excessive backpressure.
Tip 5: Regulatory Compliance: Ensure the selected device complies with all applicable noise regulations in the operating area. Non-compliance can result in fines and operational restrictions.
Tip 6: Consider Flow Dynamics: When upgrading or replacing, consider the engine’s flow requirements. Selecting an appropriately sized and designed device can optimize performance while maintaining acceptable noise levels.
These guidelines serve to maximize the efficacy and lifespan of your exhaust sound management equipment. Careful consideration of materials, installation, maintenance, performance monitoring, and regulatory compliance ensures optimal operation and minimizes potential issues.
The final section will summarize the key elements discussed and provide a comprehensive overview of the principles involved in utilizing such components effectively.
1. Noise level reduction
The operational requirement for reducing noise levels generated by heavy-duty vehicles necessitates the integration of specialized components within the exhaust system. The device in question, characterized by its capacity for partial sound attenuation, plays a critical role in meeting regulatory standards and enhancing operational environments.
- Frequency Attenuation Characteristics
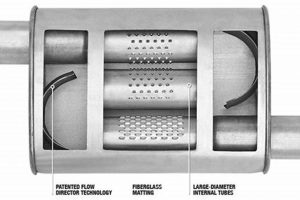
These devices are engineered to attenuate specific frequency ranges associated with engine exhaust noise. Lower frequencies, often associated with the primary combustion events, are partially suppressed to minimize overall sound output. The design parameters of the device, including internal baffling and chamber dimensions, dictate its frequency-dependent attenuation capabilities. The design and implementation impacts its intended performance for the engine.
- Backpressure Considerations
A critical factor in noise level reduction is the inherent trade-off with backpressure. The exhaust system can impede engine performance if the backpressure is excessive. Devices used in achieving partial sound reduction are specifically designed to minimize backpressure effects while still achieving meaningful noise attenuation. This careful balancing of backpressure is critical for maintaining optimal engine operation.
- Material Acoustic Properties
The selection of materials used in the construction of the device influences its ability to absorb and dampen sound waves. Materials with high density and specific damping coefficients are commonly employed to enhance sound reduction capabilities. Stainless steel is frequently used, balancing durability with acoustic performance. The properties of steel selected will determine its application.
- Regulatory Compliance Imperatives
Federal, state, and local regulations often mandate specific noise limits for commercial vehicles. The device contributes to meeting these legal requirements, preventing fines and operational restrictions. Noise testing protocols are used to verify compliance, with specific decibel limits established for vehicles operating in different environments.
The above points highlight the complex interplay between noise level reduction, design considerations, material science, and regulatory adherence. A properly engineered device, striking a balance between noise attenuation and operational efficiency, is essential for responsible operation of commercial vehicles in compliance with stringent environmental standards.
2. Backpressure optimization
The relationship between backpressure optimization and a partially attenuating exhaust component is fundamental to the performance and efficiency of internal combustion engines, particularly in commercial vehicles. The core function of the exhaust system is to evacuate combustion gases from the engine cylinders. However, unrestricted flow can negatively impact scavenging, leading to reduced cylinder filling and compromised power output. Exhaust backpressure, the resistance to this flow, plays a vital role in engine tuning. A fully restrictive device would cause excessive backpressure, decreasing engine efficiency and potentially damaging engine components. The crucial aspect is finding the optimal level of resistance. The device in question offers a compromise by partially attenuating sound while minimizing backpressure. This balanced approach ensures that noise regulations are met without significantly hindering engine performance. Without the appropriate balance, backpressure may significantly affect the engine.
For example, consider two identical commercial trucks operating under the same conditions. One is fitted with a standard, fully restrictive muffler, while the other employs a partially attenuating device engineered for backpressure optimization. The truck with the standard muffler might exhibit slightly lower noise levels, but it will likely experience reduced fuel economy and a decrease in horsepower due to the higher backpressure. Conversely, the truck with the optimized component will demonstrate a balance between acceptable noise levels and maintained engine efficiency. In industries such as long-haul trucking, the cumulative effect of even slight improvements in fuel economy can translate into significant cost savings over time. This illustrates the practical significance of optimizing backpressure in conjunction with noise reduction efforts. It’s a performance choice related to sound.
In summary, the effective design and implementation of a sound attenuation device are intrinsically linked to backpressure optimization. The goal is not simply to reduce noise but to achieve this reduction without unduly compromising engine performance. The engineering challenge lies in creating a component that provides sufficient sound damping while also allowing for efficient exhaust gas flow, ensuring optimal engine operation and fuel economy. Continuous research and development in exhaust system technology are aimed at refining this balance, allowing commercial vehicles to meet increasingly stringent noise regulations without sacrificing performance or increasing operational costs. The overall effectiveness is a balance of variables.
3. Material durability
The longevity and operational effectiveness of a partial exhaust sound dampener are directly contingent on the durability of its constituent materials. The demanding operating environment, characterized by high temperatures, corrosive exhaust gases, and mechanical vibrations, necessitates the selection of materials capable of withstanding these stressors. Material failure can result in diminished sound attenuation, increased backpressure, and, ultimately, complete system failure, leading to vehicle downtime and associated costs. For instance, a common failure mode involves the corrosion of internal baffles or the outer casing, compromising the device’s structural integrity and acoustic performance. This failure often stems from the use of lower-grade steel alloys susceptible to oxidation and chemical attack from exhaust byproducts.
The choice of materials directly impacts the device’s service life and maintenance requirements. Stainless steel, particularly grades 304 and 316, offers superior corrosion resistance compared to aluminized steel or mild steel. While stainless steel incurs a higher initial cost, its extended lifespan and reduced maintenance needs often result in lower lifecycle costs, especially for vehicles operating in corrosive environments, such as those exposed to road salt during winter months. Furthermore, the use of high-temperature coatings can further enhance material durability by providing an additional barrier against corrosion and heat-induced degradation. An example can be found in high-performance vehicles, where Inconel alloys are sometimes employed for exhaust components due to their exceptional heat resistance and strength.
In conclusion, material durability is not merely a design consideration but a critical factor determining the overall value and reliability of a sound management component. The selection of appropriate materials, coupled with robust manufacturing processes, ensures that the device can withstand the rigors of daily operation, delivering consistent performance and minimizing the risk of premature failure. This emphasis on material durability translates directly into reduced operational costs, extended vehicle lifespan, and improved environmental responsibility through decreased component replacement frequency.
4. Installation integrity
The correct installation is a crucial determinant of the operational efficiency and longevity of a partial exhaust sound dampener. Deviation from specified installation procedures can compromise the device’s performance, leading to potential engine damage and regulatory non-compliance. The subsequent points outline essential facets of ensuring installation integrity.
- Proper Alignment and Mounting
Precise alignment of the component within the exhaust system is paramount. Misalignment can induce stress on the connecting pipes, leading to premature cracking and exhaust leaks. Secure mounting, utilizing appropriate hangers and brackets, prevents excessive vibration, which can also contribute to structural failure. An example is seen in commercial truck applications, where vibrations and physical stress are common; improper mounting leads to rapid deterioration of the exhaust system.
- Leak-Free Connections
Ensuring airtight connections at all joints is critical to prevent exhaust gas leaks. Exhaust leaks not only diminish the component’s sound attenuation capabilities but also pose a safety hazard by potentially introducing harmful gases into the vehicle cabin. Proper gasket selection and torque specifications are essential for achieving leak-free connections. A common issue is the reuse of old gaskets, which often fail to provide a sufficient seal, resulting in exhaust leaks and reduced performance.
- Correct Orientation and Flow Direction
Many components are designed to function with a specific exhaust gas flow direction. Installing the device in the reverse orientation can severely impede exhaust flow, leading to increased backpressure and reduced engine performance. Adherence to manufacturer-specified installation diagrams is essential. Incorrect orientation has resulted in engine overheating due to exhaust restrictions in some instances.
- Compliance with Torque Specifications
Over-tightening or under-tightening fasteners can compromise the integrity of the installation. Over-tightening can strip threads or distort flanges, while under-tightening can result in loose connections and exhaust leaks. Utilizing a torque wrench and adhering to manufacturer-specified torque values is essential for ensuring secure and reliable connections. Bolt breakage has been noted where torque specifications were not followed during installation.
The listed components demonstrate the multifaceted nature of ensuring robust installation. Ignoring these details can undermine the engineering and design of the exhaust device, resulting in sub-optimal performance, reduced lifespan, and potential safety hazards. Adherence to best practices during installation is thus an investment in the long-term reliability and operational efficiency of the vehicle.
5. Regulatory compliance
The connection between regulatory compliance and the use of a partial exhaust sound attenuation device is direct and consequential. Noise regulations, established by governmental bodies at various levels, impose limits on the sound emissions produced by commercial vehicles. These regulations are intended to mitigate noise pollution, improve public health, and enhance the quality of life in urban and residential areas. The device plays a crucial role in enabling vehicles to meet these mandated sound thresholds, thereby ensuring adherence to legal requirements and avoiding penalties such as fines, operational restrictions, or vehicle impoundment.
The implementation of a device that achieves partial, rather than complete, sound reduction is often a strategic choice driven by the need to balance noise control with engine performance. In many jurisdictions, regulations stipulate specific decibel limits that vehicles must not exceed, particularly during acceleration and steady-state operation. A device offering partial attenuation allows vehicle operators to reduce noise emissions to acceptable levels while minimizing the impact on engine efficiency and fuel economy. Failing to meet these regulations can lead to significant financial repercussions for fleet operators, disrupting their business operations. In addition, repeated violations may result in more severe consequences, including the suspension of operating permits.
Ultimately, understanding the interplay between sound attenuation technology and regulatory frameworks is essential for commercial vehicle operators. Proactive selection and maintenance of appropriate sound reduction components, coupled with adherence to local noise ordinances, contribute to responsible environmental stewardship and sustainable business practices. Maintaining current awareness of evolving noise regulations and proactively adapting vehicle technology to comply with these mandates is a crucial element of responsible fleet management and ensures the long-term viability of commercial transportation operations.
Frequently Asked Questions About Partial Exhaust Sound Dampening Components
This section addresses common inquiries regarding the use and functionality of exhaust sound reduction devices designed for partial noise attenuation in vehicular applications.
Question 1: What is the primary benefit of using a “semi muffler” instead of a fully restrictive muffler?
The primary benefit lies in the balance between noise reduction and engine performance. Fully restrictive mufflers can significantly reduce noise but often at the expense of increased backpressure, leading to decreased engine efficiency. The device in question offers a compromise, providing sufficient noise attenuation to meet regulatory requirements while minimizing the negative impact on engine performance.
Question 2: How does a “semi muffler” impact fuel efficiency?
By reducing backpressure compared to fully restrictive mufflers, a device that offers partial noise attenuation can contribute to improved fuel efficiency. The degree of improvement depends on the specific engine design and operating conditions, but generally, reduced backpressure translates to more efficient exhaust gas flow and optimized engine performance.
Question 3: Are “semi muffler” designs legal for on-road use?
Legality depends on adherence to local and national noise regulations. A “semi muffler” must meet the decibel limits specified by the relevant authorities for the vehicle’s operating environment. It is the vehicle operator’s responsibility to ensure compliance with all applicable noise regulations.
Question 4: What materials are commonly used in the construction of a “semi muffler”, and why?
Common materials include stainless steel and aluminized steel. Stainless steel offers superior corrosion resistance and durability, making it suitable for harsh operating environments. Aluminized steel provides a more cost-effective alternative with reasonable corrosion resistance. The choice of material depends on the intended application and budget considerations.
Question 5: How often should a “semi muffler” be inspected and/or replaced?
Inspection frequency depends on operating conditions, but a visual inspection for signs of damage or corrosion should be performed at regular maintenance intervals. Replacement is necessary when the device exhibits significant damage, corrosion, or a noticeable increase in exhaust noise levels. A proactive maintenance approach is recommended.
Question 6: What are some signs that a “semi muffler” is failing?
Signs of failure include increased exhaust noise, reduced engine performance, visible signs of rust or damage, and exhaust leaks. Any of these symptoms warrant a thorough inspection and potential replacement of the device.
This FAQ section provides a concise overview of key considerations related to exhaust sound reduction devices. Understanding these aspects is crucial for making informed decisions regarding vehicle maintenance and regulatory compliance.
The following section will delve into case studies, providing real-world examples of the application and performance of these devices in various commercial settings.
Conclusion
The preceding analysis underscores the critical role of the device in managing exhaust noise while maintaining engine performance within commercial vehicle operations. The interplay between sound attenuation, backpressure optimization, material durability, installation integrity, and regulatory compliance has been examined, revealing the complexities inherent in selecting and maintaining effective exhaust systems. The device is a carefully engineered compromise, balancing environmental concerns with operational necessities.
Continued research and development in exhaust technology are essential for addressing evolving noise regulations and optimizing engine efficiency. Further innovation is needed to refine material science, improve installation techniques, and enhance noise reduction strategies. Stakeholders across the transportation industry must prioritize a commitment to sustainable practices, ensuring responsible operation and minimizing the impact on both the environment and public health. Only through diligent attention to these aspects can the device continue to serve as a valuable component in the pursuit of quieter, more efficient commercial vehicle operations.