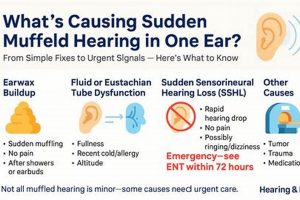
The sensation of reduced sound clarity or a feeling of blockage in the ear upon awakening signifies a common auditory experience. This can manifest as a difficulty in discerning sounds, a sense of fullness within the ear canal, or the perception that external noises are dampened. For example, individuals may report struggling to hear clearly upon waking, describing sounds as if they are coming from a distance or being filtered.
Understanding the potential causes of this morning ear issue is beneficial for proactive management. Its frequent occurrence highlights the need for awareness and potential mitigation strategies. Historically, anecdotal evidence has suggested various contributing factors, but modern audiological understanding provides a more scientific basis for explanation and possible remedies. Timely identification of potential underlying causes promotes better auditory health and reduces anxiety associated with the experience.
This article will now delve into the physiological mechanisms and common conditions that may contribute to this morning auditory phenomenon, exploring potential causes, preventative measures, and appropriate courses of action when experiencing this condition.
Addressing the issue of experiencing reduced auditory acuity upon waking requires understanding and proactive measures. The following tips offer insights into potential causes and mitigation strategies.
Tip 1: Identify Potential Allergens. Environmental allergens, such as dust mites or pet dander, can contribute to nasal congestion and subsequent Eustachian tube dysfunction, leading to ear pressure and muffling. Regular cleaning and air purification may alleviate symptoms.
Tip 2: Manage Sinus Congestion. Nasal congestion, whether due to allergies or infection, impacts the pressure within the middle ear. Consider using a saline nasal spray before sleeping to help clear nasal passages.
Tip 3: Evaluate Sleeping Position. Sleeping on one’s side can exacerbate pressure on the ear closest to the pillow. Experimenting with different sleeping positions or using a contoured pillow may help redistribute pressure and improve drainage.
Tip 4: Hydrate Adequately. Maintaining sufficient hydration levels supports overall bodily functions, including the production of mucus. Proper hydration can prevent thickened mucus that contributes to Eustachian tube blockage.
Tip 5: Avoid Irritants Before Sleep. Exposure to irritants like cigarette smoke or strong perfumes can inflame the nasal passages and Eustachian tubes. Minimizing exposure to these irritants prior to sleeping is recommended.
Tip 6: Consider a Humidifier. Dry air can exacerbate sinus congestion and thicken mucus. Utilizing a humidifier in the bedroom can help maintain optimal humidity levels and promote clear nasal passages.
Tip 7: Consult a Healthcare Professional. If the experience persists or is accompanied by pain, dizziness, or hearing loss, seek medical evaluation. These symptoms may indicate an underlying condition requiring professional intervention.
Adopting these strategies may reduce the frequency and severity of morning ear issues. Understanding individual triggers and implementing appropriate lifestyle adjustments are key to managing this condition.
The following sections will address the various medical conditions and interventions associated with persistent instances of this condition, offering a more in-depth look at possible solutions.
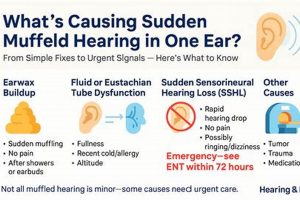
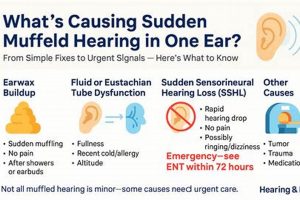
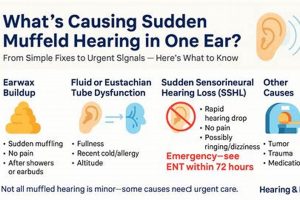
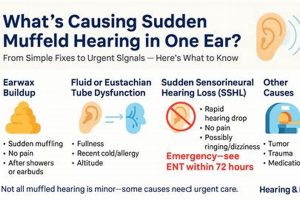
1. Eustachian Tube Dysfunction and Morning Ear Muffling
Eustachian tube dysfunction, characterized by the inability of the Eustachian tube to properly equalize pressure between the middle ear and the environment, is a primary contributor to the experience of auditory muffling upon awakening. The Eustachian tube’s normal function involves opening and closing to regulate pressure fluctuations caused by altitude changes, swallowing, or other bodily processes. When this function is impaired, negative pressure can develop within the middle ear, drawing the eardrum inward and creating a sensation of fullness, blockage, and reduced sound transmission. For example, if the Eustachian tube remains closed overnight due to inflammation or congestion, the middle ear pressure will be lower than the surrounding atmospheric pressure, causing the eardrum to retract. This can result in muffled hearing until the tube is able to properly open and equalize the pressure.
Several factors can induce or exacerbate Eustachian tube dysfunction. Upper respiratory infections, allergies, and anatomical abnormalities are common causes. During sleep, lying down can promote fluid accumulation in the Eustachian tube, further hindering its function. Moreover, individuals with pre-existing conditions, such as chronic sinusitis or enlarged adenoids, may be more susceptible to experiencing this phenomenon. Persistent dysfunction not only impacts auditory acuity but can also lead to complications like middle ear effusion or infection. Understanding the relationship between Eustachian tube functionality and the morning perception of muffled hearing is crucial for identifying individuals at risk and implementing appropriate management strategies.
In summary, Eustachian tube dysfunction frequently underlies the sensation of muffled hearing experienced upon waking. Its impact is amplified by factors such as sleep posture, pre-existing respiratory conditions, and inflammatory processes. Addressing this dysfunction through targeted interventions, such as decongestants or nasal irrigation, may provide relief. When symptoms persist, medical evaluation is warranted to rule out underlying conditions and prevent potential complications. By understanding this connection, individuals can proactively manage their ear health and improve their auditory experience upon awakening.
2. Sinus Congestion Overnight
Overnight sinus congestion significantly contributes to the sensation of ear muffling upon awakening. Nasal passages become obstructed due to inflammation, increased mucus production, or structural abnormalities. When an individual lies down, gravity facilitates the pooling of mucus and inflammatory fluids within the sinuses. This accumulation exerts pressure on adjacent structures, most notably the Eustachian tube. Given the proximity of the sinuses to the middle ear space via the Eustachian tube, sinus congestion directly impacts middle ear pressure regulation.
The Eustachian tube, responsible for equalizing pressure between the middle ear and the nasopharynx, becomes compromised when surrounding tissues are swollen and inflamed due to sinus congestion. The swollen tissue impedes the Eustachian tube’s ability to open and close effectively. This malfunction leads to negative pressure within the middle ear, retracting the tympanic membrane and thus diminishing sound transmission. For example, an individual with seasonal allergies may experience increased sinus congestion during specific times of the year. Upon waking after a night of increased allergen exposure and subsequent nasal congestion, they might report a noticeable muffling in one or both ears. This muffling generally diminishes as the sinus congestion clears throughout the day and Eustachian tube function normalizes. Untreated chronic sinusitis, an ongoing inflammatory condition of the sinuses, results in persistent sinus congestion and frequent occurrences of ear muffling.
Understanding the connection between overnight sinus congestion and ear muffling enables individuals to adopt preventative measures. Nasal saline rinses before sleep can help clear nasal passages and reduce mucus accumulation. Elevating the head during sleep may also improve sinus drainage and diminish pressure on the Eustachian tube. Should the ear muffling persist or be accompanied by pain, dizziness, or hearing loss, medical intervention is crucial to address potential underlying sinus infections or structural issues. Addressing sinus congestion can significantly improve Eustachian tube function and alleviate the common symptom of ear muffling upon waking.
3. Fluid Accumulation (Middle Ear)
The presence of fluid within the middle ear, known as middle ear effusion, represents a significant factor contributing to the experience of auditory muffling upon awakening. This condition disrupts the normal mechanics of sound transmission, leading to altered perception of sound.
- Serous Effusion and Morning Symptoms
Serous effusion, characterized by the accumulation of thin, watery fluid, often results from Eustachian tube dysfunction or barometric pressure changes. Upon assuming a recumbent position during sleep, this fluid may pool within the middle ear cavity, directly impacting the vibration of the tympanic membrane and ossicles. This mechanical impedance reduces sound conduction, resulting in a muffled auditory sensation that is particularly noticeable upon waking. An individual may experience a noticeable reduction in auditory clarity that gradually improves as the fluid is mobilized and drained during upright activity.
- Mucoid Effusion and Auditory Impedance
Mucoid effusion involves a thicker, more viscous fluid accumulation, typically associated with chronic inflammation or infection. The increased density of mucoid fluid significantly impedes the movement of the ossicular chain, responsible for amplifying and transmitting sound vibrations. The presence of this viscous fluid diminishes the transmission of sounds, especially low-frequency sounds, leading to a persistent muffled sensation. This type of effusion may result in more prolonged and pronounced auditory impairment compared to serous effusion.
- Impact on Tympanic Membrane Vibration
The tympanic membrane’s ability to vibrate freely is critical for accurate sound transmission. Fluid accumulation in the middle ear dampens these vibrations, requiring greater sound pressure to achieve the same level of auditory perception. This dampening effect disproportionately affects certain frequencies, leading to a distorted or unbalanced auditory experience. The extent of dampening is correlated to the amount and viscosity of the fluid present, which will directly affect the muffled sensation. Individuals may notice a reduction in the clarity of speech, particularly in environments with background noise.
- Consequences of Untreated Effusion
Persistent fluid accumulation in the middle ear, if left unaddressed, can lead to various complications. Chronic effusions can contribute to adhesive otitis media, characterized by scarring and stiffening of the tympanic membrane. Prolonged exposure to fluid can also increase the risk of bacterial infection, resulting in acute otitis media, further exacerbating auditory symptoms and potentially leading to more severe complications. Addressing and managing fluid accumulation is therefore essential in preserving auditory function and preventing long-term sequelae.
In conclusion, fluid accumulation within the middle ear profoundly affects sound transmission, directly contributing to the perception of auditory muffling experienced upon awakening. Factors such as the type and volume of fluid, as well as the duration of accumulation, dictate the severity and persistence of the symptoms. Understanding the underlying mechanisms and potential consequences is crucial for effective diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of auditory complications.
4. Sleeping Position's Impact
Sleeping position exerts a demonstrable influence on the occurrence of a muffled sensation in the ear upon awakening. Gravitational forces and pressure distribution during sleep directly affect the Eustachian tube’s function, sinus drainage, and overall fluid dynamics within the middle ear, thereby contributing to this auditory phenomenon.
- Lateral Decubitus and Ear Compression
The lateral decubitus position, or sleeping on one’s side, can lead to direct compression of the lower ear against the pillow or mattress. Sustained pressure may impede Eustachian tube function, preventing proper pressure equalization within the middle ear. An individual who consistently sleeps on their right side, for example, may experience a muffled sensation in the right ear upon waking due to prolonged compression during the night. This mechanical impedance can reduce sound transmission, leading to the perception of a blocked or muffled ear.
- Sinus Drainage and Head Elevation
Sleeping with the head relatively flat or in a declined position can hinder sinus drainage, promoting fluid accumulation in the nasal passages and increasing pressure on the Eustachian tube. Conversely, elevating the head during sleep can facilitate sinus drainage and reduce pressure on the Eustachian tube. Individuals experiencing chronic sinusitis may find that sleeping with their head elevated reduces the likelihood of waking up with a muffled ear.
- Fluid Shift and Middle Ear Pressure
During sleep, the body’s fluid distribution shifts due to changes in hydrostatic pressure. Depending on the sleeping position, this fluid shift can increase the accumulation of fluid within the middle ear. Those who sleep supine, or on their back, may be more susceptible to fluid pooling in the middle ear. Individuals with pre-existing Eustachian tube dysfunction may experience a greater impact from these fluid shifts, leading to a more pronounced muffled sensation.
- Pillow Material and Allergic Response
Pillow material composition can indirectly affect auditory perception through its potential to trigger allergic responses. Certain materials, such as feather or down, may harbor allergens like dust mites, leading to nasal congestion and Eustachian tube dysfunction. An individual with a dust mite allergy may experience increased nasal congestion and subsequent ear muffling when sleeping on a feather pillow, compared to a hypoallergenic alternative.
These facets highlight the intricate interplay between sleeping posture, physiological processes, and external factors. By understanding the impact of sleeping position on Eustachian tube function, sinus drainage, and fluid dynamics, individuals can make informed choices to mitigate the occurrence of ear muffling upon waking, potentially improving overall auditory comfort and health.
5. Inflammatory response triggers
An inflammatory response, whether triggered by allergens, infections, or irritants, can significantly contribute to experiencing a muffled sensation in the ear upon awakening. Inflammation in the nasal passages, sinuses, or middle ear directly impacts the function of the Eustachian tube, which is responsible for equalizing pressure between the middle ear and the nasopharynx. When inflamed, tissues surrounding the Eustachian tube swell, potentially obstructing its opening and closing mechanism. This obstruction results in negative pressure within the middle ear, drawing the tympanic membrane inward and impairing its ability to vibrate freely. For instance, individuals with allergic rhinitis may experience heightened sensitivity to airborne allergens like pollen or dust mites. Upon exposure, the immune system initiates an inflammatory cascade, leading to nasal congestion, increased mucus production, and Eustachian tube dysfunction. Consequently, these individuals may wake up with a sensation of fullness or muffling in one or both ears.
The type and duration of the inflammatory trigger also influence the severity and persistence of the auditory symptoms. Acute infections, such as otitis media or sinusitis, induce a rapid and intense inflammatory response, often accompanied by pain, fever, and significant auditory impairment. Chronic inflammatory conditions, such as chronic sinusitis or allergic rhinitis, lead to more subtle but persistent inflammation, resulting in recurrent or continuous ear muffling. Furthermore, exposure to irritants, such as cigarette smoke or air pollution, can exacerbate existing inflammatory conditions and contribute to Eustachian tube dysfunction. Understanding the specific inflammatory triggers that affect an individual is crucial for implementing effective management strategies, such as allergen avoidance, anti-inflammatory medications, or immunotherapy.
In summary, inflammatory response triggers represent a key factor in the etiology of ear muffling upon awakening. Inflammation-induced Eustachian tube dysfunction leads to middle ear pressure imbalances and subsequent auditory impairment. Identifying and managing the underlying inflammatory triggers, whether allergic, infectious, or irritant-related, are essential for alleviating symptoms and preventing long-term complications. Addressing these triggers can restore Eustachian tube function, improve middle ear pressure regulation, and ultimately, enhance auditory clarity upon waking.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common queries regarding the sensation of reduced auditory acuity or ear blockage experienced upon waking, providing informative and evidence-based responses.
Question 1: What are the primary causes of experiencing a muffled ear upon waking?
Several factors may contribute, including Eustachian tube dysfunction, overnight sinus congestion, middle ear fluid accumulation (effusion), sleeping position impacting ear pressure, and inflammatory responses to allergens or irritants.
Question 2: How does Eustachian tube dysfunction lead to a muffled ear sensation?
Eustachian tube dysfunction impairs pressure equalization between the middle ear and the environment. The resulting negative pressure causes the eardrum to retract, reducing its ability to vibrate freely and transmit sound effectively, thus creating a muffled sound.
Question 3: Can allergies contribute to a muffled ear in the morning?
Yes. Allergic reactions trigger inflammation in the nasal passages and Eustachian tube, leading to congestion and impaired pressure regulation in the middle ear. The resulting pressure imbalance and fluid accumulation can cause a muffled sensation.
Question 4: What role does sleeping position play in causing a muffled ear?
Sleeping on one’s side can compress the lower ear, impeding Eustachian tube function. Moreover, head elevation during sleep affects sinus drainage and fluid dynamics, potentially influencing middle ear pressure and auditory perception.
Question 5: When is it necessary to seek medical evaluation for morning ear muffling?
Medical consultation is warranted if the issue persists, is accompanied by pain, dizziness, hearing loss, or drainage from the ear. These symptoms may indicate an underlying condition requiring professional intervention.
Question 6: What are some self-care strategies to help alleviate the sensation of a muffled ear upon waking?
Potential strategies include using a saline nasal spray before sleeping, elevating the head during sleep, identifying and avoiding allergens, and ensuring adequate hydration to prevent thickened mucus. If symptoms do not improve or worsen, professional medical advice should be sought.
Understanding the various potential causes and appropriate interventions associated with this auditory phenomenon is crucial for effective management and prevention.
The following section will provide a detailed summary of the information presented, highlighting key takeaways and suggesting further steps for managing the condition.
Conclusion
This exploration has illuminated the multifaceted nature of experiencing a muffled ear upon awakening. The convergence of Eustachian tube dysfunction, sinus congestion, fluid accumulation, sleeping position, and inflammatory triggers contributes to the altered auditory perception. Successfully addressing this issue demands a comprehensive understanding of the potential underlying causes and contributing factors.
Persistent or recurrent instances of experiencing a muffled ear upon waking necessitate professional medical evaluation to identify potential underlying conditions and implement appropriate interventions. Prioritizing auditory health and seeking timely medical assistance is crucial for preventing long-term complications and ensuring optimal hearing.