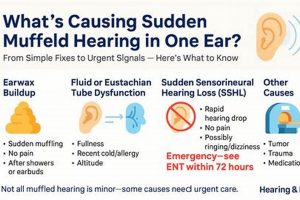
A sensation of reduced sound clarity or blocked hearing upon waking is a common experience. This temporary auditory distortion can range from a mild stuffiness to a feeling of significant blockage, impacting the ability to perceive sounds accurately and comfortably.
Understanding the underlying causes of this phenomenon is beneficial for managing and potentially preventing it. Identifying contributing factors allows for proactive measures to be taken, potentially mitigating the discomfort and ensuring optimal auditory function throughout the day. Furthermore, recognizing when the muffled sensation warrants professional evaluation is crucial for safeguarding long-term hearing health.
The subsequent sections will explore potential physiological and environmental factors that contribute to this morning auditory phenomenon, including fluid buildup, sinus pressure changes, earwax accumulation, and environmental considerations. Each of these aspects plays a distinct role in the temporary alteration of auditory perception.
Managing Morning Auditory Muffling
The following guidelines offer practical approaches to potentially alleviate the experience of diminished auditory clarity upon awakening.
Tip 1: Adjust Sleeping Position: Elevating the head with an additional pillow can minimize fluid accumulation in the head and neck region, potentially reducing pressure on the Eustachian tube and inner ear.
Tip 2: Hydrate Adequately: Maintaining sufficient hydration levels supports overall bodily functions, including the regulation of fluid balance within the ear. Dehydration can exacerbate fluid imbalances.
Tip 3: Manage Allergies: If allergies are a contributing factor, adhering to prescribed allergy medication regimens and minimizing exposure to allergens within the sleeping environment can reduce sinus congestion and subsequent ear pressure.
Tip 4: Utilize a Humidifier: Employing a humidifier in the bedroom can increase moisture levels in the air, potentially preventing the drying of nasal passages and subsequent ear canal irritation.
Tip 5: Practice Sinus Rinse: Performing a nasal rinse with a saline solution before sleep can help clear nasal passages and reduce sinus pressure that may contribute to auditory muffling.
Tip 6: Address Earwax Accumulation: If excessive earwax is suspected, consult a healthcare professional for safe and effective removal. Avoid using cotton swabs, as they can further impacted earwax.
Tip 7: Avoid Irritants: Minimize exposure to irritants such as smoke or strong perfumes in the sleeping environment, as they can exacerbate inflammation and congestion within the respiratory system and ears.
These suggestions offer potential strategies for managing morning auditory muffling. However, persistent or severe symptoms necessitate professional evaluation.
The concluding section will summarize the key points discussed and emphasize the importance of seeking professional guidance when necessary.
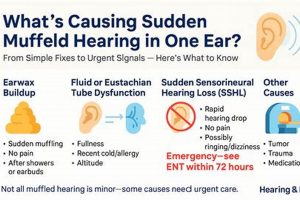
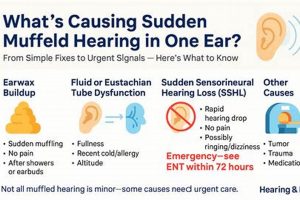
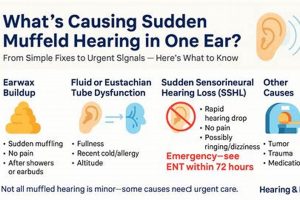
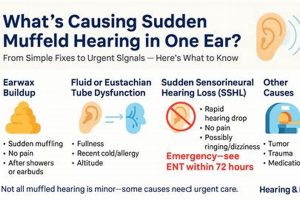
1. Fluid accumulation
Fluid accumulation within the middle ear represents a significant factor contributing to the sensation of muffled hearing upon awakening. The middle ear, an air-filled cavity behind the eardrum, relies on unimpeded air pressure to facilitate the efficient transmission of sound vibrations. When fluid accumulates within this space, typically due to Eustachian tube dysfunction or an upper respiratory infection, the fluid dampens the movement of the ossicles (tiny bones responsible for sound amplification), thereby disrupting the transmission of sound waves to the inner ear. This disruption translates to a perceived reduction in sound clarity and volume, resulting in a muffled sensation.
Consider, for example, the case of an individual experiencing a common cold. The resulting nasal congestion can inflame the Eustachian tube, preventing its proper functioning. Consequently, fluid that normally drains from the middle ear accumulates, leading to a noticeable reduction in hearing sensitivity. Furthermore, sleeping in a horizontal position can exacerbate this issue, as gravity impedes fluid drainage and promotes pooling within the middle ear cavity. The practical significance of understanding this connection lies in recognizing the importance of addressing underlying conditions, such as allergies or infections, that contribute to Eustachian tube dysfunction and fluid accumulation.
In summary, fluid accumulation in the middle ear directly impairs sound transmission, resulting in the experience of muffled hearing, particularly upon waking. Recognizing the role of conditions impacting Eustachian tube function and adopting strategies to facilitate fluid drainage is crucial. Persistently muffled hearing, especially when accompanied by pain or other symptoms, requires prompt medical evaluation to prevent potential complications and ensure optimal auditory health. The influence of fluid on proper hearing can’t be understated.
2. Eustachian Tube Dysfunction
Eustachian tube dysfunction is a common underlying factor in the sensation of muffled hearing experienced upon awakening. The Eustachian tube’s primary role is to equalize pressure between the middle ear and the outside environment. When this function is impaired, a pressure imbalance can develop, leading to auditory distortion.
- Role of Pressure Equalization
The Eustachian tube connects the middle ear to the nasopharynx, allowing air to enter or exit the middle ear cavity. This pressure regulation ensures the eardrum vibrates optimally in response to sound waves. When the tube fails to open properly, air pressure in the middle ear drops, creating a relative vacuum. This vacuum pulls the eardrum inward, restricting its movement and diminishing sound transmission efficiency.
- Inflammation and Congestion
Upper respiratory infections, allergies, and sinus infections often cause inflammation and swelling of the Eustachian tube lining. This inflammation narrows the tube’s passage, hindering its ability to open and equalize pressure. The resulting congestion can lead to fluid buildup in the middle ear, further contributing to muffled hearing. For example, an individual with seasonal allergies may experience Eustachian tube dysfunction during pollen season, with the associated muffled hearing being more pronounced upon waking due to prolonged horizontal positioning.
- Anatomical Factors
Certain anatomical features can predispose individuals to Eustachian tube dysfunction. Children, for instance, have shorter and more horizontal Eustachian tubes compared to adults, making them more susceptible to dysfunction. Additionally, individuals with nasal polyps or enlarged adenoids may experience chronic Eustachian tube obstruction. The structural aspect of the eustachian tube may influence the reason to “why is my ear muffled when i wake up”.
- Barotrauma
Rapid changes in atmospheric pressure, such as during air travel or scuba diving, can overwhelm the Eustachian tube’s ability to equalize pressure quickly enough. This can result in barotrauma, causing significant pressure imbalances and potential damage to the eardrum. While typically associated with specific events, repeated mild barotrauma can contribute to chronic Eustachian tube dysfunction and increase the likelihood of muffled hearing, particularly after periods of sleep where pressure regulation is less frequent.
These facets illustrate the complex interplay between Eustachian tube function, environmental factors, and individual anatomy in contributing to muffled hearing upon waking. Addressing underlying causes, such as infections or allergies, and employing techniques to promote Eustachian tube opening, like yawning or swallowing, can often alleviate the symptom. However, persistent or severe symptoms warrant professional medical evaluation to rule out more serious conditions and prevent potential complications.
3. Sinus pressure changes
Sinus pressure changes significantly impact the perception of auditory clarity, contributing directly to the sensation of muffled hearing upon waking. The sinuses, air-filled cavities within the skull, are connected to the nasal passages. Inflammation or congestion within these sinuses, stemming from conditions such as sinusitis or allergic rhinitis, can lead to increased pressure. This elevated pressure exerts force on surrounding structures, including the Eustachian tube, which connects the middle ear to the nasopharynx. The Eustachian tube’s primary function is to equalize pressure, ensuring the efficient transmission of sound. When sinus pressure impedes the Eustachian tube’s proper function, a pressure differential arises between the middle ear and the external environment. This imbalance hinders the eardrum’s ability to vibrate freely, leading to the perception of muffled sounds. For instance, an individual experiencing a sinus infection may find that their hearing is noticeably diminished in the morning due to the accumulation of mucus and increased sinus pressure during sleep. The importance of managing sinus conditions becomes clear when considering the detrimental effects of persistent sinus pressure on auditory function.
Furthermore, the horizontal position assumed during sleep can exacerbate the effects of sinus pressure on the ears. When lying down, mucus and fluid within the sinuses are less likely to drain efficiently, increasing the pressure exerted on the Eustachian tube. This is particularly relevant for individuals prone to sinus congestion or those with anatomical predispositions that hinder sinus drainage. Practical applications of this understanding include employing strategies to facilitate sinus drainage before sleep, such as using a nasal saline rinse or sleeping with the head elevated. Such measures may alleviate the pressure exerted on the Eustachian tube, thereby mitigating the sensation of muffled hearing upon awakening. The combination of sinus congestion and postural effects highlights the complex interplay between sinus health and auditory perception.
In summary, sinus pressure changes directly impact Eustachian tube function, leading to pressure imbalances within the middle ear and subsequent muffled hearing. Understanding this connection emphasizes the importance of managing sinus conditions and implementing strategies to promote sinus drainage, particularly before sleep. While simple measures can often alleviate the symptom, persistent or severe cases warrant medical evaluation to address underlying sinus issues and prevent potential complications affecting auditory health. Recognition of sinus as a component influencing why is my ear muffled when i wake up serves as a great knowledge to tackle the issue.
4. Earwax impaction
Earwax impaction, characterized by the excessive buildup and hardening of cerumen within the ear canal, directly contributes to the sensation of muffled hearing. Cerumen, a naturally produced substance designed to protect the ear canal from foreign debris and infection, is typically expelled from the ear canal through natural jaw movements and skin migration. However, when this process is disrupted, cerumen can accumulate and solidify, creating a physical barrier that impedes the passage of sound waves to the eardrum. The obstruction dampens sound transmission, resulting in a perceived reduction in auditory clarity and overall volume. For example, an individual who habitually uses cotton swabs to clean the ears may inadvertently push earwax further into the ear canal, compacting it and leading to impaction. This impaction becomes more noticeable upon waking, as overnight accumulation and minor swelling within the ear canal exacerbate the blockage. Understanding the role of earwax impaction in auditory muffling is crucial for adopting preventive measures and seeking appropriate intervention.
The horizontal position assumed during sleep can further contribute to the perception of muffled hearing due to earwax impaction. While lying down, gravity can cause already impacted earwax to shift and press more firmly against the eardrum, intensifying the sensation of blockage. Additionally, slight increases in ear canal moisture or humidity overnight can soften the outer layers of the impacted earwax, causing it to expand and further occlude the ear canal. This explains why some individuals may experience a noticeable worsening of muffled hearing specifically upon waking, only to have the sensation slightly diminish as the day progresses and the ear canal dries. Practical applications of this understanding include avoiding the use of cotton swabs for ear cleaning, seeking professional earwax removal when necessary, and considering sleeping with the head slightly elevated to promote ear canal ventilation. These actions aim to prevent the aggravation of existing impactions and minimize the potential for nocturnal exacerbation of symptoms.
In summary, earwax impaction serves as a prominent factor in the experience of muffled hearing, particularly upon waking. The physical obstruction caused by impacted cerumen dampens sound transmission, and the overnight positional and environmental factors can exacerbate this effect. Recognizing the connection between earwax impaction and auditory perception highlights the importance of proper ear hygiene and timely professional intervention when necessary. While preventative measures can mitigate the risk of impaction, persistent or severe symptoms warrant medical evaluation to ensure appropriate management and prevent potential complications affecting long-term auditory health.
5. Allergic reactions
Allergic reactions frequently contribute to the phenomenon of muffled hearing experienced upon awakening. Exposure to allergens triggers an immune response, leading to the release of histamine and other inflammatory mediators. These substances cause swelling and inflammation within the nasal passages, sinuses, and Eustachian tube. The Eustachian tube, responsible for equalizing pressure in the middle ear, becomes compromised when inflamed, restricting airflow and leading to pressure imbalances. This pressure imbalance impairs the eardrum’s ability to vibrate freely, thus reducing sound transmission efficiency and resulting in a muffled auditory sensation. For instance, an individual with seasonal allergies may experience heightened nasal congestion and Eustachian tube dysfunction during pollen season, resulting in pronounced muffled hearing upon waking after prolonged exposure to airborne allergens during sleep.
The practical significance of understanding this connection lies in implementing proactive measures to mitigate allergic responses. Minimizing exposure to allergens within the sleeping environment, such as using allergen-proof bedding and regularly cleaning dust and mold, can reduce the severity of allergic reactions. Additionally, the use of antihistamines or nasal corticosteroids, as prescribed by a healthcare professional, can help control inflammation and congestion, thereby improving Eustachian tube function and alleviating muffled hearing. Furthermore, identifying and addressing the specific allergens triggering the reaction is crucial for long-term management. The inflammatory response to such external components serves as catalyst for the muffled sensation.
In summary, allergic reactions contribute to muffled hearing upon waking primarily through inflammation and congestion affecting the Eustachian tube. Understanding this link underscores the importance of allergen avoidance and appropriate medical management to alleviate symptoms. While preventive measures can minimize the impact of allergies on auditory perception, persistent or severe symptoms necessitate professional evaluation to identify the underlying allergens and implement tailored treatment strategies, ensuring optimal respiratory and auditory health.
6. Inflammation
Inflammation, characterized by the body’s protective response to injury or infection, plays a significant role in the experience of muffled hearing upon awakening. This physiological process, while essential for healing, can disrupt auditory function when occurring in or around the ear.
- Eustachian Tube Inflammation
Inflammation of the Eustachian tube, the narrow passage connecting the middle ear to the nasopharynx, is a primary mechanism by which inflammation contributes to auditory muffling. When inflamed, the Eustachian tube swells, restricting its ability to equalize pressure between the middle ear and the external environment. This pressure imbalance impedes the eardrum’s vibration, resulting in diminished sound transmission. Common causes of Eustachian tube inflammation include upper respiratory infections, allergies, and exposure to irritants. For example, an individual with a cold may experience Eustachian tube inflammation, leading to temporary muffled hearing. Addressing the underlying cause of inflammation is vital for restoring proper Eustachian tube function and alleviating the associated auditory symptoms.
- Middle Ear Inflammation (Otitis Media)
Middle ear inflammation, clinically known as otitis media, is frequently associated with infections. Inflammation of the middle ear lining causes fluid accumulation, which dampens the movement of the ossicles (tiny bones responsible for sound amplification). This fluid buildup impairs sound transmission and leads to a sensation of muffled hearing. Acute otitis media, often characterized by ear pain, fever, and hearing loss, is a common cause of muffled hearing in children and adults. Chronic otitis media can lead to persistent inflammation and structural damage, resulting in long-term auditory impairment. Effective management of otitis media involves addressing the underlying infection and reducing inflammation to restore optimal middle ear function.
- Inner Ear Inflammation (Labyrinthitis)
Inflammation affecting the inner ear, known as labyrinthitis, can also contribute to muffled hearing, although it typically presents with additional symptoms such as vertigo and balance disturbances. The inner ear contains the cochlea, responsible for sound processing, and the vestibular system, responsible for balance. Inflammation can disrupt the function of these structures, leading to a combination of hearing loss, tinnitus (ringing in the ears), and dizziness. Viral infections are a common cause of labyrinthitis. While the acute symptoms may subside over time, residual inflammation can sometimes persist, resulting in chronic auditory and vestibular dysfunction. Prompt medical evaluation and treatment are essential for managing labyrinthitis and minimizing the risk of long-term complications.
- External Ear Canal Inflammation (Otitis Externa)
Inflammation of the external ear canal, or otitis externa (swimmer’s ear), can indirectly lead to muffled hearing if the swelling is severe enough to obstruct the ear canal. This condition is commonly caused by bacterial or fungal infections, often resulting from excessive moisture exposure or improper ear cleaning. The inflammation causes pain, redness, and swelling, which can physically block the passage of sound waves to the eardrum. Although primarily affecting the outer ear, the resulting obstruction can mimic the sensation of muffled hearing. Appropriate treatment, including antibiotics or antifungal medications, is necessary to resolve the infection and reduce inflammation, thereby restoring normal hearing.
These inflammatory processes, whether affecting the Eustachian tube, middle ear, inner ear, or external ear canal, all contribute to the experience of muffled hearing. Recognizing the underlying cause of inflammation is critical for implementing appropriate treatment strategies and preventing long-term auditory damage. While temporary muffled hearing due to mild inflammation may resolve spontaneously, persistent or severe symptoms warrant prompt medical evaluation to ensure accurate diagnosis and effective management.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following section addresses common inquiries regarding the experience of diminished auditory clarity upon awakening. These questions aim to provide informative answers based on current understanding of the underlying causes and potential management strategies.
Question 1: Is a muffled ear upon waking always a cause for concern?
Not necessarily. Transient auditory muffling upon waking can often be attributed to temporary factors such as fluid accumulation or mild Eustachian tube dysfunction. However, persistent or severe symptoms warrant evaluation by a healthcare professional.
Question 2: What home remedies can be attempted to alleviate a muffled ear in the morning?
Several strategies may provide relief. Elevating the head during sleep, ensuring adequate hydration, and employing a humidifier to maintain optimal humidity levels are potential options. Additionally, managing allergies and practicing nasal irrigation can aid in reducing congestion.
Question 3: Can earwax buildup cause auditory muffling specifically in the morning?
Yes, earwax impaction can contribute to muffled hearing, particularly upon waking. The horizontal position during sleep may cause impacted earwax to shift and press against the eardrum, exacerbating the blockage. Furthermore, overnight accumulation of moisture can cause expansion of the earwax.
Question 4: Is there a link between sinus infections and the sensation of a muffled ear upon waking?
Yes, a connection exists. Sinus infections can lead to increased pressure in the sinuses, which can affect the Eustachian tube’s ability to equalize pressure in the middle ear. This pressure imbalance may result in a muffled auditory experience.
Question 5: When is it essential to seek professional medical advice for morning auditory muffling?
Prompt medical evaluation is warranted if the muffled sensation persists for more than a few days, is accompanied by pain, dizziness, or drainage from the ear, or is associated with a sudden loss of hearing. These symptoms may indicate a more serious underlying condition requiring prompt attention.
Question 6: Can allergic reactions contribute to the experience of auditory muffling upon waking?
Yes, allergic reactions can trigger inflammation and congestion in the nasal passages and Eustachian tube, leading to pressure imbalances in the middle ear and a subsequent sensation of muffled hearing.
These FAQs offer concise responses to prevalent queries regarding the experience of diminished auditory clarity upon awakening. While many instances of morning auditory muffling are transient and self-resolving, persistent or concerning symptoms necessitate professional medical attention to ensure appropriate management and prevent potential complications.
The subsequent article section will synthesize the key insights discussed and provide concluding remarks, emphasizing the significance of proactive care and informed decision-making regarding auditory health.
Conclusion
The exploration of “why is my ear muffled when i wake up” has revealed a multifaceted phenomenon with various contributing factors. Fluid accumulation, Eustachian tube dysfunction, sinus pressure changes, earwax impaction, allergic reactions, and inflammation have each been identified as potential causes for diminished auditory clarity upon awakening. While transient occurrences are often benign, persistent or severe symptoms warrant professional medical evaluation.
The ability to recognize potential etiologies and implement appropriate management strategies empowers individuals to proactively address concerns regarding auditory health. Early intervention and diligent monitoring of symptoms are paramount in preventing complications and preserving optimal hearing function. Seeking qualified medical guidance remains critical for accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment plans, ensuring long-term well-being.