A component often found within a vehicle’s exhaust system serves to reduce noise pollution generated by the engine’s combustion process. This component typically consists of a series of chambers and tubes designed to cancel out sound waves before they exit the vehicle. Its effectiveness is measured by the decibel reduction it achieves and its ability to maintain optimal engine performance. For example, a properly functioning unit ensures that a vehicle meets legal noise emission standards and contributes to a quieter driving experience.
This particular exhaust system element plays a vital role in minimizing environmental impact and enhancing driver comfort. Its presence contributes to compliance with environmental regulations, reduces noise pollution in urban areas, and enhances the overall driving experience. Historically, advancements in materials and design have led to increased efficiency and durability of these components, resulting in quieter vehicles and longer lifespans.
The functionality, maintenance, and selection of such components are critical considerations for vehicle owners and automotive technicians. Understanding its role within the broader exhaust system and its impact on vehicle performance will be explored in further detail within this article. Subsequent sections will delve into specific types, potential issues, and best practices for ensuring optimal performance.
Allied Muffler
Maintaining the integrity of a vehicle’s exhaust system is crucial for both environmental compliance and optimal engine operation. The following tips provide essential guidance on ensuring the long-term performance of the noise reduction component within that system.
Tip 1: Regular Visual Inspection: Conduct periodic visual inspections for signs of corrosion, rust, or physical damage. Early detection of these issues can prevent more extensive damage and costly repairs later.
Tip 2: Prompt Addressing of Unusual Noises: Investigate any unusual noises emanating from the exhaust system immediately. Rattling, hissing, or excessively loud exhaust sounds often indicate a problem with the component’s structural integrity or internal baffling.
Tip 3: Ensure Proper Mounting and Support: Verify that the mountings and supports are secure and intact. Loose or damaged supports can lead to excessive vibration, stress, and premature failure of the unit.
Tip 4: Monitor for Exhaust Leaks: Check for exhaust leaks, particularly around connections and seams. Leaks not only reduce the unit’s effectiveness in noise reduction but also pose a safety hazard due to the potential for carbon monoxide exposure.
Tip 5: Consult a Qualified Technician: If unsure about any aspect of its condition or maintenance, consult a qualified automotive technician. Professional inspection and diagnosis can identify hidden problems and ensure proper repairs.
Tip 6: Consider Material Upgrades: When replacement is necessary, explore options for upgrading to more durable materials, such as stainless steel. This can extend the lifespan of the component and provide greater resistance to corrosion.
By adhering to these tips, vehicle owners can proactively maintain the effectiveness of the exhaust noise reduction component, ensuring compliance with environmental regulations, reducing noise pollution, and prolonging the lifespan of the vehicle’s exhaust system.
The subsequent sections of this article will delve further into troubleshooting common issues and selecting appropriate replacement units when necessary.
1. Noise Reduction Efficiency
Noise reduction efficiency is a critical performance metric for any exhaust system component designed to mitigate engine noise. It directly relates to the component’s ability to reduce sound levels generated by the engine’s combustion process, impacting both environmental compliance and the overall driving experience.
- Decibel Reduction Levels
Decibel reduction levels quantify the amount of sound attenuated by the exhaust system component. A higher decibel reduction indicates greater efficiency. For instance, a component designed for heavy-duty trucks may require a higher decibel reduction rating compared to one designed for passenger cars to meet specific noise emission standards. This reduction is achieved through internal baffling and absorption materials.
- Frequency Range Attenuation
Frequency range attenuation refers to the component’s effectiveness in reducing noise across different frequencies. Engine noise typically comprises a spectrum of frequencies, and an efficient component will attenuate a broad range. Some designs focus on reducing low-frequency rumble, while others target high-frequency whine. The design must consider the specific noise characteristics of the engine it serves.
- Material Composition and Design
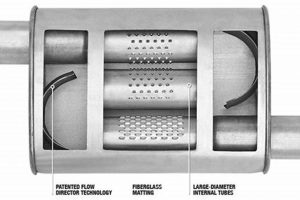
Material composition and internal design directly influence noise reduction efficiency. Sound-absorbing materials, such as fiberglass or specialized packing, convert sound energy into heat. The internal chamber design, including the size, shape, and arrangement of baffles, affects how sound waves are reflected and canceled out. Corrosion-resistant materials, while not directly impacting noise reduction, ensure long-term performance and prevent degradation of the component’s acoustic properties.
- Backpressure Impact
Achieving optimal noise reduction efficiency must be balanced with the need to minimize exhaust backpressure. Excessive backpressure can reduce engine horsepower and fuel economy. An efficient component design minimizes backpressure while maximizing noise reduction, often requiring sophisticated engineering and testing to achieve the right balance. For example, straight-through designs may offer minimal backpressure but require more advanced sound absorption techniques to maintain noise reduction efficiency.
These facets collectively determine the effectiveness of the noise reduction component in meeting regulatory requirements and providing a quieter driving experience. Understanding these factors is crucial for selecting the appropriate component and ensuring optimal vehicle performance while minimizing environmental impact.
2. Exhaust backpressure
Exhaust backpressure is a crucial parameter affecting engine performance, with a direct relationship to the function and design of the exhaust system component, specifically, the noise-reducing element. This pressure arises from the restriction of exhaust gases as they flow through the exhaust system. The internal structure of the component, including baffles and chambers designed to attenuate sound waves, inherently creates a degree of resistance. Excessive backpressure can impede the efficient expulsion of exhaust gases from the cylinders, leading to reduced engine power, increased fuel consumption, and elevated operating temperatures. The design objective involves balancing noise reduction with minimal backpressure to maintain optimal engine performance. Consider a scenario where the internal baffling within this exhaust system element is excessively dense or improperly designed; this will increase backpressure, noticeably reducing horsepower, especially at higher RPMs. In contrast, a straight-through design minimizes backpressure but may compromise noise reduction capabilities.
The selection of materials and the internal geometry are carefully considered to mitigate the negative effects of backpressure. For instance, a component manufactured with larger diameter passages or utilizing perforated baffles can reduce flow restriction while still achieving adequate noise suppression. Computer-aided design (CAD) and computational fluid dynamics (CFD) are employed to simulate exhaust flow and optimize the component’s internal structure. These simulations enable engineers to fine-tune the design, ensuring that backpressure remains within acceptable limits without sacrificing noise reduction performance. An example would be the development of a spiral baffle design, which extends the exhaust gas path for noise attenuation while minimizing the direct resistance that a conventional baffle array would impose.
In summary, backpressure is an unavoidable consequence of noise reduction within an exhaust system, and its management is critical for preserving engine efficiency. The design of the noise-reducing element requires a careful balancing act to minimize backpressure while achieving the desired sound attenuation. The practical significance of this understanding lies in enabling vehicle owners and technicians to select components that provide both adequate noise reduction and optimal engine performance. Furthermore, it highlights the importance of regular maintenance to prevent the buildup of exhaust deposits within the component, which can further increase backpressure and degrade engine performance over time.
3. Material durability
Material durability is a paramount concern in the design and functionality of an exhaust noise reduction component. The harsh environment within an exhaust system, characterized by high temperatures, corrosive gases, and constant vibration, places significant stress on the materials used in its construction. Consequently, the selection of durable materials directly affects the component’s lifespan and its ability to maintain performance over time. For example, a component constructed from low-grade steel is susceptible to rapid corrosion, leading to structural failure and a decrease in noise reduction efficiency. Conversely, the utilization of materials like stainless steel or aluminized steel extends the component’s lifespan, reducing the need for frequent replacements and ensuring continued compliance with noise emission standards. The practical significance of this lies in the long-term cost savings and environmental benefits associated with reduced waste and resource consumption.
The cause-and-effect relationship between material durability and the noise reduction component’s performance is readily observable in real-world scenarios. Consider a vehicle operating in a region with harsh winter conditions, where road salt accelerates corrosion. An exhaust component constructed from a less durable material will exhibit accelerated degradation, leading to exhaust leaks, increased noise levels, and potential damage to other vehicle components. In contrast, a component made from corrosion-resistant materials will maintain its structural integrity and performance, even under these adverse conditions. Furthermore, the selection of appropriate materials can impact the component’s resistance to thermal fatigue, a phenomenon where repeated heating and cooling cycles cause material weakening. Therefore, material selection is not merely a matter of cost but rather a crucial engineering decision that impacts the component’s long-term reliability and performance.
In summary, material durability is an indispensable aspect of the design and function of noise-reducing exhaust components. The selection of appropriate materials directly impacts the component’s lifespan, performance, and overall cost-effectiveness. While challenges exist in balancing material cost with durability requirements, the long-term benefits of selecting durable materials, including reduced maintenance costs, improved environmental performance, and increased vehicle reliability, far outweigh the initial investment. The increasing emphasis on environmental sustainability and vehicle longevity underscores the importance of material durability in the design and manufacturing of exhaust components.
4. System Compatibility
System compatibility is a critical factor in the successful integration and function of any exhaust noise reduction component, often referred to by the keyword phrase. A component’s physical dimensions, inlet and outlet diameters, and mounting configurations must align precisely with the vehicle’s existing exhaust system. Failure to ensure compatibility can result in improper fitment, exhaust leaks, reduced noise reduction efficiency, and potentially damage to the vehicle’s exhaust manifold or other components. For instance, installing a unit designed for a four-cylinder engine on a V6 engine will likely result in inadequate noise reduction and may create excessive backpressure, negatively impacting engine performance. Therefore, verifying compatibility before installation is paramount.
The importance of system compatibility extends beyond physical dimensions. The component’s internal design and flow characteristics must also be suitable for the engine’s specifications. Mismatched components can alter exhaust gas velocity and temperature, affecting catalytic converter efficiency and potentially triggering diagnostic trouble codes. A real-life example includes installing a high-flow aftermarket noise reduction component on a vehicle with a sensitive engine management system. While the component may reduce backpressure, the altered exhaust flow could disrupt the air-fuel ratio, leading to decreased fuel economy and potential engine damage. Thus, a careful assessment of the vehicle’s specific requirements and the component’s specifications is essential. Moreover, consider the impact on emissions control systems; an incompatible unit could compromise their functionality, resulting in non-compliance with environmental regulations.
In summary, system compatibility represents a vital aspect of exhaust noise reduction component selection and installation. Precise physical fitment and appropriate flow characteristics are necessary to ensure optimal performance, prevent damage to the vehicle, and maintain compliance with environmental standards. While selecting a “high-performance” unit may seem appealing, prioritizing system compatibility is crucial to avoiding potential negative consequences. Therefore, careful consideration of the vehicle’s specifications and the component’s characteristics is essential before proceeding with any installation. Challenges remain in ensuring compatibility across a wide range of vehicle models and engine configurations, underscoring the need for clear and accurate product information and professional installation services.
5. Regulatory Adherence
The manufacturing, distribution, and use of exhaust noise reduction components are subject to stringent regulations aimed at minimizing noise pollution and ensuring environmental protection. These regulations, often varying by jurisdiction, mandate specific noise emission standards that these components must meet. Non-compliance can result in significant penalties for manufacturers, distributors, and vehicle owners. The connection between regulatory adherence and these components is direct; they are engineered and designed to achieve specific noise reduction levels mandated by law. Failure to meet these standards can result in fines, legal action, and the recall of non-compliant products. The importance of regulatory adherence is therefore paramount, ensuring that these components function effectively to reduce noise pollution and protect public health. A practical example includes the implementation of noise emission testing procedures by regulatory bodies, where vehicles equipped with these components are subjected to standardized tests to verify compliance.
The design and material selection for these components are influenced by regulatory requirements. Manufacturers must consider factors such as noise reduction efficiency, backpressure, and material durability to meet or exceed prescribed standards. Exhaust systems incorporating noise reduction components are often certified to comply with specific regulations, and the certification process involves rigorous testing and documentation. The component must not only reduce noise to acceptable levels but also maintain its performance over time, ensuring continued compliance throughout its service life. Aftermarket components must also adhere to these regulations, and their installation may be subject to inspection to verify compliance. An example would be the requirement for aftermarket systems to provide equal or better noise reduction compared to the original equipment manufacturer (OEM) system.
In summary, regulatory adherence forms a cornerstone in the production and application of exhaust noise reduction components. Manufacturers must demonstrate compliance through rigorous testing and certification processes. Vehicle owners must ensure that the components installed on their vehicles meet applicable regulations to avoid penalties and contribute to environmental protection. While achieving compliance can present engineering and cost challenges, the benefits of reduced noise pollution and a healthier environment underscore the importance of adhering to regulatory standards. The long-term trend is toward increasingly stringent noise emission regulations, highlighting the ongoing need for innovation in component design and manufacturing to meet these evolving requirements.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following questions address common inquiries regarding the function, maintenance, and regulatory aspects of vehicle exhaust noise reduction components, also known as an Allied Muffler.
Question 1: What is the primary function?
The primary function is to reduce the noise generated by an internal combustion engine’s exhaust. It achieves this through internal baffling and sound-absorbing materials, minimizing noise pollution emitted into the environment.
Question 2: How does a malfunctioning Allied Muffler affect vehicle performance?
A malfunctioning component can lead to increased noise levels, reduced fuel efficiency due to increased backpressure, and potential failure to meet local noise emission regulations. In extreme cases, it may also contribute to exhaust leaks, posing a safety hazard.
Question 3: What are the typical signs of failure requiring Allied Muffler replacement?
Typical signs include excessively loud exhaust noise, rattling sounds originating from the exhaust system, visible rust or corrosion, and exhaust leaks. A visual inspection of the component is recommended to identify these issues.
Question 4: What materials are commonly used in Allied Muffler construction?
Common materials include aluminized steel, stainless steel, and mild steel. Stainless steel offers superior corrosion resistance and longer lifespan compared to other materials.
Question 5: How does backpressure influence Allied Muffler design and performance?
Backpressure, the resistance to exhaust flow, directly affects engine efficiency. The design balances noise reduction with minimal backpressure to optimize engine performance. Excessive backpressure reduces horsepower and fuel economy.
Question 6: What regulatory standards govern Allied Muffler noise emissions?
Noise emissions are governed by local, state, and federal regulations, varying by jurisdiction. Components must meet specific decibel limits to comply with these regulations, ensuring minimal noise pollution.
Understanding these key aspects is critical for responsible vehicle ownership and maintenance. Proper functioning of the noise reduction component ensures compliance with environmental regulations, minimizes noise pollution, and promotes a more comfortable driving experience.
Further sections will delve into advanced troubleshooting and selection guidelines for various noise reduction component types.
Conclusion
This exploration has illuminated various critical facets of the allied muffler, encompassing its functionality, maintenance, design elements, regulatory considerations, and impact on overall vehicle performance. The discussions highlighted the importance of material durability, system compatibility, and noise reduction efficiency in ensuring long-term performance and regulatory compliance. Emphasis was placed on balancing noise reduction with minimal exhaust backpressure to optimize engine output and fuel economy.
The effective functioning of the allied muffler is an essential aspect of responsible vehicle operation and environmental stewardship. Continued advancements in material science, design methodologies, and noise reduction technologies will undoubtedly shape the future of exhaust system components. A commitment to proper maintenance, informed component selection, and adherence to regulatory standards will contribute to quieter, more efficient, and environmentally sound transportation practices.