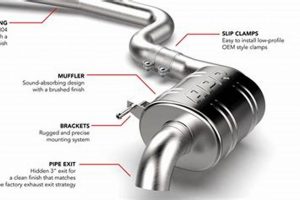
An automotive component designed to reduce the noise emitted by an internal combustion engine’s exhaust system. Functionally, it dampens sound waves created during the combustion process before they are released into the atmosphere. For example, a damaged or ineffective component can result in a vehicle producing excessive noise, potentially violating local ordinances.
Its importance lies in its contribution to noise pollution reduction and vehicle emission control. Historically, advancements in its design have focused on achieving a balance between sound dampening, exhaust flow efficiency, and overall vehicle performance. Modern iterations often incorporate sophisticated acoustic chambers and materials to optimize sound reduction without significantly impacting engine output.
This explanation provides a foundation for understanding the role of this critical element in vehicle operation. Subsequent discussions will delve into specific types, common issues, and best practices for maintenance and replacement.
Maintenance and Longevity Tips
Maintaining optimal performance and extending the lifespan of the exhaust silencing system requires attention to specific factors. Consistent monitoring and proactive measures can prevent costly repairs and ensure compliance with noise regulations.
Tip 1: Regular Visual Inspection: Conduct routine visual checks for signs of corrosion, rust, or physical damage. Early detection of these issues can prevent them from escalating into more significant problems. For example, rust spots on the exterior should be addressed promptly with rust inhibitors.
Tip 2: Address Unusual Noises: Pay attention to any changes in the vehicle’s exhaust sound. Rattling, hissing, or excessively loud noises may indicate a leak or internal damage. Addressing these sounds immediately can prevent further deterioration of the system.
Tip 3: Monitor Fuel Efficiency: A malfunctioning exhaust system can negatively impact fuel economy. A noticeable decrease in miles per gallon may signal a problem requiring professional diagnosis.
Tip 4: Avoid Short Trips: Short trips do not allow the exhaust system to reach its optimal operating temperature, leading to moisture accumulation and accelerated corrosion. Whenever possible, incorporate longer drives to burn off accumulated moisture.
Tip 5: Promptly Replace Worn Components: When replacing the component, opt for high-quality materials designed for the vehicle’s make and model. Inferior replacements may not provide adequate noise reduction or longevity.
Tip 6: Professional Inspection: Schedule regular inspections with a qualified mechanic. A professional can identify potential issues that may not be apparent during a visual inspection.
Tip 7: Undercoating Protection: Consider applying an undercoating treatment to the vehicle’s undercarriage, especially in regions with harsh winter conditions. This protective layer can help prevent corrosion caused by road salt and other chemicals.
Adhering to these maintenance tips can significantly extend the operational life and maintain the performance. Proactive attention ensures that the system functions effectively and complies with environmental standards.
The preceding insights offer a path toward preserving its integrity. The following sections will address common issues and resolution strategies.
1. Noise Reduction
The effective minimization of exhaust sound emanating from internal combustion engines is a principal function achieved through the utilization of this exhaust silencing component. It operates to diminish the amplitude of sound waves generated by the engine, thereby contributing to a quieter operating environment and adherence to noise pollution regulations.
- Acoustic Absorption
Internal construction incorporates sound-absorbing materials, such as fiberglass or mineral wool, to convert sound energy into heat. This process reduces the overall sound level transmitted through the exhaust system. For example, dense packing of acoustic material is more effective at absorbing a broader range of frequencies.
- Resonance Chambers
Designed with chambers that exploit the principles of destructive interference. Sound waves are reflected within these chambers, causing them to collide and cancel each other out. These chambers are specifically tuned to target particular frequencies, such as those prominent in engine exhaust noise.
- Baffle Systems
Employ a series of strategically placed baffles that force exhaust gases to follow a tortuous path. This labyrinthine passage causes sound waves to reflect and dissipate, reducing their intensity before exiting the exhaust system. The complexity and arrangement of baffles directly influence noise reduction effectiveness.
- Helmholtz Resonators
Utilize Helmholtz resonance, a phenomenon where air within a cavity resonates at a specific frequency. These resonators are tuned to counteract dominant exhaust frequencies, effectively neutralizing those specific sound components. The size and shape of the resonator determine its resonant frequency.
The integration of these noise reduction techniques exemplifies the functional complexity of this device. By combining acoustic absorption, resonance chambers, baffle systems, and Helmholtz resonators, it effectively manages exhaust sound. The selection and implementation of these methods depend on factors such as engine type, vehicle design, and regulatory requirements.
2. Exhaust Flow
Effective exhaust flow is critically linked to the performance of an exhaust silencing system. The design of this component directly influences the expulsion of exhaust gases from the engine, impacting both power output and fuel efficiency.
- Backpressure Minimization
Excessive backpressure restricts the engine’s ability to expel exhaust gases, reducing power and increasing fuel consumption. An exhaust silencing component designed for optimal flow minimizes this backpressure through careful internal structuring. For instance, a straight-through design with minimal obstructions promotes efficient gas expulsion. This design contrasts with baffled systems, which, while effective at noise reduction, can create more backpressure.
- Pipe Diameter Considerations
The diameter of the exhaust pipe leading to and from the silencing component affects flow characteristics. Insufficient diameter restricts flow, while excessive diameter can reduce exhaust velocity, impacting scavenging efficiency. The appropriate diameter is typically calculated based on engine displacement and intended power output. An incorrectly sized pipe can negate the benefits of a well-designed noise reduction chamber.
- Smooth Bends and Transitions
Abrupt bends and transitions in the exhaust piping create turbulence, impeding flow. Gradual bends and smooth transitions are crucial for maintaining consistent gas velocity. Mandrel bending, a process that preserves pipe diameter during bending, is often employed to minimize flow restriction. These smooth transitions are particularly important in high-performance applications where maximizing exhaust flow is paramount.
- Internal Surface Finish
The smoothness of the internal surface of the silencing component affects the boundary layer of exhaust gas, which can influence overall flow. Polished or coated internal surfaces reduce friction and turbulence, promoting more efficient gas expulsion. While the impact of surface finish may be less pronounced than pipe diameter or bend radius, it contributes incrementally to overall exhaust flow optimization.
The interplay between these factors determines the overall effectiveness of the exhaust system. Careful consideration of backpressure minimization, pipe diameter, bend geometry, and surface finish is essential when selecting or designing a system. The goal is to strike a balance between noise reduction and exhaust flow optimization to achieve optimal engine performance and fuel efficiency.
3. Backpressure Effects
The exhaust silencing system, while primarily designed to mitigate noise, inevitably influences exhaust backpressure. Backpressure arises from the restriction of exhaust gas flow, a consequence inherent in the design of most silencing components. The extent of this backpressure is determined by the internal structure of the silencing system, including baffle configuration, chamber design, and pipe diameter. Excessive backpressure impedes the efficient expulsion of exhaust gases from the engine cylinders. This impedance leads to a reduction in volumetric efficiency, which directly translates to decreased power output and increased fuel consumption. For instance, a system utilizing numerous baffles for maximum sound attenuation will inherently generate higher backpressure compared to a straight-through design with minimal internal obstructions. This increase in backpressure forces the engine to work harder to expel exhaust gases, diminishing its overall performance.
The proper consideration of backpressure is especially pertinent when modifying or replacing factory-installed exhaust systems. Aftermarket exhaust silencers boasting superior sound reduction may inadvertently introduce excessive backpressure, negating potential performance gains. Conversely, “performance” silencers prioritizing exhaust flow at the expense of noise reduction might compromise vehicle compliance with local sound ordinances. Real-world examples highlight the need for careful selection. A vehicle equipped with an overly restrictive system may exhibit noticeable sluggishness and reduced acceleration, particularly at higher engine speeds. Diagnostic procedures, such as measuring exhaust manifold pressure, can quantitatively assess the level of backpressure and identify potential restrictions within the exhaust system. Furthermore, computer-controlled engine management systems often compensate for increased backpressure by adjusting fuel delivery and ignition timing, further diminishing engine output.
In summary, a thorough understanding of backpressure effects is crucial when evaluating the performance characteristics of any exhaust silencing system. The goal is to achieve a balance between noise reduction and exhaust flow efficiency, ensuring compliance with noise regulations without significantly compromising engine power or fuel economy. Challenges lie in designing systems that effectively attenuate sound while minimizing flow restriction. Future advancements in silencing technology may focus on innovative internal designs and materials to achieve optimal performance in both areas.
4. Material Durability
The longevity and operational effectiveness of an exhaust silencing component are intrinsically linked to the durability of the materials from which it is constructed. The harsh operating environment, characterized by high temperatures, corrosive exhaust gases, and exposure to road debris and environmental elements, necessitates materials capable of withstanding significant stress. Material failure directly translates to reduced noise attenuation, increased emissions, and potential component failure, necessitating costly repairs or replacements. For instance, the use of mild steel in regions with frequent road salting leads to rapid corrosion and premature failure, rendering the silencer ineffective and potentially damaging other exhaust system components.
The selection of appropriate materials, therefore, becomes a critical design consideration. Stainless steel, particularly grades 304 and 409, is frequently employed due to its superior corrosion resistance and high-temperature strength. Aluminized steel offers a cost-effective alternative with enhanced corrosion protection compared to mild steel, though it lacks the ultimate durability of stainless steel. The thickness of the material also plays a crucial role. Thicker gauge steel provides increased resistance to physical damage from road debris and extends the component’s lifespan. Premium aftermarket systems often utilize thicker gauge stainless steel and incorporate reinforced welds to enhance durability in demanding operating conditions. The type of acoustic packing material used internally also affects durability. Certain packing materials degrade over time due to heat and chemical exposure, reducing their sound-absorbing capabilities and potentially contributing to internal corrosion.
In summary, material durability is a paramount factor influencing the performance and lifespan of an exhaust silencing system. The choice of materials directly impacts the component’s ability to withstand the rigors of its operating environment, affecting noise reduction, emissions control, and overall vehicle reliability. A thorough understanding of material properties and their susceptibility to corrosion, heat, and physical damage is essential for selecting or designing exhaust components that provide long-term performance and value.
5. Corrosion Resistance
Corrosion resistance is a pivotal factor influencing the lifespan and performance of exhaust silencing systems. The exposure to corrosive exhaust gases, moisture, and road salts presents a continuous threat to the structural integrity of these components. Therefore, the selection of materials and protective measures to mitigate corrosion is paramount.
- Material Selection
The choice of materials significantly impacts the component’s resistance to corrosion. Stainless steel, particularly grades like 304 and 409, offers superior corrosion resistance compared to aluminized or mild steel. These alloys form a passive chromium oxide layer on the surface, inhibiting further oxidation. For instance, a silencing system constructed from 304 stainless steel is more resistant to rust and degradation in coastal regions with high salt content in the air.
- Protective Coatings
Coatings, such as ceramic or aluminized coatings, provide an additional barrier against corrosive elements. These coatings prevent direct contact between the exhaust gases and the base metal. A ceramic coating can withstand high temperatures and chemical exposure, while aluminized coatings offer sacrificial protection, corroding preferentially to the underlying metal. A silencing system with an aluminized coating might experience surface corrosion, but the base metal remains protected, extending the system’s lifespan.
- Welding Techniques
Welding processes significantly affect corrosion resistance, and proper welding techniques are crucial to prevent corrosion. Welding can create heat-affected zones that are more susceptible to corrosion. Inert gas welding techniques, such as TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) welding, minimize oxidation and produce stronger, more corrosion-resistant welds. A poorly welded system may exhibit premature corrosion at the weld joints, leading to exhaust leaks and structural failure.
- Drainage Design
The design of the silencing system to facilitate drainage of accumulated moisture is important for corrosion prevention. Moisture trapped within the system accelerates corrosion. Incorporating drainage holes at strategic locations allows water to escape, reducing the duration of exposure to corrosive elements. For instance, a design with small drainage holes at the lowest points prevents water from pooling inside.
These considerations underscore the importance of corrosion resistance in ensuring the long-term durability and effectiveness of exhaust silencing systems. Proper material selection, protective coatings, welding techniques, and drainage design are essential strategies for mitigating corrosion and maintaining optimal performance over the component’s lifespan.
6. Vehicle Emissions
Exhaust silencing components play a crucial role in regulating vehicle emissions, though not in the same manner as catalytic converters or other dedicated emissions control devices. While the component primarily focuses on noise reduction, its design and operational condition significantly impact the efficiency of the engine’s combustion process, indirectly affecting emissions output. A malfunctioning or improperly designed exhaust silencing system can contribute to increased backpressure, leading to incomplete combustion and a rise in harmful emissions, such as hydrocarbons (HC), carbon monoxide (CO), and nitrogen oxides (NOx). For example, a severely corroded system creating excessive backpressure forces the engine to work harder, resulting in richer air-fuel mixtures and elevated levels of unburned fuel in the exhaust stream. This, in turn, contributes to higher overall emissions.
The relationship between exhaust flow characteristics and emissions is complex. Optimizing exhaust flow through a well-designed exhaust system can enhance engine efficiency and reduce emissions. Conversely, modifications to the exhaust system that disrupt flow patterns or increase turbulence can have detrimental effects. A common example is the removal of the factory-installed silencing component in favor of a straight pipe. While this may increase exhaust flow, it can also negatively impact engine tuning and emissions control strategies, resulting in increased pollutant output. Modern vehicles equipped with sophisticated engine management systems rely on precise exhaust backpressure readings for optimal fuel delivery and ignition timing. Alterations to the exhaust system can disrupt these readings, leading to suboptimal engine performance and increased emissions.
In summary, while the exhaust silencing component is not a primary emissions control device, its design and operational condition significantly influence vehicle emissions. Maintaining the integrity of the system and avoiding modifications that disrupt exhaust flow are essential for minimizing emissions and ensuring compliance with environmental regulations. The challenge lies in balancing noise reduction with exhaust flow optimization to achieve both acoustic comfort and environmental responsibility. Future advancements in exhaust silencing technology may focus on incorporating features that actively contribute to emissions reduction while effectively mitigating noise.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following addresses common inquiries regarding the application, maintenance, and functionality.
Question 1: What is the typical lifespan?
Lifespan varies significantly based on material, environmental conditions, and driving habits. Components constructed from stainless steel in moderate climates generally exhibit longer lifespans than those made from mild steel in regions with road salting. A lifespan of 5-10 years is achievable with proper maintenance and care.
Question 2: Does replacement impact vehicle warranty?
Replacement with an aftermarket component could impact the vehicle warranty if it is demonstrated the aftermarket component directly caused damage to another warranted part. However, simply replacing it will not void the entire warranty.
Question 3: How do I identify a failing?
Common symptoms of failure include increased exhaust noise, rattling sounds emanating from underneath the vehicle, visible corrosion or rust, and a potential decrease in fuel efficiency.
Question 4: What are the different types available?
Various types exist, including chambered, baffled, and straight-through designs. Chambered and baffled versions prioritize noise reduction, while straight-through types prioritize exhaust flow. Selection depends on the vehicle’s intended use and performance requirements.
Question 5: Can a damaged component affect engine performance?
Yes, a damaged component, particularly one causing excessive backpressure, can negatively affect engine performance. Increased backpressure reduces volumetric efficiency, leading to decreased power output and increased fuel consumption.
Question 6: Is it possible to repair a damaged ?
Minor damage, such as small holes or cracks, may be repairable through welding or patching. However, extensive damage or severe corrosion generally necessitates complete replacement for optimal performance and safety.
These answers provide clarity on aspects critical to system understanding. Vigilant observation and appropriate action optimize functionality.
The subsequent section will address diagnostic procedures related to it.
Conclusion
This exploration has detailed the function, maintenance, and implications of exhaust silencing components. Critical areas examined included noise reduction mechanisms, exhaust flow dynamics, material durability, and the nuanced relationship with vehicle emissions. Proper maintenance and informed selection directly contribute to operational longevity and compliance with noise regulations.
Understanding the principles outlined enables responsible vehicle ownership. Continued adherence to best practices promotes environmental consideration and ensures sustained vehicle performance. Investment in quality components and diligent upkeep translates to long-term value and contributes to a quieter, more efficient transportation landscape.