An automotive exhaust component designed to reduce noise levels, specifically employing stainless steel (SS) construction, provides a durable and corrosion-resistant solution for sound attenuation. This type of device is integrated within the exhaust system to dampen pressure pulses generated by the engine, resulting in a quieter operational experience. For example, a vehicle owner seeking to decrease exhaust sound output while maintaining system longevity might opt for this particular type of muffler.
The selection of a stainless steel variant offers a significant advantage in terms of lifespan compared to aluminized steel alternatives, particularly in environments with high exposure to moisture and road salts. Its resistance to rust and corrosion ensures consistent performance and reduces the need for frequent replacements. This characteristic contributes to long-term cost savings and minimizes maintenance requirements, enhancing overall vehicle reliability and value retention.
The following sections will delve into the specific construction techniques employed in these devices, explore the various performance characteristics related to backpressure and sound reduction, and examine considerations for selecting the appropriate model based on vehicle type and performance requirements. The discussion will also cover installation procedures and maintenance best practices.
Installation and Maintenance Guidelines
Proper handling and upkeep are crucial for maximizing the lifespan and performance of this exhaust component.
Tip 1: Verify Compatibility. Prior to installation, ensure the selected unit is specifically designed for the vehicle’s make, model, and engine configuration. Incompatible models can negatively impact engine performance and may result in improper fitment, voiding any applicable warranty.
Tip 2: Professional Installation Recommended. While DIY installation is possible, engaging a qualified mechanic is advisable. Incorrect installation can lead to exhaust leaks, reduced performance, and potential damage to the vehicle.
Tip 3: Use Appropriate Hardware. Always utilize new gaskets, bolts, and hangers during the installation process. Reusing old hardware can compromise the seal and structural integrity of the exhaust system, leading to premature failure.
Tip 4: Proper Alignment is Essential. After installation, carefully inspect the alignment of the exhaust system. Ensure there is adequate clearance between the muffler and any surrounding components, such as the vehicle’s frame, fuel lines, and brake lines, to prevent rubbing and potential damage.
Tip 5: Regular Visual Inspections. Conduct routine visual inspections of the muffler and associated exhaust components. Look for signs of corrosion, damage, or leaks. Address any issues promptly to prevent further deterioration.
Tip 6: Avoid Abrasive Cleaners. When cleaning the exterior of the muffler, refrain from using abrasive cleaners or scouring pads. These can scratch the stainless steel finish and accelerate corrosion. Use a mild soap and water solution with a soft cloth.
Tip 7: Address Unusual Noises Immediately. If experiencing rattling or excessive exhaust noise, promptly investigate the source. Such noises may indicate a loose connection, a failing hanger, or internal damage within the muffler.
Adhering to these guidelines will ensure optimal performance, extended lifespan, and continued noise reduction benefits.
The subsequent section will discuss troubleshooting common issues and identifying potential problems related to exhaust system performance.
1. Material Durability
Material durability constitutes a core characteristic of the “quiet flow ss muffler,” directly influencing its lifespan and overall value proposition. The selection of stainless steel as the primary construction material directly correlates to the component’s ability to withstand the harsh conditions inherent in automotive exhaust systems. Exposure to extreme temperatures, corrosive exhaust gases, road salts, and physical impacts necessitates a material capable of maintaining structural integrity over extended periods. The direct effect of utilizing stainless steel is a reduction in the frequency of required replacements, translating to cost savings for the vehicle owner. A real-life example is the comparison between a stainless steel muffler and an aluminized steel equivalent in regions with significant winter road salting; the stainless steel version demonstrably outlasts the aluminized version, often by a factor of several years. The practical significance of this understanding lies in the ability of consumers to make informed purchasing decisions based on long-term cost-effectiveness rather than solely on initial price.
Further analysis reveals that the specific grade of stainless steel employed also impacts durability. Alloys with higher chromium and nickel content exhibit enhanced resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion, which are common failure modes in exhaust systems. The welding techniques utilized during manufacturing further contribute to overall structural robustness. High-quality welds minimize stress concentrations and prevent premature cracking or separation of components. For instance, a robotic welding process that ensures consistent weld penetration and quality can significantly extend the service life of the muffler compared to manual welding methods. Beyond material properties and manufacturing processes, proper installation and maintenance practices are also critical for maximizing the durability of the unit. Avoiding physical damage from road debris and promptly addressing any signs of corrosion or exhaust leaks contribute to the long-term preservation of the muffler.
In conclusion, material durability, achieved through the strategic selection of stainless steel and meticulous manufacturing processes, is paramount to the overall performance and longevity of a “quiet flow ss muffler.” The practical benefits are reduced replacement costs, improved reliability, and sustained noise reduction performance. Challenges exist in balancing material costs with performance requirements, necessitating a careful consideration of the vehicle’s operating environment and the owner’s expectations. The pursuit of enhanced material durability remains central to the continued improvement of this exhaust component, aligning with the broader goal of creating more sustainable and cost-effective automotive solutions.
2. Sound Attenuation
Sound attenuation is a primary function of the “quiet flow ss muffler,” directly impacting vehicle noise emissions and overall driving experience. The design and construction of the muffler are intrinsically linked to its ability to effectively reduce exhaust noise.
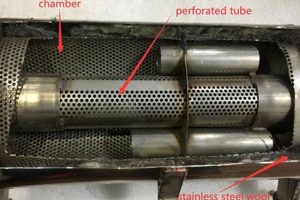
- Internal Chamber Design
The configuration of internal chambers within the muffler plays a critical role in sound wave cancellation. Baffles, resonators, and strategically placed perforations disrupt the propagation of sound waves, causing them to reflect and interfere with each other. This destructive interference reduces the amplitude of the sound waves exiting the muffler. An example is the use of Helmholtz resonators tuned to specific frequencies to neutralize dominant exhaust tones. The effectiveness of this design directly affects the perceived loudness of the vehicle exhaust.
- Acoustic Absorption Materials
Some designs incorporate sound-absorbing materials, such as fiberglass or mineral wool packing, to further dampen noise levels. These materials convert acoustic energy into heat through friction, reducing the intensity of sound waves passing through the muffler. The lifespan and effectiveness of these materials are contingent upon their resistance to high temperatures and exhaust gas corrosion. Degradation of these materials over time can lead to increased exhaust noise.
- Muffler Casing Construction
The construction of the muffler casing also contributes to sound attenuation. Multi-layer casing designs, often incorporating insulating air gaps, minimize the transmission of noise through the muffler walls. The thickness and density of the stainless steel used in the casing affect its ability to dampen vibrations and prevent resonance. Thicker-gauge stainless steel typically results in quieter operation compared to thinner-gauge materials.
- Exhaust Flow Dynamics
The internal design must balance sound attenuation with the need to maintain adequate exhaust flow. Excessive backpressure can negatively impact engine performance. A well-designed muffler minimizes backpressure while maximizing sound reduction. This often involves careful optimization of chamber sizes, perforation patterns, and exhaust flow pathways. For instance, a straight-through muffler design minimizes backpressure but may offer less sound attenuation compared to a chambered design.
The successful integration of these elements determines the overall sound attenuation performance of the “quiet flow ss muffler.” Design trade-offs between noise reduction, backpressure, and durability are inherent in the development process. Continuous advancements in materials science and acoustic engineering are driving improvements in muffler design, leading to quieter and more efficient exhaust systems.
3. Exhaust Backpressure
Exhaust backpressure, defined as the resistance to exhaust gas flow within an exhaust system, is a critical performance parameter intricately linked to the design and functionality of a “quiet flow ss muffler.” Its influence on engine efficiency, power output, and noise reduction necessitates careful consideration during the muffler’s development and selection.
- Muffler Design and Flow Restriction
Internal muffler designs, particularly those employing chambers, baffles, and convoluted pathways to achieve sound attenuation, inherently introduce some degree of flow restriction. This resistance to exhaust gas flow creates backpressure. A “quiet flow ss muffler” aims to minimize this backpressure while maintaining effective noise reduction. For example, a multi-chambered muffler, while highly effective at silencing exhaust, may create significantly more backpressure compared to a straight-through design.
- Impact on Engine Performance
Excessive exhaust backpressure can impede the scavenging process within the engine cylinders, reducing volumetric efficiency and ultimately diminishing power output. The engine must expend more energy to expel exhaust gases, resulting in decreased fuel economy and potentially increased engine temperatures. A “quiet flow ss muffler” with suboptimal design can exacerbate this effect, leading to noticeable performance degradation, especially in high-performance engines. Conversely, insufficient backpressure can also be detrimental, disrupting proper cylinder filling in some engine designs.
- Balancing Noise Reduction and Performance
The design of a “quiet flow ss muffler” involves a trade-off between sound attenuation and backpressure. Aggressive noise reduction strategies, such as complex chamber designs and dense packing materials, often increase backpressure. Engineers must carefully optimize the internal geometry and material selection to strike a balance between these competing objectives. Simulation tools and flow testing are employed to evaluate the impact of various designs on both sound levels and exhaust flow characteristics.
- Application-Specific Considerations
The acceptable level of exhaust backpressure varies depending on the vehicle’s intended use and engine characteristics. High-performance vehicles typically require mufflers with minimal backpressure to maximize power output. Conversely, vehicles prioritizing fuel economy or noise reduction may tolerate higher backpressure. Selecting the appropriate “quiet flow ss muffler” necessitates considering the vehicle’s operating parameters and performance requirements to ensure optimal overall system efficiency.
The relationship between exhaust backpressure and the “quiet flow ss muffler” underscores the importance of a holistic design approach. Optimizing the muffler’s internal geometry and material selection is paramount to achieving the desired balance between noise reduction, engine performance, and fuel efficiency. Proper selection, installation, and maintenance of the muffler contribute to the overall health and performance of the vehicle’s exhaust system.
4. Corrosion Resistance
Corrosion resistance represents a critical performance attribute of any exhaust system component, particularly for a “quiet flow ss muffler.” The operating environment within an exhaust system is inherently corrosive, exposing materials to high temperatures, acidic condensates, and road de-icing agents. The materials capacity to withstand these conditions directly determines the lifespan and sustained effectiveness of the muffler.
- Material Composition and Resistance
The selection of stainless steel alloys directly influences corrosion resistance. Specific grades, such as 304 or 409 stainless steel, offer varying levels of chromium and nickel content, which form a passive oxide layer on the material’s surface, impeding corrosive attack. For example, a “quiet flow ss muffler” constructed from 304 stainless steel exhibits superior resistance to chloride-induced pitting corrosion compared to a 409 stainless steel counterpart. The composition of the alloy is therefore a primary determinant of long-term durability.
- Welding Processes and Corrosion Vulnerability
Welding introduces potential points of corrosion vulnerability. Improper welding techniques can compromise the protective oxide layer on the stainless steel, leading to localized corrosion. The use of appropriate filler metals and shielding gases during welding minimizes this risk. For instance, using a filler metal with a higher chromium content than the base metal can enhance the corrosion resistance of the weld joint. Post-weld passivation treatments can further restore the protective oxide layer.
- Environmental Factors and Accelerated Corrosion
Exposure to specific environmental factors, such as road salts and coastal environments, accelerates corrosion. Chlorides from road salts penetrate the passive oxide layer on stainless steel, promoting pitting and crevice corrosion. Coastal environments with high humidity and salt concentrations exacerbate this effect. Regular washing of the vehicle undercarriage can mitigate the effects of road salts, extending the lifespan of the muffler.
- Galvanic Corrosion Considerations
Galvanic corrosion can occur when dissimilar metals are in contact in the presence of an electrolyte. If a “quiet flow ss muffler” is connected to exhaust components made of different metals (e.g., aluminized steel), galvanic corrosion can occur at the interface. Using isolation sleeves or corrosion-resistant fasteners can minimize this risk. Ensuring compatibility between the materials used in the entire exhaust system is crucial for preventing premature failure.
The selection of appropriate stainless steel alloys, the implementation of proper welding techniques, and the mitigation of environmental factors are all essential for maximizing the corrosion resistance of a “quiet flow ss muffler.” These considerations directly influence the component’s lifespan, performance, and overall value. Understanding and addressing these factors is vital for both manufacturers and consumers seeking a durable and reliable exhaust system solution.
5. Vehicle Compatibility
Vehicle compatibility represents a fundamental prerequisite for the proper functioning and longevity of a “quiet flow ss muffler.” The selection and installation of a muffler not specifically designed for a particular vehicle can lead to performance degradation, potential damage to the exhaust system or engine, and voiding of warranties. Meticulous attention to vehicle-specific requirements is therefore paramount.
- Engine Size and Configuration Matching
The internal design of a “quiet flow ss muffler,” including chamber dimensions and flow pathways, must be compatible with the engine’s displacement and cylinder configuration. A muffler designed for a small displacement four-cylinder engine will likely create excessive backpressure on a large displacement V8, resulting in reduced power output and potential overheating. Conversely, a muffler designed for a V8 may not provide sufficient sound attenuation on a smaller engine. Vehicle manufacturers often specify exhaust system components tailored to specific engine variants.
- Exhaust System Dimensional Conformance
Physical dimensions, including inlet and outlet pipe diameters and overall muffler length, must align with the vehicle’s existing exhaust system configuration. Mismatched pipe diameters will necessitate the use of adapters, creating potential leak points and flow restrictions. Incorrect muffler length can complicate installation and require modifications to the exhaust system. Many aftermarket suppliers offer direct-fit replacements designed to match original equipment manufacturer (OEM) specifications.
- Mounting Point Compatibility
The location and type of mounting points on the “quiet flow ss muffler” must correspond with the vehicle’s chassis or exhaust system hangers. Incompatible mounting points will necessitate fabrication of custom brackets, potentially compromising structural integrity and increasing vibration. Direct-fit replacements typically include mounting points that mirror the OEM design, simplifying installation.
- Emissions System Integration
In vehicles equipped with catalytic converters or other emissions control devices, the “quiet flow ss muffler” must not impede their function. Excessive backpressure or improper flow characteristics can negatively impact catalytic converter efficiency, leading to increased emissions and potential regulatory non-compliance. Some mufflers are specifically designed to meet stringent emissions standards, particularly in jurisdictions with rigorous testing requirements.
The interplay of these factors underscores the critical importance of verifying vehicle compatibility prior to selecting and installing a “quiet flow ss muffler.” Utilizing vehicle-specific fitment guides and consulting with qualified automotive professionals can mitigate the risk of incompatibility, ensuring optimal performance, longevity, and compliance with applicable regulations. The pursuit of precise vehicle compatibility remains a cornerstone of responsible exhaust system design and modification.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following addresses common inquiries regarding the selection, installation, and maintenance of stainless steel mufflers designed for noise reduction in automotive exhaust systems. This information aims to provide clarity and promote informed decision-making.
Question 1: What distinguishes a stainless steel muffler from an aluminized steel muffler?
Stainless steel mufflers exhibit superior corrosion resistance compared to aluminized steel counterparts. The chromium and nickel content in stainless steel forms a passive oxide layer, impeding rust formation. Aluminized steel features a thin aluminum coating, which offers limited protection and is prone to degradation in harsh environments. Stainless steel typically provides a longer service life.
Question 2: Does a “quiet flow” muffler negatively impact engine performance?
A properly designed “quiet flow ss muffler” minimizes backpressure, thereby mitigating any adverse effects on engine performance. Excessive backpressure can reduce horsepower and fuel efficiency. However, mufflers engineered to strike a balance between sound attenuation and exhaust flow restriction should not significantly impair engine output.
Question 3: How frequently should a stainless steel muffler be replaced?
The lifespan of a stainless steel muffler depends on factors such as environmental conditions, driving habits, and the quality of the steel. Under normal operating conditions, a high-quality stainless steel muffler can last for 5-10 years or more. Regular inspections can identify signs of corrosion or damage that may necessitate replacement.
Question 4: Can a “quiet flow ss muffler” be installed on any vehicle?
Vehicle compatibility is crucial. Muffler dimensions, inlet/outlet diameters, and mounting points must align with the vehicle’s exhaust system. An incompatible muffler can create leaks, increase backpressure, or be impossible to install without extensive modifications. Always verify fitment using vehicle-specific guides.
Question 5: Does the gauge of stainless steel affect muffler performance or longevity?
The gauge (thickness) of the stainless steel directly impacts durability and sound attenuation. Thicker-gauge stainless steel offers greater resistance to corrosion and physical damage, resulting in a longer lifespan. It also tends to dampen vibrations more effectively, contributing to quieter operation. However, thicker-gauge steel also increases the muffler’s weight and cost.
Question 6: Are there any specific maintenance procedures for stainless steel mufflers?
While stainless steel is corrosion-resistant, periodic cleaning is advisable, especially in regions with road salts. Washing the undercarriage of the vehicle removes corrosive deposits. Avoid using abrasive cleaners, as they can scratch the surface. Inspecting the muffler for signs of damage or loose connections is also recommended.
These FAQs provide a fundamental understanding of “quiet flow ss mufflers.” Careful consideration of these factors will facilitate informed decisions regarding selection, installation, and maintenance.
The subsequent section explores advanced topics related to exhaust system design and performance optimization.
In Conclusion
This exploration has detailed the construction, function, and considerations surrounding the quiet flow SS muffler. The synthesis of durable stainless steel construction with effective sound attenuation principles results in a component that addresses both longevity and noise reduction requirements within automotive exhaust systems. Key aspects include material grade selection, internal design optimization to balance backpressure and noise suppression, and vehicle-specific fitment considerations. These elements coalesce to define the overall performance and suitability of the device.
As regulatory pressures regarding noise pollution intensify and consumer demand for refined vehicle operation increases, the significance of the quiet flow SS muffler will likely grow. Continued advancements in materials science and acoustic engineering are anticipated to further enhance the capabilities of these components. Therefore, understanding the core principles governing their design and application remains paramount for both automotive professionals and informed consumers.