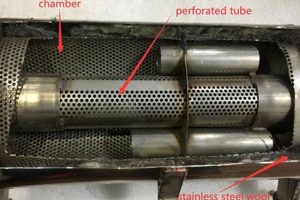
A component integrated within a vehicle’s exhaust system is designed to mitigate specific sound frequencies, effectively reducing noise levels. Its construction generally involves a chamber, often cylindrical, that uses sound wave interference to cancel out unwanted tones. This results in a quieter and more refined exhaust note. For instance, the component can target drone, a low-frequency hum often associated with aftermarket exhaust systems.
The integration of this element offers several advantages. Primarily, it enhances the driving experience by minimizing irritating noises. Furthermore, in certain regions, it contributes to compliance with noise regulations, which are increasingly stringent. Historically, these devices were simpler in design, but advancements in materials and acoustic engineering have led to more effective and precisely tuned units.
Understanding this noise-reduction technology is crucial for informed decisions regarding exhaust system modifications and maintenance. Subsequent discussions will delve into specific designs, installation considerations, and potential performance implications.
Muffler Resonator
Optimal performance and longevity of an exhaust system incorporating a sound-dampening component requires adherence to specific guidelines. These tips address crucial aspects of selection, installation, and maintenance.
Tip 1: Select the Appropriate Type: Choose a sound-dampening component specifically designed for the vehicle’s make and model. Generic options may not provide optimal noise reduction or may introduce unwanted performance issues. Refer to manufacturer specifications and consult with exhaust system specialists.
Tip 2: Ensure Proper Installation: Correct placement is critical. The component should be installed at the location recommended by the manufacturer to effectively target the desired sound frequencies. Incorrect positioning can render it ineffective.
Tip 3: Verify Compatibility with Existing Exhaust Components: When upgrading or modifying an exhaust system, confirm that the new sound-dampening component is compatible with the existing muffler and piping. Mismatched components can negatively impact exhaust flow and noise levels.
Tip 4: Inspect Regularly for Damage: Periodic inspections are necessary to identify any signs of damage, such as rust, cracks, or dents. Damaged components can lead to increased noise levels and potential exhaust leaks.
Tip 5: Address Issues Promptly: Any noticeable change in exhaust sound, such as increased loudness or the presence of unusual noises, should be investigated immediately. A failing component can indicate a more significant exhaust system problem.
Tip 6: Consider Professional Installation: For complex exhaust systems or if unsure about the installation process, seek professional assistance. A qualified technician can ensure proper installation and prevent potential issues.
Tip 7: Understand the Trade-offs: While this component reduces noise, it may also slightly impact exhaust flow and, consequently, engine performance. Be aware of these potential trade-offs when selecting a component.
Adhering to these guidelines maximizes the benefits of the system while minimizing potential drawbacks. Proper selection, installation, and maintenance ensure continued noise reduction and contribute to the overall efficiency of the exhaust system.
The following sections will explore common issues, troubleshooting methods, and advanced customization options related to this component.
1. Noise frequency reduction
The capacity to attenuate specific acoustic frequencies is a fundamental characteristic of the sound-dampening exhaust component. This ability directly governs the component’s effectiveness in creating a more refined and acceptable exhaust sound.
- Helmholtz Resonance Application
Some components utilize Helmholtz resonance to target and cancel specific frequencies. A chamber of defined volume and neck length is designed to resonate at a targeted frequency, effectively canceling it out through destructive interference. This is applicable when addressing a distinct drone frequency.
- Reactive Sound Cancellation Mechanisms
This involves strategically placed chambers and tubes within the exhaust system. These elements create reflected sound waves that are out of phase with the original sound waves, resulting in cancellation and a reduction in noise intensity at specific frequencies. They are implemented to mitigate broader frequency ranges.
- Internal Baffle Design Influence
The internal structure, including baffles and flow paths, can be engineered to attenuate specific frequencies. Baffles redirect and disrupt sound waves, leading to energy dissipation and noise reduction, particularly in the higher frequency ranges. A good design improves noise quality.
- Material Properties and Damping
The materials used in construction play a role in noise reduction. Certain materials exhibit superior sound-absorbing properties, dampening vibrations and reducing the transmission of noise frequencies. For example, certain types of packing can reduce high-frequency raspiness
The ability to precisely manipulate noise frequencies is paramount to the success of this sound-dampening technology. These various methods provide a nuanced approach to exhaust sound control. The optimal implementation of each is dependent on vehicle specifications and desired result.
2. Sound wave interference
Sound wave interference is the fundamental principle underpinning the operation of the exhaust system’s noise-reduction component. Its effectiveness hinges on the manipulation and cancellation of acoustic energy within the exhaust stream.
- Destructive Interference and Frequency Cancellation
Destructive interference occurs when two sound waves with opposite phases combine, resulting in a cancellation effect and a reduction in sound intensity. The component is engineered to generate sound waves that are 180 degrees out of phase with specific frequencies produced by the engine. The destructive interference reduces the amplitude of the targeted noise.
- Helmholtz Resonance and Anti-Phase Generation
Some implementations leverage Helmholtz resonance to create anti-phase sound waves. A specifically sized chamber is designed to resonate at a target frequency. The resonating chamber emits a sound wave that opposes the original engine noise, leading to a reduction in noise pollution.
- Reflective Wave Path Manipulation
Internal baffles and strategically designed flow paths within the component cause sound waves to reflect and interact with each other. The reflective design cancels unwanted frequencies while allowing exhaust gas flow to continue.
- Constructive Interference Avoidance
While destructive interference is crucial for noise reduction, it is equally important to avoid constructive interference. Constructive interference occurs when sound waves are in phase, which amplifies the sound. The component’s design is optimized to minimize constructive interference.
Sound wave interference principles enable the sound-dampening component to selectively attenuate specific noise frequencies. By engineering controlled interactions of sound waves, it achieves noise reduction. Understanding these interferences is vital for optimizing exhaust system sound and performance.
3. Exhaust note refinement
Exhaust note refinement, in the context of vehicle exhaust systems, refers to the shaping and controlling of the sound produced by the engine’s exhaust gases. The sound-dampening exhaust component directly influences this refinement process. By strategically targeting and reducing undesirable frequencies, this component contributes to a more pleasant and controlled auditory experience. Without this device, an exhaust system may produce excessive noise, drone, or harsh tones. Consider, for example, a performance car modified with an aftermarket exhaust system. While such a system may enhance engine performance, it often introduces a noticeable drone at cruising speeds. Integration of this sound-dampening part within the exhaust system would mitigate this drone, resulting in a refined, yet sporty, exhaust note.
The connection between exhaust sound refinement and the sound-dampening component is causal. The system is designed to directly alter the characteristics of the exhaust sound. For instance, certain models of this component are designed to suppress specific frequencies, such as the aforementioned drone, while others are engineered to enhance desirable frequencies, such as a deep rumble. The effectiveness of this sound-dampening component in this role often dictates overall satisfaction. Car enthusiasts often value refined exhaust notes, signifying performance without excessive harshness.
In summary, this component forms a central element in the refining of a vehicle’s exhaust note. The component influences the noise properties, either by suppressing undesirable frequencies or enhancing more pleasing sounds. A greater understanding on exhaust sounds directly correlates with an improved driving experience. By targeting noise and optimizing sound characteristics, it plays a vital role in balancing engine performance with auditory refinement.
4. Chambered construction
Chambered construction is a fundamental design approach employed in the creation of sound-dampening exhaust components. The arrangement and configuration of chambers within this component directly influence its ability to modify and attenuate sound waves, thereby dictating its effectiveness in noise reduction.
- Resonance Chamber Design
A resonance chamber is a specifically sized and shaped cavity engineered to resonate at a particular frequency. In the context of this noise-reduction device, these chambers target specific, undesirable frequencies, such as exhaust drone. The dimensions of the chamber are calculated to create a resonant frequency that cancels out the targeted sound wave through destructive interference. An example is the use of Helmholtz resonators to eliminate low-frequency rumble in performance vehicles.
- Expansion Chamber Functionality
Expansion chambers facilitate the sudden increase in volume available to the exhaust gases. This expansion reduces the velocity of the gas flow, allowing sound waves to dissipate and lose energy. These chambers typically feature internal baffles or deflectors to further disrupt the sound waves and promote energy dissipation. Expansion chambers are commonly found in systems designed to reduce overall exhaust noise across a broad frequency range.
- Baffle Arrangement and Flow Path
The strategic arrangement of baffles within the internal chambers defines the flow path of the exhaust gases. Baffles redirect sound waves, forcing them to travel along a convoluted path, which encourages interference and dissipation. The specific geometry and positioning of these baffles dictate the frequencies attenuated and the overall noise-reduction profile of the component. Variations in baffle design will influence noise characteristics.
- Material Impact on Chamber Performance
The material used in the construction of the chambers influences the component’s ability to absorb and dampen sound waves. Certain materials exhibit superior sound-absorbing properties, reducing the transmission of noise through the component itself. This selection can mitigate high-frequency sounds and raspiness. The material considerations are important for noise output.
The chambered construction method provides a versatile approach to exhaust sound control. The individual chamber attributes and overall configurations directly impact the noise output quality. Understanding how chambers operate is essential for maximizing noise reduction.
5. Drone cancellation
Drone cancellation is a primary function frequently served by the sound-dampening exhaust component. The term “drone” refers to a persistent, low-frequency humming or booming sound often generated within an exhaust system at specific engine speeds, typically during steady-state cruising. This phenomenon is particularly prevalent in vehicles equipped with aftermarket exhaust systems designed for performance enhancement, where less restrictive flow paths can amplify undesirable frequencies. The implementation of this dampening component aims to mitigate or eliminate this drone, thereby improving the overall auditory comfort within the vehicle’s cabin.
The component achieves drone cancellation through various acoustic engineering techniques, primarily employing the principle of destructive interference. Resonators, specifically designed chambers within the component, are tuned to resonate at the problematic drone frequency. These resonators generate sound waves that are 180 degrees out of phase with the drone frequency, effectively canceling it out through destructive interference. Alternative approaches involve strategically placed baffles and expansion chambers that disrupt and diffuse the drone frequencies. As an example, many sport utility vehicles and pickup trucks, known for their spacious interiors that can amplify exhaust noise, often utilize complex exhaust systems incorporating multiple noise-reduction devices tuned to mitigate drone. Without effective drone cancellation, long drives in these vehicles can become tiresome due to the persistent low-frequency hum.
In conclusion, drone cancellation represents a crucial feature for components of the exhaust system, especially in vehicles where exhaust noise can be intrusive. The component’s ability to suppress drone significantly enhances the driving experience, improving the noise and the exhaust sound. Understanding the mechanics of drone cancellation, primarily the use of destructive interference and tuned resonators, is essential for selecting and maintaining an exhaust system. This consideration is particularly relevant for enthusiasts seeking performance upgrades without sacrificing daily driving comfort and driving pleasure.
6. System compatibility
The effective functioning of the exhaust noise-reduction component is intrinsically linked to its compatibility with the broader vehicle exhaust system. A failure to ensure such compatibility can negate the component’s intended benefits, leading to performance degradation or increased noise levels, thereby undermining the purpose of this noise reduction technology.
- Exhaust Gas Flow Dynamics
The internal design of an exhaust affects gas flow, and installing an incompatible component could impede flow, resulting in reduced engine power or fuel efficiency. For instance, a component designed for a high-performance engine with a large diameter may restrict the flow in a smaller engine, leading to a loss of power. This necessitates considering gas flow of both the existing exhaust system and the new component.
- Pipe Diameter Matching
Incompatibilities in pipe diameter are critical for efficient function of the entire exhaust. A component with an inlet or outlet diameter mismatched to the existing system can create turbulence and backpressure, negatively impacting engine performance and potentially increasing noise. Proper matching of pipe diameters ensures a smooth transition of exhaust gases and maintains optimal performance.
- Sensor Integration and Clearance
Modern exhaust systems often incorporate sensors, such as oxygen sensors, to monitor engine performance. A component that obstructs sensor placement or interferes with their function can trigger error codes and negatively impact engine management. In some cases, physical interference with other vehicle components due to size and shape of this component can lead to physical damage to the overall exhaust system.
- Material Compatibility and Corrosion
Using components constructed from dissimilar metals can accelerate corrosion due to galvanic reactions. For instance, connecting a stainless steel component to a mild steel exhaust system can lead to rapid corrosion of the mild steel. Selecting compatible materials ensures the longevity and reliability of the entire exhaust system.
Therefore, ensuring system-wide compatibility during the design or installation of a noise reducing component is paramount for achieving its intended noise reduction without compromising performance or longevity. Proper evaluation and consideration of these factors are critical for maximizing the benefits of this element within the broader context of vehicle engineering.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding the characteristics, functionality, and implementation of a sound-dampening exhaust component.
Question 1: What constitutes the primary function of the exhaust noise-reduction component?
The primary function involves the attenuation of specific sound frequencies within the exhaust system, thereby diminishing overall noise output and refining the exhaust note.
Question 2: How does the exhaust noise-reduction component achieve noise reduction?
Noise reduction is typically achieved through the manipulation of sound waves via interference, resonance, or absorption, depending on the design of the component. Internal chambers and baffles contribute to this process.
Question 3: Is this component universally compatible across all vehicle makes and models?
No, compatibility depends on various factors including engine displacement, exhaust system design, and vehicle-specific noise regulations. Selecting a component designed for a specific vehicle is essential.
Question 4: What are the potential consequences of installing an incompatible exhaust noise-reduction component?
Incompatibility can lead to reduced engine performance, increased backpressure, amplified noise levels, or damage to the exhaust system itself.
Question 5: Does the installation of the exhaust noise-reduction component invariably result in a reduction of engine power?
While some designs may slightly impact exhaust flow and, consequently, engine performance, modern components are engineered to minimize any power reduction. A properly designed and installed component should not significantly affect engine output.
Question 6: What maintenance procedures are recommended for the exhaust noise-reduction component?
Regular inspection for damage, such as rust or cracks, is advisable. Any noticeable change in exhaust sound may indicate a problem requiring attention. Adherence to manufacturer-recommended maintenance schedules is also crucial.
In summation, the proper selection, installation, and maintenance of this sound-dampening component are paramount for achieving optimal noise reduction without compromising vehicle performance.
The following section will explore advanced customization options and troubleshooting techniques related to this component.
Conclusion
The preceding exploration has elucidated the function, design principles, and implications associated with the exhaust system component designed for sound dampening. This detailed analysis of the “what is muffler resonator” question underscores the importance of understanding its role in controlling exhaust noise, optimizing engine performance, and ensuring regulatory compliance. The principles of sound wave interference, chambered construction, and frequency tuning all contribute to the effectiveness of this component.
Moving forward, continued research and development in materials science and acoustic engineering will likely yield even more sophisticated solutions for exhaust noise management. As environmental regulations tighten and consumer demand for refined vehicle acoustics grows, the importance of this component will only increase, further solidifying its significance within the automotive industry. Careful consideration of these factors remains essential for informed decision-making in vehicle design, modification, and maintenance.