The fabrication of an exhaust noise reduction device involves the precise assembly of components designed to attenuate sound waves generated by internal combustion engines. This process generally entails constructing a housing, incorporating internal baffles or chambers, and ensuring gas-tight seals to redirect and dampen sound propagation. This fabrication can be customized to specific engine characteristics and noise reduction requirements.
Effectively reducing engine noise offers multiple advantages, including compliance with noise regulations, improved vehicle operator and passenger comfort, and mitigation of environmental noise pollution. Historically, advancements in noise reduction technology have significantly contributed to more environmentally responsible and socially acceptable vehicle operation. Efficient designs can also contribute to improved engine performance by optimizing exhaust flow.
The subsequent sections will detail the selection of appropriate materials, the design considerations for internal structures, the welding or joining techniques required for robust construction, and the testing procedures to validate the device’s acoustic performance and durability, as well as essential safety precautions.
Essential Considerations for Exhaust Noise Reduction Device Construction
Successful fabrication of an exhaust noise reduction device demands meticulous planning and execution. Adherence to best practices ensures both acoustic effectiveness and long-term durability.
Tip 1: Material Selection: Employ high-quality, corrosion-resistant materials such as stainless steel or aluminized steel. These materials withstand high temperatures and corrosive exhaust gases, extending the lifespan of the device.
Tip 2: Design for Acoustic Performance: Optimize the internal baffle or chamber configuration based on target frequency ranges and engine characteristics. Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) modeling can aid in predicting acoustic performance.
Tip 3: Precision Welding Techniques: Utilize Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW) or Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW) techniques to ensure strong, leak-proof seams. Proper weld penetration is critical for preventing exhaust leaks and maintaining structural integrity.
Tip 4: Accurate Measurement and Cutting: Employ precise measuring tools and cutting equipment, such as laser cutters or plasma cutters, to ensure accurate component dimensions. Accurate fitting minimizes gaps and stress points.
Tip 5: Leak Testing Protocol: Conduct thorough leak testing using pressure testing equipment or soapy water solutions post-assembly. Identifying and rectifying leaks is crucial for optimal noise reduction and preventing exhaust gas escape.
Tip 6: Consider Mounting and Vibration: Design robust mounting brackets and incorporate vibration isolation techniques to minimize stress on the exhaust system. Excessive vibration can lead to premature failure.
Tip 7: Surface Treatment and Coating: Apply high-temperature coatings or surface treatments to further enhance corrosion resistance and improve the aesthetic appearance. Such treatments protect against oxidation and environmental degradation.
Implementing these considerations during the fabrication process maximizes the effectiveness and longevity of the exhaust noise reduction device, contributing to improved vehicle performance and reduced environmental impact.
The concluding section will address safety protocols, regulatory compliance, and ongoing maintenance recommendations.
1. Material Selection
The selection of appropriate materials is paramount in the fabrication of an exhaust noise reduction device. The operational environment necessitates materials capable of withstanding high temperatures, corrosive exhaust gases, and constant vibration, thereby dictating the device’s longevity and performance.
- Corrosion Resistance
Materials must exhibit high resistance to corrosion caused by acidic compounds present in exhaust gases. Stainless steel alloys, particularly 304 and 316, are frequently employed due to their chromium content, which forms a protective oxide layer, preventing rust. Failure to utilize corrosion-resistant materials results in premature degradation and subsequent failure of the device, leading to increased noise emissions and potential exhaust leaks.
- Thermal Stability
The chosen material must maintain its structural integrity at elevated temperatures encountered in exhaust systems. Stainless steel and aluminized steel demonstrate superior thermal stability compared to mild steel, resisting warping and cracking under prolonged heat exposure. Thermal expansion properties also need consideration to avoid stress concentrations at welded joints.
- Acoustic Properties
Material density and thickness influence the damping characteristics of the device. Denser materials generally provide better sound attenuation, although they also add weight. The material’s ability to absorb or reflect sound waves is a critical factor in optimizing noise reduction effectiveness. Material selection must balance acoustic performance with weight considerations.
- Weldability and Formability
The ease with which a material can be welded or formed into complex shapes is crucial for efficient fabrication. Stainless steel offers excellent weldability using various techniques, such as GTAW or GMAW. The material should also be sufficiently malleable to allow for bending, shaping, and fabrication of internal baffles and chambers. Difficulties in welding or forming can lead to compromised structural integrity and increased manufacturing costs.
The strategic selection of materials fundamentally determines the effectiveness and lifespan of the exhaust noise reduction device. By carefully considering factors such as corrosion resistance, thermal stability, acoustic properties, weldability, and formability, a robust and durable device can be fabricated, contributing to reduced noise pollution and improved vehicle performance.
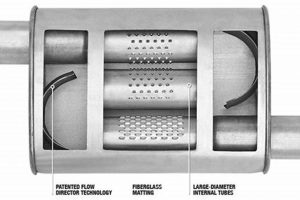
2. Internal Configuration
The internal configuration is a pivotal determinant of performance in the construction of exhaust noise reduction devices. The arrangement of chambers, baffles, and resonating elements directly influences the attenuation of sound waves generated by the engine. A suboptimal internal configuration compromises the device’s effectiveness, leading to inadequate noise reduction and potential regulatory non-compliance. The design of these internal structures must consider the frequency range of the engine’s exhaust noise and the desired level of sound attenuation. A well-designed configuration manipulates sound waves through reflection, absorption, and interference, achieving a reduction in overall noise levels.
Consider, for instance, a straight-through design lacking internal baffles. This configuration offers minimal resistance to exhaust flow, potentially improving engine performance. However, the noise reduction is substantially lower compared to a multi-chamber design with strategically placed baffles. Another example involves the use of Helmholtz resonators within the device. These resonators are tuned to specific frequencies, effectively canceling out dominant tones in the exhaust noise spectrum. The placement and dimensions of these resonators are critical for optimal performance. Incorrectly sized or positioned resonators can amplify noise rather than attenuate it.
In summary, the internal configuration directly dictates the acoustic performance of the fabricated device. It is not merely a structural element but a functional component responsible for sound wave manipulation. Accurate design and implementation are crucial to achieving the desired noise reduction while minimizing backpressure. The integration of appropriate internal features is indispensable for building an effective and compliant exhaust noise reduction system. The design and construction of internal components are essential for maximizing performance.
3. Welding Integrity
Welding integrity constitutes a critical factor in the successful fabrication of exhaust noise reduction devices. The structural robustness and gas-tightness of welds directly impact the performance, longevity, and safety of the completed assembly. Compromised welds lead to exhaust leaks, noise amplification, and potential premature failure of the device.
- Weld Penetration and Fusion
Adequate weld penetration, ensuring complete fusion between the joined materials, is essential for withstanding the high-pressure environment within the exhaust system. Insufficient penetration results in weak points susceptible to cracking under stress. For example, incomplete fusion at the weld root creates a pathway for exhaust gases to escape, negating the intended noise reduction.
- Porosity and Inclusions
Porosity (gas pockets) and inclusions (foreign material trapped within the weld) weaken the weld joint and provide initiation points for corrosion. These defects compromise the mechanical strength of the weld and can lead to fatigue failure under vibration. Stringent welding procedures and proper shielding gas usage are necessary to minimize these defects.
- Weld Bead Profile and Overlap
A consistent and properly shaped weld bead profile ensures uniform stress distribution across the joint. Excessive overlap creates stress concentrations, while undercutting weakens the weld. Proper welding technique and electrode selection are crucial for achieving an optimal bead profile that minimizes stress risers.
- Material Compatibility and Welding Parameters
Matching the welding filler metal to the base material is essential for achieving a sound weld. Incorrect filler metal selection leads to metallurgical incompatibilities and weakened joints. Furthermore, precise control of welding parameters, such as voltage, amperage, and travel speed, is crucial for optimizing weld quality and preventing defects. Improper parameter settings result in excessive heat input, leading to distortion and potential cracking.
The integrity of the welds is inextricably linked to the overall performance and durability of the exhaust noise reduction device. Adherence to established welding best practices, including proper material selection, technique, and inspection, ensures the creation of a robust and reliable system capable of effectively mitigating exhaust noise for the vehicle lifespan. Prioritization of welding quality directly translates to a reduction in noise pollution and improved operational safety.
4. Acoustic Design
Acoustic design is central to the successful fabrication of an exhaust noise reduction device. It dictates the device’s effectiveness in attenuating unwanted sound frequencies and maximizing vehicle performance, requiring precise engineering considerations.
- Target Frequency Range
Effective acoustic design begins with identifying the dominant frequencies generated by the engine’s exhaust. The design then optimizes for attenuating these specific frequencies through various mechanisms such as destructive interference and sound absorption. For example, a four-cylinder engine typically generates different dominant frequencies compared to a V8 engine, requiring different internal muffler designs for optimal noise reduction. Failure to accurately target the relevant frequency range results in suboptimal noise reduction.
- Chamber and Baffle Configuration
The arrangement and dimensions of internal chambers and baffles dictate how sound waves are reflected, absorbed, and redirected within the device. Multi-chamber designs utilize changes in cross-sectional area to create impedance mismatches, causing reflections that cancel out specific frequencies. Baffles direct the flow of exhaust gases and sound waves, increasing the path length and promoting absorption. A poorly configured internal structure allows sound waves to propagate unimpeded, resulting in minimal noise reduction.
- Resonator Integration
Helmholtz resonators are strategically positioned to cancel out specific frequencies through destructive interference. These resonators consist of a neck and a cavity, tuned to resonate at a particular frequency. When sound waves at that frequency enter the resonator, they cause the air within to vibrate, creating a canceling effect. An improperly tuned resonator can amplify the targeted frequency rather than attenuate it, rendering the design ineffective.
- Material Properties and Sound Absorption
The materials used in constructing the device influence its ability to absorb sound energy. Materials with high sound absorption coefficients, such as fiberglass or mineral wool, are often incorporated into the muffler’s internal structure. These materials convert sound energy into heat, reducing the amplitude of sound waves. The correct selection of absorbent materials, combined with strategic placement within the muffler, significantly contributes to overall noise reduction effectiveness. Ignoring the sound absorption properties of materials will result in a less effective device.
The factors discussed above demonstrate the vital role of acoustic design in the construction of exhaust noise reduction systems. Careful consideration of frequency targeting, internal configuration, resonator integration, and material properties are crucial for achieving optimal noise attenuation and vehicle performance. The successful execution of acoustic design principles is fundamental to the construction of an effective device.
5. Mounting Stability
Mounting stability represents a critical element in the construction of effective exhaust noise reduction devices. Secure and properly designed mounting systems ensure the device’s longevity, prevent structural damage, and maintain acoustic performance. Inadequate mounting compromises the device’s integrity and can lead to premature failure, increased noise emissions, and potential safety hazards. Therefore, mounting considerations must be integrated throughout the fabrication process.
- Bracket Design and Material Strength
Bracket design must account for the weight of the noise reduction device, exhaust system vibration, and thermal expansion stresses. Employing high-strength materials, such as steel or reinforced alloys, is crucial for preventing bracket fatigue and failure. For instance, poorly designed brackets can fracture under stress, causing the device to detach from the vehicle, resulting in potential damage to the vehicle and a complete loss of noise reduction capabilities. The bracket should include vibration dampening properties and the proper material, which makes it more durable.
- Weld Integrity and Attachment Points
The welds connecting the mounting brackets to the device housing must exhibit high integrity to withstand the stresses of vehicle operation. Insufficient weld penetration or porosity weakens the attachment points, leading to bracket detachment and device instability. Further, proper placement and design of the attachment points are critical for distributing stress evenly across the housing. Poorly positioned attachment points can create stress concentrations, causing localized cracking and eventual failure.
- Vibration Isolation Techniques
Effective mounting systems incorporate vibration isolation techniques to minimize the transmission of engine and exhaust system vibrations to the noise reduction device. Rubber isolators or flexible mounting bushings dampen vibrations, reducing stress on the device housing and attachment points. The omission of vibration isolation leads to accelerated fatigue and premature failure of the device due to excessive stress cycling, causing loud rattling.
- Clearance and Thermal Expansion
Sufficient clearance must be provided between the device housing and surrounding vehicle components to accommodate thermal expansion during operation. Contact between the hot exhaust system and other components can lead to heat transfer, potentially damaging sensitive parts. Inadequate clearance also restricts thermal expansion, generating stress on the device housing and mounting brackets. Such stresses will damage nearby parts.
These facets underscore the significance of mounting stability in the fabrication of exhaust noise reduction devices. By carefully considering bracket design, weld integrity, vibration isolation, and clearance requirements, a robust and durable mounting system can be achieved. This, in turn, ensures the long-term performance, safety, and acoustic effectiveness of the device, thereby contributing to improved vehicle operation and reduced noise pollution.
6. Leak Prevention
Leak prevention constitutes a cornerstone of effective exhaust noise reduction device fabrication. The presence of exhaust leaks undermines the acoustic performance, compromises fuel efficiency, and poses safety hazards. Therefore, meticulous attention to leak prevention is paramount throughout the construction process.
- Seam Welding Techniques
Achieving gas-tight seams requires employing appropriate welding techniques, such as Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW) or Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW), with full penetration. Overlapping weld beads and meticulous surface preparation minimize the potential for pinhole leaks. Inadequate welding allows exhaust gases to escape, reducing noise attenuation and creating potential fire hazards. For example, uneven welds or inadequate shielding gas during welding can lead to porosity, creating leak paths.
- Flange and Gasket Design
Proper flange design and gasket selection are crucial for sealing joints between the noise reduction device and other exhaust system components. Flanges must be flat and dimensionally accurate to ensure uniform gasket compression. Gasket materials must be compatible with exhaust gas temperatures and pressures. Deformed flanges or incompatible gasket materials result in exhaust leaks at the connections, diminishing overall system performance. Choosing the right gasket is crucial for a sealed bond.
- Material Selection and Corrosion Resistance
Utilizing corrosion-resistant materials, such as stainless steel, minimizes the risk of rust and perforation, which can create leak paths over time. Exposure to corrosive exhaust gases degrades less resistant materials, eventually leading to leaks. Routine use of low-quality materials can lead to premature failure and necessitate costly repairs or replacements. Regular inspection is recommended.
- Pressure Testing and Inspection
Post-fabrication pressure testing is essential for identifying and rectifying any existing leaks. Pressurizing the device with compressed air and applying a soap solution to weld seams and joints reveals leaks through bubble formation. Visual inspection further identifies potential weak points or defects that could lead to future leaks. Failure to pressure test and inspect the completed device compromises performance and increases the risk of future leaks.
Incorporating these leak prevention measures throughout the fabrication process is crucial for ensuring the long-term effectiveness, safety, and performance of the exhaust noise reduction device. Effective sealing not only optimizes noise reduction but also contributes to improved fuel economy and reduced emissions, thereby enhancing overall vehicle operation.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following addresses common inquiries concerning the design and fabrication of exhaust noise reduction devices.
Question 1: What materials are most suitable for withstanding the extreme conditions within an exhaust system?
Stainless steel alloys, particularly 304 and 316, offer superior corrosion resistance and thermal stability compared to mild steel. Aluminized steel also provides a cost-effective alternative with good corrosion resistance.
Question 2: How does the internal configuration impact noise reduction effectiveness?
The arrangement of chambers, baffles, and resonators dictates the manipulation of sound waves. Multi-chamber designs and Helmholtz resonators, tuned to specific frequencies, enhance noise attenuation through destructive interference and sound absorption.
Question 3: What welding techniques ensure a robust and leak-proof device?
Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW) and Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW) techniques, when performed with proper penetration and shielding gas, create strong, gas-tight seams, minimizing the risk of exhaust leaks.
Question 4: How is acoustic performance evaluated and optimized?
Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) modeling predicts acoustic performance and aids in optimizing internal configurations. Post-fabrication testing, including pressure testing and sound level measurements, validates the device’s effectiveness.
Question 5: What mounting considerations prevent premature failure?
Robust mounting brackets, fabricated from high-strength materials, distribute stress evenly across the device housing. Vibration isolation techniques, such as rubber isolators, minimize the transmission of engine and exhaust system vibrations.
Question 6: How are exhaust leaks detected and prevented?
Post-fabrication pressure testing, using compressed air and a soap solution, identifies leaks. Thorough visual inspection and adherence to stringent welding protocols minimize the risk of leaks during the device’s operational lifespan.
The fabrication of exhaust noise reduction systems demands attention to material selection, internal configuration, weld integrity, acoustic design, mounting stability, and leak prevention. A comprehensive understanding of these elements ensures a device’s reliability and performance.
The succeeding section will offer concluding thoughts.
Conclusion
The fabrication of exhaust noise reduction devices presents a multifaceted engineering challenge. The preceding sections have detailed the critical aspects, including material selection, internal configuration, welding integrity, acoustic design principles, mounting considerations, and leak prevention techniques. Each element contributes significantly to the overall effectiveness and longevity of the finished product.
Mastery of these principles is essential for achieving optimal noise attenuation and regulatory compliance. Continued advancements in materials science, acoustic modeling, and fabrication techniques promise further improvements in the design and performance of future exhaust noise reduction systems. It is imperative that engineers and fabricators maintain a commitment to rigorous design, meticulous execution, and continuous improvement in this critical field of vehicle engineering.