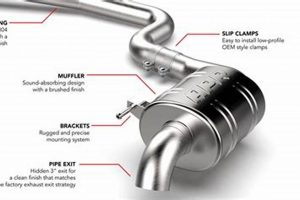
The exhaust component attached to the specified vehicle model and year serves to reduce engine noise and manage exhaust gases. It is a critical part of the vehicle’s exhaust system, contributing to a quieter and more environmentally compliant operation. Its primary function is to dampen the sound produced by the engine’s combustion process before the exhaust gases are released into the atmosphere.
The integrity of this component directly impacts the vehicle’s performance and adherence to emission standards. A properly functioning one ensures optimal backpressure, which is essential for engine efficiency. Over time, corrosion and damage can compromise its effectiveness, leading to increased noise levels, reduced fuel economy, and potential failure to meet emissions regulations. Its replacement can restore the vehicle to its optimal operating condition, ensuring a quieter ride and improved environmental performance.
Further discussion will delve into the selection criteria for a replacement, including material choices and design considerations, as well as the steps involved in its proper installation and maintenance. This ensures longevity and continued optimal function of the exhaust system.
Maintenance and Longevity Tips
Adherence to proactive maintenance practices will significantly extend the service life of the exhaust component for the specified vehicle. Regular inspections and timely interventions can prevent premature failure and ensure optimal performance.
Tip 1: Inspect Regularly for Corrosion: Conduct routine visual inspections, particularly in regions with harsh weather conditions. Salt and road debris accelerate corrosion, which weakens the metal. Address minor surface rust promptly with appropriate treatments.
Tip 2: Monitor for Exhaust Leaks: Listen for unusual noises emanating from the exhaust system. Leaks not only degrade performance but also can introduce dangerous gases into the vehicle’s cabin. A professional inspection is recommended to identify and repair leaks promptly.
Tip 3: Avoid Short Trips: Frequent short journeys prevent the exhaust system from reaching its optimal operating temperature. This leads to condensation buildup within the muffler, accelerating corrosion from the inside out. Whenever possible, incorporate longer trips to allow for complete evaporation of moisture.
Tip 4: Consider Material Upgrades: When replacing the component, consider stainless steel options for increased durability. Stainless steel offers superior resistance to corrosion compared to aluminized steel, extending the lifespan of the exhaust system.
Tip 5: Ensure Proper Installation: Adhere to the manufacturer’s installation guidelines and torque specifications during replacement. Improper installation can introduce stress points that lead to premature failure of the component and related exhaust system parts.
Tip 6: Utilize Protective Coatings: Apply high-temperature protective coatings to the exterior of the muffler. These coatings create a barrier against corrosion-inducing elements, extending its lifespan, especially in environments with high salt exposure.
Consistent application of these maintenance practices not only maximizes the lifespan of the exhaust component but also contributes to the vehicle’s overall performance and environmental compliance. Neglecting these preventative measures can lead to costly repairs and potential safety hazards.
The subsequent sections will cover the environmental impact of exhaust system maintenance and the importance of selecting appropriate replacement parts that meet or exceed original equipment manufacturer (OEM) specifications.
1. Sound Dampening
The primary function of the exhaust component for the specified vehicle, like all mufflers, is the attenuation of engine noise. Combustion events within the engine cylinders generate significant acoustic energy. The muffler’s internal structure is designed to disrupt and dissipate these sound waves before they exit the exhaust system. This is achieved through a combination of resonance chambers, baffles, and sound-absorbing materials, all calibrated to reduce noise levels across a range of engine operating conditions. Damage or deterioration of the muffler’s internal components directly compromises its capacity to dampen sound effectively, resulting in a louder vehicle operation.
Consider a scenario where the internal baffles of this component corrode and break apart. This degradation alters the intended flow path of exhaust gases, reducing the effectiveness of the noise cancellation mechanisms. The resulting increase in exhaust noise can be significant, leading to complaints from drivers and potentially violating local noise ordinances. This effect demonstrates the direct relationship between the physical integrity of this component and its performance in noise reduction. Properly sound dampened can also improve ride quality as the sounds are reduced inside the vehicle.
Understanding this connection is critical for vehicle owners and technicians. Identifying excessive exhaust noise early on can indicate the need for inspection or replacement of the component, preempting further damage to the exhaust system and ensuring compliance with noise regulations. Maintenance focused on preserving the integrity of the component, through regular inspections and prompt repairs, will maintain its sound-dampening capabilities and contribute to a quieter and more enjoyable driving experience.
2. Exhaust Routing
Exhaust routing, in the context of the specified vehicle’s exhaust component, refers to the precise pathway through which exhaust gases are channeled within the component’s internal structure. This routing is not arbitrary; it is carefully engineered to optimize sound attenuation and minimize backpressure. The internal configuration of baffles, chambers, and perforated tubes dictates the flow path, forcing the exhaust gases to undergo a series of expansions, contractions, and directional changes. This process dissipates acoustic energy and reduces the overall noise level emitted by the vehicle. A compromised muffler, due to corrosion or damage, can disrupt this carefully designed routing, resulting in increased noise and potentially affecting engine performance.
For example, a rusted-out area within the “2003 chevy trailblazer muffler” could create a shortcut in the exhaust routing. Instead of following the intended path through the muffler’s internal chambers, the exhaust gases would escape directly, bypassing the sound-dampening mechanisms. This would manifest as a noticeable increase in exhaust noise, and potentially lead to a failed emissions test if the exhaust system’s backpressure is significantly altered. Proper routing is also critical for ensuring that catalytic converters, located upstream of the muffler, operate within their optimal temperature range, further supporting emissions control.
Understanding the importance of exhaust routing within the vehicle’s exhaust component highlights the need for careful inspection and maintenance. Replacement with a component that accurately replicates the original design is crucial. Deviations from the original exhaust routing can negatively impact noise levels, emissions performance, and fuel economy. The functionality relies heavily on the precision of its internal exhaust routing. This factor should be emphasized when considering replacements or repairs to the exhaust system.
3. Material Durability
Material durability is a critical determinant of the service life and overall performance of the exhaust component in the specified vehicle. The component is constantly exposed to corrosive elements, high temperatures, and mechanical stresses. The material’s ability to withstand these conditions directly influences its longevity and functionality. Inferior materials will degrade rapidly, leading to premature failure, increased noise levels, and potential emission control issues.
For instance, an exhaust component constructed from low-grade steel will be susceptible to rust and corrosion, especially in regions where road salt is used during winter. This corrosion weakens the metal, leading to exhaust leaks and a reduction in sound dampening effectiveness. The consequence is a louder vehicle operation and potential failure to meet emissions standards. Conversely, a component manufactured from higher-grade stainless steel exhibits superior resistance to corrosion, extending its service life and maintaining its performance characteristics for a longer period.
Selecting a replacement exhaust component with appropriate material durability is therefore a practical consideration for vehicle owners. Investing in a more durable component, while potentially more expensive initially, can result in long-term cost savings by reducing the frequency of replacements. A robust material choice contributes not only to the component’s extended lifespan but also to the continued efficient and compliant operation of the vehicle’s exhaust system. This ensures fewer repairs, sustained performance, and reduced environmental impact.
4. Corrosion Resistance
Corrosion resistance is a paramount attribute for the exhaust component associated with the 2003 Chevrolet Trailblazer, directly affecting its operational lifespan and performance. The exhaust system is subjected to a harsh environment, including high temperatures, condensation, road salts, and exposure to various chemicals. Understanding the nuances of corrosion resistance is essential for informed maintenance and replacement decisions.
- Material Composition and its Impact on Corrosion
The specific alloy used in manufacturing the exhaust component directly influences its resistance to corrosive elements. Lower-grade steel is highly susceptible to rust, leading to premature degradation. Aluminized steel offers improved resistance compared to standard steel, while stainless steel provides the highest level of protection against corrosion. The choice of material significantly impacts the component’s longevity, particularly in regions with severe weather conditions and road salt usage.
- The Role of Protective Coatings
Protective coatings, such as specialized paints or ceramic coatings, can enhance the corrosion resistance of the exhaust component. These coatings act as a barrier, preventing corrosive substances from directly contacting the underlying metal. The effectiveness of these coatings depends on their composition, application method, and ability to withstand high temperatures and mechanical abrasion. Regular inspection and maintenance of these coatings are crucial for preserving their protective function.
- Impact of Operating Temperature on Corrosion Rates
The exhaust component operates at elevated temperatures, which can accelerate the rate of corrosion. Higher temperatures increase the reactivity of corrosive substances, leading to faster degradation of the metal. The presence of condensation within the exhaust system, particularly during short trips, exacerbates corrosion by providing a medium for chemical reactions to occur. Maintaining optimal engine operating temperatures and minimizing short trips can help mitigate this effect.
- Galvanic Corrosion Considerations
Galvanic corrosion can occur when dissimilar metals are in contact within the exhaust system, especially in the presence of an electrolyte such as water or road salt. This electrochemical process causes one metal to corrode preferentially, while the other is protected. Proper insulation and the use of compatible materials can minimize the risk of galvanic corrosion. Ensuring that replacement components are compatible with the existing exhaust system is crucial for preventing this type of corrosion.
The integration of these factors significantly influences the long-term performance and reliability of the 2003 Chevrolet Trailblazer exhaust component. Addressing these aspects of corrosion resistance will ensure extended service life, optimal function, and minimized maintenance costs. Neglecting these preventative measures can lead to premature component failure, increased noise levels, and potential environmental concerns.
5. Backpressure Management
Backpressure management, relating to the exhaust component in the specified vehicle, refers to controlling the resistance to exhaust gas flow within the exhaust system. The 2003 Chevrolet Trailblazer engine is designed to operate with a specific level of backpressure for optimal performance. The muffler, as a key component of the exhaust system, plays a significant role in regulating this backpressure. Excessive or insufficient backpressure can negatively impact engine efficiency, power output, and fuel economy. The muffler’s internal design, including its baffling and chamber configurations, directly influences the level of backpressure experienced by the engine. Deviations from the original design can lead to undesirable consequences. For example, an aftermarket muffler with a significantly reduced flow restriction may decrease backpressure to a point that compromises low-end torque. Conversely, a clogged or heavily restrictive muffler can cause excessive backpressure, leading to reduced horsepower and potential engine damage.
The importance of backpressure management becomes evident in the context of engine tuning and modifications. Altering the exhaust system without considering the effects on backpressure can produce unintended results. While a less restrictive exhaust system may improve airflow at higher engine speeds, it can also reduce low-end torque, making the vehicle feel sluggish during normal driving conditions. Maintaining a balanced level of backpressure is essential for achieving optimal engine performance across the entire RPM range. The selection of a replacement muffler, therefore, requires careful consideration of its internal design and its impact on the overall exhaust system’s backpressure characteristics. A malfunctioning muffler or a poorly chosen replacement can create an imbalance in backpressure leading to inefficient performance and other component failure.
In summary, backpressure management is an essential function of the “2003 chevy trailblazer muffler,” directly influencing engine performance and efficiency. Understanding the relationship between the muffler’s design and backpressure levels is critical for selecting appropriate replacement components and avoiding unintended consequences. Maintaining the proper level of backpressure ensures optimal engine operation, fuel economy, and emissions compliance. Neglecting this aspect of exhaust system design can lead to compromised performance and potential engine damage, highlighting the practical significance of this understanding in vehicle maintenance and modification.
6. Emission Compliance
Emission compliance, in the context of the 2003 Chevrolet Trailblazer exhaust component, signifies adherence to government regulations governing the release of harmful pollutants into the atmosphere. The muffler, while primarily responsible for noise reduction, also plays a role in ensuring that the vehicle’s emissions remain within acceptable limits. This is particularly important given the age of the vehicle and the potential for deterioration of other emission control components.
- Catalytic Converter Efficiency and Backpressure
The catalytic converter, located upstream of the muffler, relies on a specific exhaust gas temperature and flow rate to function effectively. A properly functioning muffler maintains appropriate backpressure, which is crucial for the catalytic converter to reach its optimal operating temperature. A deteriorated or excessively restrictive muffler can disrupt this balance, reducing the catalytic converter’s efficiency and leading to increased emissions of hydrocarbons, carbon monoxide, and nitrogen oxides. These emissions directly contribute to air pollution and can result in the vehicle failing an emissions test.
- Exhaust Leaks and Unmetered Air
Exhaust leaks, often caused by corrosion or damage to the “2003 chevy trailblazer muffler” or its connecting pipes, allow unmetered air to enter the exhaust stream. This excess air can interfere with the oxygen sensors that provide feedback to the engine control unit (ECU). The ECU uses this information to adjust the air-fuel mixture, ensuring optimal combustion and minimizing emissions. Exhaust leaks can skew the oxygen sensor readings, leading to an imbalanced air-fuel mixture and increased emissions. Repairing or replacing the muffler to eliminate exhaust leaks is essential for maintaining proper emissions control.
- Sound Attenuation and Emission Testing
While the primary function of the muffler is sound attenuation, its physical condition can indirectly affect emissions testing. A muffler that is excessively loud or has been tampered with can raise suspicion during an emissions inspection. While not directly related to emissions levels, a non-compliant exhaust system may prompt a more thorough inspection, potentially revealing other underlying issues that could contribute to elevated emissions. Maintaining a stock or compliant exhaust system, including the muffler, helps to ensure a smooth and successful emissions testing process.
- Aftermarket Muffler Compatibility and Certification
When replacing the “2003 chevy trailblazer muffler,” it is crucial to select a component that is specifically designed for the vehicle and meets or exceeds original equipment manufacturer (OEM) specifications. Aftermarket mufflers that are not properly engineered or certified may not provide the correct backpressure or sound attenuation, potentially leading to increased emissions or failure to comply with local noise regulations. Choosing a certified and compatible replacement muffler ensures that the vehicle’s emissions remain within acceptable limits and that it operates in compliance with applicable laws.
These interconnected factors highlight the importance of maintaining a properly functioning exhaust system, including the muffler, for ensuring emission compliance in the 2003 Chevrolet Trailblazer. Addressing issues such as exhaust leaks, catalytic converter efficiency, and muffler selection contributes directly to reducing harmful emissions and promoting environmental responsibility. The muffler is not merely a noise reduction device; it is an integral component of the vehicle’s overall emissions control system.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries concerning the exhaust component for the specified vehicle model and year. The intent is to provide clarity on its function, maintenance, and potential replacement needs.
Question 1: What is the expected lifespan of this exhaust component?
The lifespan is influenced by several factors, including climate, driving conditions, and the material composition of the muffler. Under normal operating conditions, a muffler constructed of aluminized steel may last between 5 to 7 years. Stainless steel variants typically offer a longer lifespan, potentially exceeding 10 years.
Question 2: How does a failing exhaust component affect vehicle performance?
A compromised muffler can lead to reduced engine efficiency due to altered backpressure. This may manifest as decreased fuel economy, diminished horsepower, and increased exhaust noise. Additionally, exhaust leaks can introduce unmetered air into the system, affecting the accuracy of the oxygen sensors and potentially causing the engine to run improperly.
Question 3: What are the symptoms of a failing exhaust component?
Common indicators include a noticeable increase in exhaust noise, the presence of rust or physical damage to the muffler, and a rattling sound emanating from the exhaust system. A decrease in fuel economy or a noticeable decline in engine performance may also suggest a problem with the muffler or other components of the exhaust system.
Question 4: Can a damaged exhaust component affect emissions testing?
Yes, a damaged muffler can cause a vehicle to fail an emissions test. Exhaust leaks can disrupt the proper functioning of the catalytic converter, leading to increased emissions of harmful pollutants. Additionally, excessive exhaust noise may raise concerns during the inspection process, potentially prompting a more thorough examination of the vehicle’s emission control systems.
Question 5: Is it possible to repair a damaged exhaust component, or is replacement always necessary?
Minor exhaust leaks can sometimes be repaired using specialized patching compounds or welding techniques. However, significant damage, such as extensive rust or structural failure, typically necessitates replacement of the entire muffler. Attempting to repair severely damaged mufflers may compromise their structural integrity and could lead to further problems down the road.
Question 6: What factors should be considered when selecting a replacement?
When choosing a replacement, factors such as material composition, compatibility with the vehicle’s exhaust system, and compliance with local noise regulations should be considered. Stainless steel mufflers offer superior corrosion resistance and a longer lifespan. Ensuring that the replacement muffler is designed to maintain the correct level of backpressure is also crucial for optimal engine performance. It is advisable to consult with a qualified mechanic to determine the most suitable replacement option.
In summary, understanding the function, maintenance requirements, and potential issues associated with the vehicles muffler is essential for ensuring its longevity and the vehicle’s overall performance. Timely attention to any signs of damage or deterioration can prevent more significant problems and help to maintain compliance with emission standards.
Subsequent sections will delve into the specifics of selecting replacement components and the recommended procedures for their installation.
Conclusion
The preceding analysis has explored the various facets of the 2003 Chevrolet Trailblazer muffler, encompassing its function, maintenance, and potential replacement considerations. Emphasis has been placed on material durability, corrosion resistance, backpressure management, and emission compliance all critical factors influencing the component’s performance and longevity. Understanding these elements enables informed decisions regarding upkeep and potential remediation.
The effective operation of the exhaust system in the specified vehicle necessitates ongoing awareness of the condition of its constituent parts. Regular inspections and timely interventions, when necessary, will ensure continued performance and compliance. The diligent maintenance of this component serves not only to sustain the vehicle’s operational integrity but also contributes to broader environmental responsibility.