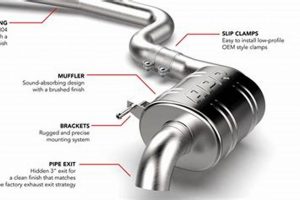
The exhaust system component designed for maximum sound reduction is crucial for minimizing noise pollution from internal combustion engines. This component’s efficiency is typically measured by its ability to attenuate sound waves across a broad frequency spectrum. For example, high-performance vehicles may utilize advanced designs to achieve acceptable noise levels without significantly restricting exhaust flow.
Effective noise control offers significant benefits, including compliance with environmental regulations, improved driver and passenger comfort, and reduced community noise impact. Historically, advancements in materials and acoustic engineering have driven the evolution of these components, leading to more efficient and durable solutions. Such advancements are important for maintaining vehicle operability, resale value, and ensuring peace of mind.
The following article will delve into the various types, construction materials, performance metrics, and maintenance considerations surrounding exhaust noise reduction technologies. It will also examine the impact of these technologies on vehicle performance and regulatory compliance.
Guidance on Exhaust Noise Reduction
Optimizing the functionality and longevity of an exhaust systems sound-dampening component requires adherence to specific practices. The following outlines essential steps for maintaining optimal performance.
Tip 1: Select Components Based on Application: Choose exhaust silencing devices engineered for the specific vehicle type and operating conditions. Consider factors such as engine size, horsepower, and intended use (e.g., street, track) to ensure proper noise attenuation and minimal backpressure.
Tip 2: Prioritize Quality Materials: Opt for silencing devices constructed from corrosion-resistant materials, such as stainless steel or aluminized steel. These materials provide enhanced durability and extend the service life of the component, particularly in harsh environments.
Tip 3: Inspect Regularly for Damage: Conduct routine visual inspections of the exhaust silencing component, checking for signs of corrosion, physical damage (dents, cracks), and loose connections. Address any issues promptly to prevent further deterioration and maintain optimal performance.
Tip 4: Ensure Proper Installation: Adhere strictly to the manufacturer’s installation instructions. Correct alignment and secure mounting are crucial for preventing leaks, vibration, and premature failure of the exhaust silencing device.
Tip 5: Monitor Exhaust System Backpressure: Regularly monitor exhaust system backpressure. Excessive backpressure can indicate a clogged or damaged silencing component, leading to reduced engine performance and potential engine damage. Consult a qualified technician if backpressure exceeds recommended levels.
Tip 6: Address Unusual Noises Promptly: Investigate any unusual noises emanating from the exhaust system, such as rattles, hisses, or drones. These noises may indicate a failing or damaged silencing component requiring repair or replacement.
Tip 7: Follow Recommended Maintenance Intervals: Adhere to the vehicle manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule for the exhaust system. This may include periodic inspection of hangers, clamps, and gaskets to ensure proper sealing and support.
Implementing these practices enhances the performance and lifespan of exhaust silencing components, contributing to reduced noise pollution and improved vehicle operation. These measures uphold both compliance and community well-being.
The subsequent section will explore troubleshooting common problems associated with exhaust silencing devices and provide solutions for addressing these issues effectively.
1. Sound Attenuation
Sound attenuation is the core function of a comprehensive exhaust silencing system, dictating its effectiveness in reducing noise emissions. It represents the degree to which sound waves are dampened as they pass through the device. The design and materials used directly influence sound attenuation. For example, a complex internal chamber design with strategically placed baffles causes sound waves to reflect and cancel each other, leading to a reduction in sound pressure levels emitted from the exhaust. A faulty exhaust silencing component shows diminished sound attenuation, evidenced by increased exhaust noise levels, potentially violating noise ordinances.
Sound attenuation performance directly affects vehicle compliance with noise regulations. Manufacturers rigorously test and design to meet stringent noise limits. Practical applications involve diverse designs tailored for specific vehicle types. Performance vehicles might integrate sound dampening technologies that balance noise reduction with minimizing exhaust restriction to retain horsepower. In contrast, family vehicles prioritize maximum sound attenuation for occupant comfort. The effectiveness of sound attenuation, measured in decibels, directly reflects the quality and engineering of the exhaust component.
Therefore, sound attenuation is an inseparable aspect of a comprehensive exhaust silencing system. Challenges persist in achieving optimal attenuation without compromising vehicle performance or durability. A solid understanding of the principles of sound attenuation, combined with appropriate design and material choices, leads to effective noise control in vehicles.
2. Material Durability
The longevity and efficacy of the complete exhaust silencing device are inextricably linked to the material composition used in its construction. Material durability directly influences the ability to withstand the harsh operating conditions within an exhaust system. Exposure to high temperatures, corrosive exhaust gases, road salts, and mechanical stresses necessitates the use of materials capable of maintaining structural integrity over extended periods. Insufficient material durability leads to premature failure, resulting in increased noise emissions, exhaust leaks, and potential engine damage. As an example, exhaust silencing components manufactured from low-grade steel are susceptible to rapid corrosion in regions with prevalent road salt usage, leading to decreased performance and eventual replacement.
The selection of appropriate materials, such as stainless steel or aluminized steel, significantly enhances the lifespan and performance of the component. Stainless steel offers superior corrosion resistance, especially in humid climates or areas with extensive salt usage. Aluminized steel provides a cost-effective alternative with improved resistance compared to standard steel. Practical applications involve the strategic use of these materials in different sections of the component to maximize durability while managing costs. For instance, stainless steel is often used in areas most exposed to exhaust gases and moisture, while aluminized steel is used in less critical sections.
In summary, material durability is a fundamental aspect of a comprehensive exhaust silencing system. The choice of materials dictates its ability to withstand harsh conditions and maintain optimal performance over its service life. Understanding the relationship between material properties and operating environment is crucial for selecting and maintaining exhaust silencing devices that provide effective noise reduction and reliable operation. Compromises on material quality can result in diminished performance, increased maintenance costs, and potential environmental concerns.
3. Exhaust Backpressure
Exhaust backpressure, the resistance to the flow of exhaust gases in an engine’s exhaust system, directly impacts the performance and longevity of the comprehensive silencing device. Understanding this relationship is crucial for optimizing both engine efficiency and noise reduction.
- Restriction and Sound Attenuation
Increased restriction within an exhaust silencing component, engineered for superior sound attenuation, inevitably contributes to higher backpressure. Complex internal designs, baffles, and sound-absorbing materials restrict the free flow of exhaust gases. This trade-off is evident in performance vehicles where aftermarket units often sacrifice some sound reduction in exchange for reduced backpressure and enhanced horsepower.
- Engine Performance Implications
Excessive backpressure can hinder the engine’s ability to efficiently expel exhaust gases. This can result in reduced power output, decreased fuel economy, and increased engine operating temperatures. For example, a severely clogged silencing component significantly elevates backpressure, leading to noticeable performance degradation, particularly at higher engine speeds.
- Material and Design Considerations
The materials and internal design of the component profoundly influence backpressure levels. Smooth, unrestricted flow paths and materials with low surface roughness minimize resistance. High-flow designs, utilizing larger diameter pipes and less restrictive baffles, are specifically engineered to reduce backpressure while still providing adequate sound attenuation.
- Diagnostic and Maintenance
Monitoring exhaust backpressure is a vital diagnostic procedure for assessing the condition of the exhaust system. Elevated backpressure readings often indicate a restriction within the silencing component, prompting further inspection for blockages or internal damage. Regular maintenance, including visual inspections and periodic backpressure testing, can prevent performance issues and ensure optimal system operation.
The interplay between exhaust backpressure and comprehensive silencing device design necessitates careful consideration to achieve the desired balance between noise reduction and engine performance. Optimizing this balance is vital for maximizing efficiency, ensuring compliance with noise regulations, and prolonging the lifespan of both the exhaust system and the engine itself. For example, proper sizing of an exhaust silencing device based on engine displacement and horsepower ratings is critical for minimizing backpressure while meeting specified noise level requirements.
4. Regulatory Compliance
Regulatory compliance forms an integral part of an exhaust silencing device, directly affecting its design, manufacturing, and operational parameters. National and local regulations govern permissible noise emissions from vehicles, necessitating that exhaust systems, and particularly the noise-reducing component, meet specific sound level standards. Failure to comply results in penalties for manufacturers and vehicle owners. For example, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in the United States sets noise limits for motor vehicles, requiring exhaust systems to undergo testing and certification processes to ensure adherence. These regulations drive innovation in silencing technologies, pushing manufacturers to develop more efficient and effective noise reduction solutions.
The requirements of regulatory compliance extend beyond simple noise reduction. They often mandate specific construction materials, durability standards, and testing procedures. The exhaust system must maintain its noise reduction capabilities throughout its intended lifespan, with regulations often specifying the duration and conditions for durability testing. A real-world example is the European Union’s (EU) noise emission standards, which require rigorous testing of exhaust systems under various driving conditions to ensure consistent compliance. The cost of compliance can be substantial, as manufacturers must invest in research, development, and testing facilities. However, failing to meet these requirements results in product recalls, fines, and damage to brand reputation.
In summary, regulatory compliance is not merely an external constraint, but an active force shaping the design and performance of exhaust noise-reducing devices. It necessitates a holistic approach, encompassing material selection, acoustic engineering, manufacturing processes, and rigorous testing. While challenges persist in balancing noise reduction, engine performance, and cost-effectiveness, adherence to regulations ensures environmental protection and public health. Understanding the practical implications of regulatory compliance is vital for all stakeholders, from manufacturers to vehicle owners, ensuring responsible and sustainable vehicle operation.
5. Installation Integrity
Installation integrity is paramount for the long-term performance and effectiveness of a comprehensive exhaust silencing device. Proper installation ensures the device functions as designed, maintaining noise reduction capabilities and preventing premature failure. Deviations from recommended installation procedures compromise the system’s overall integrity and can lead to operational issues.
- Correct Mounting and Alignment
Accurate mounting and alignment are essential for preventing stress on the exhaust silencing component and ensuring a secure fit. Misalignment can introduce undue stress, leading to cracks, leaks, and reduced noise reduction effectiveness. For example, an improperly aligned connection point can vibrate excessively, causing premature wear and potential detachment. Correct alignment, adhering to manufacturer specifications, is crucial for longevity.
- Secure Connections and Sealing
Leak-free connections are vital for maintaining optimal exhaust gas flow and preventing noise leakage. Loose or improperly sealed connections allow exhaust gases to escape, increasing noise levels and potentially posing safety hazards. Using the correct gaskets and clamps, torqued to specification, ensures a tight seal and prevents exhaust leaks. Omission of this process results in compromised noise reduction and potential exhaust system damage.
- Proper Hanger Support
Adequate hanger support is necessary to prevent excessive vibration and stress on the exhaust silencing device. Insufficient or damaged hangers allow the component to move excessively, leading to fatigue and potential failure of mounting points. Proper hanger placement, utilizing durable hangers designed for the application, distributes weight evenly and minimizes vibration, extending the device’s lifespan.
- Protection from Environmental Factors
Shielding the exhaust silencing device from direct exposure to road debris, moisture, and corrosive elements enhances its durability. Underbody coatings or protective wraps can help mitigate the effects of these environmental factors. For instance, applying a rust inhibitor to exposed surfaces prevents corrosion and extends the component’s service life, particularly in regions with harsh winter conditions.
These aspects of installation integrity directly influence the long-term performance and reliability of the comprehensive exhaust silencing device. Adhering to manufacturer’s guidelines and best practices during installation is crucial for maximizing the device’s effectiveness in noise reduction, preventing premature failure, and ensuring safe and efficient vehicle operation. Compromising installation integrity undermines the investment in a quality component and can lead to costly repairs and environmental concerns.
6. System Compatibility
System compatibility is a critical determinant of an exhaust system’s performance, particularly concerning the comprehensive noise-reduction capabilities. The extent to which individual components, including the noise-reducing device, are designed to integrate seamlessly with the vehicle’s existing exhaust architecture directly influences overall efficiency and longevity. A mismatch between components can result in reduced sound attenuation, increased backpressure, and premature system failure. For example, installing a high-performance unit designed for a turbocharged engine on a naturally aspirated engine can create excessive backpressure, diminishing engine performance and potentially damaging the catalytic converter. This underscores the necessity of considering system compatibility when selecting or replacing noise reduction components.
The practical implications of ensuring system compatibility extend to several aspects of vehicle operation. The noise-reducing component must be dimensionally appropriate for the vehicle’s exhaust piping diameter and configuration to prevent leaks and maintain optimal gas flow. Material compatibility is also essential; using dissimilar metals can lead to galvanic corrosion, shortening the system’s lifespan. A specific illustration involves the use of stainless steel tubing with standard steel hangers, resulting in accelerated corrosion at the points of contact. Furthermore, the overall exhaust design, including pipe routing and muffler placement, must consider vehicle chassis layout to avoid interference with other components and ensure adequate ground clearance. Neglecting this aspect can lead to physical damage from road hazards and reduced reliability.
In conclusion, system compatibility is a prerequisite for the effective and durable operation of comprehensive noise reduction systems. A thorough understanding of a vehicle’s exhaust specifications, coupled with careful selection of compatible components, is essential to maximize noise attenuation, minimize backpressure, and ensure the long-term integrity of the exhaust system. Overlooking system compatibility not only compromises noise reduction but also jeopardizes engine performance, increases maintenance costs, and potentially creates safety hazards. The interconnected nature of exhaust system components mandates a holistic approach to design, installation, and maintenance to achieve optimal results.
Frequently Asked Questions Regarding Total Muffler
The following addresses common inquiries concerning comprehensive exhaust noise reduction components, providing clarity on functionality, maintenance, and performance aspects.
Question 1: What constitutes a total muffler and how does it differ from standard mufflers?
A total muffler, often referred to as a comprehensive exhaust silencing device, is engineered for maximum sound attenuation across a broad frequency range. Unlike standard mufflers which may prioritize cost or performance, a total muffler emphasizes complete noise reduction while balancing backpressure and durability considerations. Performance capabilities and components are generally more comprehensive.
Question 2: What factors influence the lifespan of a total muffler?
Several factors determine the service life, including the quality of construction materials, exposure to corrosive elements (such as road salt), operating temperatures, and the engine’s combustion characteristics. Routine inspection and maintenance, particularly in regions with harsh winter conditions, can significantly extend the lifespan.
Question 3: How does the selection of a total muffler affect engine performance?
The design of the noise-reducing device impacts exhaust backpressure, which in turn influences engine efficiency. A poorly designed muffler can create excessive backpressure, diminishing power output and fuel economy. A carefully selected high-flow unit minimizes backpressure while providing adequate sound reduction for the intended application.
Question 4: What are the signs of a failing total muffler?
Indications of a failing unit include increased exhaust noise levels, rattling or hissing sounds emanating from the exhaust system, visible corrosion or physical damage, and a noticeable decline in engine performance. Prompt inspection and replacement are advisable to prevent further damage and maintain regulatory compliance.
Question 5: Are there specific maintenance procedures to prolong the life of a total muffler?
Regular visual inspections for corrosion, physical damage, and loose connections are recommended. Applying rust inhibitors to exposed surfaces, ensuring proper hanger support, and promptly addressing any unusual noises can extend the service life. Avoid prolonged exposure to extreme temperatures or harsh chemicals.
Question 6: How can one ensure regulatory compliance when replacing a total muffler?
It is essential to select a replacement component that meets or exceeds the noise emission standards mandated by local and national regulations. Verify that the selected muffler is certified for the vehicle’s make and model and adheres to applicable noise level limits. Consult with a qualified technician to ensure proper installation and compliance.
Understanding these key aspects of the technology is essential for informed decision-making regarding maintenance and upgrades.
The following section explores troubleshooting common problems associated with comprehensive noise-reducing devices and provides solutions for effectively addressing these issues.
Conclusion
The preceding exploration of the total muffler underscores its importance in vehicle operation and environmental responsibility. From detailing material durability to analyzing system compatibility and regulatory compliance, the discussion highlights the multifaceted considerations essential for effective noise reduction. The balance between sound attenuation, engine performance, and longevity necessitates careful attention to design, installation, and maintenance.
As noise pollution remains a significant environmental concern, the demand for advanced and reliable exhaust silencing solutions will continue to grow. Prioritizing comprehensive systems and employing diligent maintenance practices are crucial steps toward minimizing noise impact and ensuring sustainable vehicle operation. Continued research and development in this field are paramount for achieving even greater noise reduction without compromising performance or durability. The future of vehicle exhaust systems hinges on responsible choices that prioritize both individual vehicle efficiency and community well-being.