The exhaust component tailored for the Kawasaki Ninja 500 motorcycle plays a critical role in managing engine emissions and sound output. As a part of the exhaust system, this component facilitates the expulsion of spent gases from the combustion chamber, contributing to engine performance and overall operational efficiency. For example, a modified component can alter backpressure, which can, in turn, influence horsepower and torque delivery.
The significance of this part extends beyond mere functionality. It impacts sound levels, adhering to regulatory standards and influencing the riding experience. Historically, improvements in materials and design have led to lighter, more efficient, and aesthetically pleasing components. Aftermarket options cater to diverse rider preferences, allowing for customization of sound and performance characteristics. Proper maintenance ensures optimal function, preventing performance degradation and potential damage to the engine.
The following sections will delve into the selection considerations, performance implications, common maintenance procedures, and potential upgrades related to this critical element of the motorcycle.
Ninja 500 Muffler
This section offers crucial advice concerning the replacement, maintenance, and performance optimization of the component.
Tip 1: Inspect Regularly for Corrosion: A periodic visual inspection reveals potential corrosion. The location of the component subjects it to environmental exposure, increasing the risk of rust and degradation. Early detection allows for preventative measures, extending the lifespan of the system.
Tip 2: Ensure Proper Sealing at Joints: Exhaust leaks diminish performance and alter the sound profile. Verify tight connections at all junctions within the exhaust system. Replace gaskets and seals as needed to maintain optimal pressure and flow.
Tip 3: Consider Material for Longevity: Stainless steel offers superior corrosion resistance compared to mild steel, resulting in extended durability, especially in regions with harsh weather conditions or frequent road salt usage.
Tip 4: Evaluate Aftermarket Options Carefully: Numerous aftermarket systems exist, promising improved performance and sound. Research specifications and reviews to ensure compatibility and adherence to noise regulations. Verify compliance with local laws before installation.
Tip 5: Maintain Correct Backpressure: Alterations to the exhaust system, including the component, impact engine backpressure. Excessive reduction may lead to decreased low-end torque. Consult with a qualified mechanic to optimize for the desired performance characteristics.
Tip 6: Torque Fasteners to Specification: When installing or replacing the component, adhere to the manufacturers recommended torque values for all fasteners. Over-tightening can damage threads, while under-tightening leads to leaks and potential component failure.
Tip 7: Clean Regularly: Road debris and contaminants accumulate. Periodic cleaning helps prevent corrosion and maintain appearance. Use appropriate cleaning agents to avoid damage to the material or finish.
Adhering to these recommendations prolongs the life of the exhaust system, ensures optimal performance, and maintains compliance with relevant regulations.
The final section summarizes key considerations for selecting and maintaining this important motorcycle part.
1. Compatibility
The successful operation and performance of the exhaust component depend critically on its compatibility with the Kawasaki Ninja 500 motorcycle. Mismatched parts lead to performance degradation, potential damage, and regulatory non-compliance. Selecting a component specifically designed for the Ninja 500 is paramount.
- Mounting Point Alignment
The physical dimensions and placement of mounting brackets must precisely match the corresponding points on the motorcycle’s frame and exhaust system. Discrepancies necessitate modifications or render the component unusable, potentially causing stress on the exhaust manifold and frame.
- Exhaust Port Diameter
The inner diameter of the components inlet must correspond accurately to the diameter of the exhaust port on the motorcycle’s engine. An improper fit leads to exhaust leaks, reduced backpressure, and compromised engine performance. Gaskets and sealing surfaces must align correctly to ensure a gas-tight seal.
- Sensor Integration
If the motorcycle is equipped with an oxygen sensor or other emissions-related sensors, the component must provide appropriate ports and fittings for sensor installation. Failure to accommodate sensors will trigger warning lights and affect fuel management, possibly resulting in poor performance or emissions violations.
- Backpressure Characteristics
Even with proper fitment, the internal design of the replacement part must produce backpressure within the engine manufacturers specified range. A component producing significantly different backpressure can negatively impact the engines torque curve and overall power output, even if it physically fits the motorcycle.
Therefore, verifying component compatibility involves more than just physical fitment. It encompasses matching inlet and outlet dimensions, accommodating sensor integration, and maintaining appropriate backpressure characteristics. Careful attention to these details ensures optimal performance and avoids potential damage to the motorcycle.
2. Backpressure
Backpressure, the resistance encountered by exhaust gases as they exit an engine, is a critical parameter influenced by the exhaust system and, specifically, the component designed for the Ninja 500. Its manipulation affects engine performance characteristics, fuel efficiency, and emissions levels. The design of this component plays a central role in determining the degree of restriction presented to the exhaust flow.
- Influence on Torque Delivery
Excessive backpressure can restrict the efficient scavenging of exhaust gases from the combustion chamber, leading to reduced volumetric efficiency and lower engine torque, particularly at higher RPMs. Conversely, insufficient backpressure can diminish low-end torque, as the engine relies on a certain amount of resistance to maintain optimal cylinder filling at lower speeds. The component influences the balance between these extremes.
- Impact on Horsepower
While backpressure is essential for low-end torque, it can impede horsepower at higher RPMs. A less restrictive part allows for more efficient evacuation of exhaust gases, leading to increased horsepower in the upper RPM range. However, altering the component without considering its effect on backpressure could lead to a reduction in overall power output if not properly tuned.
- Role in Fuel Efficiency
Modifications to the exhaust system that drastically alter backpressure affect the air-fuel ratio and combustion efficiency. Insufficient backpressure can lead to lean conditions, potentially harming the engine and reducing fuel economy. Excessive backpressure can cause rich conditions, increasing fuel consumption and emissions. The component should ideally be selected to maintain the optimal air-fuel ratio for efficient combustion.
- Considerations for Aftermarket Components
Many aftermarket exhaust components are designed to reduce backpressure, aiming to increase horsepower. However, installing a component without appropriate engine tuning or fuel management modifications can negatively affect performance and engine longevity. Careful consideration of the trade-offs between backpressure, torque, horsepower, and fuel efficiency is essential when selecting this motorcycle part.
Therefore, the selection and design of this component directly impact the engine’s backpressure, affecting its torque curve, horsepower output, fuel efficiency, and overall performance. Alterations to this element require a comprehensive understanding of its interplay with engine characteristics to achieve the desired results without compromising engine health or regulatory compliance.
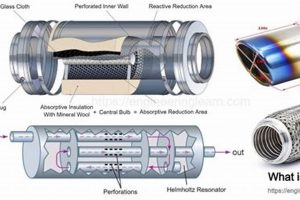
3. Sound Reduction
The degree to which the component diminishes the sound output of the Kawasaki Ninja 500 is a significant factor influencing both rider comfort and regulatory compliance. Its design and construction directly impact the decibel levels emitted by the motorcycle.
- Internal Baffling and Absorption Materials
Internal structures, such as baffles, redirect and dissipate sound waves, reducing their amplitude. Absorption materials, like fiberglass or steel wool packing, convert sound energy into heat through friction. The quantity and arrangement of these elements determine the degree of sound attenuation. For example, a component with multiple chambers and dense packing generally provides greater sound reduction compared to a straight-through design with minimal baffling. This difference is readily apparent in the measured decibel levels at various engine speeds.
- Resonator Chamber Design
Some components incorporate resonator chambers that utilize the principle of destructive interference. These chambers are tuned to specific frequencies, causing sound waves to cancel each other out, resulting in noise reduction. The effectiveness of a resonator depends on its size, shape, and positioning within the assembly. A poorly designed resonator may amplify certain frequencies, exacerbating noise pollution rather than mitigating it.
- Outlet Size and Configuration
The diameter and shape of the exhaust outlet influence the velocity and dispersion of sound waves. A smaller outlet typically increases backpressure and attenuates some frequencies, while a larger outlet can result in a louder, more aggressive exhaust note. The angle and shape of the outlet can also affect the directionality of the sound, influencing how it is perceived by nearby individuals and potentially affecting compliance with noise ordinances.
- Material Thickness and Density
The thickness and density of the materials used in the construction of the component contribute to its ability to absorb and dampen vibrations, reducing noise transmission. Thicker, denser materials generally provide better sound insulation. A component constructed from thin, lightweight materials may resonate more readily, amplifying noise levels. The choice of materials directly impacts the overall sound profile and perceived quality of the product.
The level of sound reduction achieved by a particular component results from the interplay of these factors. Aftermarket options provide varying degrees of sound attenuation, impacting not only the auditory experience of the rider and surrounding environment but also the motorcycle’s compliance with noise regulations. Careful consideration of these design elements is essential for selecting a component that balances performance, sound levels, and legal requirements.
4. Material durability
The longevity and operational effectiveness of the exhaust component for the Ninja 500 are intrinsically linked to the durability of the materials used in its construction. Exposure to high temperatures, corrosive exhaust gases, road debris, and environmental elements precipitates material degradation. The choice of materials directly influences the component’s resistance to these factors, thereby affecting its lifespan and performance consistency. Degradation manifests as corrosion, cracking, and structural weakening, ultimately leading to exhaust leaks, reduced performance, and eventual component failure. For instance, a component constructed from low-grade steel will succumb to rust far more rapidly than one made from stainless steel, especially in regions where road salt is prevalent during winter months.
The selection of materials also affects the component’s ability to withstand thermal stress. Repeated heating and cooling cycles induce expansion and contraction, potentially causing fatigue and cracking, especially at weld points. Higher-grade materials, such as titanium alloys, exhibit superior thermal stability and resistance to fatigue, extending the service life of the component under demanding operating conditions. Practical implications of understanding material durability are evident in the cost-effectiveness of choosing a more durable, albeit initially more expensive, component that requires less frequent replacement and maintenance. This translates to lower long-term ownership costs and reduced downtime for repairs.
In summary, material durability constitutes a critical design consideration for the exhaust component of the Ninja 500. Understanding the properties and limitations of various materials allows for informed decisions that balance cost, performance, and longevity. While cost considerations may tempt the selection of less durable materials, the long-term consequences of premature failure and increased maintenance outweigh the initial savings. Consequently, prioritizing material durability is paramount to ensuring the sustained performance and reliability of the exhaust system.
5. Aesthetic Design
The visual appearance of the exhaust component for the Ninja 500 significantly contributes to the motorcycle’s overall aesthetic appeal. Beyond its functional purpose, the component serves as a visible design element, influencing the perception of performance and style.
- Shape and Silhouette
The contours and profile of the component complement the lines of the motorcycle. Sport-oriented designs often feature angular, aggressive shapes, while more classic styles may incorporate rounded or tapered forms. The silhouette contributes to the overall impression of speed and agility. For example, a short, stubby component accentuates a modern, minimalist aesthetic, while a longer, more flowing design can evoke a sense of classic performance. The visual balance between the component and the rest of the motorcycle is essential for a cohesive design.
- Surface Finish and Material Texture
The surface finish of the component, whether polished, brushed, or coated, affects its visual impact and perceived quality. Polished finishes create a bright, reflective surface, conveying a sense of premium quality, while brushed finishes offer a more subtle, understated look. Coatings, such as ceramic or powder coating, provide color and texture, allowing for customization and integration with the motorcycle’s color scheme. The material texture, whether smooth or patterned, adds another layer of visual interest and can enhance the tactile experience.
- End Cap Design
The design of the end cap, the visible extremity of the component, is a focal point that can significantly impact its aesthetic appeal. End caps can feature a variety of shapes, materials, and finishes, ranging from simple, unadorned designs to elaborate, multi-faceted configurations. Carbon fiber end caps, for instance, add a high-tech, performance-oriented touch. The design of the end cap should harmonize with the overall aesthetic of the component and the motorcycle.
- Branding and Logos
The presence, placement, and style of branding elements, such as logos and model designations, contribute to the component’s visual identity. Subtly integrated logos convey a sense of refinement and quality, while overly prominent or garish branding can detract from the overall aesthetic. The font, size, and color of the branding elements should align with the motorcycle’s design language.
The aesthetic design of the exhaust component enhances the visual appeal of the Ninja 500. Considerations such as shape, surface finish, end cap design, and branding contribute to a cohesive and visually compelling motorcycle. Beyond functionality, a well-designed component elevates the overall ownership experience.
6. Regulatory compliance
Regulatory compliance is a paramount consideration regarding the exhaust component designed for the Kawasaki Ninja 500 motorcycle. The component must adhere to specific noise and emissions standards mandated by governmental bodies to ensure environmental protection and public health. Non-compliance can result in legal penalties, vehicle impoundment, and restrictions on usage.
- Noise Emission Standards
Motorcycle exhaust systems are subject to noise emission limits, typically measured in decibels (dB) at specified engine speeds. The component must be designed to attenuate exhaust noise to levels below these regulatory thresholds. Enforcement often involves roadside inspections using calibrated sound meters. Exceeding established noise limits results in fines and mandates for corrective action, such as replacing the non-compliant component with a legal alternative. The component’s design, including baffling and sound-dampening materials, directly influences noise emission levels.
- Exhaust Emission Regulations
Regulations dictate permissible levels of pollutants, including hydrocarbons (HC), carbon monoxide (CO), and nitrogen oxides (NOx), emitted from the exhaust system. The component is integral to managing exhaust gases and can influence emission levels. While catalytic converters, often located upstream of this component, primarily address emissions, the component’s design can impact backpressure and, consequently, engine combustion efficiency, indirectly affecting emissions. Tampering with or removing emission control devices is strictly prohibited and carries severe penalties.
- Type Approval and Certification
Many jurisdictions require exhaust components to undergo type approval or certification processes before they can be legally sold and used on public roads. This involves independent testing to verify compliance with applicable noise and emission standards. Certified components typically bear markings or labels indicating their approval status. Installing non-certified components can void vehicle warranties and lead to legal repercussions during inspections.
- State and Local Ordinances
In addition to federal or national regulations, individual states, provinces, and municipalities may have their own noise and emission ordinances. These local regulations can be more stringent than overarching national standards. Compliance with local ordinances requires careful consideration of the specific requirements of the region where the motorcycle is operated. Some areas may impose restrictions on aftermarket components or enforce stricter noise limits, necessitating the use of quieter exhaust systems. Modifying the component should be in compliance with all applicable local codes.
Adherence to regulatory requirements is critical when selecting and installing an exhaust component for the Ninja 500. Non-compliant components can result in significant legal and financial consequences. Verification of type approval and compliance with applicable noise and emission standards is essential to ensure the motorcycle operates legally and responsibly.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following addresses common inquiries regarding the function, selection, and maintenance of this vital exhaust component.
Question 1: What is the primary function of this component?
The component serves to reduce exhaust noise and direct exhaust gases away from the engine. This functionality contributes to rider comfort, regulatory compliance, and optimized engine performance.
Question 2: How does a modified or aftermarket component affect engine performance?
Altering the component can influence backpressure, which, in turn, affects torque and horsepower. Reduced backpressure can improve high-end horsepower, potentially sacrificing low-end torque. Proper tuning is necessary to optimize performance.
Question 3: What are the common signs of component failure?
Indicators include excessive exhaust noise, visible rust or corrosion, exhaust leaks, decreased engine performance, and fuel inefficiency. Visual inspection and performance monitoring are essential for early detection.
Question 4: Is it legal to remove the component?
Removal violates noise and emissions regulations in most jurisdictions. Furthermore, it can negatively affect engine performance and render the motorcycle non-compliant with safety standards. Such actions may incur legal penalties.
Question 5: What materials offer the best durability?
Stainless steel and titanium alloys exhibit superior resistance to corrosion and thermal stress compared to mild steel. These materials enhance the lifespan and reliability of the component, especially in harsh environments.
Question 6: How does the component influence fuel efficiency?
The component affects backpressure, which directly influences air-fuel mixture and combustion efficiency. Incorrectly designed or modified components can lead to lean or rich conditions, reducing fuel economy and potentially damaging the engine.
Proper understanding and responsible management of this system promotes safety and regulatory compliance.
The article proceeds to summarize practical advice.
Ninja 500 Muffler
The preceding analysis has explored various facets of the exhaust component tailored for the Kawasaki Ninja 500 motorcycle. Crucial considerations include compatibility, backpressure management, sound reduction capabilities, material durability, aesthetic design, and adherence to regulatory standards. Optimal performance and longevity hinge upon informed decision-making regarding selection, installation, and maintenance.
Given the component’s impact on engine performance, environmental compliance, and overall rider experience, diligent attention to its characteristics is warranted. Future advancements in materials science and engineering promise further enhancements in exhaust system design, potentially leading to improved efficiency and reduced environmental impact. Continued awareness of evolving regulations and technological innovations remains essential for responsible motorcycle operation.