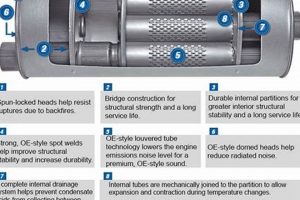
This automotive component facilitates exhaust gas flow with minimal obstruction. Its internal design prioritizes a direct path, enabling gases to pass through the device with significantly reduced backpressure compared to baffled or chambered alternatives. A typical configuration incorporates a perforated core surrounded by sound-absorbing material, such as fiberglass packing, within a cylindrical housing.
Employing such a design can yield multiple performance benefits. Lowering exhaust backpressure generally results in enhanced engine efficiency and increased horsepower, particularly at higher engine speeds. Historically, these designs were favored in racing applications where maximizing power output was paramount. Moreover, the distinct sound profile produced is often perceived as more aggressive and sporty, influencing consumer preference.
The following sections will delve into the specific characteristics, performance implications, and maintenance considerations associated with this type of exhaust system component, exploring its suitability for various vehicle types and driving styles.
Guidance on Selection and Application
The following outlines important considerations when selecting and applying a performance exhaust component characterized by a direct flow path.
Tip 1: Performance Assessment: Evaluate horsepower and torque gains claimed by manufacturers critically. Dyno testing data from independent sources provides more objective verification of actual performance improvements.
Tip 2: Noise Level Considerations: Be cognizant of local noise ordinances before installation. Systems designed for maximum flow often produce elevated sound levels that may violate legal restrictions.
Tip 3: Material Selection: Stainless steel provides superior corrosion resistance compared to aluminized steel, extending service life, particularly in regions with harsh winter climates or coastal environments.
Tip 4: Proper Installation: Ensure correct alignment and secure mounting to prevent leaks and vibration. Improper installation can lead to premature failure of exhaust components and potential damage to other vehicle systems.
Tip 5: Periodic Inspection: Regularly inspect the exhaust system for signs of damage, corrosion, or leaks. Addressing issues promptly prevents more extensive and costly repairs.
Tip 6: Tuning Requirements: Significant alterations to exhaust flow can impact engine air-fuel ratio. Consider professional engine tuning to optimize performance and prevent potential engine damage.
Tip 7: Backpressure Impact: While reduced backpressure is often desired, excessively low backpressure can negatively affect low-end torque. A balance between high-end power gains and low-speed drivability is essential.
Careful attention to these considerations will contribute to optimal performance, longevity, and compliance with applicable regulations.
The next section will cover maintenance procedures and troubleshooting common issues related to this specific exhaust design.
1. Minimal Backpressure
Minimal backpressure is a defining characteristic of an exhaust component designed with a direct flow path. This reduction in resistance to exhaust gas flow is central to its performance and operational principles, influencing engine efficiency and overall system behavior.
- Engine Performance Implications
Reduced backpressure facilitates more efficient scavenging of exhaust gases from the engine cylinders. This improved scavenging allows for a greater volume of fresh air and fuel to enter the cylinders during the intake stroke, leading to increased power output, particularly at higher engine speeds. Conversely, excessively low backpressure can negatively impact low-end torque in some engine configurations.
- Exhaust Gas Velocity
The design promotes a higher velocity of exhaust gases through the system. This increased velocity helps to prevent the build-up of exhaust gases within the system, further reducing backpressure and enhancing overall flow efficiency. The diameter and internal surface characteristics of the component significantly influence this velocity.
- Catalytic Converter Considerations
When used in conjunction with a catalytic converter, this design must be carefully considered to ensure the converter operates within its optimal temperature range. Excessive exhaust gas velocity or temperature fluctuations due to reduced backpressure can potentially compromise the converter’s efficiency and longevity.
- Acoustic Characteristics
Minimizing backpressure often results in a louder and more aggressive exhaust note. The absence of baffles or restrictive chambers allows sound waves to propagate more freely through the system. This characteristic is frequently sought after by performance enthusiasts but may require consideration of noise regulations and community standards.
In conclusion, the attribute of minimal backpressure in a direct-flow exhaust component is a critical factor determining its performance characteristics and suitability for various applications. Careful consideration of its impact on engine performance, exhaust gas velocity, catalytic converter function, and acoustic properties is essential for optimal implementation.
2. Direct exhaust flow
Direct exhaust flow is the defining principle behind the design and function of a component characterized by a straight, unobstructed path for exhaust gases. It dictates how efficiently gases exit the engine and is instrumental in achieving desired performance characteristics. This principle distinguishes the “straight through muffler” from other muffler designs.
- Unimpeded Gas Passage
The primary role of a direct-flow exhaust component is to minimize resistance to exhaust gases. Unlike baffled or chambered designs that force gases to change direction, this design allows gases to exit the engine with minimal obstruction. This unimpeded flow contributes to reduced backpressure, a key performance metric. For example, in high-performance engines, restricted exhaust flow can limit power output. Conversely, a direct-flow design mitigates this restriction, facilitating greater power generation.
- Core Design & Perforation
The internal structure typically consists of a perforated core surrounded by sound-absorbing material. The perforation pattern and core diameter are carefully engineered to maximize flow while maintaining structural integrity. The perforations enable exhaust gases to expand into the surrounding sound-absorbing material, reducing noise without significantly impeding flow. An example of this can be found in aftermarket performance systems where the perforation density is optimized for specific engine types.
- Impact on Engine Performance
Direct exhaust flow influences engine performance in several ways. By reducing backpressure, it improves volumetric efficiency, allowing more air and fuel to enter the engine cylinders. This results in increased horsepower and torque, particularly at higher engine speeds. However, excessively free-flowing exhaust can, in some cases, negatively impact low-end torque. For instance, smaller displacement engines may experience a loss of responsiveness at lower RPMs if exhaust flow is too unrestricted.
- Acoustic Characteristics & Sound Attenuation
While prioritizing flow, a direct-flow design incorporates sound-absorbing materials to mitigate noise. The fiberglass packing or other sound-dampening materials absorb sound waves as they pass through the component. However, due to the minimal obstruction of the exhaust flow, the sound profile is often louder and more aggressive compared to baffled mufflers. The precise balance between flow optimization and sound attenuation is a critical design consideration. An example is the use of variable-density packing materials to target specific frequency ranges.
The interplay between direct exhaust flow and the internal construction directly influences the component’s ability to enhance engine performance while managing noise levels. Its suitability for a particular application hinges on a comprehensive understanding of these interconnected facets.
3. Aggressive Sound Profile
The audible signature emanating from a vehicle equipped with an exhaust component characterized by a direct flow path often exhibits an assertive and distinctive quality. This “aggressive sound profile” is a direct consequence of the design principles employed, influencing consumer perception and contributing to the overall driving experience.
- Absence of Baffling and Chambers
Unlike traditional baffled or chambered mufflers, this particular component facilitates minimal obstruction to exhaust gas flow. The lack of internal barriers allows sound waves to propagate with greater freedom, resulting in a louder and more pronounced exhaust note. For instance, a baffled muffler directs exhaust gases through a series of chambers, which effectively dampens sound waves. In contrast, the direct-flow design allows sound waves to travel relatively unhindered, resulting in a more resonant and aggressive tone.
- Frequency Amplification
The internal structure can, under certain conditions, amplify specific frequencies within the exhaust sound spectrum. The dimensions and materials used in construction can create resonance effects that enhance certain sound frequencies, contributing to the characteristic rumble or roar associated with performance exhaust systems. For instance, the length and diameter of the internal core influence the frequencies that are most effectively amplified.
- Correlation with Engine Characteristics
The aggressive sound profile is intimately linked to the engine’s displacement, firing order, and overall design. Engines with larger displacements or specific firing orders tend to produce more pronounced and aggressive exhaust notes. The component enhances these inherent sound characteristics, accentuating the engine’s natural voice. As an example, a V8 engine typically produces a deeper and more resonant sound than an inline-four engine, and this difference is further amplified by the design.
- Subjective Perception and Consumer Preference
The perception of an aggressive sound profile is subjective and often influenced by individual preferences. Some enthusiasts seek a loud and attention-grabbing exhaust note, while others prefer a more subdued tone. The aggressive sound is often associated with performance and power, appealing to individuals who desire a more visceral driving experience. For instance, aftermarket exhaust manufacturers cater to diverse preferences by offering a range of components with varying degrees of sound aggression.
In essence, the aggressive sound profile resulting from the use of a component with direct exhaust flow is a confluence of design characteristics, engine attributes, and subjective perception. This audible signature contributes significantly to the vehicle’s overall character and appeal, playing a crucial role in the purchasing decisions of performance-oriented consumers.
4. Performance enhancement
The direct relationship between performance enhancement and a muffler design that facilitates unobstructed exhaust flow is rooted in the principles of engine thermodynamics. By minimizing backpressure, this specific muffler design allows for more efficient scavenging of exhaust gases from the combustion chamber. This, in turn, leads to a more complete intake charge, resulting in a more powerful combustion event. Consequently, engines equipped with such components often exhibit increased horsepower and torque, particularly at higher engine speeds. For example, in racing applications, where even marginal gains are critical, this muffler type is frequently utilized to maximize engine output. Real-world tests often demonstrate quantifiable improvements in dyno readings, confirming the direct link between the design and measurable performance gains. Understanding this relationship is practically significant for automotive enthusiasts seeking to optimize their vehicle’s performance profile.
Further analysis reveals that the extent of performance enhancement is contingent upon several factors, including engine displacement, camshaft profile, and the overall design of the exhaust system. A well-matched exhaust system, incorporating this type of muffler, can significantly improve engine breathing, leading to noticeable improvements in throttle response and acceleration. Conversely, an improperly sized exhaust system or one that introduces excessive backpressure can negate the benefits of a direct-flow muffler. For instance, a high-performance sports car can leverage the reduced backpressure to unlock additional horsepower, while a small, naturally aspirated engine might experience negligible gains or even a slight reduction in low-end torque. Practical applications range from track-day vehicles to modified street cars, where the focus is on achieving optimal performance characteristics.
In summary, the connection between performance enhancement and a muffler design that prioritizes unobstructed flow is a direct and quantifiable one. The degree of enhancement is influenced by engine characteristics and the overall exhaust system design. While the benefits are most pronounced in high-performance applications, careful consideration is essential to ensure that the selected component is appropriately matched to the vehicle’s engine and intended use. Challenges include balancing the desire for increased power with considerations for noise regulations and potential impact on low-end torque. Ultimately, the intelligent application of this muffler design can contribute significantly to optimizing engine performance and enhancing the overall driving experience.
5. Simple internal design
The efficacy of a “straight through muffler” is intrinsically linked to its uncomplicated internal structure. This design philosophy, prioritizing minimal obstruction, directly facilitates the free flow of exhaust gases. The absence of complex chambers or intricate baffles, common in other muffler types, serves as the primary cause for the reduced backpressure associated with this particular design. This effect is not merely incidental; the deliberate simplification of the internal structure is paramount to achieving the intended performance characteristics.
One exemplary illustration of this connection is the use of a perforated core surrounded by sound-absorbing material. This configuration allows exhaust gases to expand into the surrounding packing, dissipating sound energy without significantly impeding flow. Unlike baffled systems that redirect gases and create turbulence, the direct path afforded by the perforated core ensures minimal resistance. The practical significance of this lies in the potential for increased engine horsepower and torque, particularly at higher engine speeds, as the engine expends less energy forcing exhaust gases through the system. Aftermarket performance exhaust systems routinely leverage this straightforward design to deliver measurable gains in vehicle performance.
In summary, the functional benefits of a “straight through muffler,” notably reduced backpressure and enhanced engine performance, are directly attributable to its simple internal design. The absence of complex internal components ensures a direct and unimpeded flow path for exhaust gases, contributing significantly to its performance characteristics. This inherent simplicity, while seemingly rudimentary, is a critical element in achieving the desired outcome, highlighting the direct correlation between design and performance.
6. Fiberglass packing
Fiberglass packing plays a crucial role in the functional operation of a “straight through muffler.” Serving primarily as a sound-absorbing material, it lines the outer perimeter of the muffler’s internal core. This strategic placement facilitates the dissipation of sound energy as exhaust gases traverse the component. The perforated core allows sound waves to radiate outwards into the fiberglass, where they are converted into thermal energy through frictional damping. Without fiberglass packing, the aggressive sound profile, characteristic of a “straight through muffler,” would be significantly amplified, potentially exceeding acceptable noise levels. Therefore, the inclusion of fiberglass packing is not merely an ancillary feature but a vital element in managing the acoustic output of the muffler.
The effectiveness of fiberglass packing is contingent upon several factors, including density, fiber diameter, and packing thickness. Higher density packing generally provides greater sound attenuation but can also contribute to increased backpressure. Fiber diameter influences the frequency range most effectively absorbed, with finer fibers typically more efficient at absorbing higher frequencies. Packing thickness directly affects the total amount of sound energy absorbed. Over time, fiberglass packing can degrade due to exposure to high temperatures and exhaust gas contaminants, leading to a gradual increase in exhaust noise. Regular inspection and replacement of the packing are therefore essential for maintaining optimal performance and sound levels. Aftermarket performance mufflers often offer replaceable packing cartridges to facilitate this maintenance.
In summary, fiberglass packing is integral to the operation of a “straight through muffler,” serving as the primary means of sound attenuation. Its effectiveness is determined by material properties and installation parameters, while its long-term performance depends on regular maintenance. The absence or degradation of fiberglass packing directly impacts the muffler’s ability to manage exhaust noise, underscoring its importance as a critical component of the overall design.
7. Stainless steel option
The availability of a stainless steel construction variant for “straight through muffler” designs represents a significant consideration for longevity and performance, particularly in environments conducive to corrosion. The material’s inherent resistance to degradation directly influences the lifespan and operational effectiveness of the exhaust component.
- Corrosion Resistance
Stainless steel alloys, typically containing chromium, form a passive oxide layer on the surface, preventing rust and resisting degradation from exposure to moisture, road salt, and acidic exhaust gases. This characteristic is particularly relevant in regions with harsh winter climates where road de-icing agents are prevalent. A “straight through muffler” constructed from stainless steel will demonstrably outlast comparable aluminized steel versions in such conditions.
- Elevated Temperature Resilience
Exhaust system components, including “straight through muffler” designs, are subjected to high operating temperatures. Stainless steel exhibits superior resistance to oxidation and creep at elevated temperatures compared to other common materials. This resistance minimizes the risk of structural failure and maintains the component’s integrity over prolonged periods of use.
- Aesthetic Durability
Beyond structural integrity, stainless steel retains its cosmetic appearance for a longer duration compared to materials prone to surface corrosion. This is particularly relevant for visible exhaust components, where maintaining a presentable appearance contributes to the vehicle’s overall aesthetic appeal. The “straight through muffler,” when constructed from stainless steel, will maintain its polished finish or resist unsightly rust formation.
- Life Cycle Cost Considerations
While the initial cost of a stainless steel “straight through muffler” is generally higher than that of an aluminized steel counterpart, the extended service life often translates to a lower total cost of ownership. The reduced need for replacement due to corrosion damage offsets the initial price premium, making it an economically viable option over the long term.
The selection of a stainless steel “straight through muffler” represents a trade-off between initial investment and long-term durability. The material’s inherent resistance to corrosion and high temperatures makes it a particularly suitable choice for vehicles operating in harsh environments or for owners seeking a long-lasting exhaust component. The decreased life cycle costs provide a substantial return on investment.
Frequently Asked Questions about Straight Through Mufflers
The following addresses common inquiries regarding exhaust components designed with a direct flow path, providing objective insights into their function and application.
Question 1: What distinguishes a straight through muffler from other muffler designs?
A straight through muffler is characterized by its internal design, which prioritizes a direct, unobstructed path for exhaust gases. This contrasts with baffled or chambered designs that force gases to change direction, creating backpressure. The straight through configuration typically employs a perforated core surrounded by sound-absorbing material.
Question 2: Does the use of a straight through muffler guarantee increased horsepower?
While a straight through muffler can contribute to increased horsepower, particularly at higher engine speeds, the actual gains depend on several factors, including engine displacement, camshaft profile, and overall exhaust system design. The muffler alone does not guarantee a specific horsepower increase.
Question 3: Are straight through mufflers excessively loud?
Straight through mufflers generally produce a louder and more aggressive exhaust note compared to baffled designs. However, the sound level can be managed through the selection of appropriate sound-absorbing materials and careful design of the surrounding exhaust system. Compliance with local noise ordinances should always be considered.
Question 4: How does fiberglass packing affect the performance of a straight through muffler?
Fiberglass packing serves primarily as a sound-absorbing material, mitigating the aggressive sound associated with a direct-flow design. Over time, the packing can degrade, leading to increased exhaust noise. Regular inspection and replacement are necessary to maintain optimal performance and sound levels.
Question 5: Is stainless steel a necessary material for a straight through muffler?
While not strictly necessary, stainless steel offers superior corrosion resistance compared to aluminized steel, extending the lifespan of the muffler, particularly in harsh environments. The increased initial cost may be offset by the reduced need for replacement due to corrosion damage.
Question 6: Can a straight through muffler negatively affect engine performance?
In some instances, excessively free-flowing exhaust, resulting from a poorly matched straight through muffler, can negatively affect low-end torque. Careful consideration should be given to engine characteristics and overall exhaust system design to ensure optimal performance across the entire RPM range.
The selection and application of a straight through muffler should be based on a comprehensive understanding of its design principles, performance characteristics, and potential impact on both sound levels and engine operation.
The following section will explore specific applications and use-cases for these types of mufflers.
Conclusion
The preceding analysis has explored the multifaceted characteristics of the “straight through muffler.” Its defining features minimal backpressure, direct exhaust flow, simple internal design, and the option for stainless steel construction collectively determine its suitability for diverse automotive applications. The integration of fiberglass packing plays a crucial role in managing the acoustic output associated with this design. Performance enhancement, while a potential benefit, is contingent upon careful matching of the component to specific engine parameters and overall exhaust system configuration.
The intelligent application of “straight through muffler” technology requires a comprehensive understanding of its inherent trade-offs. Factors such as noise level considerations, potential impact on low-end torque, and the long-term cost implications of material selection warrant thorough evaluation. Informed decision-making, grounded in empirical data and a clear understanding of vehicle-specific requirements, is paramount to realizing the full potential of this exhaust system component.



![Unleash Power: Best Sport Muffler Upgrades [Year] Best Mufflers for Cars & Trucks | Performance, Sound & Durability Upgrades Unleash Power: Best Sport Muffler Upgrades [Year] | Best Mufflers for Cars & Trucks | Performance, Sound & Durability Upgrades](https://dnamufflers.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/02/th-353-300x200.jpg)