A performance exhaust component, designed to augment engine output and modify exhaust sound characteristics, is commonly installed on vehicles to enhance the driving experience. These devices typically feature a less restrictive internal design compared to factory-installed counterparts, allowing for increased exhaust gas flow. The result is often a noticeable increase in horsepower and torque, particularly at higher engine speeds. The audible output also changes, often producing a deeper, more aggressive tone.
The appeal of these systems lies in the potential for improved vehicle performance and a more engaging auditory experience. Historically, modifications of this nature were primarily the domain of racing and high-performance applications. However, they have become increasingly popular among everyday drivers seeking to personalize their vehicles. The benefits, while quantifiable in terms of power gains, are often perceived subjectively, with the enhanced sound contributing significantly to the driver’s satisfaction.
Understanding the specific design attributes, material composition, and installation considerations of aftermarket exhaust components is crucial for selecting the appropriate system. The following sections will delve deeper into various aspects of these systems, exploring their impact on vehicle performance, regulatory compliance, and long-term durability.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Optimizing the performance and longevity of an enhanced exhaust system requires careful attention to both installation procedures and ongoing maintenance practices. Improper installation can negate potential performance gains and may even damage the vehicle. Neglecting routine maintenance can lead to premature wear and corrosion, ultimately reducing the system’s lifespan.
Tip 1: Verify Compatibility: Before purchasing, ensure that the selected unit is specifically designed for the vehicle’s make, model, and year. Incompatibility can lead to fitment issues, performance degradation, and potential engine damage. Consult manufacturer specifications and cross-reference part numbers.
Tip 2: Professional Installation Recommended: While some installations can be performed by experienced individuals, professional installation is generally recommended. Certified technicians possess the necessary tools and expertise to ensure proper fitment, alignment, and torque specifications are met.
Tip 3: Check for Leaks: After installation, thoroughly inspect all connections for exhaust leaks. Leaks can reduce performance, increase noise levels, and potentially allow harmful gases to enter the vehicle cabin. Use a soapy water solution to identify leaks at flanges and joints.
Tip 4: Regular Inspections: Periodically inspect the system for signs of corrosion, damage, or loose connections. Early detection of potential problems can prevent more serious issues from developing.
Tip 5: Clean Regularly: Depending on driving conditions, road salt and other debris can accumulate on the exhaust system, accelerating corrosion. Regularly cleaning the system with a mild soap and water solution can help to prevent this.
Tip 6: Address Rattling or Vibration: Investigate any unusual rattling or vibration emanating from the exhaust system. These symptoms can indicate loose hangers, contact with other vehicle components, or internal damage within the unit itself. Promptly addressing these issues can prevent further damage and potential safety hazards.
Tip 7: Consider Heat Shielding: In certain applications, particularly those involving forced induction, consider installing heat shielding to protect surrounding components from excessive heat generated by the exhaust system. This can help to prevent heat-related damage to wiring harnesses, fuel lines, and other sensitive components.
Proper installation and regular maintenance are essential for maximizing the benefits and extending the lifespan of an aftermarket exhaust system. Adhering to these guidelines will ensure optimal performance, minimize potential problems, and preserve the vehicle’s overall integrity.
With proper care and attention, the exhaust system will continue to provide enhanced performance and an engaging driving experience for years to come. The following sections will explore additional aspects of exhaust system technology, including regulatory compliance and future trends.
1. Performance Enhancement
Performance enhancement, in the context of aftermarket exhaust components, specifically concerns modifications designed to improve engine output and overall vehicle responsiveness. The core objective is to optimize the flow of exhaust gases, thereby reducing backpressure and allowing the engine to operate more efficiently. This optimization is intrinsically linked to the design and construction of the component and significantly influences the engine’s power delivery characteristics.
- Reduced Backpressure
The primary function of an enhanced exhaust component is to minimize backpressure within the exhaust system. This is achieved through larger diameter piping, smoother bends, and a less restrictive internal design. Reduced backpressure allows the engine to expel exhaust gases more efficiently, resulting in increased horsepower and torque, particularly at higher engine speeds. Factory-installed systems often prioritize noise reduction and emissions control, which can inherently create higher levels of backpressure.
- Optimized Flow Dynamics
The internal design dictates the flow characteristics of exhaust gases. Straight-through designs, as opposed to baffled designs, offer the least resistance to gas flow. The smoother and more direct the exhaust path, the more efficiently the engine can operate. This improvement in flow dynamics directly translates to increased engine power and responsiveness. The design must consider both flow rate and velocity to maximize performance gains.
- Engine Tuning Synergies
The full potential of a performance exhaust component is often realized when combined with complementary engine tuning modifications. Aftermarket engine control unit (ECU) calibrations can optimize fuel delivery and ignition timing to take advantage of the increased exhaust flow. This synergistic relationship between hardware and software modifications can yield significantly greater performance gains than either modification alone. An integrated approach to performance enhancement is often the most effective.
- Weight Reduction Considerations
Many aftermarket exhaust systems are constructed from lighter materials, such as stainless steel or titanium, compared to factory-installed steel systems. This reduction in weight not only contributes to improved handling and acceleration but also enhances overall fuel efficiency. The cumulative effect of weight reduction, combined with increased engine power, can significantly improve the vehicle’s performance characteristics.
The aforementioned aspects of reduced backpressure, optimized flow dynamics, engine tuning synergies, and weight reduction are crucial elements in performance enhancement associated with aftermarket exhaust components. These components, when properly selected and installed, offer the potential to significantly improve vehicle performance and provide a more engaging driving experience. However, careful consideration must be given to compatibility, installation, and legal compliance to ensure optimal results and avoid potential issues.
2. Audible Characteristics
Audible characteristics represent a significant factor in the selection and perception of aftermarket exhaust components. These characteristics are not merely a byproduct of design but are often a primary consideration for vehicle owners seeking a specific auditory experience. The sound produced can influence the perceived performance and overall driving enjoyment.
- Frequency and Pitch
The frequency and pitch of the exhaust note are determined by the dimensions and materials used. Systems designed for higher engine speeds tend to produce higher-pitched notes, while those focused on low-end torque may generate deeper, more resonant tones. Stainless steel often yields a brighter, more metallic sound compared to aluminized steel. The internal baffling and chamber design further shape the frequency profile.
- Volume and Decibel Level
The volume, measured in decibels (dB), is a crucial factor, especially in relation to local noise ordinances. Aftermarket systems generally produce a louder exhaust note compared to stock systems. This increase in volume can enhance the perceived sportiness of the vehicle but may also attract unwanted attention from law enforcement. Some systems incorporate adjustable valves or resonators to modulate the volume output based on driving conditions.
- Resonance and Drone
Resonance, often referred to as drone, describes the low-frequency vibrations that can occur within the vehicle cabin at specific engine speeds. Excessive drone can be fatiguing and unpleasant for the driver and passengers. Careful design, including the use of resonators and Helmholtz chambers, can mitigate drone and create a more comfortable driving experience.
- Sound Quality and Tone
Beyond the measurable aspects of frequency and volume, the subjective quality of the exhaust note is paramount. Terms like “raspy,” “smooth,” “aggressive,” and “exotic” are often used to describe the tonal characteristics. This subjective evaluation is highly personal and depends on individual preferences. Sound quality is influenced by a combination of material composition, internal design, and the overall tuning of the exhaust system.
The audible characteristics of aftermarket exhaust components are multifaceted, encompassing frequency, volume, resonance, and subjective sound quality. These elements contribute significantly to the overall driving experience and should be carefully considered when selecting an appropriate system. Understanding these characteristics allows for a more informed decision-making process, ensuring that the chosen system aligns with the driver’s preferences and local regulations.
3. Flow Dynamics
Flow dynamics, concerning aftermarket exhaust components, specifically focuses on the movement of exhaust gases through the system. Efficient evacuation of these gases is paramount for optimizing engine performance. Therefore, the design of a system directly influences its ability to facilitate unimpeded flow, thereby affecting engine power and efficiency.
- Internal Geometry and Pathing
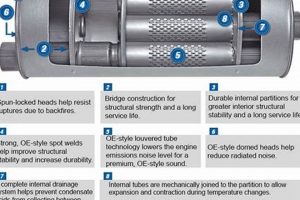
The internal geometry of the component is a primary determinant of flow efficiency. Straight-through designs, characterized by minimal obstructions and smooth transitions, generally offer superior flow characteristics compared to baffled or chambered designs. The pathing of exhaust gases should minimize turbulence and pressure drops. Sharp bends and constrictions impede flow, reducing engine performance. An optimized design ensures a laminar flow regime, minimizing energy loss and maximizing gas velocity.
- Pipe Diameter and Expansion Ratios
The diameter of the exhaust piping plays a crucial role in flow capacity. Increasing the pipe diameter can reduce backpressure, particularly at higher engine speeds. However, excessive diameter can decrease exhaust gas velocity at lower speeds, potentially reducing low-end torque. Expansion ratios, referring to the gradual increase in pipe diameter, are strategically implemented to optimize gas velocity and minimize turbulence as gases expand and cool.
- Surface Finish and Material Properties
The surface finish of the internal walls influences the boundary layer effect, wherein friction between the exhaust gases and the pipe surface can impede flow. Smooth internal surfaces minimize friction, thereby enhancing flow efficiency. Material properties also contribute to flow dynamics. Materials with lower thermal conductivity reduce heat loss, maintaining exhaust gas velocity and reducing condensation, which can increase backpressure.
- Collector Design and Merge Quality
The collector, where exhaust gases from multiple cylinders converge, is a critical area for optimizing flow. A well-designed collector minimizes turbulence and promotes smooth merging of exhaust streams. Merge quality, referring to the precision and smoothness of the welds and transitions within the collector, directly impacts flow efficiency. Poorly designed or constructed collectors can create backpressure and reduce engine performance.
These facetsinternal geometry, pipe diameter, surface finish, and collector designcollectively determine the flow dynamics of an aftermarket exhaust system. Optimizing these factors allows for the creation of a system that enhances engine performance by minimizing backpressure and maximizing the efficient evacuation of exhaust gases. The careful consideration of these elements is essential for achieving the desired performance characteristics and ensuring the system’s effectiveness.
4. Material Composition
Material composition fundamentally influences the performance, durability, and acoustic properties of a performance exhaust component. The selection of materials directly affects the component’s ability to withstand high temperatures, resist corrosion, and contribute to the desired exhaust note. Different alloys and composites offer varying degrees of thermal stability, strength, and weight, each impacting the component’s suitability for specific applications. For instance, stainless steel, known for its corrosion resistance, is frequently employed in environments exposed to road salt and moisture. Titanium, valued for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, finds use in high-performance applications where minimizing mass is critical. The chosen material, therefore, represents a compromise between cost, performance, and longevity.
The material’s inherent properties significantly affect the exhaust’s sound characteristics. Stainless steel tends to produce a brighter, more metallic tone, while aluminized steel often results in a deeper, more subdued sound. The thickness of the material also contributes to the sound profile, with thicker gauge materials generally producing a more robust and resonant tone. Furthermore, the material’s thermal conductivity influences the rate at which heat dissipates, impacting the exhaust gas temperature and, consequently, the sound produced. A practical example lies in comparing two systems: a thin-walled titanium component delivers a high-pitched, race-inspired sound, while a thick-walled stainless steel system provides a deep, throaty rumble.
Understanding the interplay between material composition and performance exhaust characteristics is paramount for selecting an appropriate system. Challenges arise in balancing desired performance gains, acoustic properties, and budget constraints. The optimal choice depends on the intended use, environmental conditions, and individual preferences. Considering the effects of different materials allows informed decisions that maximize the benefit and lifespan of the performance exhaust system. The selection of material is a foundational aspect of both its functionality and perceived value.
5. Vehicle Compatibility
Vehicle compatibility is a critical parameter in the selection and installation of performance exhaust components. The design and specifications of a particular performance exhaust unit must align with the target vehicle’s make, model, year, and engine configuration. Incompatible components can lead to significant performance degradation, potential engine damage, and installation difficulties. The selection process requires verifying that the aftermarket system is engineered to function seamlessly with the vehicle’s existing exhaust manifold, catalytic converter, and chassis mounting points. For example, attempting to install a system designed for a four-cylinder engine onto a V6 engine is unlikely to yield any performance benefits and will likely result in improper fitment and exhaust leaks.
The repercussions of neglecting vehicle compatibility are multifaceted. An improperly fitted unit may cause exhaust leaks, reducing engine power and potentially allowing harmful gases to enter the vehicle cabin. Physical incompatibility can damage the vehicle’s chassis or exhaust manifold. Furthermore, electronic control unit (ECU) errors may arise if the backpressure characteristics of the new system deviate significantly from the factory-specified parameters. Consider the example of a performance exhaust system designed for a turbocharged engine installed on a naturally aspirated engine; the reduced backpressure could negatively affect the engine’s volumetric efficiency, leading to decreased low-end torque and potential engine damage.
Ultimately, careful consideration of vehicle compatibility represents a fundamental aspect of the exhaust modification process. Confirming compatibility through manufacturer specifications, part number cross-referencing, and professional consultation minimizes the risk of installation errors, performance issues, and potential damage. The practical significance of this understanding stems from the need to maintain vehicle reliability, performance, and compliance with local regulations. Proper selection ensures the enhancement achieves its intended objectives without introducing unintended negative consequences, providing optimal performance and safety.
6. Installation Complexity
The degree of intricacy associated with installing a performance exhaust component, specifically a “sport muffler”, is a critical factor influencing both the overall cost and the potential for successful integration with the vehicle’s existing systems. Varying levels of technical expertise, specialized tools, and the potential for unforeseen complications during the process necessitate a comprehensive understanding of the inherent installation complexity.
- Direct Bolt-On vs. Custom Fabrication
Some performance exhaust components are designed as direct replacements for the factory muffler, utilizing existing mounting points and hardware. These “bolt-on” systems minimize installation complexity, requiring only basic tools and mechanical aptitude. However, other systems may necessitate custom fabrication, including cutting, welding, and modification of existing exhaust piping. This level of complexity demands advanced skills and specialized equipment, often necessitating professional installation.
- Sensor and Emission System Integration
Modern vehicles incorporate sophisticated sensor systems and emission control devices within the exhaust stream. Installation complexity increases significantly when the performance exhaust component requires integration with oxygen sensors, catalytic converters, or exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) systems. Improper installation or modification of these components can trigger check engine lights, reduce fuel efficiency, and potentially violate emission regulations. Proper alignment and sealing are paramount to avoid leaks that could compromise system performance.
- Clearance and Fitment Issues
The physical dimensions and routing of the performance exhaust component must be compatible with the vehicle’s chassis, suspension components, and fuel lines. Clearance issues can arise if the aftermarket system is not designed precisely for the target vehicle. These issues may necessitate modifications to the exhaust system or the vehicle itself, increasing installation complexity and potentially compromising structural integrity. Correct hanger placement is essential to prevent vibration and premature wear.
- Potential for Corrosion and Seizing
The removal of the existing muffler can be complicated by corrosion and seizing of fasteners, particularly in older vehicles or those operated in harsh environments. Applying penetrating oil and utilizing specialized tools can mitigate this issue, but the potential for broken bolts and damaged exhaust components remains. The replacement of corroded hardware is often necessary to ensure a secure and leak-free installation, adding to the overall complexity and time required.
The aforementioned factors underscore the importance of accurately assessing the installation complexity associated with a “sport muffler” before undertaking the project. Factors ranging from system design, sensor integration, physical fitment, and potential corrosion pose different obstacles that vary with technical expertise. Proper planning, the right tools, and, when necessary, professional assistance is critical for ensuring successful integration and optimal vehicle performance. Addressing installation complexity is an investment in realizing the intended benefits of the performance upgrade while safeguarding the vehicle’s reliability.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following section addresses common inquiries and misconceptions surrounding aftermarket exhaust components, specifically sport mufflers, providing factual and objective information to aid in informed decision-making.
Question 1: Will installing a sport muffler void the vehicle’s warranty?
The installation of an aftermarket component generally does not automatically void the entire vehicle warranty. However, if the component is determined to be the direct cause of a failure, the warranty claim for that specific failure may be denied. It is advisable to consult the vehicle manufacturer’s warranty policy or a qualified service advisor to determine specific implications.
Question 2: What is the typical performance gain associated with a sport muffler?
Performance gains vary significantly depending on factors such as the vehicle’s engine, the design of the system, and the presence of other modifications. Measurable gains typically range from 5 to 15 horsepower. However, the perceived increase in responsiveness and audible enhancement often contribute significantly to the overall driving experience.
Question 3: Does a sport muffler increase fuel consumption?
Under normal driving conditions, a properly installed system should not significantly increase fuel consumption. In some cases, with optimized engine tuning, a minor improvement in fuel economy may be observed. However, aggressive driving styles, often associated with the enhanced sound, may lead to increased fuel usage.
Question 4: Are sport mufflers legal for street use?
Legality varies significantly depending on local regulations. Many jurisdictions have noise restrictions that limit the permissible decibel level of vehicle exhaust systems. Some systems may also require compliance with emissions standards. It is essential to research and adhere to local laws to avoid potential fines or penalties.
Question 5: How long does a sport muffler typically last?
The lifespan of a performance exhaust component depends largely on the material composition and environmental conditions. Stainless steel systems generally offer greater corrosion resistance and a longer lifespan compared to aluminized steel systems. Regular maintenance, including cleaning and inspection, can extend the component’s longevity.
Question 6: Can a sport muffler be installed on any vehicle?
While universal fit systems are available, optimal performance and fitment are typically achieved with systems specifically designed for the vehicle’s make, model, year, and engine configuration. Universal systems may require significant modification and may not provide the same level of performance or durability.
In summary, selecting and installing an aftermarket component requires careful consideration of compatibility, legality, and potential impacts on warranty and fuel consumption. Addressing these concerns ensures a positive and compliant ownership experience.
The subsequent section will examine future trends and technological advancements in exhaust system design.
Sport Muffler
This exposition has detailed various facets of the “sport muffler,” ranging from its functional principles and performance implications to installation complexities and regulatory considerations. The investigation underscores that the selection and integration of such a component represents a multifaceted decision, requiring a comprehensive understanding of its impact on vehicle performance, acoustics, and overall operational integrity.
The pursuit of enhanced performance and auditory gratification necessitates a careful assessment of individual needs, vehicle compatibility, and legal compliance. Continued advancements in material science and exhaust system design suggest a future characterized by increasingly sophisticated and efficient components. It is incumbent upon vehicle owners to remain informed and exercise diligence when engaging with this technology, ensuring a harmonious balance between performance enhancement and responsible vehicle operation.