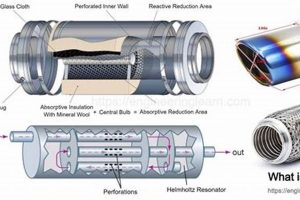
Determining the operational status of a vehicle’s exhaust silencing component is crucial for maintaining optimal vehicle performance and adherence to noise regulations. A compromised muffler can lead to increased noise pollution and potential engine inefficiency.
A properly functioning muffler plays a vital role in reducing engine noise, improving fuel economy, and contributing to overall vehicle efficiency. Historically, mufflers have evolved from simple noise dampeners to complex systems designed to meet stringent environmental standards and enhance driving comfort.
The subsequent sections will outline specific indicators and diagnostic methods employed to assess the condition of the exhaust silencing component, providing a comprehensive understanding of potential malfunctions.
Assessing Muffler Condition
The following indicators provide insights into the potential malfunction of a vehicle’s exhaust silencing component. Regular monitoring can facilitate early detection and prevent further system degradation.
Tip 1: Auditory Inspection: Increased exhaust volume, characterized by a louder or more aggressive engine sound, often indicates a compromised muffler. Compare the current sound level to the vehicle’s typical operational noise.
Tip 2: Visual Examination for Corrosion: Rust, holes, or other forms of physical damage on the muffler’s exterior can directly impair its functionality. Inspect the entire muffler body and connecting pipes for visible deterioration.
Tip 3: Leak Detection Through Condensation: During cold starts, observe the exhaust system for excessive condensation leaks originating from the muffler itself, rather than the tailpipe. This suggests internal corrosion and perforation.
Tip 4: Physical Stability Assessment: A loose or rattling muffler may indicate damaged mounting points or internal component failure. Gently attempt to move the muffler; excessive movement suggests a problem.
Tip 5: Fuel Efficiency Monitoring: A deteriorating muffler can indirectly affect engine performance and fuel economy. Note any significant decrease in miles per gallon, especially if accompanied by other symptoms.
Tip 6: Exhaust Smell Anomaly: An unusual or pungent exhaust odor, differing from the typical exhaust smell, could signify incomplete combustion due to backpressure issues stemming from a failing muffler.
Tip 7: Vibration Analysis: Excessive vibration emanating from the exhaust system, particularly at specific engine speeds, might point to internal muffler damage or detached baffles.
Addressing these indicators promptly can prevent further damage to the exhaust system and maintain optimal vehicle performance. Failure to address muffler issues can result in increased noise pollution and potential safety hazards.
The subsequent section will detail potential solutions and repair strategies for compromised mufflers, offering options for restoring vehicle performance and minimizing environmental impact.
1. Louder exhaust
The phenomenon of amplified exhaust noise serves as a primary indicator of a compromised exhaust silencing component. A properly functioning muffler attenuates engine noise, producing a relatively quiet exhaust note. When internal components of the muffler degrade, typically through corrosion or mechanical failure of baffles, the muffler’s ability to dampen sound is significantly reduced. This results in a noticeable increase in exhaust volume, often described as a roaring or rumbling sound, particularly during acceleration.
The presence of louder exhaust is a direct consequence of the muffler’s inability to effectively mitigate sound waves generated by the engine’s combustion process. Real-world examples include vehicles with rusted-through mufflers exhibiting a significantly increased noise level compared to their original state. This symptom is readily detectable and constitutes a critical component in assessing the overall health of the exhaust system. Moreover, increased noise levels can result in regulatory violations in areas with noise pollution ordinances. Early detection of increased exhaust noise facilitates timely intervention and repair, preventing further system deterioration and potential legal ramifications.
In summary, amplified exhaust noise directly correlates with a malfunctioning or damaged muffler. Recognizing and addressing this symptom promptly is vital for maintaining vehicle performance, adhering to noise regulations, and avoiding costly repairs down the line. The presence of increased exhaust noise should prompt a thorough inspection of the muffler and associated exhaust components to identify the underlying cause and implement appropriate remedial action.
2. Visible rust
Visible rust on a vehicle’s exhaust silencing component represents a critical indicator of degradation, frequently correlating with internal damage and reduced functionality. Its presence necessitates immediate investigation to prevent further system compromise.
- Material Degradation
Exhaust systems are typically constructed from steel, which is susceptible to corrosion when exposed to moisture, road salts, and high temperatures. Visible rust indicates the breakdown of the metal’s structural integrity, reducing its capacity to contain exhaust gases and dampen noise. For example, heavy surface rust can weaken the muffler casing, leading to leaks and altered exhaust sounds.
- Internal Component Exposure
The outer casing of the muffler protects internal baffles and chambers responsible for sound attenuation. When visible rust progresses to the point of perforation, these internal components become exposed to the elements, accelerating their degradation. This results in decreased sound dampening efficiency and increased noise levels.
- Leak Development
Rust weakens the metal, increasing the likelihood of exhaust leaks. Leaks not only compromise noise reduction but also pose safety hazards due to the potential for carbon monoxide intrusion into the vehicle cabin. An example is a rust-induced hole in the muffler, allowing exhaust gases to escape before being adequately silenced.
- Structural Weakening
Extensive rust can compromise the structural integrity of the muffler, potentially leading to detachment from its mounting points. A detached or partially detached muffler can create a rattling noise and pose a safety hazard, particularly at high speeds. Moreover, the additional strain on the remaining exhaust system components can accelerate their wear.
In summary, the presence of visible rust on the exhaust silencing component is a clear warning sign indicative of its declining health. The facets outlined above collectively demonstrate the various ways in which rust compromises muffler functionality and poses potential safety risks. Prompt detection and repair are essential to maintain vehicle performance, safety, and compliance with noise regulations.
3. Exhaust Leaks
Exhaust leaks, especially those originating from or near the exhaust silencing component, represent a critical indicator of its compromised state. The presence of unintended exhaust gas escape signifies a breach in the system’s integrity, directly impacting performance and safety. This connection is essential in determining the overall health and functionality of the vehicle’s exhaust system.
- Compromised Noise Reduction
Exhaust leaks bypass the designed silencing mechanisms within the muffler. Gases escaping prematurely circumvent the internal baffles and chambers intended to attenuate noise, resulting in a noticeable increase in exhaust volume. For example, a small hole in the muffler body can produce a hissing or sputtering sound, while a larger breach can manifest as a louder, more aggressive exhaust note.
- Reduced Engine Efficiency
Exhaust leaks can disrupt the delicate balance of backpressure within the exhaust system. Altered backpressure can negatively impact engine performance, leading to reduced fuel efficiency and potentially affecting engine power output. An exhaust leak near the muffler could allow gases to escape prematurely, causing the engine to work harder to maintain optimal performance.
- Safety Hazards: Carbon Monoxide Intrusion
Exhaust gases contain carbon monoxide (CO), a colorless, odorless, and highly toxic gas. Exhaust leaks, particularly those located near the passenger cabin, can allow CO to enter the vehicle, posing a significant health risk to occupants. Even small leaks, over time, can lead to dangerous CO accumulation inside the vehicle. This is particularly concerning in situations where the vehicle is idling or operating in enclosed spaces.
- Emissions Violations
Exhaust leaks can result in increased emissions of pollutants into the atmosphere. A compromised muffler can release uncombusted hydrocarbons and other harmful gases, contributing to air pollution and potentially violating emissions regulations. Vehicles with exhaust leaks may fail emissions testing, resulting in fines or the inability to legally operate the vehicle.
These facets collectively highlight the significant impact of exhaust leaks on vehicle performance, safety, and environmental responsibility. Identifying and addressing exhaust leaks originating from the vicinity of the exhaust silencing component is crucial in assessing its condition and ensuring the continued proper operation of the vehicle’s exhaust system. The presence of exhaust leaks should prompt a comprehensive inspection and necessary repairs to mitigate these potential hazards.
4. Rattling sound
A rattling sound emanating from the undercarriage of a vehicle often serves as a salient indicator of a failing exhaust silencing component. The presence of such auditory anomalies frequently suggests internal disintegration within the muffler or the degradation of its supporting structures. The significance of this sound lies in its ability to pinpoint potential issues that might otherwise remain undetected during routine visual inspections. A rattling noise signifies that components within the muffler have become detached or that the muffler itself has loosened, compromising its intended function. For example, internal baffles, designed to dampen sound waves, can break free due to corrosion or mechanical stress, resulting in a distinct rattling sound, particularly during engine operation or vibration. Similarly, deteriorated muffler hangers or mounting brackets can cause the entire muffler assembly to rattle against the vehicle’s chassis.
The practical application of recognizing a rattling sound involves a systematic diagnostic approach. While a visual inspection may reveal obvious damage, the rattling sound provides an audible clue pointing toward internal issues that are not immediately apparent. Automotive technicians often use this auditory cue as a starting point for a more thorough examination of the exhaust system. Employing a stethoscope or similar diagnostic tool can further isolate the source of the rattling, helping to differentiate between internal muffler damage and loose external components. Addressing the source of the rattling promptly is vital, as continued operation with a damaged muffler can lead to further degradation of the exhaust system, potentially affecting engine performance and fuel efficiency. Moreover, a detached or loosely mounted muffler can pose a safety hazard, especially if it were to completely separate from the vehicle while in motion.
In summary, the presence of a rattling sound associated with the exhaust silencing component represents a critical diagnostic indicator. This auditory signal often points to internal or external structural damage that compromises the muffler’s performance and structural integrity. Promptly investigating and addressing the source of the rattling sound is essential to maintain vehicle safety, optimize performance, and prevent further system degradation. The ability to correlate this sound with potential muffler issues underscores the importance of comprehensive vehicle maintenance practices and proactive diagnostic procedures.
5. Reduced MPG
Decreased fuel efficiency, commonly referred to as reduced miles per gallon (MPG), can serve as an indirect indicator of a malfunctioning exhaust silencing component. While not a direct symptom like increased exhaust noise, a noticeable drop in MPG can signify underlying issues within the exhaust system, prompting further investigation into the muffler’s condition. This connection arises from the intricate relationship between exhaust system function and engine performance. A properly functioning muffler facilitates efficient exhaust gas flow, which, in turn, contributes to optimal engine combustion and fuel economy. If the muffler is compromised, such as through internal blockage or external leaks, this process can be disrupted.
One possible mechanism linking a failing muffler to reduced MPG is increased backpressure. A clogged or partially obstructed muffler impedes the free flow of exhaust gases, creating excessive backpressure within the engine. This forces the engine to work harder to expel exhaust, consuming more fuel in the process. For instance, a muffler with collapsed internal baffles can significantly restrict exhaust flow, leading to a measurable decrease in MPG. Another scenario involves exhaust leaks near the muffler. These leaks can disrupt the designed backpressure balance, potentially altering air-fuel ratios and combustion efficiency, thus impacting fuel economy. Real-world examples include vehicles with severely rusted mufflers exhibiting both increased exhaust noise and a simultaneous decrease in MPG, highlighting the interconnectedness of these symptoms.
In conclusion, while reduced MPG alone is not definitive proof of a bad muffler, its presence in conjunction with other symptoms such as increased exhaust noise, visible rust, or rattling sounds should raise suspicion. Recognizing this connection allows for a more comprehensive diagnostic approach, potentially identifying muffler-related issues before they escalate into more significant problems. Regular monitoring of fuel efficiency, coupled with awareness of other potential indicators, contributes to proactive vehicle maintenance and helps ensure optimal engine performance and fuel economy.
6. Unusual odors
Unusual odors emanating from a vehicle’s exhaust system can be indicative of a compromised exhaust silencing component. These atypical scents, diverging from the typical exhaust aroma, often signal incomplete combustion or the release of substances that would normally be neutralized by a functioning catalytic converter, an auxiliary component of the exhaust system typically positioned upstream of the muffler. A failing muffler, particularly one with internal corrosion or structural damage, can disrupt exhaust gas flow, negatively impacting catalytic converter efficiency. The correlation between unusual odors and muffler condition stems from the muffler’s role in maintaining proper backpressure and exhaust gas temperature, factors essential for optimal catalytic converter operation. For example, a heavily rusted muffler with internal leaks may allow unburned hydrocarbons to escape, resulting in a distinct gasoline-like smell. Alternatively, a malfunctioning muffler could lead to excessive engine backpressure, causing incomplete combustion and the release of sulfurous compounds, producing a rotten egg-like odor.
The practical significance of recognizing unusual exhaust odors lies in their diagnostic value. While a visual inspection might reveal external damage, the detection of atypical scents provides insight into the internal functionality of the exhaust system and its impact on the catalytic converter. The presence of these odors often necessitates a more comprehensive evaluation, including checks for exhaust leaks, catalytic converter performance, and muffler integrity. Automotive technicians utilize specialized diagnostic tools, such as exhaust gas analyzers, to identify the specific compounds responsible for the unusual odors and pinpoint the underlying cause. Prompt detection of these issues can prevent further damage to the catalytic converter and other exhaust system components, potentially avoiding costly repairs. Moreover, addressing these issues contributes to environmental responsibility by ensuring that the vehicle meets emissions standards.
In summary, unusual exhaust odors represent a valuable, albeit indirect, indicator of a potentially faulty exhaust silencing component. These atypical scents often reflect underlying issues with exhaust gas flow, catalytic converter performance, and combustion efficiency, all of which can be influenced by muffler condition. Recognizing and responding to these olfactory cues allows for proactive vehicle maintenance, preventing further system degradation and promoting environmental stewardship.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding the identification of a compromised exhaust silencing component, providing detailed explanations to facilitate accurate diagnosis.
Question 1: What constitutes an ‘unusual’ exhaust odor, and why is it significant?
An ‘unusual’ exhaust odor refers to any scent diverging from the typical exhaust gas smell. This includes, but is not limited to, the scent of gasoline, rotten eggs (sulfur), or a burning smell. Such odors often indicate incomplete combustion or catalytic converter malfunction, potentially linked to muffler-related backpressure issues or exhaust leaks. Identification of these odors warrants immediate inspection.
Question 2: Can a malfunctioning muffler directly impact engine performance?
Yes, a malfunctioning muffler can directly impact engine performance. Restrictions or leaks in the muffler can alter exhaust backpressure, affecting engine efficiency, fuel economy, and potentially reducing horsepower. Significant performance degradation necessitates thorough exhaust system evaluation.
Question 3: How does rust specifically compromise a muffler’s functionality?
Rust compromises the structural integrity of the muffler, leading to exhaust leaks, internal component degradation, and altered sound attenuation. Perforation due to rust exposes internal baffles, reducing their effectiveness and potentially causing rattling noises. Extensive rust can weaken mounting points, leading to detachment and safety hazards.
Question 4: Is increased exhaust noise always indicative of a faulty muffler?
While increased exhaust noise often points to a faulty muffler, other exhaust system components, such as damaged exhaust pipes or a failing catalytic converter, can also contribute. A comprehensive inspection is essential to isolate the specific source of the noise.
Question 5: How often should a vehicle’s muffler be inspected?
A visual inspection of the muffler should be conducted during routine vehicle maintenance, typically every 12 months or 12,000 miles. More frequent inspections may be necessary in regions with harsh climates or excessive road salt usage.
Question 6: What are the potential safety hazards associated with a damaged muffler?
Damaged mufflers can pose several safety hazards, including carbon monoxide (CO) intrusion into the vehicle cabin, increased noise pollution, and the risk of muffler detachment, potentially causing damage to other vehicles or road hazards. Prompt repair is crucial for mitigating these risks.
The indicators and diagnostic methods outlined underscore the importance of regular muffler inspections and prompt repairs to ensure optimal vehicle performance, safety, and environmental compliance.
The subsequent section will address potential solutions and repair strategies for compromised mufflers, offering options for restoring vehicle performance and minimizing environmental impact.
Determining Muffler Integrity
This exploration has outlined critical indicators to determine the operational status of an exhaust silencing component. Identifying increased noise, visible corrosion, exhaust leaks, unusual sounds or odors, and monitoring fuel efficiency are essential steps in assessing muffler health. Recognizing these signs facilitates timely intervention, preventing further system degradation and potential safety risks.
Vigilance in observing these indicators is paramount. Neglecting muffler maintenance can lead to regulatory non-compliance, environmental impact, and compromised vehicle performance. Prioritizing regular inspections and addressing identified issues promptly ensures continued vehicle safety, efficiency, and adherence to environmental standards.