The sound output from the receiver, the small speaker located at the top of an iPhone’s screen used during phone calls, can sometimes be diminished or unclear. This issue manifests as reduced volume or a lack of clarity, making conversations difficult to understand. As an illustration, a user might find it challenging to hear the other party, even when the volume is set to maximum during a phone call.
Consistent and clear audio output from this component is critical for effective communication. A functioning receiver ensures that users can understand conversations, which impacts productivity and convenience. Historically, issues with this particular hardware component have been a recurring problem, requiring troubleshooting steps or hardware repair over time.
The following sections will explore potential causes for diminished sound quality, provide practical troubleshooting steps that can be employed, and outline when professional repair services may be required to resolve the issue.
Addressing Diminished iPhone Receiver Audio
The following guidelines offer practical steps to diagnose and potentially resolve issues related to reduced sound output from the iPhone’s receiver.
Tip 1: Assess External Obstructions: Examine the receiver opening for any visible blockages. Lint, dust, or debris can accumulate and physically impede sound transmission. Use a soft, dry brush or compressed air to carefully clear any obstructions.
Tip 2: Evaluate Volume Settings: While on a phone call, verify the in-call volume is set to the maximum level. Adjust the volume using the volume buttons on the side of the device during an active call.
Tip 3: Clean the Receiver with Caution: If a dry brush is insufficient, use a slightly damp, lint-free cloth. Ensure minimal moisture is applied and avoid inserting anything into the receiver opening.
Tip 4: Disable Noise Cancellation Features: In some cases, software-based noise cancellation can inadvertently reduce the receiver volume. Temporarily disable noise cancellation features in the iPhone’s settings to assess if this improves audio clarity.
Tip 5: Restart the iPhone: A simple restart can resolve temporary software glitches that may be affecting audio output. Power the iPhone off completely, wait a few seconds, and then power it back on.
Tip 6: Update iOS Software: Ensure the iPhone is running the latest version of iOS. Software updates often include bug fixes that can address audio-related issues. Navigate to Settings > General > Software Update to check for available updates.
Tip 7: Test with Different Callers: Determine if the issue is consistent across all calls or isolated to specific callers. A problem with the other party’s microphone or network connection could be mistaken for a receiver malfunction.
These steps provide a methodical approach to addressing diminished sound from the receiver. Following these guidelines may restore normal audio functionality and improve call quality.
If these steps do not resolve the issue, a hardware fault may be present, necessitating professional repair or replacement of the affected component.
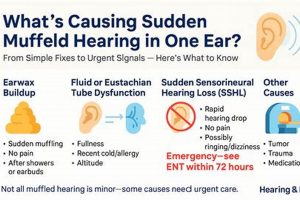
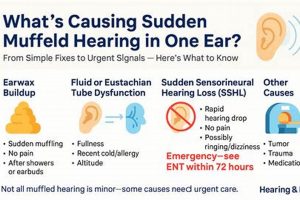
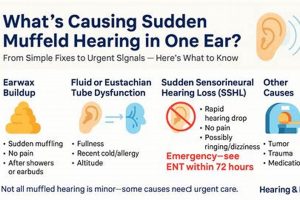
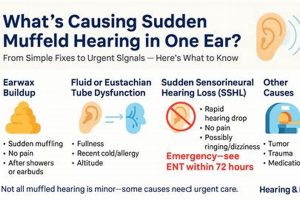
1. Obstruction
Physical obstruction of the iPhone receiver, often referred to as the earpiece speaker, is a common cause of diminished sound quality during calls. The receiver’s small opening is vulnerable to blockage by various materials, directly impacting the volume and clarity of sound transmission to the user.
- Accumulation of Debris
Lint, dust, and earwax can gradually accumulate within the receiver opening. This build-up physically impedes sound waves, reducing the perceived volume and clarity. The degree of impact correlates with the amount and density of the accumulated material. For instance, a layer of compacted lint can significantly dampen the sound, making it difficult to hear the other party during a call.
- Protective Film Misalignment
Screen protectors, if not precisely aligned during application, can partially cover the receiver opening. Even a slight overlap can muffle the sound. Some protectors use lower quality adhesive that can seep and cover the earpiece, further compounding the problem. This misalignment can cause sound distortion and reduction and is a common oversight when users experience audio issues after applying a new screen protector.
- Foreign Objects
Small particles, such as sand or metal shavings, can enter the receiver opening. These objects can vibrate within the speaker chamber, creating extraneous noise or further obstructing sound waves. The presence of a foreign object can cause a noticeable degradation in sound quality and, in some cases, damage the speaker itself.
- Protective Case Interference
Certain protective cases may inadvertently cover or partially obstruct the receiver. Some case designs are not precisely engineered to account for the receiver’s placement, resulting in muffling. The case material also plays a role. Thick, dense materials are more likely to reduce sound volume, causing audio distortion. Cases with poorly designed openings around the receiver can significantly impact call clarity.
These various forms of physical obstruction highlight the importance of regularly inspecting and maintaining the iPhone receiver. Addressing these potential blockages can often restore normal audio functionality, leading to improved call clarity and overall user experience. Failure to address these obstructions can lead to user frustration and misdiagnosis of a more complex hardware issue.
2. Software
The iPhone’s operating system, iOS, plays a critical role in managing audio output, including the receiver. Software glitches or configuration errors can manifest as reduced volume or distorted sound emanating from the receiver, mimicking the symptoms of hardware malfunction. For example, an outdated or corrupted audio driver, though not a discrete driver as found in desktop operating systems, can lead to incorrect audio processing, causing muffled sound. Similarly, a bug introduced through a software update could inadvertently lower the maximum volume level for the receiver, impacting call clarity. In such scenarios, the physical speaker itself may be fully functional, but the software layer imposes a limitation on performance.
Furthermore, specific software features designed to enhance audio, such as noise cancellation or equalizer settings, can paradoxically contribute to diminished sound quality if improperly configured. If noise cancellation aggressively filters ambient sound, it may inadvertently attenuate the caller’s voice, resulting in a muffled effect. Similarly, incorrect equalizer settings might emphasize certain frequencies while suppressing others, impacting overall audio balance and clarity. Diagnostic tools and software updates released by Apple often aim to rectify these software-related audio issues, demonstrating the practical significance of the software component in maintaining optimal receiver performance. For instance, an iOS update might specifically address a known issue where call volume is unexpectedly low on certain iPhone models.
In summary, software directly influences the functionality of the iPhone receiver, and software-related problems are a potential cause of muffled sound output. Recognizing this connection is crucial for effective troubleshooting, often resolving audio issues through software updates, configuration adjustments, or system resets, without resorting to hardware repairs. Identifying and addressing such issues are challenges, as it requires differentiating between physical damage and software glitches that affect sound output and volume.
3. Hardware
The physical components of the iPhone, specifically the receiver (ear speaker), are fundamental to the delivery of clear audio during phone calls. Hardware failures, either due to manufacturing defects, physical damage, or component degradation over time, can directly manifest as the issue described by “iPhone muffled ear speaker”. For example, a detached or partially damaged speaker coil within the receiver will significantly reduce audio output, leading to a perception of muffled or inaudible sound. Similarly, a cracked speaker diaphragm will distort the sound waves, resulting in unclear audio quality. The direct causal relationship between the physical state of the speaker and its audio performance underscores the importance of the hardware in achieving optimal call clarity.
Physical damage, such as exposure to liquids or impact from drops, frequently precipitates hardware failures. Liquid intrusion can corrode the delicate internal components of the speaker, disrupting electrical conductivity and reducing sound output. A drop, even from a moderate height, can dislodge the speaker from its mounting or fracture internal elements. The practical implication of these vulnerabilities is that the physical integrity of the iPhone directly correlates with the reliability of its receiver. Routine handling and environmental conditions, therefore, play a significant role in the long-term functionality of the speaker. Regular inspection and preventative measures, such as the use of protective cases, can mitigate these risks and preserve the speaker’s performance. Repairing or replacing damaged hardware may solve the issues of muffled ear speaker.
In summary, the physical state of the iPhone’s receiver is a critical determinant of audio quality during phone calls. Hardware malfunctions, whether stemming from manufacturing defects or physical damage, can directly result in the “iPhone muffled ear speaker” symptom. Understanding the hardware’s role and potential vulnerabilities is vital for effective troubleshooting and for implementing preventative measures that prolong the speaker’s lifespan and maintain clear audio communication, and thus, professional hardware repair becomes the solution.
4. Connectivity
Cellular network connectivity significantly impacts the perceived audio quality transmitted through an iPhone’s receiver. Even if the physical speaker is fully functional, weak or unstable network connections can introduce audio distortions that manifest as reduced volume or unclear sound. This impact is often misinterpreted as a problem within the iPhone itself, but rather originates from the quality of the network signal.
- Signal Strength and Stability
A weak cellular signal results in compressed audio codecs to conserve bandwidth. These codecs prioritize data transmission over audio fidelity, often leading to reduced sound quality, dropped words, or a “muffled” effect. In areas with poor coverage, the iPhone continually adjusts the audio compression, causing fluctuations in volume and clarity. For instance, a user moving between areas with differing signal strengths may experience inconsistent receiver audio, despite no changes to the device’s settings or environment. The signal strength plays a vital role in ensuring clear, crisp, sound during a call.
- Network Congestion
Even with adequate signal strength, network congestion can degrade audio quality. During peak usage times, the network struggles to allocate sufficient bandwidth to each user, resulting in audio packet loss and delayed transmission. This manifests as choppy or distorted sound, effectively reducing the perceived volume and clarity. An example of this phenomenon is a call made during rush hour in a densely populated area, where the high volume of simultaneous connections strains the network infrastructure. This strain can contribute to diminished sound fidelity.
- VoLTE and Codec Compatibility
Voice over LTE (VoLTE) technology relies on specific audio codecs to transmit voice data efficiently. Incompatibilities between the codecs supported by the iPhone and those used by the cellular network can lead to audio degradation. For example, if the iPhone attempts to use a higher-quality codec that the network cannot support, it may fallback to a lower-quality codec that compromises audio clarity. Such codec mismatch issues contribute to the perception of muffled sound. This creates an indirect relationship between the device and carrier connection.
- Interference from Other Devices
External electronic devices operating on similar frequencies can interfere with cellular signals, disrupting the transmission of voice data. Microwaves, Bluetooth devices, and even poorly shielded electronic equipment can introduce noise that degrades the audio signal. This interference can manifest as static or distortion, which reduces the perceived clarity and volume of the audio from the receiver. The closer and stronger the devices, the more affect they have on the audio transmission.
In conclusion, cellular network connectivity profoundly influences the audio quality delivered through the iPhone receiver. Factors such as signal strength, network congestion, codec compatibility, and external interference can all contribute to the “iPhone muffled ear speaker” symptom. Addressing these connectivity-related factors is essential for troubleshooting audio issues and ensuring clear, reliable voice communication.
5. Settings
The configuration of settings on an iPhone exerts a direct influence on the audio output from the receiver. Incorrect or suboptimal settings can lead to diminished sound quality, resulting in the perception of a “muffled” ear speaker, regardless of the physical condition of the device’s hardware. Audio accessibility features, volume limits, and even call audio routing options all contribute to the overall audio experience. As an example, a user inadvertently enabling the “Phone Noise Cancellation” feature in a noisy environment might experience a reduction in the caller’s voice volume, leading to the erroneous conclusion that the speaker is malfunctioning. The precise configuration of the iOS settings determines the sound output, directly affecting the receiver’s function and the user’s auditory experience during a phone call.
Further analysis reveals that accessibility settings intended to improve hearing for individuals with auditory impairments can inadvertently reduce sound quality for users with normal hearing. The “Mono Audio” setting, designed to combine stereo channels into a single channel for users with hearing in only one ear, can create a flattened and less dynamic sound profile, which is perceived as muffled. Moreover, volume limits, designed to protect hearing by restricting the maximum audio output, can be set at excessively low levels, resulting in inadequate volume for calls in moderate or noisy environments. Another setting, “audio routing”, if configured to external headphones or bluetooth, will affect the call. The iPhone will attempt to connect to configured device rather than the ear speaker. Thus, the manipulation of accessibility settings and volume limits may improve individual hearing abilities, but it may harm overall auditory communication.
In summary, iPhone settings play a critical role in shaping the audio output from the receiver. While some settings enhance accessibility or protect hearing, incorrect configurations can lead to the perception of a “muffled” ear speaker. Correcting these settings often resolves audio issues without requiring hardware interventions. The iOS settings allow users to tailor call-based sound output, but it also contributes to muffled sounds during calls. As such, the role of audio settings must not be overlooked.
6. Environment
The surrounding environment profoundly impacts the perception of sound emanating from an iPhone’s receiver. Elevated ambient noise levels directly mask the relatively quiet output of the ear speaker, making it challenging to discern clear audio, thus contributing to the sensation of a muffled sound. For instance, attempting to conduct a phone conversation on a busy city street or in a crowded public transportation setting introduces competing auditory stimuli that effectively drown out the caller’s voice. The effect intensifies as the environment’s noise floor increases, requiring the user to strain to hear and potentially misinterpreting the diminished clarity as a hardware or software malfunction within the device. Consequently, the ambient sound conditions directly affect how one interprets the speaker performance.
Furthermore, specific environmental factors, such as acoustic properties of a confined space, can exacerbate the issue. Echoes and reverberations within a small room or enclosed vehicle can distort the sound, making it more difficult to understand speech. The reflections of sound waves create interference patterns that muddy the original audio signal, effectively reducing clarity. The listener thus perceives a muffled sound, even if the iPhone’s receiver is functioning optimally. Conversely, open outdoor environments tend to minimize these acoustic distortions, allowing for clearer sound transmission, provided that ambient noise levels are manageable.
In conclusion, the surrounding environment is an indispensable factor in the perception of audio quality from an iPhone’s receiver. High ambient noise levels and unfavorable acoustic conditions can mask or distort the sound, leading to the sensation of a muffled ear speaker. Understanding this environmental influence is crucial for accurate troubleshooting of perceived audio issues and for adopting practical strategies, such as seeking quieter locations or using noise-canceling headphones, to mitigate the negative effects of the surrounding environment and enhance call clarity.
7. Interference
Electromagnetic interference presents a potential, though often overlooked, factor affecting audio quality in iPhones. This interference, originating from various sources, can disrupt the intended signal path, leading to a perceived reduction in volume or clarity from the earpiece speaker.
- Radio Frequency (RF) Interference
External RF sources, such as nearby radio transmitters, cellular towers, or even poorly shielded electronic devices, can introduce unwanted signals into the iPhone’s audio circuitry. These signals manifest as static, buzzing, or a general degradation of sound quality, effectively masking the intended audio output from the earpiece. The proximity of the iPhone to these RF sources determines the severity of the interference. For instance, operating an iPhone near a high-powered radio transmitter could significantly degrade audio clarity during a phone call.
- Bluetooth Device Proximity
While Bluetooth technology is ubiquitous, the close proximity of other Bluetooth devices can interfere with the iPhone’s internal audio processing. The Bluetooth signal, particularly during active data transmission, generates electromagnetic radiation that can induce noise in the audio circuitry. This noise translates to a reduction in perceived volume or clarity from the earpiece speaker. The severity of this effect depends on the strength of the Bluetooth signal and the distance between the iPhone and the interfering device.
- Internal Component Shielding
The effectiveness of the iPhone’s internal shielding plays a critical role in mitigating interference. Inadequate or damaged shielding allows external electromagnetic radiation to penetrate the device’s circuitry, disrupting the audio signal. Furthermore, internal components, such as the logic board or power supply, can generate their own electromagnetic fields, which, if not properly contained, can interfere with the audio pathway. Consequently, a manufacturing defect or physical damage compromising the shielding integrity can lead to persistent audio degradation and muffled earpiece output.
- Power Supply Noise
The iPhone’s power supply, if generating excessive electrical noise, can introduce audible artifacts into the audio signal. This noise, often characterized as a humming or buzzing sound, masks the intended audio output from the earpiece, resulting in a perception of reduced volume or clarity. Power supply noise can originate from faulty components or from external factors, such as fluctuations in the power grid during charging. A malfunctioning charger, for instance, may introduce noise into the iPhone’s power supply, which, in turn, degrades audio quality during calls or audio playback.
The various forms of electromagnetic interference highlight the susceptibility of iPhone audio quality to external and internal factors. Addressing potential sources of interference, such as minimizing proximity to RF transmitters or ensuring adequate internal shielding, can mitigate these effects and improve the user’s auditory experience during phone calls and audio playback. Understanding the role of interference provides a comprehensive approach to resolving issues where “iPhone muffled ear speaker” becomes a matter of concern.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries concerning diminished audio output from an iPhone’s receiver, commonly described as a “muffled ear speaker”. The goal is to provide clear and factual information to aid in understanding and resolving the issue.
Question 1: What are the primary causes of the “iPhone muffled ear speaker” phenomenon?
The phenomenon arises from a combination of factors, including physical obstruction of the receiver by debris, software glitches affecting audio processing, hardware failures within the speaker itself, connectivity issues with the cellular network, environmental noise masking the audio, incorrect device settings, and electromagnetic interference. The relative contribution of each factor varies depending on the specific circumstances.
Question 2: Can the “iPhone muffled ear speaker” issue be resolved without professional assistance?
In many cases, yes. Basic troubleshooting steps, such as cleaning the receiver opening, adjusting volume settings, restarting the device, and updating iOS software, can often resolve the issue. However, persistent or severe audio degradation may necessitate professional repair.
Question 3: How frequently should the iPhone receiver be cleaned to prevent muffled sound?
The frequency of cleaning depends on individual usage patterns and environmental conditions. In general, a visual inspection of the receiver opening should be performed weekly, with cleaning performed as needed to remove any visible debris. A soft, dry brush is typically sufficient for routine maintenance.
Question 4: Does the type of protective case used with an iPhone affect receiver audio quality?
Yes. Cases with poorly designed openings around the receiver can obstruct or muffle the sound. Thick, dense materials are more likely to reduce audio volume. Selecting a case designed with precise cutouts for the receiver minimizes the potential for audio degradation.
Question 5: Are certain iPhone models more prone to the “muffled ear speaker” issue than others?
Anecdotal evidence suggests that certain models may exhibit a higher incidence of receiver-related issues. However, a definitive correlation is difficult to establish due to variations in usage patterns, environmental conditions, and manufacturing tolerances. Software-related issues are more likely to be shared across models running the same version of iOS.
Question 6: What are the potential long-term consequences of neglecting a “muffled ear speaker” issue?
Neglecting the issue may lead to increased frustration and difficulty in conducting phone conversations. In cases where the underlying cause is physical damage or component failure, the condition may worsen over time, potentially requiring more extensive and costly repairs. Furthermore, straining to hear can cause unnecessary auditory fatigue.
These FAQs provide a foundational understanding of the “iPhone muffled ear speaker” issue. Understanding the multifaceted nature of the problem aids in more effective troubleshooting and resolution.
The next section delves into advanced troubleshooting techniques and when professional repair becomes necessary.
Conclusion
The preceding analysis provides a comprehensive overview of the “iphone muffled ear speaker” issue. From physical obstructions and software anomalies to hardware vulnerabilities, network connectivity challenges, environmental factors, and electromagnetic interference, multiple variables contribute to diminished audio quality during iPhone calls. Effective resolution requires a systematic approach, encompassing both basic troubleshooting and, when necessary, professional intervention. Understanding these multifaceted aspects of the issue leads to more accurate diagnoses and appropriate remedial action.
The continued reliance on mobile communication underscores the importance of addressing and preventing audio degradation. Consistent maintenance, prudent device handling, and awareness of environmental influences contribute to prolonged device performance. The pursuit of technological advancements that mitigate interference and enhance audio clarity remains crucial for the sustained utility of mobile communication devices. Prioritizing audio quality is paramount, ensuring effective and reliable communication capabilities for all users.