Medications administered directly into the auditory canal are frequently employed to address conditions that cause a sensation of reduced sound clarity. These solutions can target a variety of underlying issues, ranging from wax accumulation to infections. For example, a specific formulation may soften impacted cerumen, facilitating its removal and restoring normal hearing perception.
The strategic application of these liquid medications offers significant advantages in managing certain auditory ailments. Their localized delivery minimizes systemic exposure, potentially reducing the risk of widespread side effects. Furthermore, historical use demonstrates their efficacy in resolving temporary hearing impairments caused by blockages or inflammatory processes, contributing to improved auditory health and quality of life.
The subsequent sections will delve into the common causes of diminished auditory acuity treatable with topical ear preparations, the different types of formulations available, proper administration techniques, and potential risks and contraindications associated with their use.
Guidance for Addressing Diminished Auditory Clarity
The following recommendations are intended to provide insights into the effective use of topical ear medications for the management of subjective auditory reduction.
Tip 1: Consult a Medical Professional: Prior to initiating any treatment, a thorough examination by an otolaryngologist or qualified healthcare provider is crucial. Self-diagnosis can be inaccurate, and the sensation of reduced sound clarity may stem from various underlying causes requiring specific interventions.
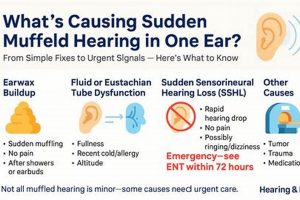
Tip 2: Identify the Underlying Cause: Determine the etiology of the auditory reduction. Common causes include cerumen impaction, otitis externa, or Eustachian tube dysfunction. The appropriate treatment will vary depending on the diagnosed condition.
Tip 3: Select Appropriate Formulations: Choose formulations specifically designed to address the identified cause. For instance, ceruminolytic agents are indicated for wax buildup, while antibiotic or antifungal solutions are appropriate for infections. Ensure the medication is prescribed or recommended by a healthcare professional.
Tip 4: Adhere to Dosage Instructions: Strictly follow the prescribed dosage and administration frequency. Overuse or misuse may lead to adverse effects or reduced efficacy. Pay close attention to any specific instructions provided by the physician or pharmacist.
Tip 5: Employ Proper Administration Technique: Correct administration is essential for optimal results. Tilt the head to the side, gently pull the earlobe to straighten the ear canal, and instill the designated number of drops. Maintain the tilted position for several minutes to allow the medication to reach the affected area.
Tip 6: Monitor for Adverse Reactions: Observe for any signs of adverse reactions, such as irritation, pain, or allergic reactions. Discontinue use and consult a healthcare professional if any concerning symptoms arise.
Tip 7: Maintain Aseptic Conditions: Prevent contamination of the medication applicator. Avoid touching the dropper tip to the ear or any other surface. Use a fresh applicator for each ear, if applicable.
Consistent adherence to these guidelines promotes safe and effective utilization of topical ear medications, leading to improved auditory perception and overall ear health.
The subsequent discussion will address potential complications and preventative measures related to the management of impaired auditory acuity.
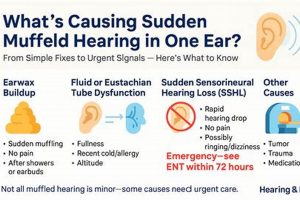
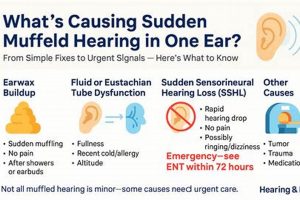
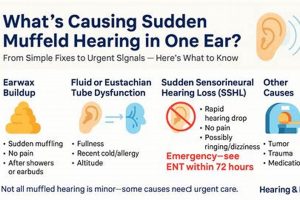
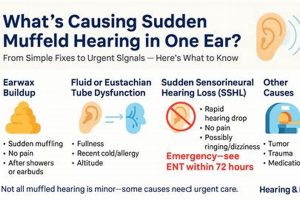
1. Cause Identification
The efficacy of topical ear medications in resolving diminished auditory clarity is intrinsically linked to accurate cause identification. These medications are formulated to address specific etiologies, and their inappropriate use can be ineffective or potentially harmful. Therefore, a precise diagnosis is a critical prerequisite for successful therapeutic intervention.
- Cerumen Impaction
Accumulation of earwax is a common cause of reduced sound transmission. Ceruminolytic agents, designed to soften and dissolve wax, are effective in these cases. However, their use is contraindicated if a perforated tympanic membrane is present, highlighting the need for examination prior to administration.
- Otitis Externa (Swimmer’s Ear)
Infections of the external auditory canal often result in inflammation and fluid accumulation, leading to impaired hearing. Antibiotic or antifungal formulations, tailored to the specific pathogen identified, are indicated. Viral infections, however, would not respond to these treatments, underscoring the importance of distinguishing between bacterial, fungal, and viral etiologies.
- Eustachian Tube Dysfunction
Impaired Eustachian tube function can create pressure imbalances in the middle ear, affecting sound conduction. While topical medications are not a primary treatment for this condition, they may be used to address secondary infections that develop. Decongestants and other systemic medications are often more appropriate for the underlying dysfunction.
- Foreign Body Obstruction
The presence of a foreign object within the ear canal can physically block sound waves from reaching the eardrum. In such instances, attempting to use topical medications without first removing the object is ineffective and potentially dangerous. Manual removal by a qualified healthcare provider is the necessary initial step.
In summary, the successful application of topical ear medications for diminished auditory clarity relies heavily on accurate cause identification. Failing to differentiate between conditions like cerumen impaction, infection, Eustachian tube dysfunction, and foreign body obstruction can lead to inappropriate treatment choices and suboptimal outcomes, emphasizing the need for professional evaluation.
2. Medication Type
The selection of an appropriate medication type is paramount in effectively addressing diminished auditory clarity through topical ear administration. The precise nature of the underlying cause dictates the specific pharmacological properties required to restore normal hearing perception. Misdiagnosis and subsequent selection of an inappropriate medication can lead to treatment failure or, in some cases, exacerbate the condition.
- Ceruminolytics
These agents are designed to soften and facilitate the removal of impacted cerumen, a common cause of diminished auditory acuity. Common examples include carbamide peroxide and docusate sodium. Their mechanism of action involves emulsifying the wax, thereby enabling its easier extraction. In cases where a tympanic membrane perforation is suspected or confirmed, ceruminolytics are contraindicated due to the risk of ototoxicity.
- Antibiotics
Topical antibiotic formulations are indicated for the treatment of bacterial infections of the external auditory canal, often manifested as otitis externa. Common antibiotics employed include neomycin, polymyxin B, and ofloxacin. The selection of a specific antibiotic should be guided by culture and sensitivity testing, when feasible, to ensure efficacy against the causative organism. Prolonged use of topical antibiotics can lead to the development of resistant bacterial strains, necessitating judicious application.
- Antifungals
Fungal infections of the ear canal, known as otomycosis, require the use of antifungal medications. Clotrimazole, miconazole, and tolnaftate are commonly prescribed topical antifungals. Effective treatment necessitates thorough cleansing of the ear canal to remove fungal debris, followed by consistent application of the antifungal medication as directed. Resistance to topical antifungals is less common than with antibiotics, but may occur in immunocompromised individuals.
- Corticosteroids
Topical corticosteroids, such as hydrocortisone, are employed to reduce inflammation and edema associated with various ear conditions, including otitis externa and allergic reactions. They do not directly address infection but can alleviate associated symptoms, such as pain and pruritus. Combination formulations containing both an antibiotic and a corticosteroid are frequently used in cases of suspected bacterial infection with significant inflammation. Prolonged use of topical corticosteroids can lead to skin atrophy and other adverse effects.
The successful resolution of reduced auditory clarity using topical ear medications hinges on the accurate diagnosis of the underlying etiology and the subsequent selection of an appropriate medication type. Understanding the mechanisms of action, indications, and contraindications of each medication class is essential for optimizing treatment outcomes and minimizing the risk of adverse events. Empirical treatment without proper diagnosis is discouraged, and consultation with a qualified healthcare professional is recommended.
3. Administration Technique
The efficacy of topical ear medications in addressing diminished auditory clarity is directly contingent upon the precision of the administration technique. Improper delivery methods can significantly reduce the therapeutic benefit, even when the correct medication has been selected. The objective of proper administration is to ensure that the medication reaches the affected area within the ear canal and remains in contact with the tissue for a sufficient duration to exert its intended effect. For instance, failure to adequately straighten the ear canal during instillation may result in the medication pooling in the outer portion of the canal, preventing it from reaching impacted cerumen or infected tissues deeper within. Similarly, inadequate dosage or premature drainage of the medication compromises its ability to effectively treat the underlying condition.
Specific steps involved in effective administration include proper positioning of the patient’s head to facilitate gravity-assisted flow of the medication into the ear canal. Gentle traction on the pinna, the external part of the ear, can straighten the canal, particularly in adults. Instilling the prescribed number of drops, while avoiding contamination of the dropper tip, is also crucial. Maintaining the tilted head position for several minutes after instillation allows the medication to adequately coat the affected area. Cotton balls are sometimes recommended to prevent leakage, but they must be inserted loosely to avoid absorbing the medication. In cases involving thick or impacted cerumen, pre-treatment with a ceruminolytic agent may be necessary to improve penetration of the subsequent medication.
In conclusion, while appropriate medication selection is vital, the benefits derived from its use are intrinsically linked to meticulous execution of the administration technique. Suboptimal administration reduces the medication’s ability to target and resolve the underlying cause of diminished auditory clarity. Patient education and clear instructions from healthcare providers are essential to ensure consistent and effective application, thereby optimizing treatment outcomes and improving auditory health.
4. Dosage Adherence
The effectiveness of topical ear medications in resolving diminished auditory clarity is critically dependent on strict adherence to prescribed dosage regimens. Insufficient dosage may fail to reach therapeutic concentrations within the ear canal, leading to incomplete resolution of the underlying pathology, whether it be cerumen impaction, infection, or inflammation. Conversely, exceeding the recommended dosage does not necessarily expedite recovery and may increase the risk of adverse effects, such as local irritation or, in rare cases, systemic absorption. Consistent administration, as directed by a healthcare professional, is, therefore, a non-negotiable factor influencing treatment success. For example, a patient prescribed antibiotic ear drops for otitis externa who only applies half the recommended dose may experience persistent infection and the potential for antimicrobial resistance to develop. Dosage adherence represents a pivotal link in the cause-and-effect chain between medication use and improved auditory perception. A clear understanding of the importance of dosage adherence is essential for successful treatment.
Practical applications of this understanding include meticulous reading and comprehension of prescription labels and instructions provided by pharmacists. Patients should utilize measuring devices, such as calibrated droppers, to ensure accurate dosing. Furthermore, healthcare providers should emphasize the importance of adherence during patient consultations and provide strategies for remembering medication schedules. In cases where patients have difficulty administering ear drops themselves, assistance from a caregiver may be necessary. Open communication with healthcare providers regarding any challenges in adhering to the prescribed regimen is crucial for identifying and addressing barriers to treatment success. Moreover, reminding patients about the risks of non-adherence to medical treatments has been shown to improve treatment outcomes.
In summary, dosage adherence is an indispensable component of successful topical ear medication therapy for diminished auditory clarity. Suboptimal adherence can undermine treatment effectiveness and potentially exacerbate underlying conditions. Educating patients about the importance of accurate dosing and providing support to overcome adherence barriers are essential steps in optimizing patient outcomes and promoting responsible medication use. Dosage non-adherence could have negative consequences which emphasizes the need for it.
5. Adverse Reactions
Topical ear medications, while often effective in addressing diminished auditory clarity, carry the potential for adverse reactions. These reactions can range from mild and transient discomfort to more severe complications, necessitating careful consideration prior to and during treatment.
- Local Irritation and Allergic Contact Dermatitis
Inflammation, pruritus, and erythema of the external auditory canal can occur as a result of direct irritation from the medication or as a manifestation of allergic contact dermatitis to one or more components of the formulation. For example, neomycin, a common ingredient in antibiotic ear drops, is a known sensitizer. Discontinuation of the medication and, in some cases, topical corticosteroids may be required to manage these reactions. The presence of such reactions may further occlude the ear canal, exacerbating the sensation of diminished auditory clarity.
- Ototoxicity
Although rare with topical administration, certain medications, particularly aminoglycoside antibiotics, possess the potential for ototoxicity, especially if the tympanic membrane is perforated. Ototoxicity can manifest as tinnitus, vertigo, or sensorineural hearing loss. The risk is increased with prolonged use or high concentrations. Routine monitoring for ototoxic symptoms is advisable in patients receiving these medications, particularly those with known or suspected tympanic membrane perforations.
- Superinfection
Prolonged use of antibiotic or antifungal ear drops can disrupt the normal microbial flora of the ear canal, leading to superinfection with resistant organisms. For example, prolonged antibiotic use can promote the overgrowth of Candida species, resulting in otomycosis. Culture and sensitivity testing are essential for identifying the causative organism and guiding appropriate treatment.
- Tympanic Membrane Perforation
Improper administration of ear drops, particularly in the presence of a pre-existing but undiagnosed tympanic membrane perforation, can introduce medications into the middle ear, potentially causing irritation or infection. Furthermore, certain medications are contraindicated in the presence of a perforation due to the risk of ototoxicity. A thorough otoscopic examination is, therefore, essential prior to initiating treatment with topical ear medications.
Adverse reactions associated with topical ear medications can paradoxically contribute to or worsen the sensation of diminished auditory clarity. Prudent medication selection, proper administration technique, and careful monitoring for adverse effects are crucial for minimizing the risk of these complications and ensuring optimal therapeutic outcomes. Understanding these potential issues is critical for appropriate assessment and management of individuals experiencing muffled hearing.
6. Medical Consultation
The utilization of ear drops for the management of diminished auditory acuity necessitates informed decision-making, typically initiated through a medical consultation. This interaction serves as a critical juncture where the patient’s subjective symptoms are evaluated, a diagnosis is established, and an appropriate treatment plan, which may or may not include topical ear medications, is formulated. The absence of such a consultation can lead to misdiagnosis, inappropriate treatment, and potentially adverse outcomes.
- Diagnostic Accuracy
A medical consultation enables accurate identification of the underlying cause of diminished auditory clarity. An otolaryngologist or qualified healthcare provider employs otoscopic examination and other diagnostic tools to differentiate between cerumen impaction, otitis externa, Eustachian tube dysfunction, and other potential etiologies. This diagnostic precision is essential for selecting the appropriate course of action, as ear drops targeting cerumen impaction are ineffective for treating otitis externa, and vice versa. Failure to obtain a professional diagnosis can result in delayed or ineffective treatment, potentially leading to chronic complications.
- Medication Appropriateness
During a medical consultation, the healthcare provider assesses the suitability of ear drops as a treatment modality, considering the patient’s medical history, current medications, and potential allergies. Certain ear drops may be contraindicated in individuals with specific conditions, such as perforated tympanic membranes or known hypersensitivity to certain ingredients. The consultation ensures that the prescribed ear drops are safe and appropriate for the individual patient, minimizing the risk of adverse reactions or drug interactions. This assessment is particularly crucial given the potential for ototoxicity associated with some topical ear medications.
- Instruction and Guidance
A medical consultation provides an opportunity for the healthcare provider to educate the patient on the proper administration technique for ear drops. Detailed instructions on positioning, dosage, and duration of treatment are conveyed, along with guidance on potential side effects and warning signs to monitor for. Proper administration maximizes the therapeutic benefit of the medication and minimizes the risk of complications. The consultation also allows patients to ask questions and clarify any uncertainties, fostering a better understanding of their treatment plan and promoting adherence.
- Monitoring and Follow-Up
A medical consultation often includes plans for follow-up appointments to monitor the patient’s response to treatment and assess for any adverse effects. These follow-up evaluations allow the healthcare provider to adjust the treatment plan as needed and ensure that the desired therapeutic outcomes are being achieved. In cases where ear drops are ineffective or adverse reactions occur, alternative treatment strategies can be explored. This ongoing monitoring is particularly important for managing chronic or recurrent ear conditions and preventing long-term complications.
The facets discussed underscore the significance of medical consultation in managing diminished auditory acuity and using ear drops effectively. Consulting a medical professional ensures accurate diagnosis, appropriate medication selection, proper administration, and ongoing monitoring. While ear drops offer a valuable treatment option for certain conditions, their safe and effective utilization depends on a comprehensive evaluation and guidance from a qualified healthcare provider. Bypassing medical expertise may compromise treatment efficacy and patient safety.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following questions and answers aim to clarify common concerns and misconceptions regarding the use of topical ear preparations for individuals experiencing a sensation of muffled hearing.
Question 1: What are the primary indications for utilizing topical ear medications to address a sensation of reduced auditory acuity?
Topical ear medications are primarily indicated in cases where diminished auditory clarity is attributable to conditions affecting the external auditory canal, such as cerumen impaction or otitis externa. These medications are designed to soften and remove wax buildup or to combat bacterial or fungal infections within the ear canal.
Question 2: Are over-the-counter ear drops a suitable solution for all instances of diminished auditory clarity?
Over-the-counter ear drops, such as those containing carbamide peroxide for wax removal, may be appropriate for uncomplicated cerumen impaction. However, they are not a substitute for professional medical evaluation. If the cause of the diminished auditory clarity is unclear or if other symptoms, such as pain, drainage, or fever, are present, seeking consultation with a healthcare provider is imperative.
Question 3: What are the potential risks associated with the use of ear drops when a tympanic membrane perforation is present?
The use of certain ear drops, particularly those containing aminoglycoside antibiotics, is contraindicated in the presence of a tympanic membrane perforation due to the risk of ototoxicity. The direct introduction of these medications into the middle ear can damage sensitive structures responsible for hearing and balance, potentially leading to permanent hearing loss or vestibular dysfunction.
Question 4: How can one differentiate between cerumen impaction and otitis externa as the cause of diminished auditory clarity?
Cerumen impaction typically presents with a gradual onset of reduced hearing, a feeling of fullness in the ear, and possibly tinnitus. Otitis externa, on the other hand, is often characterized by ear pain, itching, drainage, and tenderness upon palpation of the tragus. While these symptoms can provide clues, definitive diagnosis requires otoscopic examination by a healthcare professional.
Question 5: What steps should be taken if an adverse reaction, such as skin irritation or allergic reaction, occurs following the use of ear drops?
If an adverse reaction develops following the use of ear drops, the medication should be discontinued immediately. The affected area should be gently cleansed with lukewarm water. Antihistamines or topical corticosteroids may be used to alleviate itching and inflammation. If symptoms persist or worsen, seeking medical attention is warranted.
Question 6: How does the duration of treatment with ear drops impact the likelihood of developing complications, such as superinfection or antimicrobial resistance?
Prolonged use of antibiotic or antifungal ear drops can disrupt the natural microbial balance within the ear canal, increasing the risk of superinfection with resistant organisms. The duration of treatment should be limited to the minimum necessary to resolve the underlying condition. Unnecessary or prolonged use of these medications can contribute to the emergence of antimicrobial resistance, rendering future infections more difficult to treat.
The information provided above serves as a general guide and should not be interpreted as a substitute for professional medical advice. Individuals experiencing persistent or concerning symptoms should consult with a qualified healthcare provider for personalized evaluation and treatment.
The next segment will concentrate on preventative strategies for avoiding conditions that may cause diminished auditory perception.
Ear Drops for Muffled Ears
This exploration has delineated the multifaceted aspects of employing aural medications to address a diminished perception of sound. Key considerations encompass accurate diagnosis, appropriate medication selection, precise administration techniques, and diligent monitoring for potential adverse effects. The narrative underscored the critical role of professional medical consultation in ensuring patient safety and optimizing treatment efficacy. Deviation from these established principles may compromise therapeutic outcomes and potentially exacerbate existing conditions.
The prudent and informed application of ear drops for muffled ears necessitates a commitment to evidence-based practices and a thorough understanding of individual patient needs. Future advancements in diagnostic modalities and pharmacological formulations may further refine treatment strategies. However, the core principles of responsible medication use and professional oversight remain paramount in safeguarding auditory health and well-being.