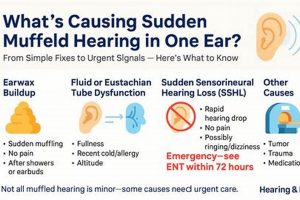
Experiencing a sudden decrease in hearing sensitivity in a single ear upon awakening, often described as a feeling of fullness or blockage, is a relatively common occurrence. This can manifest as difficulty clearly hearing sounds, or perceiving them as quieter than usual in the affected ear. The sensation may be accompanied by other symptoms such as tinnitus (ringing in the ear) or a feeling of pressure.
The significance of this symptom lies in its potential underlying causes, which can range from benign and self-resolving to conditions requiring medical intervention. The potential disruption to daily communication and overall quality of life makes understanding the possible etiologies and appropriate management strategies important. Historically, such experiences were often dismissed, but increased awareness and diagnostic capabilities now allow for more accurate identification of the root cause.
The following sections will delve into the specific causes, diagnostic approaches, and potential treatment options associated with the sudden onset of unilateral hearing reduction experienced upon waking.
Addressing Unilateral Hearing Reduction Upon Awakening
The following recommendations are intended to provide guidance in managing the experience of waking with muffled hearing in one ear. These tips emphasize proactive measures and awareness of potential underlying issues.
Tip 1: Observe and Document: Carefully note the onset time and any accompanying symptoms, such as tinnitus, vertigo, or pressure. Detailed records can assist medical professionals in diagnosis.
Tip 2: Attempt Simple Remedies: Gently manipulate the outer ear and jaw. Yawning or swallowing may help equalize pressure if fluid is present. Avoid forceful actions.
Tip 3: Rule Out External Factors: Consider potential external causes such as earwax buildup. Over-the-counter earwax softening solutions may be used cautiously, following product instructions precisely.
Tip 4: Monitor for Associated Symptoms: Pay close attention to any related symptoms, such as nasal congestion, sore throat, or headache. These may indicate an upper respiratory infection contributing to the issue.
Tip 5: Limit Noise Exposure: Avoid loud environments, especially during and immediately following the onset of hearing reduction. Further noise exposure could exacerbate the condition.
Tip 6: Seek Prompt Medical Evaluation: If the hearing reduction persists for more than 24 hours, worsens, or is accompanied by pain, drainage, or vertigo, prompt medical evaluation is essential.
Tip 7: Follow Medical Advice: Adhere strictly to any prescribed treatment plan, which may include medications, ear cleaning procedures, or further diagnostic testing.
These tips provide a framework for initial management and underscore the importance of vigilant self-monitoring and timely professional evaluation to identify and address potential underlying causes.
The subsequent sections will provide a more detailed examination of the potential medical conditions associated with this symptom and their respective treatment strategies.
1. Sudden Hearing Loss
Sudden hearing loss, characterized by a rapid decrease in hearing acuity, is a significant potential underlying cause when an individual experiences a muffled sensation in one ear upon waking. This symptom presentation necessitates careful evaluation due to the time-sensitive nature of some potential diagnoses. For example, Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss (SSNHL), a condition involving rapid loss of hearing due to inner ear dysfunction, often presents as a unilateral muffled sensation. The immediate recognition of this connection is critical because the effectiveness of treatment for SSNHL, such as corticosteroid therapy, is greatly diminished with delayed intervention.
The identification of sudden hearing loss as the etiology of a muffled ear upon awakening mandates prompt audiological assessment. This assessment typically includes pure-tone audiometry to quantify the degree and type of hearing loss. Further investigations, such as MRI, may be necessary to rule out other possible causes, including acoustic neuroma or other structural abnormalities. Recognizing the potential severity of sudden hearing loss allows for expedited diagnostic testing and the initiation of appropriate therapies aimed at recovering hearing function.
In summary, the presentation of a muffled ear sensation upon waking must be evaluated with sudden hearing loss as a primary diagnostic consideration. Understanding this connection, performing rapid diagnostic evaluations, and implementing therapies within a defined time window are essential for optimizing patient outcomes and minimizing the long-term impact on auditory function. The challenge lies in differentiating sudden hearing loss from other, less urgent, causes, thus highlighting the importance of a thorough medical evaluation.
2. Etiology Identification
Determining the underlying cause of unilateral muffled hearing upon awakening is essential for appropriate medical management. Etiology identification involves a systematic approach to differentiate among various potential factors contributing to this symptom. Without a precise diagnosis, effective and targeted treatment is impossible.
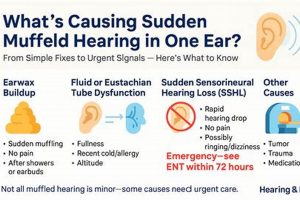
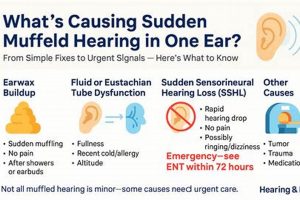
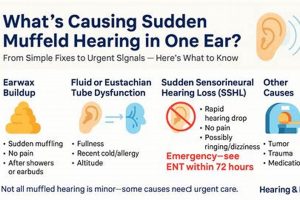
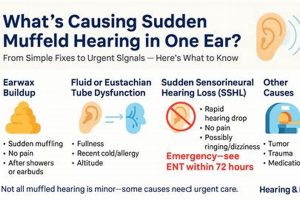
- Cerumen Impaction
Excessive earwax accumulation can lead to physical obstruction of the ear canal, resulting in a sensation of muffled hearing. This is often identified through otoscopic examination. Management includes manual removal by a healthcare provider or the use of cerumenolytic agents. Failure to address cerumen impaction can lead to continued hearing reduction and potentially exacerbate other ear conditions.
- Eustachian Tube Dysfunction
Malfunction of the Eustachian tube, which connects the middle ear to the nasopharynx, can disrupt pressure equalization, resulting in fluid accumulation and a muffled sensation. Factors such as upper respiratory infections or allergies can trigger this. Diagnosis may involve pneumatic otoscopy or tympanometry. Treatments range from decongestants to, in severe cases, surgical intervention to ventilate the middle ear.
- Inner Ear Disorders
Conditions affecting the inner ear, such as sudden sensorineural hearing loss (SSNHL) or Meniere’s disease, can manifest as a sudden onset of unilateral muffled hearing. SSNHL requires rapid assessment and intervention with corticosteroids, while Meniere’s disease involves a constellation of symptoms, including fluctuating hearing loss, vertigo, and tinnitus. The distinction between these conditions requires audiological and vestibular testing.
- Infections
Otitis media (middle ear infection) or otitis externa (outer ear infection) can both present with a feeling of fullness and muffled hearing. Diagnosis typically involves otoscopic examination and may include cultures to identify causative organisms. Treatment typically involves antibiotics or antifungal agents, depending on the nature of the infection.
In each of these examples, the precise etiology directs the course of treatment. Delayed or inaccurate diagnosis can lead to prolonged symptoms, potential complications, and reduced quality of life. The importance of a comprehensive diagnostic approach, involving physical examination and specialized testing, cannot be overstated in managing unilateral muffled hearing upon awakening.
3. Earwax Impaction
Earwax impaction, the excessive accumulation of cerumen within the ear canal, frequently presents as a primary cause of unilateral muffled hearing, particularly when experienced upon awakening. The obstruction physically impedes sound transmission, leading to a subjective sensation of diminished auditory acuity in the affected ear. This condition warrants specific attention due to its common occurrence and potential for straightforward management.
- Physical Obstruction of the Ear Canal
Earwax, a naturally produced substance, serves a protective function within the ear canal. However, when produced in excess or improperly cleared, it can harden and form a blockage. This physical barrier attenuates sound waves, leading to a perceived muffling effect. Individuals may awaken with this sensation if earwax has migrated further into the canal during sleep, exacerbating the obstruction.
- Aggravation During Sleep
The supine position assumed during sleep can facilitate the migration of earwax deeper into the ear canal. This movement can compound pre-existing partial blockages, culminating in a more pronounced sensation of muffled hearing upon waking. Positional changes can therefore influence the perceived severity of symptoms.
- Contributing Factors to Impaction
Several factors contribute to earwax impaction. These include the use of cotton swabs, which can push earwax further into the canal, the presence of narrow or irregularly shaped ear canals, and the use of hearing aids, which can impede natural earwax expulsion. Recognizing these predisposing factors is essential in preventive strategies.
- Management and Resolution
Management of earwax impaction involves physical removal by a healthcare professional or the use of cerumenolytic agents to soften and dissolve the earwax. Self-treatment with inappropriate tools, such as cotton swabs or sharp objects, is strongly discouraged due to the risk of ear canal damage. Once the impaction is resolved, normal hearing is typically restored.
The connection between earwax impaction and the experience of waking with a muffled ear underscores the importance of routine ear hygiene practices and professional evaluation when symptoms arise. The simplicity of resolution in many cases highlights the need for prompt assessment to differentiate it from more complex audiological conditions.
4. Eustachian Tube Dysfunction
Eustachian tube dysfunction is a recognized contributor to the sensation of muffled hearing experienced upon awakening in one ear. The Eustachian tube’s role in pressure regulation within the middle ear makes its malfunction a notable cause of this auditory disturbance.
- Impaired Pressure Regulation
The Eustachian tube’s primary function is to equalize pressure between the middle ear and the ambient environment. When this function is compromised, a pressure imbalance can occur, leading to a retracted tympanic membrane and a perceived reduction in sound transmission. During sleep, prolonged dysfunction can result in increased pressure differential, culminating in a pronounced muffled sensation upon awakening.
- Fluid Accumulation in the Middle Ear
Eustachian tube dysfunction can impair drainage of fluids from the middle ear. This accumulation of fluid, known as middle ear effusion, creates a barrier to sound conduction, resulting in muffled hearing. Conditions such as upper respiratory infections or allergies can exacerbate fluid buildup, leading to a more significant auditory impact.
- Inflammation and Congestion
Inflammation of the Eustachian tube lining, often associated with allergies or infections, can obstruct the tube’s opening and impede its function. This inflammation can cause swelling and congestion, further disrupting pressure equalization and drainage, thereby contributing to a sensation of muffled hearing upon waking.
- Barometric Pressure Sensitivity
Individuals with pre-existing Eustachian tube dysfunction may experience exacerbated symptoms during periods of barometric pressure change, such as those occurring during air travel or seasonal weather shifts. These pressure changes can place additional stress on the Eustachian tube, leading to increased discomfort and a greater likelihood of experiencing muffled hearing upon awakening.
The interplay between Eustachian tube dysfunction and the experience of waking with unilateral muffled hearing underscores the importance of addressing underlying conditions, such as allergies or infections, that may contribute to Eustachian tube malfunction. Recognizing this connection allows for targeted medical interventions aimed at restoring proper Eustachian tube function and alleviating associated auditory symptoms.
5. Infection Possibility
The potential for infection is a critical consideration when assessing the experience of waking with a muffled ear. Both middle ear infections (otitis media) and outer ear infections (otitis externa) can manifest as unilateral hearing reduction upon awakening. The inflammatory response and subsequent fluid accumulation or tissue swelling associated with these infections disrupt the normal mechanics of sound transmission. For example, a child with a resolving upper respiratory infection may experience Eustachian tube dysfunction, leading to fluid buildup in the middle ear overnight, resulting in muffled hearing in the morning. In adults, otitis externa, potentially triggered by minor trauma or moisture retention in the ear canal, can rapidly progress, causing swelling and a feeling of blockage.
The importance of considering infection lies in the necessity for prompt and appropriate treatment. Bacterial or fungal infections require targeted antimicrobial therapy to prevent complications such as persistent hearing loss, mastoiditis (in the case of untreated otitis media), or cellulitis (in the case of severe otitis externa). Distinguishing between viral, bacterial, and fungal etiologies is vital for selecting the appropriate treatment strategy. Diagnostic tools, such as otoscopy and tympanometry, are often used to evaluate the middle ear and identify signs of infection. Furthermore, a careful history, including recent exposure to water (swimming) or trauma to the ear canal (cotton swab use), can provide clues to the source of infection.
In conclusion, the possibility of infection as the underlying cause of waking with a muffled ear emphasizes the need for timely medical evaluation. While some infections may resolve spontaneously, others require intervention to prevent long-term sequelae. A thorough examination and appropriate diagnostic testing are essential to differentiate infection from other potential causes and to guide effective management strategies. This underscores the practical significance of recognizing infection as a key consideration in such cases.
6. Medical Evaluation Urgency
The sudden onset of unilateral muffled hearing upon awakening necessitates a consideration of medical evaluation urgency. The promptness with which professional medical attention is sought directly influences diagnostic accuracy and therapeutic efficacy, with potential implications for long-term auditory health.
- Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss (SSNHL)
SSNHL requires intervention within a limited timeframe for optimal outcomes. Corticosteroid therapy, a primary treatment, exhibits diminishing effectiveness if initiated beyond approximately two weeks from symptom onset. Consequently, delayed evaluation significantly reduces the likelihood of hearing recovery.
- Infection Complications
Untreated ear infections, whether otitis media or otitis externa, can progress to more serious conditions, including mastoiditis, labyrinthitis, or cellulitis. These complications require aggressive medical or surgical management. Prompt diagnosis and treatment with appropriate antimicrobial agents mitigate the risk of such sequelae.
- Acoustic Neuroma/Vestibular Schwannoma
While less common, a unilateral muffled ear can be an early symptom of an acoustic neuroma. Delayed diagnosis allows for continued tumor growth, potentially impacting cranial nerve function and complicating surgical removal. Early detection facilitates more conservative treatment options and reduces the risk of neurological deficits.
- Vascular Events
In rare instances, unilateral sudden hearing loss may be indicative of a vascular event affecting the inner ear. This is more likely to occur in individuals with pre-existing cardiovascular risk factors. While less common, immediate medical evaluation is crucial to rule out emergent conditions and potentially initiate appropriate vascular management strategies.
The preceding facets collectively underscore the critical role of timely medical evaluation in cases of sudden unilateral muffled hearing. The potential for time-sensitive diagnoses and the prevention of long-term complications necessitate a proactive approach to seeking professional medical attention when such symptoms arise. The urgency stems from the limited windows of opportunity for effective intervention and the potential consequences of delayed or missed diagnoses.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following addresses common inquiries regarding the experience of waking with a muffled sensation in one ear. This information is intended to provide clarity on causes, management, and the importance of seeking professional medical advice.
Question 1: What are the most common causes of waking up with one ear muffled?
Common causes include earwax impaction, Eustachian tube dysfunction, middle ear infections, and, less frequently, sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Other less frequent etiologies exist and require investigation.
Question 2: When is it necessary to seek immediate medical attention for a muffled ear upon awakening?
Immediate medical attention is warranted if the muffled sensation is accompanied by sudden hearing loss, vertigo, ear pain, drainage, or persists beyond 24 hours. Delays in seeking care for sudden hearing loss can compromise treatment effectiveness.
Question 3: Can earwax buildup cause a muffled ear, and how is it treated?
Yes, earwax impaction is a common cause. Treatment involves manual removal by a healthcare professional or the use of earwax softening solutions. Self-removal with cotton swabs is discouraged due to the risk of impaction and injury.
Question 4: How does Eustachian tube dysfunction contribute to a muffled ear?
Eustachian tube dysfunction impairs pressure equalization in the middle ear, potentially leading to fluid accumulation and a sensation of muffled hearing. This is often associated with allergies or upper respiratory infections.
Question 5: What should be done if an ear infection is suspected as the cause?
Suspected ear infections require medical evaluation to determine the type of infection and prescribe appropriate antimicrobial therapy. Untreated infections can lead to serious complications.
Question 6: Is there a connection between allergies and a muffled ear upon awakening?
Yes, allergies can cause inflammation and congestion in the Eustachian tube, leading to impaired function and fluid buildup in the middle ear, resulting in a muffled sensation.
These questions address frequently encountered concerns related to waking with a muffled ear. Seeking timely medical advice remains paramount for accurate diagnosis and appropriate management.
The following section will address home remedies. Please remember to consult a doctor before taking any action.
Conclusion
The phenomenon of waking with unilateral muffled hearing encompasses a spectrum of potential etiologies, ranging from benign and self-resolving conditions to those requiring immediate medical intervention. This presentation necessitates careful self-assessment and a judicious approach to seeking timely professional evaluation. Factors such as earwax impaction, Eustachian tube dysfunction, infection, and the possibility of sudden sensorineural hearing loss all contribute to this symptom. A failure to differentiate between these potential causes can result in delayed or inappropriate treatment, potentially leading to adverse long-term outcomes.
Therefore, the persistent or worsening experience of unilateral muffled hearing upon awakening should be regarded as a potentially significant health concern. Proactive engagement with medical professionals is critical for accurate diagnosis and the implementation of effective management strategies. A focus on early detection and appropriate intervention is essential to safeguarding auditory health and minimizing the impact on overall quality of life.