A sensation of reduced sound clarity or a feeling of blockage in the ear is commonly described as having impaired or dulled hearing. This experience often presents as if sounds are distant or muted. For instance, speech may seem indistinct, or environmental noises may lack their usual crispness and volume.
Addressing this condition promptly can prevent potential complications such as temporary hearing loss becoming prolonged or, in rare cases, masking underlying medical issues. Early intervention and appropriate management contribute significantly to preserving auditory function and overall well-being. Historically, various methods, ranging from simple home remedies to specialized medical procedures, have been employed to alleviate this uncomfortable auditory symptom.
The subsequent sections will detail common causes for the experience, effective methods for alleviating the sensation, and when seeking professional medical evaluation is recommended. Understanding the underlying factors and available interventions is crucial for effectively addressing and managing this frequently encountered hearing issue.
Strategies for Alleviating a Sensation of Impaired Hearing
The following strategies may provide relief from the feeling of reduced sound clarity or blockage in the ear. If symptoms persist, consult a medical professional.
Tip 1: Employ the Valsalva Maneuver: Gently attempt to exhale while pinching the nostrils and closing the mouth. This may equalize pressure in the Eustachian tube, potentially clearing a blockage. Exercise caution and avoid excessive force.
Tip 2: Utilize Over-the-Counter Decongestants: In cases of nasal congestion contributing to the sensation, decongestants may help reduce swelling and improve Eustachian tube function. Adhere strictly to the manufacturer’s instructions and contraindications.
Tip 3: Apply Warm Compresses: Place a warm, damp cloth over the affected ear for several minutes. The warmth may help loosen earwax and relieve discomfort.
Tip 4: Consider Earwax Removal Products: Over-the-counter earwax softening drops can aid in breaking down impacted earwax. Follow product instructions carefully. If uncertain about earwax impaction, seek professional evaluation.
Tip 5: Ensure Adequate Hydration: Maintaining proper hydration can help thin mucus and facilitate drainage from the Eustachian tube.
Tip 6: Avoid Exposure to Loud Noises: Refrain from exposure to loud environments to prevent further auditory strain and potential exacerbation of the condition.
Tip 7: Manage Allergies: If allergies are suspected as a contributing factor, consider taking antihistamines or consulting an allergist for appropriate management.
These approaches aim to address common causes of diminished sound perception and promote improved auditory function. Remember that persistent symptoms warrant professional medical assessment to rule out more serious underlying conditions.
The following sections will address scenarios where seeking expert medical attention becomes necessary for adequate diagnosis and treatment.
1. Identify the Cause
Determining the etiology of diminished auditory clarity is paramount to effective management. The sensation of a muffled ear is not a singular condition but a symptom stemming from various underlying factors. Therefore, implementing any remedial strategy without first ascertaining the root cause is often ineffective and potentially detrimental. For instance, attempting earwax removal techniques when the true issue is a middle ear infection could exacerbate the infection and delay appropriate treatment.
The diagnostic process requires a systematic approach. A detailed medical history, encompassing recent illnesses, allergies, and exposure to loud noises, offers valuable insights. A physical examination of the ear canal and tympanic membrane aids in identifying visible obstructions or signs of inflammation. Further investigations, such as audiometry or tympanometry, may be necessary to assess the extent and nature of any hearing impairment. A real-world example highlights the significance: a swimmer experiencing muffled hearing after prolonged water exposure may simply have water trapped in the ear canal. However, if accompanied by pain or discharge, it could indicate an infection requiring antibiotic intervention. Ignoring the pain and only trying to get rid of water may lead to complications of an ear infection.
In summary, accurately identifying the cause of a muffled ear is the cornerstone of successful resolution. It enables targeted interventions, prevents inappropriate treatments, and minimizes the risk of complications. Failure to undertake this crucial first step often leads to prolonged discomfort, frustration, and potentially irreversible auditory damage. Consequently, a comprehensive diagnostic evaluation is indispensable for individuals experiencing persistent or recurrent episodes of impaired sound perception.
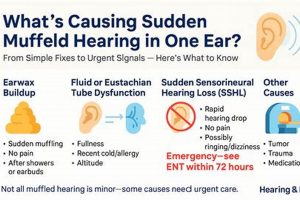
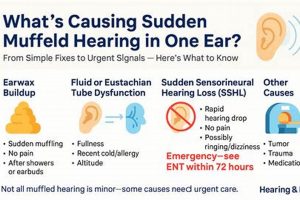
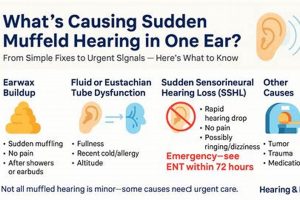
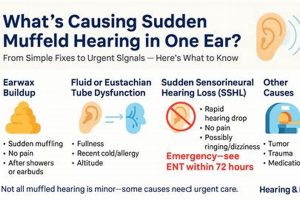
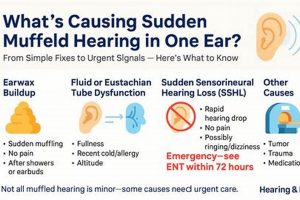
2. Earwax Impaction
Earwax impaction represents a prevalent cause of the sensation of diminished hearing or blockage within the ear. Its occurrence significantly impacts efforts to restore normal auditory function. Understanding its characteristics and management is therefore essential when addressing the concern of “how to get rid of a muffled ear.”
- Formation and Accumulation
Earwax, or cerumen, is naturally produced within the ear canal to protect and lubricate the delicate skin. However, factors such as narrow ear canals, use of cotton swabs, or overproduction can lead to excessive accumulation. This buildup can obstruct the ear canal, physically impeding sound transmission and creating the perception of muffled hearing. Consider the example of individuals who habitually use cotton swabs to clean their ears. While intending to remove earwax, they often inadvertently push it further into the canal, compacting it and increasing the likelihood of impaction.
- Symptoms and Identification
Besides the primary symptom of muffled hearing, earwax impaction can manifest as earache, a feeling of fullness in the ear, tinnitus (ringing in the ears), and even dizziness. These symptoms arise from the pressure exerted by the impacted earwax on the surrounding structures. Identifying these signs is crucial for differentiating earwax impaction from other potential causes of hearing impairment. For instance, sudden onset of muffled hearing after swimming may suggest water trapped behind impacted earwax.
- Management and Removal Techniques
Several methods exist for addressing earwax impaction. Over-the-counter earwax softening drops, containing ingredients like carbamide peroxide, can help to dissolve and loosen the impacted wax. Irrigation with warm water, performed gently, can then flush out the softened earwax. However, forceful irrigation or the use of sharp objects to remove earwax is strongly discouraged due to the risk of injury to the ear canal and eardrum. In cases of severe impaction or when self-treatment is unsuccessful, professional removal by a healthcare provider is recommended. These professionals employ specialized instruments and techniques to safely and effectively clear the ear canal.
- Prevention Strategies
Preventing earwax impaction involves minimizing factors that contribute to its development. Limiting the use of cotton swabs and other objects within the ear canal is paramount. Instead, allowing the ear’s natural cleaning mechanisms to function is preferable. In individuals prone to excessive earwax production, regular check-ups with a healthcare provider for professional cleaning may be beneficial. Recognizing and addressing underlying factors, such as skin conditions that increase earwax production, is also essential for long-term prevention.
In summary, earwax impaction plays a significant role in the occurrence of muffled hearing. Understanding the mechanisms of its formation, recognizing its characteristic symptoms, and employing appropriate management strategies are critical steps in effectively restoring normal auditory perception and addressing the problem. Proper management leads to getting rid of the sensation. When self-treatment proves inadequate or symptoms persist, seeking professional medical assistance is essential to ensure safe and effective removal of impacted earwax and to rule out other potential causes of hearing impairment.
3. Eustachian Tube Dysfunction
Eustachian tube dysfunction (ETD) frequently underlies the sensation of impaired auditory clarity, or “muffled ear.” A thorough understanding of its mechanisms and implications is, therefore, crucial for devising effective strategies to alleviate this auditory symptom. Proper Eustachian tube function is essential for pressure equalization in the middle ear. When this tube malfunctions, it can cause the described sensation.
- Pressure Regulation Impairment
The primary function of the Eustachian tube is to equalize pressure between the middle ear and the ambient environment. When ETD occurs, this pressure regulation mechanism is compromised, resulting in negative pressure within the middle ear cavity. This negative pressure can draw the eardrum inward, reducing its ability to vibrate freely and transmit sound effectively. For example, rapid altitude changes during air travel or scuba diving can exacerbate ETD symptoms, as the Eustachian tube struggles to equalize pressure quickly enough. The resulting pressure imbalance is perceived as a muffled sound or a feeling of fullness.
- Fluid Accumulation
ETD can also lead to fluid accumulation in the middle ear. The Eustachian tube normally drains mucus and debris from the middle ear into the nasopharynx. When the tube is blocked or malfunctioning, this drainage process is impaired, allowing fluid to accumulate. The presence of fluid in the middle ear dampens the eardrum’s vibrations, further contributing to the sensation of muffled hearing. Consider the scenario of a child with a cold; nasal congestion can obstruct the Eustachian tube, leading to fluid buildup and temporary hearing impairment.
- Inflammation and Obstruction
Inflammation of the Eustachian tube lining, often caused by allergies or upper respiratory infections, can narrow or completely obstruct the tube’s passage. This obstruction prevents proper pressure equalization and drainage, leading to the previously described symptoms. Allergic rhinitis, for instance, can trigger Eustachian tube inflammation, resulting in recurrent episodes of muffled hearing, particularly during allergy season. Exposure to irritants, such as cigarette smoke, can similarly contribute to inflammation and ETD.
- Chronic Dysfunction and Complications
Chronic ETD, if left untreated, can lead to more severe complications. Prolonged negative pressure in the middle ear can cause the formation of a middle ear effusion (fluid collection). In some cases, this can progress to adhesive otitis, where the eardrum adheres to the middle ear structures, resulting in significant and potentially irreversible hearing loss. Furthermore, chronic ETD increases the risk of recurrent middle ear infections (otitis media). Consequently, timely diagnosis and management of ETD are crucial to prevent these long-term sequelae.
These facets illuminate the significant role of Eustachian tube dysfunction in eliciting the sensation of diminished auditory clarity. Addressing ETD involves strategies aimed at restoring proper tube function, such as decongestants, nasal steroids, or, in severe cases, surgical intervention. Prompt and appropriate management of ETD is essential to alleviate the experience and mitigate the risk of long-term auditory complications. Effective management helps resolve a muffled ear by targeting the cause.
4. Infection Management
The presence of an infection within the ear, whether in the outer, middle, or, less commonly, inner ear, frequently manifests as a sensation of reduced sound clarity or a feeling of blockage. Effective infection management is, therefore, a critical component in restoring normal auditory perception. Infections cause inflammation and fluid accumulation, which directly impede sound transmission. The success of attempts aimed at resolving the sensation is inextricably linked to the successful management of any underlying infection.
Specific strategies for infection management depend on the location and nature of the infection. Outer ear infections (otitis externa), often caused by bacteria or fungi, typically require topical antibiotic or antifungal drops. Middle ear infections (otitis media), commonly seen in children, may necessitate oral antibiotics. Viral infections are typically managed with supportive care, such as pain relievers and decongestants. Prompt and appropriate antimicrobial therapy is essential to eradicate the infection, reduce inflammation, and allow fluid to drain from the middle ear. The real-world significance is evident in cases of untreated otitis media, which can lead to persistent hearing loss, tympanic membrane perforation, or, in rare instances, mastoiditis. For example, delaying antibiotic treatment for a child with a bacterial middle ear infection can prolong the period of diminished hearing and increase the risk of complications. Furthermore, understanding the specific type of infection and the appropriate antimicrobial agent is crucial to prevent antibiotic resistance.
In summary, infection management is not merely a treatment modality but an indispensable prerequisite for restoring unimpeded sound transmission and eradicating the sensation associated with it. Effective strategies include targeted antimicrobial therapy, supportive care, and prevention of complications. Addressing the infection at its source is vital for reversing its impact on auditory function and preventing lasting damage.
5. Pressure Equalization
An imbalance in pressure between the middle ear and the external environment frequently contributes to the sensation of reduced auditory clarity. When the Eustachian tube, which connects the middle ear to the back of the throat, fails to regulate this pressure difference effectively, a feeling of blockage or muffled hearing arises. The act of equalizing this pressure is, therefore, integral to resolving the sensation. Its importance is highlighted in situations where rapid changes in altitude or ambient pressure occur, such as during air travel or scuba diving. Without proper pressure equalization, the eardrum may be unable to vibrate freely, resulting in diminished sound transmission. For instance, individuals experiencing difficulty equalizing pressure during descent in an airplane often report a feeling of muffled hearing that persists until the pressure is normalized. This underlines the practical significance of techniques such as the Valsalva maneuver (gentle exhalation against a closed nose and mouth) or yawning, which facilitate the opening of the Eustachian tube and promote pressure balance.
The efficacy of pressure equalization as a component of addressing a muffled ear relies on the underlying cause of the pressure imbalance. If the Eustachian tube dysfunction stems from inflammation due to allergies or upper respiratory infections, decongestants or nasal corticosteroids may be necessary to reduce swelling and improve tube function. In cases of persistent pressure imbalance, a healthcare professional may recommend more invasive interventions, such as tympanostomy tubes, to provide a permanent pathway for pressure equalization. Success in this area directly correlates to restoring a patient’s normal auditory acuity. This direct connection underscores the importance of understanding and addressing this factor in cases of diminished hearing.
In conclusion, pressure equalization represents a crucial aspect of managing the sensation of reduced auditory clarity. Its effectiveness depends on accurately identifying the underlying cause of the pressure imbalance and implementing appropriate strategies to restore normal Eustachian tube function. While simple techniques such as the Valsalva maneuver can provide temporary relief, persistent issues may require medical intervention. The ability to effectively equalize pressure is not merely a symptomatic treatment but a fundamental step toward restoring normal hearing and overall auditory well-being.
6. Avoid Irritants
Exposure to irritants, both environmental and chemical, can significantly contribute to the sensation of diminished sound clarity. Addressing the sensation necessitates minimizing or eliminating contact with such irritants. Irritants trigger inflammatory responses within the delicate structures of the ear and upper respiratory tract. This inflammation can directly impact Eustachian tube function, leading to pressure imbalances and fluid accumulation within the middle ear. It can also directly inflame the ear canal skin. Consequently, individuals experiencing persistent muffled hearing should carefully evaluate their environment and lifestyle for potential irritant exposures.
Common culprits include cigarette smoke, allergens (such as pollen, dust mites, and animal dander), and certain chemicals found in cleaning products or industrial settings. Cigarette smoke, for example, contains numerous irritants that can inflame the nasal passages and Eustachian tube, impeding its ability to equalize pressure. Similarly, exposure to high levels of dust or allergens can trigger allergic rhinitis, resulting in Eustachian tube dysfunction and the sensation of muffled hearing. In industrial settings, airborne chemicals can directly irritate the ear canal lining. A practical application of this understanding involves individuals with known allergies. During high pollen seasons, taking antihistamines and limiting outdoor activities can reduce allergic inflammation and improve Eustachian tube function, thereby diminishing the sensation. The link between exposure and symptoms is a crucial piece of information when treating such conditions.
In summary, avoiding irritants is a proactive and essential step toward alleviating muffled hearing caused by environmental or chemical factors. By minimizing exposure to common irritants such as smoke, allergens, and certain chemicals, individuals can reduce inflammation, improve Eustachian tube function, and promote normal sound transmission. This approach is not always a standalone solution but a critical component of comprehensive management, often complementing other strategies such as pressure equalization techniques or medical interventions when required. Understanding and mitigating the role of irritants contributes significantly to restoring optimal auditory clarity. It reinforces the link between environment, health, and addressing a symptom.
7. Professional Evaluation
The phrase “how to get rid of a muffled ear” often leads individuals to explore self-treatment options. While many cases resolve with simple home remedies, persistent or recurrent instances necessitate professional medical evaluation. Professional assessment is crucial because muffled hearing is a symptom with diverse underlying causes, ranging from benign conditions like earwax impaction to more serious issues like infections or structural abnormalities. A qualified healthcare provider, such as an audiologist or otolaryngologist (ENT specialist), possesses the expertise and diagnostic tools to accurately identify the root cause of the hearing impairment. For example, what an individual perceives as simple earwax may be a cholesteatoma, a skin growth in the middle ear that requires surgical intervention to prevent further damage. Attempting self-treatment in such a scenario could be detrimental.
Professional evaluation typically involves a comprehensive medical history, a physical examination of the ear canal and eardrum, and audiometric testing. Audiometry assesses the extent and type of hearing loss, providing valuable information about the location of the problem within the auditory system. Furthermore, specialized tests such as tympanometry can evaluate the function of the middle ear and Eustachian tube. A real-world instance illustrates the importance of these tests: an individual experiencing sudden onset muffled hearing may be diagnosed with sudden sensorineural hearing loss (SSHL), a medical emergency requiring prompt treatment with corticosteroids to maximize the chances of hearing recovery. Without professional audiometric evaluation, SSHL can be easily missed, leading to permanent hearing damage. Also, not all hearing loss can be resolved. Therefore, professional evaluation also helps with managing hearing problems to improve life qualities.
In conclusion, while self-care strategies may provide relief in some situations, professional evaluation is indispensable for persistent or unexplained muffled hearing. It ensures accurate diagnosis, facilitates targeted treatment, and prevents potential complications. Delaying or forgoing professional assessment can have significant consequences, ranging from prolonged discomfort to irreversible hearing loss. The value of expert evaluation lies in its ability to differentiate between self-treatable conditions and those requiring specialized medical intervention, ultimately safeguarding auditory health and well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following questions and answers address common concerns and misconceptions regarding the sensation of muffled hearing and strategies to restore normal sound perception.
Question 1: What are the most common causes of a muffled ear?
Earwax impaction, Eustachian tube dysfunction, and middle ear infections are among the most frequent causes. Other potential contributing factors include exposure to loud noises, upper respiratory infections, allergies, and certain medications.
Question 2: When is it necessary to seek professional medical evaluation for muffled hearing?
Professional assessment is recommended for persistent or recurrent episodes, sudden onset of symptoms, presence of pain or drainage from the ear, dizziness, or any associated neurological symptoms.
Question 3: Can over-the-counter earwax removal products safely resolve earwax impaction?
Over-the-counter earwax softening drops, used according to the manufacturer’s instructions, can be effective for mild to moderate impaction. However, forceful irrigation or the use of sharp objects is strongly discouraged due to the risk of injury. Professional removal is recommended for severe impaction or if self-treatment is unsuccessful.
Question 4: How does Eustachian tube dysfunction contribute to muffled hearing, and what can be done about it?
Eustachian tube dysfunction impairs pressure equalization between the middle ear and the environment, leading to negative pressure and fluid accumulation. Decongestants, nasal steroids, and pressure equalization techniques (e.g., Valsalva maneuver) may provide relief. In severe cases, surgical intervention may be necessary.
Question 5: Can exposure to loud noises cause permanent muffled hearing?
Yes, prolonged or excessive exposure to loud noises can damage the delicate hair cells in the inner ear, leading to noise-induced hearing loss. This type of hearing loss is often irreversible. Preventative measures, such as wearing ear protection in noisy environments, are crucial.
Question 6: Are there any long-term consequences of ignoring muffled hearing?
Untreated muffled hearing can lead to social isolation, communication difficulties, and decreased quality of life. Furthermore, in some cases, it may indicate an underlying medical condition that requires prompt treatment to prevent further complications.
Early identification of the cause and implementation of appropriate measures are critical for preventing long-term complications and improving quality of life.
The subsequent section will summarize the key points discussed and provide concluding remarks.
Conclusion
This article has explored the multifaceted nature of experiencing diminished auditory clarity. Strategies range from simple home remedies addressing earwax accumulation and pressure imbalances to medical interventions targeting infections or structural abnormalities. The effectiveness of each approach hinges on accurate identification of the underlying cause. Self-treatment may provide relief in some instances, but persistent or recurrent episodes necessitate professional medical evaluation to prevent complications.
Addressing a muffled ear requires proactive management, informed decision-making, and, when necessary, timely access to medical expertise. Prioritizing auditory health is crucial for maintaining communication abilities and overall quality of life. Ignoring symptoms may lead to long-term consequences that could potentially have been avoided with proper interventions. Therefore, vigilance and diligence in attending to auditory changes are imperative for preserving aural well-being.