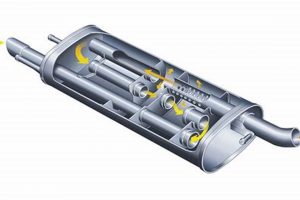
An automotive exhaust component designed to reduce noise levels generated by the engine. This device utilizes a specific internal construction, often involving baffles or chambers, to dampen sound waves as they pass through the exhaust system. For example, a vehicle owner seeking a more aggressive exhaust note might choose this type of component for its balance between performance and sound attenuation.
The significance of this component lies in its ability to manage noise pollution while potentially contributing to engine performance. Historically, it provided an alternative to more restrictive mufflers, offering a compromise between a quiet, stock exhaust and a loud, un-muffled system. Its advantages include a distinctive sound profile and, in some applications, a less restrictive exhaust flow compared to certain alternative designs.
The following sections will further detail the construction, performance characteristics, installation considerations, and typical applications of these exhaust components, providing a comprehensive understanding of their role within the automotive landscape. This will explore their impact on sound, performance, and regulatory compliance.
Optimizing Performance and Longevity
The following recommendations aim to maximize the performance and service life of this exhaust component, ensuring both desired sound characteristics and prolonged functionality.
Tip 1: Material Selection: Prioritize aluminized or stainless steel construction for enhanced resistance to corrosion, particularly in regions with harsh winter conditions or high levels of road salt application. This material choice extends the lifespan of the component and maintains structural integrity.
Tip 2: Proper Installation: Ensure precise alignment and secure mounting to prevent stress fractures and exhaust leaks. Improper installation can lead to premature failure and diminished sound attenuation.
Tip 3: Regular Inspection: Periodically examine the component for signs of rust, damage from road debris, or loose connections. Early detection of these issues allows for timely repairs and prevents more significant problems.
Tip 4: Exhaust System Compatibility: Verify compatibility with the vehicle’s existing exhaust system. Mismatched components can result in reduced performance or undesirable sound characteristics.
Tip 5: Clamping Force: Use appropriate clamping force when connecting the component to the exhaust system. Over-tightening can damage the component, while insufficient force may cause leaks.
Tip 6: Heat Shielding: Consider the use of heat shields to protect surrounding components from excessive heat generated by the exhaust system. This measure can prevent damage to fuel lines, wiring harnesses, and other sensitive components.
Tip 7: Minimize Exhaust Backpressure: When possible, select components that minimize exhaust backpressure to optimize engine performance. This may involve choosing larger diameter pipes or less restrictive internal designs.
Adhering to these guidelines will contribute to improved performance, extended lifespan, and optimal sound quality. Proper installation and regular maintenance are crucial for realizing the full potential of this component within the exhaust system.
The subsequent sections will delve into more specific technical aspects, including the acoustic principles behind the component’s noise reduction capabilities and its impact on overall vehicle emissions.
1. Sound Attenuation
Sound attenuation is a primary function of an exhaust component designed to reduce noise levels. This reduction is a crucial aspect of vehicle operation, affecting driver comfort, regulatory compliance, and overall environmental impact. The effectiveness of this attenuation is determined by its internal design and materials.
- Internal Baffle Design
The internal configuration, often involving a series of baffles or chambers, plays a pivotal role in sound attenuation. These internal structures redirect and reflect sound waves, causing them to interfere with each other and diminish in intensity. For example, a series of strategically placed baffles can effectively cancel out specific frequencies, leading to a more subdued exhaust note. The design parameters, such as baffle size, shape, and spacing, are critical for achieving optimal sound reduction.
- Acoustic Absorption Materials
Certain designs incorporate acoustic absorption materials, such as fiberglass packing or specialized woven fabrics, to further dampen sound waves. These materials absorb sound energy, converting it into heat and reducing the amplitude of the sound waves as they pass through the component. The type and density of the acoustic absorption material directly affect the frequency range and overall effectiveness of sound attenuation.
- Resonance Chamber Tuning
Resonance chambers are specifically tuned cavities within the component designed to target and cancel out specific resonant frequencies within the exhaust system. By carefully adjusting the size and shape of these chambers, engineers can effectively eliminate droning sounds and unwanted noise peaks, resulting in a smoother and more pleasant exhaust note. This tuning process requires precise calculations and experimental validation to achieve optimal results.
- Material Density and Thickness
The material used and its thickness significantly impacts its ability to dampen sound. Denser materials like heavier-gauge steel provide better sound absorption and reduce vibrations that contribute to noise. Thicker materials provide more surface area for sound waves to interact with, leading to increased attenuation. The choice of material and its thickness are crucial for balancing sound attenuation with durability and weight considerations.
These facets of sound attenuation highlight the intricate design and engineering considerations involved in creating an effective exhaust component. The interplay between internal structure, acoustic absorption, and material properties determines the overall noise reduction performance, impacting vehicle sound characteristics and regulatory compliance.
2. Exhaust Flow
Exhaust flow, referring to the rate at which exhaust gases are expelled from an engine, significantly influences performance characteristics and interacts directly with components designed to manage exhaust noise, including certain types of aftermarket components. Its optimization is a crucial aspect of engine tuning and overall vehicle performance.
- Diameter and Restriction
The internal diameter of an aftermarket component, and the presence of any internal obstructions, directly affects exhaust flow. A larger diameter generally allows for greater flow, potentially reducing backpressure and improving engine output. However, overly large diameters can reduce exhaust velocity, negatively impacting scavenging effects. The internal structure, designed for sound attenuation, introduces a level of restriction. The challenge lies in balancing sound control with the need for efficient exhaust evacuation.
- Backpressure Impact
Backpressure, the resistance to exhaust flow, is a critical consideration. Excessive backpressure can impede engine performance by hindering the efficient expulsion of exhaust gases from the cylinders. Aftermarket components often aim to reduce backpressure compared to stock systems, but the specific design impacts the degree of reduction. Achieving a suitable balance is essential for optimizing power output and fuel efficiency. The internal design should minimize turbulence and flow restrictions while effectively damping sound.
- Scavenging Effect
Exhaust scavenging refers to the process of using the momentum of exiting exhaust gases to help draw out remaining gases from the combustion chamber. Properly tuned exhaust systems can enhance this scavenging effect, leading to improved cylinder filling and increased engine efficiency. The design and configuration of components influence scavenging. Careful consideration of pipe length and diameter, as well as the internal structure, is necessary to maximize scavenging benefits.
- Gas Velocity and Temperature
Exhaust gas velocity and temperature also influence the efficiency of the exhaust system. Maintaining sufficient velocity is crucial for promoting effective scavenging and reducing the risk of condensation buildup. Excessive heat can contribute to thermal stress and component degradation. Balancing gas velocity, temperature, and sound attenuation requires careful engineering design. Alterations to the exhaust system, including the installation of certain components, can affect both velocity and temperature, potentially impacting performance and durability.
The connection between exhaust flow and aftermarket components underscores the importance of a comprehensive understanding of exhaust system dynamics. Optimizing flow characteristics, minimizing backpressure, and enhancing scavenging are all essential considerations for achieving desired performance gains while maintaining acceptable noise levels. Selection and installation should be guided by a thorough understanding of the engine’s operating characteristics and the intended application.
3. Backpressure Reduction
An automotive exhaust component known for sound attenuation frequently achieves this reduction in backpressure as a secondary design characteristic. Backpressure, defined as the resistance to exhaust gas flow, inherently increases within an exhaust system due to restrictions from catalytic converters, resonators, and particularly, the sound-damping structure of conventional mufflers. Certain aftermarket exhaust components, through their internal design, minimize this resistance compared to stock systems.
The connection arises because the design prioritizes a balance between sound control and exhaust gas flow. For instance, a straight-through design, often employed in performance applications, reduces backpressure significantly by allowing exhaust gases to pass through with minimal impediment. However, this approach typically results in a louder exhaust note. In contrast, a chambered design, while effective in sound attenuation, usually introduces more backpressure due to the redirection of exhaust gases through various internal chambers. Real-world examples can be observed when comparing dyno test results of vehicles with stock exhaust systems versus those equipped with these components. These tests often reveal a measurable increase in horsepower and torque, attributable in part to reduced backpressure.
Understanding the relationship between backpressure reduction and sound attenuation allows for a more informed selection of components for specific automotive applications. While a significant reduction in backpressure can yield performance benefits, it may come at the expense of increased noise levels. The practical significance lies in achieving an optimal balance between performance, sound characteristics, and regulatory compliance. Careful consideration of the engine’s specific requirements and the intended use of the vehicle is crucial in selecting the appropriate exhaust component. Further research into specific designs and their documented performance characteristics is recommended prior to purchase and installation.
4. Material Durability
Material durability is paramount in the context of aftermarket exhaust components, directly influencing longevity, performance consistency, and overall value. These components are subjected to extreme operating conditions, including high temperatures, corrosive exhaust gases, and exposure to environmental elements such as road salt and moisture. Consequently, the choice of material significantly dictates the component’s ability to withstand these stresses and maintain its structural integrity over time. Premature failure due to corrosion or fatigue can lead to exhaust leaks, reduced performance, and the need for costly replacements. A component constructed from lower-grade steel, for example, might exhibit signs of rust and degradation within a relatively short period, particularly in regions with harsh climates, thereby negating any potential initial cost savings. Conversely, a component manufactured from a high-grade stainless steel alloy will demonstrably resist corrosion, maintaining its structural integrity and sound characteristics for an extended duration.
The selection of materials also affects the component’s acoustic properties. As a material degrades, its ability to effectively dampen sound waves can diminish, resulting in an undesirable increase in exhaust noise. Material choice influences both the initial sound quality and its long-term consistency. Examples of durable materials well-suited for these applications include 304 stainless steel and aluminized steel. 304 stainless steel offers superior corrosion resistance, making it ideal for environments with high levels of road salt or humidity. Aluminized steel provides a cost-effective alternative with reasonable corrosion resistance, suitable for milder climates. Ultimately, the material selection should align with the intended application, environmental conditions, and budget constraints. Incorrect selection results in a diminished life-span and can significantly impact performance.
In summary, material durability is a non-negotiable factor in assessing the value and suitability of any exhaust component designed for sound attenuation. The choice of material directly impacts its lifespan, performance consistency, and resistance to environmental factors. While cost may be a consideration, prioritizing durable materials translates to long-term savings and ensures that the component continues to perform as intended throughout its service life. The challenge remains in balancing material costs with performance requirements to achieve an optimal outcome.
5. Installation Complexity
The installation of an aftermarket exhaust component presents varying degrees of complexity, directly influencing both the time required for the task and the skill level necessary for successful completion. These challenges extend beyond basic mechanical aptitude, often requiring specialized tools, modifications to existing vehicle structures, or a detailed understanding of exhaust system dynamics. The nature of these difficulties varies depending on the vehicle model, the design of the component, and the presence of pre-existing modifications.
- Direct-Fit vs. Universal Applications
Direct-fit components are designed for specific vehicle models, promising a simplified installation process with minimal modifications. These kits typically include all necessary hardware and are engineered to align with existing mounting points. Conversely, universal components require significant modifications to the vehicle’s exhaust system, including cutting, welding, and custom fabrication. This necessitates advanced skills and specialized equipment, significantly increasing the complexity of the installation. A direct-fit component for a common passenger vehicle might be installed in a few hours with basic tools, while a universal component on the same vehicle could require several days of labor and the expertise of a skilled fabricator.
- Welding Requirements
Certain installations necessitate welding to securely connect the component to the existing exhaust system. Welding requires specialized equipment, safety precautions, and proficiency in various welding techniques. Improper welding can result in exhaust leaks, structural weaknesses, and potential safety hazards. Even experienced mechanics may encounter challenges when welding dissimilar metals or working in confined spaces. Installations involving welding inherently increase the level of complexity and demand a higher degree of technical expertise.
- Modification of Existing Components
In some instances, the installation may necessitate modifications to existing vehicle components, such as cutting or relocating exhaust hangers, heat shields, or even sections of the vehicle’s frame. These modifications require careful planning, precise execution, and a thorough understanding of the vehicle’s structural integrity. Improper modifications can compromise the vehicle’s safety or performance, highlighting the need for experienced professionals to undertake such tasks. The complexity escalates significantly when modifications extend beyond basic bolt-on procedures.
- Tools and Equipment
The successful installation relies heavily on the availability of appropriate tools and equipment. Standard hand tools may suffice for basic installations, but more complex tasks often require specialized tools such as exhaust pipe cutters, welders, oxygen sensors socket sets, and diagnostic equipment for identifying and resolving potential issues. The lack of access to these tools can significantly impede the installation process and potentially lead to damage to the vehicle or the component. A comprehensive toolkit is essential for navigating the challenges associated with complex installations.
These facets collectively underscore the importance of assessing the installation complexity prior to purchasing an aftermarket exhaust component. While the allure of enhanced performance or sound may be strong, the potential challenges associated with installation should not be underestimated. Seeking professional assistance from qualified mechanics or exhaust specialists is often the prudent course of action, ensuring a safe, reliable, and properly functioning exhaust system. Failure to adequately address these considerations can result in costly repairs, diminished performance, or even safety hazards.
6. Vehicle Compatibility
Vehicle compatibility is a critical determinant in the selection and effective operation of exhaust components. The successful integration of an aftermarket component into a vehicle’s exhaust system hinges on precise adherence to specifications and design parameters that align with the target vehicle’s make, model, and year.
- Exhaust Port Alignment
The flange and exhaust port alignment must precisely match the vehicle’s exhaust manifold or catalytic converter. Mismatched port configurations can lead to exhaust leaks, reduced engine performance, and potential damage to the exhaust system. A variance, even minimal, requires modification, thereby compromising the ease of installation and potentially voiding the component’s warranty. The correct alignment ensures a secure, leak-free seal and optimal exhaust gas flow.
- Mounting Point Correspondence
The mounting points on the aftermarket component must correspond with the existing hangers and mounting brackets on the vehicle’s chassis. Incompatible mounting points necessitate custom fabrication or modification, increasing installation complexity and potentially affecting the component’s stability and durability. Proper mounting is essential for preventing excessive vibrations and stress on the exhaust system, which can lead to premature failure. Incorrect placement can create undue stress causing breaks, and potential safety issues.
- Pipe Diameter Compatibility
The diameter of the component’s inlet and outlet pipes must be compatible with the vehicle’s existing exhaust piping. Mismatched pipe diameters can restrict exhaust flow, negatively impacting engine performance and fuel economy. Adapters or modifications may be required to bridge the gap between incompatible pipe sizes, but these solutions can introduce additional restrictions and potential leak points. Optimal exhaust gas flow is predicated on a consistent and appropriately sized pipe diameter.
- Sensor Compatibility
Some aftermarket components may require the relocation or adaptation of oxygen sensors or other exhaust-related sensors. Incompatibility with these sensors can trigger check engine lights, affect engine management systems, and compromise emissions control. Ensuring sensor compatibility is crucial for maintaining proper engine operation and avoiding regulatory violations. Careful consideration should be given to the sensor placement and configuration to ensure accurate readings and optimal engine performance.
The aspects of vehicle compatibility collectively underscore the importance of verifying fitment prior to purchase and installation. Incorrect fitment can result in significant performance penalties, potential engine damage, and increased installation costs. Rigorous adherence to manufacturer specifications and a thorough understanding of the vehicle’s exhaust system are essential for a successful installation.
7. Performance Enhancement
Performance enhancement, in the context of aftermarket exhaust components, centers on increasing engine output and efficiency. This enhancement typically manifests as improved horsepower, torque, and throttle response. Certain designs, prioritizing reduced backpressure, can contribute to such gains by facilitating a more efficient evacuation of exhaust gases from the engine’s cylinders. The effectiveness of this contribution, however, is heavily dependent on the specific engine configuration, the overall exhaust system design, and the extent to which the component is matched to the vehicle’s operating parameters. For example, a high-performance engine with a restrictive stock exhaust system may experience a noticeable improvement in power after the installation of a less restrictive component. In contrast, an engine already equipped with a well-designed exhaust system may exhibit minimal performance gains from a simple component replacement.
Furthermore, the perceived enhancement may not always align directly with measurable performance increases. Subjective improvements, such as a more aggressive exhaust note or a more responsive feel, can influence the driver’s perception of performance even in the absence of substantial dyno-proven gains. A balanced design optimizes exhaust flow while maintaining acceptable noise levels. Practical application involves matching the component’s characteristics with the specific needs of the vehicle and the driver’s preferences. This matching entails careful consideration of factors such as engine displacement, intended use (street, track, etc.), and desired sound profile.
In summary, the linkage to performance enhancement is nuanced and multifaceted. While certain designs can contribute to measurable gains in power and efficiency, the extent of these gains is contingent on a variety of factors. Understanding the interplay between exhaust flow, backpressure, engine characteristics, and subjective perception is crucial for making informed decisions regarding aftermarket exhaust modifications. Prioritizing quantifiable data, such as dyno results, and considering the overall system design are essential for achieving genuine and lasting performance improvements.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following addresses prevalent inquiries concerning the functionality, application, and implications of this aftermarket exhaust component.
Question 1: What is the primary function?
The primary function is to reduce the noise level of an engine’s exhaust. It achieves this through internal baffling or absorption techniques, altering sound waves as they pass through the system. The aim is to produce a more controlled and often deeper exhaust tone compared to open exhaust systems.
Question 2: Does it improve engine performance?
Performance gains are variable. A less restrictive design may reduce backpressure, potentially increasing horsepower and torque. However, the extent of these gains is dependent on the engine’s characteristics and overall exhaust system design. In some instances, performance improvements may be negligible.
Question 3: How does it compare to a chambered component?
Chambered components typically redirect exhaust gases through a series of internal chambers, resulting in greater sound attenuation but potentially increased backpressure. These components, in contrast, often employ a more direct flow path, prioritizing reduced backpressure at the expense of some sound control.
Question 4: What materials are commonly used in construction?
Common materials include aluminized steel and stainless steel. Stainless steel provides superior corrosion resistance, making it a more durable option for environments exposed to road salt or harsh weather. Aluminized steel offers a cost-effective alternative with reasonable corrosion protection.
Question 5: Is professional installation required?
Installation difficulty varies. Direct-fit components are designed for relatively straightforward installation, while universal components may require welding or fabrication, necessitating professional expertise. Improper installation can lead to exhaust leaks, reduced performance, and potential safety hazards.
Question 6: How does it affect vehicle emissions?
As a component downstream of the catalytic converter, it generally does not directly affect vehicle emissions. However, any modifications to the exhaust system must comply with local regulations. Tampering with emissions control devices is illegal and can result in fines.
These questions and answers provide a foundational understanding of this component. Further investigation into specific models and their documented performance characteristics is recommended before making a purchase.
The next section explores common misconceptions and provides clarity on the perceived advantages and disadvantages.
Concluding Remarks on the Exhaust Component
This exploration has illuminated the diverse facets of the component in question, specifically its role within an automotive exhaust system. Key considerations have included its capacity for sound attenuation, influence on exhaust flow, material durability, installation complexity, and the crucial aspect of vehicle compatibility. A thorough understanding of these attributes is essential for informed decision-making when seeking to modify or upgrade a vehicle’s exhaust system.
The integration of an exhaust component is a matter of balancing performance objectives with practical considerations. As technologies evolve and regulatory standards become more stringent, continuous evaluation and adaptation are essential. Further research and critical analysis are vital for both automotive professionals and enthusiasts seeking to maximize the benefits while mitigating potential drawbacks. Responsible implementation remains paramount.