The compromised integrity of an exhaust silencing device, resulting in altered auditory emissions, is a common automotive issue. A breach in this component typically leads to a noticeable increase in the sound level emanating from the vehicle’s exhaust system, often characterized by a louder, raspier tone. For instance, a small perforation may initially produce a whistling sound that evolves into a more pronounced rumble as the damage expands.
Addressing this problem is essential not only for maintaining compliance with noise regulations but also for ensuring optimal vehicle performance and fuel efficiency. Historically, the design and materials used in these silencing devices have evolved to balance sound reduction with minimal restriction of exhaust flow. Early detection and repair prevent further deterioration, safeguarding the entire exhaust system from potential damage and costly replacements. This directly contributes to a vehicle’s longevity and overall operational cost-effectiveness.
The following sections will delve into the specific causes of exhaust system damage, methods for identifying such issues, and the appropriate repair or replacement procedures. Understanding these factors empowers vehicle owners to proactively manage their vehicle’s maintenance and avoid potentially disruptive and expensive complications.
Mitigating Exhaust System Noise
Proactive maintenance and timely intervention are paramount in addressing alterations in exhaust system acoustics. The following tips offer actionable guidance for identifying and resolving issues stemming from compromised exhaust components.
Tip 1: Regularly Inspect the Exhaust System. Conduct visual assessments of the exhaust system, including the silencing device, at regular intervals, ideally during routine vehicle maintenance. Look for signs of corrosion, rust, or physical damage. Early detection of such issues facilitates timely intervention and prevents further deterioration.
Tip 2: Listen for Unusual Noises. Pay close attention to the sounds emanating from the exhaust system during vehicle operation. A sudden increase in noise level, a rasping sound, or an unusual whistling noise may indicate the presence of a breach in the system’s integrity. Prompt investigation is warranted.
Tip 3: Check for Exhaust Leaks. With the engine running, carefully inspect the exhaust system for leaks. Exercise caution to avoid contact with hot surfaces. A detectable leak can be indicative of a perforation or a compromised seal. Utilize soapy water applied to suspected areas; the presence of bubbles suggests a leak point.
Tip 4: Monitor Fuel Efficiency. A decrease in fuel efficiency may be a symptom of a compromised exhaust system. Altered exhaust flow can negatively impact engine performance, leading to increased fuel consumption. A decline in mileage should prompt a thorough inspection of the exhaust system.
Tip 5: Address Issues Promptly. Upon identifying a problem with the exhaust system, seek professional assistance without delay. Neglecting minor damage can lead to more extensive and costly repairs down the line. Timely repairs preserve the integrity of the system and prevent further complications.
Tip 6: Consider Material Quality during Replacement. When replacing exhaust components, opt for high-quality materials and reputable manufacturers. Durable materials offer greater resistance to corrosion and physical damage, extending the lifespan of the exhaust system and minimizing the need for frequent repairs.
Adhering to these guidelines will significantly contribute to maintaining optimal exhaust system performance, minimizing noise pollution, and ensuring continued compliance with regulatory standards. Proactive measures are essential in safeguarding a vehicle’s operational efficiency and longevity.
The subsequent sections will explore the environmental impact of compromised exhaust systems and outline best practices for responsible vehicle maintenance.
1. Increased Noise Level
A direct and measurable consequence of a compromised exhaust silencing device is a discernible increase in the auditory emissions produced by a vehicle. The presence of a breach, regardless of size, alters the intended exhaust flow dynamics. This alteration bypasses the internal baffles and chambers designed to attenuate sound waves, leading to a more pronounced and often less refined exhaust note. For example, a vehicle designed to produce 70 decibels at idle may exhibit levels exceeding 80 decibels with even a small perforation in the muffler. The magnitude of the increase typically correlates with the size and location of the breach within the exhaust system. This amplification constitutes a primary symptom of the underlying problem and a significant indicator of the exhaust system’s compromised state.
The increased noise level is not merely an auditory annoyance; it has practical and regulatory ramifications. Elevated noise levels can violate local noise ordinances, leading to fines or citations. Furthermore, prolonged exposure to excessive noise may contribute to driver fatigue and auditory discomfort, potentially affecting driver safety. Repair facilities often utilize sound level meters as a diagnostic tool to quantify the degree of compromise within the exhaust system. Analyzing the specific frequency characteristics of the amplified sound can further pinpoint the location and nature of the damage, thereby guiding the repair process effectively. Real-world examples include residential areas with strict noise regulations where residents commonly report vehicles with faulty exhaust systems to authorities.
In summary, the heightened auditory output is a critical manifestation of exhaust system compromise. Its significance extends beyond a mere increase in volume, impacting regulatory compliance, driver well-being, and diagnostic procedures. Recognizing the correlation between a breach in the silencing device and the resulting amplified noise is crucial for prompt identification, diagnosis, and remediation of the underlying issue. Addressing this symptom efficiently mitigates potential legal penalties, enhances driver comfort, and restores the vehicle’s operational integrity.
2. Exhaust System Corrosion
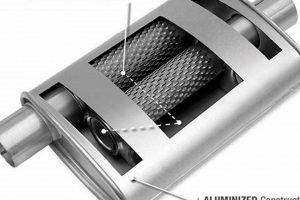
Exhaust system corrosion represents a primary causative factor in the development of breaches within silencing devices, subsequently leading to the audible phenomenon associated with compromised mufflers. The persistent exposure to high temperatures, moisture, and corrosive byproducts of combustion accelerates the degradation of the metallic components of the exhaust system. This degradation manifests as rust, pitting, and eventual perforation, effectively creating pathways for uncontrolled exhaust gas expulsion. The presence of road salts, particularly in colder climates, significantly exacerbates this corrosion process. For instance, vehicles operating in regions that employ de-icing salts on roadways often exhibit accelerated rates of exhaust system corrosion compared to vehicles in arid environments. This corrosion weakens the structural integrity of the muffler, rendering it susceptible to the development of openings and the alteration of its intended acoustic dampening properties. Therefore, exhaust system corrosion directly contributes to the emergence of undesired auditory emissions, establishing a clear cause-and-effect relationship.
The importance of addressing exhaust system corrosion lies in its preventative role. Early detection and mitigation of corrosion impede the formation of breaches that result in elevated noise levels. Techniques such as the application of rust inhibitors, protective coatings, and regular cleaning of the exhaust system can significantly extend its lifespan. Material selection also plays a critical role; stainless steel and aluminized steel offer enhanced resistance to corrosion compared to traditional carbon steel. Regular inspections, particularly in regions prone to road salt usage, are crucial for identifying and addressing corrosion before it progresses to the point of muffler compromise. The practical significance of this understanding is evident in the reduced repair costs and extended service life of vehicles that undergo proactive corrosion management.
In summary, exhaust system corrosion stands as a pivotal element in the pathogenesis of muffler breaches and the resultant auditory disturbances. Recognizing the causative link between corrosion and the compromised state of exhaust silencing devices necessitates a proactive approach to vehicle maintenance. By implementing preventative measures and selecting corrosion-resistant materials, vehicle owners can effectively mitigate the risk of premature exhaust system failure, thereby maintaining regulatory compliance and reducing the incidence of undesired auditory emissions. The integration of corrosion management strategies represents a cost-effective and environmentally responsible approach to vehicle ownership.
3. Reduced Engine Efficiency
A compromised exhaust system, indicated by the presence of extraneous auditory emissions, can correlate directly with reduced engine efficiency. The design of the exhaust system is not solely for noise reduction; it is an integral component of the engine’s overall functionality. The creation of a breach, typically manifesting in increased noise levels, disrupts the carefully calibrated backpressure necessary for optimal combustion and scavenging of exhaust gases. A disruption in the exhaust flow can affect the volumetric efficiency of the engine, leading to incomplete combustion and a subsequent decrease in power output and fuel economy. For example, a vehicle with a noticeable breach may experience a decrease in miles per gallon due to the engine compensating for the altered exhaust dynamics. The severity of the efficiency reduction is contingent upon the size and location of the breach, as well as the engine’s design.
The impact on engine efficiency extends beyond fuel consumption. Incomplete combustion increases the production of harmful emissions, contributing to environmental pollution and potentially leading to catalytic converter damage over time. The catalytic converter, designed to reduce harmful emissions, functions optimally within a specific exhaust gas temperature range. A compromised exhaust system can alter these temperatures, decreasing the converter’s effectiveness and potentially causing premature failure. Furthermore, the altered exhaust flow can impact the performance of other engine components, such as oxygen sensors, which rely on accurate exhaust gas readings to regulate the air-fuel mixture. The ripple effect underscores the interconnectedness of engine components and the importance of maintaining a properly functioning exhaust system.
In conclusion, the auditory indication of a compromised exhaust silencing device serves as a critical warning sign, signaling potential reductions in engine efficiency. The connection between noise emissions and engine performance highlights the need for prompt diagnosis and repair. Addressing the breach not only restores the intended acoustic characteristics of the vehicle but also ensures optimal engine operation, minimizing fuel consumption, reducing harmful emissions, and preserving the longevity of critical engine components. Recognizing this interrelationship promotes responsible vehicle maintenance and contributes to both economic and environmental benefits.
4. Environmental Noise Pollution
Environmental noise pollution constitutes a significant concern in urban and suburban environments, and compromised exhaust systems contribute measurably to this pervasive issue. The proliferation of motor vehicles, particularly those emitting excessive noise due to defects, amplifies ambient sound levels, impacting human health and ecological balance.
- Increased Ambient Sound Levels
Compromised silencing devices elevate the overall background noise in affected areas. Constant exposure to elevated sound levels can lead to stress, sleep disturbances, and impaired cognitive function in humans. Wildlife also experiences adverse effects, with disrupted communication patterns and altered behavior. Real-world examples include residential neighborhoods near roadways where the cumulative effect of vehicles with exhaust defects raises the baseline noise level, impacting the quality of life for residents.
- Violation of Noise Ordinances
Many municipalities enact noise ordinances to regulate permissible sound levels, aiming to mitigate the adverse effects of noise pollution. Vehicles emitting excessive noise due to defects often violate these ordinances, subjecting owners to fines and legal penalties. The enforcement of noise ordinances aims to curtail excessive emissions from individual sources, thereby safeguarding the acoustic environment for the broader community. An example includes vehicles cited for exceeding decibel limits in designated quiet zones.
- Contribution to Urban Noise “Hotspots”
Concentrations of vehicles with defective exhaust systems can create localized noise “hotspots,” where sound levels are significantly higher than the surrounding areas. These hotspots often occur near intersections, traffic congestion points, and residential areas with heavy vehicle traffic. The cumulative effect of multiple vehicles emitting excessive noise creates an environment detrimental to human health and well-being. For instance, a busy intersection with numerous vehicles accelerating and decelerating, some with compromised exhaust systems, can generate a localized noise hotspot that exceeds acceptable sound levels.
- Psychological and Physiological Effects
Prolonged exposure to elevated noise levels, attributable in part to defective exhaust systems, can trigger a range of psychological and physiological effects. These effects include increased stress hormones, elevated blood pressure, and impaired concentration. Vulnerable populations, such as children and the elderly, are particularly susceptible to the negative consequences of noise pollution. Studies have demonstrated a correlation between chronic exposure to traffic noise and increased risk of cardiovascular disease. The impact underscores the importance of mitigating all sources of environmental noise pollution, including those stemming from vehicular defects.
The multifaceted impacts of excessive vehicular noise, emanating from compromised exhaust systems, underscore the imperative for proactive maintenance, stringent enforcement of noise ordinances, and the adoption of noise-reduction strategies in urban planning. Addressing this issue is essential for safeguarding public health, preserving environmental quality, and fostering a more sustainable and livable urban environment. The collective effort in mitigating vehicle-related noise pollution contributes to a broader initiative to reduce overall environmental noise pollution and its associated harms.
5. Vehicle Safety Implications
A compromised exhaust system, often signaled by unusual auditory emissions, presents a range of vehicle safety implications that extend beyond mere noise pollution. The presence of a breach, irrespective of its size, can lead to the intrusion of exhaust gases into the vehicle cabin. Exhaust gases contain carbon monoxide (CO), a colorless, odorless, and highly toxic gas. Prolonged exposure to even low concentrations of CO can result in headaches, dizziness, nausea, and, in severe cases, loss of consciousness or death. The accumulation of CO within the vehicle cabin poses a significant health risk to occupants, especially during extended periods of operation or when the ventilation system is set to recirculate air. Real-world examples include incidents where drivers have experienced CO poisoning while operating vehicles with compromised exhaust systems, leading to accidents or medical emergencies. Therefore, auditory indications of exhaust system defects serve as a critical warning sign necessitating immediate attention.
Furthermore, the altered exhaust flow resulting from a breach can impact the vehicle’s performance and handling characteristics. Specifically, a compromised exhaust system can affect engine backpressure, leading to reduced power output and diminished acceleration capabilities. This reduction in performance can be particularly hazardous in situations requiring rapid acceleration, such as merging onto highways or avoiding potential collisions. A vehicle struggling to accelerate due to exhaust system defects may create dangerous situations for both the driver and other road users. Additionally, structural damage to the exhaust system, such as a detached or hanging component, poses a physical hazard to the vehicle itself and surrounding vehicles. A dislodged exhaust component can strike the road surface, creating a potential obstruction or damaging the undercarriage of the vehicle. The connection between exhaust system integrity and vehicle performance underscores the importance of regular inspections and prompt repairs.
In summary, the auditory manifestation of a compromised exhaust system is not merely an annoyance but a crucial indicator of potential safety hazards. The risk of carbon monoxide poisoning, coupled with diminished vehicle performance and potential physical damage, necessitates a proactive approach to exhaust system maintenance. Addressing exhaust system defects promptly mitigates the risks associated with CO exposure, preserves optimal vehicle performance, and prevents structural damage. Recognizing the multifaceted safety implications of a compromised exhaust system promotes responsible vehicle ownership and contributes to enhanced road safety for all users. The prompt rectification of exhaust system issues is thus a paramount aspect of vehicle safety management.
6. Regulatory Non-Compliance
The acoustic signature of a compromised exhaust system directly correlates with potential breaches of established noise pollution regulations. The auditory emission stemming from a defective muffler serves as an immediate indicator of regulatory non-compliance, triggering scrutiny from enforcement agencies and potentially resulting in legal repercussions for vehicle owners.
- Violation of Noise Ordinances
Municipalities frequently enact ordinances to limit permissible noise levels produced by motor vehicles. The decibel output of a vehicle with a compromised exhaust system often exceeds these legal thresholds, leading to fines, citations, and requirements for immediate repair. Enforcement actions range from warnings to mandatory vehicle inspections, underscoring the legal obligation to maintain exhaust systems in compliance with noise standards. For example, many cities have noise limits, often during specific hours (e.g., after 10 PM), and vehicles with breached mufflers are highly likely to exceed these limits, leading to violations.
- State-Level Emissions Testing Failure
In regions requiring regular vehicle emissions testing, a defective exhaust system can lead to inspection failure. While the primary focus of emissions testing is on air pollutant levels, the presence of a significant exhaust leak or breach can negatively impact the accuracy of emissions readings and directly contribute to a failure. Failure to pass these tests prohibits vehicle registration renewal and mandates corrective action. For instance, certain states require vehicles to undergo bi-annual inspections, and a visible hole in the muffler, leading to unusual sounds, would automatically result in a failed inspection.
- Federal Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) Regulations
While primarily focused on manufacturers and vehicle importers, the EPA also enforces regulations regarding tampering with or disabling emissions control devices, which implicitly includes maintaining a functioning exhaust system. Modifying or neglecting exhaust system maintenance to the point of creating excessive noise can be construed as a violation of these regulations, potentially leading to federal penalties. Even if a vehicle initially complied with EPA standards at the time of manufacture, continued operation with a severely compromised muffler can be considered a form of tampering.
- Civil Liability and Nuisance Claims
Beyond direct legal penalties, operating a vehicle with an excessively loud exhaust system can expose owners to civil liability. Individuals or communities subjected to persistent noise disturbances may pursue legal action based on nuisance laws, seeking compensation for damages and injunctive relief to abate the noise. This legal avenue underscores the responsibility of vehicle owners to mitigate the negative impacts of their vehicles on the surrounding environment. For example, a neighborhood association could potentially sue a resident whose vehicle consistently violates local noise ordinances due to a defective muffler.
In summary, the distinct auditory signature associated with a compromised exhaust silencing device serves as a readily detectable indicator of regulatory non-compliance. The legal and financial ramifications associated with these violations extend beyond mere fines, encompassing vehicle registration restrictions, civil liability, and the potential for federal penalties. Proactive maintenance of exhaust systems remains paramount in ensuring compliance with noise pollution regulations and avoiding the legal consequences arising from excessive vehicular noise.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following addresses common inquiries regarding exhaust system breaches and their associated auditory manifestations.
Question 1: What specifically causes the sound alteration when there is a perforation in the muffler?
The sound alteration stems from the disruption of designed exhaust gas flow. Mufflers contain internal baffles and chambers that attenuate sound waves. A breach allows exhaust gases to bypass these noise-reducing elements, resulting in a louder, often raspier, sound.
Question 2: How can the location of an exhaust breach be determined?
A visual inspection of the exhaust system can reveal obvious perforations or corrosion. Running the engine and carefully listening for escaping exhaust gases, combined with the application of soapy water to suspected areas, can help pinpoint the source. Professional diagnostic tools, such as smoke testers and sound level meters, offer more precise localization.
Question 3: What are the potential consequences of ignoring the sound alteration of a hole in muffler?
Ignoring a compromised exhaust system can lead to increased noise pollution, regulatory violations, reduced fuel efficiency, diminished engine performance, and the risk of carbon monoxide intrusion into the vehicle cabin. Furthermore, neglecting minor damage can result in more extensive and costly repairs in the long term.
Question 4: Does the severity of the sound alteration directly correlate with the size of the breach?
Generally, a larger breach results in a more pronounced sound alteration. However, the location of the perforation also plays a significant role. A small breach near the muffler’s inlet may produce a more dramatic sound change than a larger breach near the outlet.
Question 5: Are there any temporary fixes for a breach in an exhaust system?
Temporary fixes, such as exhaust bandages or sealant compounds, may provide short-term sound reduction and prevent further corrosion. However, these solutions are not permanent and should only be considered as a means to safely operate the vehicle until a proper repair or replacement can be performed.
Question 6: What are the factors influencing exhaust system repair/replacement costs?
Exhaust system repair/replacement costs are influenced by the extent of the damage, the type of vehicle, the materials used in the replacement components, and the labor costs associated with the repair. Replacing the entire exhaust system is generally more expensive than repairing a localized breach. Selecting high-quality, corrosion-resistant replacement parts can increase the initial cost but reduce the likelihood of future issues.
Promptly addressing exhaust system defects ensures regulatory compliance, vehicle safety, and optimal performance.
The following section will summarize key aspects regarding maintaining optimal exhaust system function.
Conclusion
This discourse has elucidated the implications of a compromised exhaust silencing device, evidenced by the auditory signature of escaping exhaust gases. The presence of such a “hole in muffler sound” signifies a cascade of potential issues ranging from regulatory non-compliance and environmental noise pollution to compromised vehicle safety and reduced engine efficiency. The root causes, primarily corrosion and physical damage, necessitate diligent inspection and proactive maintenance.
Given the far-reaching consequences of neglecting a compromised exhaust system, it is imperative that vehicle owners and maintenance professionals prioritize the timely identification and remediation of such defects. The long-term benefits of maintaining a properly functioning exhaust system extend beyond mere noise reduction, encompassing environmental responsibility, vehicle longevity, and the safeguarding of occupant well-being. Therefore, sustained vigilance and decisive action remain essential for ensuring optimal vehicle operation and adherence to established standards.


![Fix: Why Do My Audio Messages Sound Muffled? [Quick Guide] Best Mufflers for Cars & Trucks | Performance, Sound & Durability Upgrades Fix: Why Do My Audio Messages Sound Muffled? [Quick Guide] | Best Mufflers for Cars & Trucks | Performance, Sound & Durability Upgrades](https://dnamufflers.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/01/th-508-300x200.jpg)
![Fix: Why *Do* My Headphones Sound Muffled on Chromebook? [SOLVED] Best Mufflers for Cars & Trucks | Performance, Sound & Durability Upgrades Fix: Why *Do* My Headphones Sound Muffled on Chromebook? [SOLVED] | Best Mufflers for Cars & Trucks | Performance, Sound & Durability Upgrades](https://dnamufflers.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/01/th-465-300x200.jpg)


