A crucial component in exhaust systems, this device works to reduce specific sound frequencies. It is engineered to cancel out unwanted noises generated by the engine’s combustion process, contributing to a quieter and more refined driving experience. For example, some models target droning sounds at cruising speeds, while others focus on mitigating harsh tones during acceleration.
The incorporation of this element offers multiple advantages. Beyond decreasing noise pollution, it can enhance overall vehicle comfort for both the driver and passengers. Historically, its development stemmed from growing demands for quieter vehicles and stricter noise regulations. Its presence signifies a commitment to both performance and environmental responsibility.
Understanding its function is essential for comprehending the complexities of vehicle exhaust systems. The succeeding sections will delve deeper into the specific types, installation considerations, and maintenance procedures related to this important element.
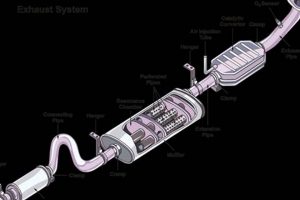
Muffler Resonator
Effective utilization of this exhaust component requires careful planning and adherence to best practices. The following tips outline key considerations for optimal performance and longevity.
Tip 1: Select Appropriate Type: Ensure compatibility with the vehicle’s make, model, and engine type. Aftermarket options vary in their construction and noise reduction capabilities; selecting the right one is critical. For instance, a performance-oriented vehicle might benefit from a straight-through design, while a daily driver may require a chambered model for maximum noise reduction.
Tip 2: Professional Installation: Installation by a qualified mechanic is strongly advised. Incorrect welding or mounting can compromise the resonator’s effectiveness and potentially damage the exhaust system. Misalignment could lead to leaks or excessive vibration.
Tip 3: Regular Inspection: Periodically inspect the component for signs of corrosion, damage from road debris, or loose connections. Early detection of issues can prevent more significant and costly repairs down the line. Check for rust, dents, or unusual sounds emanating from the exhaust system.
Tip 4: Consider Material Quality: Opt for models constructed from durable materials, such as stainless steel, to resist corrosion and extend lifespan. Lower-quality materials may degrade rapidly, requiring frequent replacements.
Tip 5: Evaluate Sound Profile: Before committing to a specific model, research its sound profile. Consider the desired noise level and tone, ensuring it aligns with personal preferences and local regulations. Online forums and product reviews can provide valuable insights.
Tip 6: Check Compatibility with Other Exhaust Components: Ensure the resonator integrates seamlessly with the existing exhaust system, including the catalytic converter and muffler. Incompatible components can hinder performance and potentially trigger error codes.
These considerations contribute to a well-functioning and compliant exhaust system. Following these guidelines can enhance vehicle performance, minimize noise pollution, and ensure long-term reliability.
The subsequent sections will address troubleshooting common issues and advanced customization options related to vehicle exhaust systems.
1. Noise Frequency Reduction
The primary function of this device centers on noise frequency reduction. This is achieved by targeting specific sound waves generated within the engine and exhaust system. These resonators are engineered with internal chambers designed to either reflect or absorb these waves, effectively canceling them out or diminishing their amplitude. The result is a noticeable decrease in overall exhaust noise levels, particularly at frequencies known to cause driver and passenger discomfort.
The effectiveness of noise frequency reduction is directly correlated with the resonator’s design and placement. Different chamber designs, such as Helmholtz resonators, are tailored to specific frequency ranges. Proper placement within the exhaust system ensures the resonator is positioned to optimally address the targeted noise. A poorly designed or positioned resonator will yield suboptimal noise reduction, potentially failing to meet regulatory standards or driver expectations. Some high-performance vehicles may employ multiple resonators, each calibrated to address a distinct set of frequencies, thus achieving a broader range of noise suppression without unduly restricting exhaust flow.
In summary, noise frequency reduction is not merely a feature but rather the defining purpose of this exhaust component. Its practical significance lies in creating a more pleasant driving experience, complying with noise regulations, and enhancing overall vehicle refinement. The ongoing challenge is to optimize resonator design and placement to achieve maximum noise reduction across a wider range of frequencies while minimizing any adverse impact on engine performance. This constant refinement ensures continued relevance in the automotive industry.
2. Exhaust Flow Optimization
Exhaust flow optimization is a critical aspect of engine performance, intrinsically linked to the design and function of exhaust system components. This optimization seeks to minimize backpressure and turbulence within the exhaust system, thereby maximizing engine efficiency and power output. The integration of a device designed to attenuate specific sound frequencies can significantly impact these flow characteristics.
- Resonator Design and Flow Restriction
The internal design of this component directly influences exhaust flow. Chambered resonators, while effective at noise reduction, can introduce flow restrictions due to their complex internal pathways. Straight-through designs, conversely, offer minimal flow obstruction but may compromise noise attenuation effectiveness. Striking a balance between noise reduction and flow optimization is a fundamental engineering challenge. For example, a poorly designed resonator can create backpressure that reduces engine horsepower, while an optimally designed unit can minimize this effect.
- Resonator Placement and Backpressure
The position of the component within the exhaust system also affects backpressure. Placing it too close to the engine can increase backpressure, especially in high-performance applications. Careful consideration of exhaust gas velocity and temperature is essential when determining the optimal location. Altering the placement can shift the point at which the device most effectively attenuates noise, but it must not come at the expense of generating excessive backpressure.
- Material and Surface Finish Considerations
The material used in constructing this component, and its internal surface finish, can impact exhaust flow. Rough internal surfaces can create turbulence, impeding flow. Polished surfaces and materials with low coefficients of friction can minimize this turbulence, improving exhaust scavenging. Stainless steel, often used in high-performance systems, offers both durability and a relatively smooth surface finish. The overall diameter must also be adequate to prevent bottlenecks in the system.
- Diameter and Matching to Engine Characteristics
The diameter should be appropriately sized for the engine’s displacement and power output. An undersized resonator can create a significant bottleneck, restricting exhaust flow and reducing engine performance. An oversized unit may not effectively attenuate noise frequencies. Matching the dimensions to the engine’s specific characteristics is vital for optimal performance. This often involves consulting with performance exhaust specialists or utilizing computational fluid dynamics (CFD) analysis during system design.
In conclusion, the relationship between this component and exhaust flow optimization is multifaceted. Design, placement, material selection, and diameter all play crucial roles in achieving the desired balance between noise reduction and engine performance. Thorough understanding of these factors is essential for maximizing the benefits of this device without compromising exhaust system efficiency.
3. Chamber Design Variation
The internal architecture of a device designed to attenuate specific sound frequencies, often referred to as a muffler resonator, is fundamentally defined by its chamber design. Chamber design variation directly influences the resonator’s effectiveness in canceling out specific sound frequencies and its impact on exhaust flow. Different chamber configurations, such as Helmholtz resonators, quarter-wave resonators, and straight-through perforated tubes with surrounding chambers, target different frequency ranges and offer varying degrees of flow restriction. For instance, a vehicle experiencing droning sounds at highway speeds might benefit from a Helmholtz resonator specifically tuned to cancel out those frequencies. Conversely, a high-performance application prioritizing minimal exhaust restriction might utilize a straight-through design, accepting a trade-off in noise reduction.
The practical significance of understanding chamber design variation lies in the ability to select the most appropriate resonator for a given application. An informed selection process, considering factors such as engine type, desired sound profile, and performance goals, is crucial for achieving optimal results. For example, an improperly designed chamber could either fail to adequately attenuate unwanted noise or create excessive backpressure, negatively impacting engine performance. Furthermore, the material used in constructing the chambers and the precision with which they are manufactured also contribute to the resonator’s overall performance. Certain designs might incorporate multiple chambers, each tuned to a different frequency range, to achieve a broader spectrum of noise reduction.
In conclusion, chamber design variation is not merely an aesthetic consideration but rather a critical determinant of a resonator’s acoustic and performance characteristics. Understanding the interplay between chamber design, target frequencies, exhaust flow, and material properties is essential for selecting and implementing effective exhaust solutions. The evolution of chamber designs continues to be driven by increasingly stringent noise regulations and the pursuit of enhanced vehicle performance, solidifying the importance of this area of research and development.
4. Material Durability Impact
The longevity and effectiveness of a device designed to attenuate specific sound frequencies within an exhaust system are inextricably linked to the materials used in its construction. The exhaust system environment presents a harsh combination of high temperatures, corrosive gases, and physical stresses, placing significant demands on material durability. Inadequate material selection directly impacts the resonator’s lifespan, performance consistency, and overall value.
- Corrosion Resistance
Exhaust gases contain corrosive compounds, including water vapor, sulfur oxides, and nitrogen oxides, which attack metallic components. Materials with inherent corrosion resistance, such as stainless steel (specifically grades 304 and 409), are preferred for resonator construction. Aluminized steel offers a lower-cost alternative, providing a protective aluminum coating over a steel substrate. However, once the aluminum coating is breached, the underlying steel is susceptible to corrosion. Premature failure due to corrosion can result in increased noise levels, exhaust leaks, and the need for costly replacements. A resonator constructed from low-grade steel, for example, might last only a year or two in regions with harsh winters and road salt usage, while a stainless steel unit could endure for a decade or more.
- Thermal Fatigue Resistance
Exhaust systems undergo rapid and significant temperature fluctuations during engine operation. These temperature cycles induce thermal stress in the resonator material, potentially leading to fatigue cracking and eventual failure. Materials with high thermal fatigue resistance, such as certain grades of stainless steel, are better equipped to withstand these cyclical stresses. Factors such as resonator design (e.g., weld quality and stress concentration points) also play a role in thermal fatigue performance. A poorly designed and constructed resonator, even if made from a relatively durable material, may still be prone to cracking in high-stress areas.
- Impact and Abrasion Resistance
Resonators are vulnerable to damage from road debris, such as rocks, gravel, and ice, particularly in exposed undercarriage locations. Materials with high impact and abrasion resistance are crucial for protecting the resonator from physical damage. Thicker gauge materials generally offer greater resistance to impact. Protective coatings, such as ceramic coatings, can also enhance abrasion resistance. A resonator located low to the ground is more susceptible to damage than one positioned higher up in the vehicle’s chassis. A simple speed bump could be detrimental for inferior materials.
- Weld Integrity and Material Compatibility
The integrity of welds is critical for maintaining the structural integrity of a resonator. Proper welding techniques and the use of compatible filler metals are essential for creating strong, durable joints. Incompatible materials can lead to galvanic corrosion at the weld interface. Furthermore, the heat-affected zone adjacent to the weld can exhibit altered mechanical properties, potentially weakening the joint. A cracked or failed weld can compromise the resonator’s ability to effectively attenuate noise and can lead to exhaust leaks. If improper welding processes are used or dissimilar metals are joined, corrosion cells can be set up, causing premature failures.
These facets of material durability highlight the complex interplay of environmental factors and material properties that dictate the service life of a resonator. Selecting resonators constructed from appropriate materials, employing sound engineering design principles, and adhering to proper installation practices are all essential for ensuring long-term performance and reliability. The initial investment in a higher-quality, more durable resonator can often outweigh the costs associated with frequent replacements and potential damage to other exhaust system components.
5. Placement System Effects
The location of an exhaust component designed to attenuate specific sound frequencies, fundamentally influences its operational effectiveness and the overall performance of the exhaust system. This relationship, termed “Placement System Effects,” considers how the position of this element impacts noise reduction, exhaust flow, and backpressure. The component’s proximity to the engine, its orientation relative to other exhaust components, and its distance from the tailpipe each contribute to the overall acoustic and performance characteristics of the vehicle. For example, locating the element too close to the engine may subject it to excessive heat, potentially reducing its lifespan or altering its sound-dampening properties. Conversely, positioning it too far downstream may diminish its ability to effectively cancel out certain frequencies.
Specific examples illustrate the significance of placement. In certain applications, positioning the component immediately after the catalytic converter can mitigate high-frequency noise emanating from the converter itself. Alternatively, incorporating a second, smaller unit near the tailpipe can target specific low-frequency “drone” often associated with aftermarket exhaust systems. Optimal placement often requires empirical testing and computational fluid dynamics (CFD) analysis to determine the ideal location for achieving the desired noise reduction and exhaust flow characteristics. Furthermore, the vehicle’s chassis design, available space, and the routing of other undercarriage components also constrain the possible locations for the resonator.
In conclusion, the “Placement System Effects” are a critical consideration in exhaust system design and modification. Understanding how the location of this component interacts with other exhaust elements, the engine, and the vehicle’s environment is essential for achieving optimal noise reduction and performance. Improper placement can negate the benefits of even the most well-designed component, while strategic placement can maximize its effectiveness and contribute to a refined and efficient vehicle. The challenges involved in optimizing placement underscore the need for careful engineering analysis and practical experimentation.
Frequently Asked Questions About Muffler Resonators
The following questions address common inquiries regarding muffler resonators, their function, and integration within vehicle exhaust systems. Each answer provides concise, factual information to enhance understanding of this component.
Question 1: What is the primary function of a muffler resonator?
The primary function is to attenuate specific sound frequencies generated by the engine and exhaust system, contributing to a quieter and more refined driving experience. It targets and cancels out undesirable noise, such as droning or harsh tones.
Question 2: How does a muffler resonator differ from a muffler?
While both reduce exhaust noise, a muffler typically targets a broader range of frequencies, whereas a resonator is designed to attenuate specific, often narrower, frequency bands. The muffler is the primary noise reduction device, while the resonator serves as a supplementary component.
Question 3: What factors influence the effectiveness of a muffler resonator?
Key factors include the resonator’s internal design (chamber type, size), its placement within the exhaust system, the materials used in its construction, and its compatibility with the engine and other exhaust components.
Question 4: Can a muffler resonator improve vehicle performance?
A properly designed and installed resonator can optimize exhaust flow, potentially leading to a marginal improvement in engine efficiency and power output. However, the primary benefit remains noise reduction. A poorly designed or installed resonator can, conversely, hinder performance.
Question 5: What are common signs of a failing muffler resonator?
Common indicators include increased exhaust noise, a change in exhaust tone (often a more pronounced droning sound), visible corrosion or damage to the resonator body, and potential exhaust leaks.
Question 6: Is professional installation of a muffler resonator recommended?
Professional installation is strongly recommended to ensure proper welding, mounting, and alignment within the exhaust system. Incorrect installation can compromise the resonator’s effectiveness and potentially damage other exhaust components.
These answers provide a foundational understanding of muffler resonators and their role in vehicle exhaust systems. Consult with a qualified mechanic for specific questions related to individual vehicle applications.
The succeeding section will delve into advanced customization and modification options related to vehicle exhaust systems and the role of this device within those modifications.
Concluding Remarks
The exploration herein has elucidated the function, design variations, and implications of “what is a muffler resonator” within vehicle exhaust systems. The analysis underscored the device’s role in attenuating specific sound frequencies, optimizing exhaust flow, and the critical considerations regarding material durability and system placement. Each of these aspects contributes significantly to the overall performance and acoustic characteristics of a vehicle.
The enduring relevance of understanding “what is a muffler resonator” lies in the automotive industry’s ongoing pursuit of refined vehicle performance and stringent noise mitigation. Further research and development in this area are essential for meeting future regulatory demands and enhancing the driving experience. Continued diligence in selecting and maintaining appropriate exhaust components remains paramount for ensuring long-term vehicle performance and environmental responsibility.



![[Guide] Muffler Sizing: Find The Right Size Muffler For Your Car Best Mufflers for Cars & Trucks | Performance, Sound & Durability Upgrades [Guide] Muffler Sizing: Find The Right Size Muffler For Your Car | Best Mufflers for Cars & Trucks | Performance, Sound & Durability Upgrades](https://dnamufflers.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/02/th-110-300x200.jpg)
![Richmond Muffler: Local Choice, Quiet Ride [Richmond, VA] Best Mufflers for Cars & Trucks | Performance, Sound & Durability Upgrades Richmond Muffler: Local Choice, Quiet Ride [Richmond, VA] | Best Mufflers for Cars & Trucks | Performance, Sound & Durability Upgrades](https://dnamufflers.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/02/th-108-300x200.jpg)