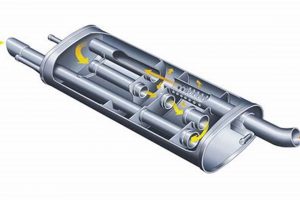
The component under discussion is a device designed to reduce the noise emitted from an internal combustion engine’s exhaust system. Specifically, it represents a high standard of quality and performance within its product category, implying superior noise reduction and durability. For example, a vehicle equipped with this type of exhaust component would exhibit a significantly quieter operation compared to those with standard or worn-out alternatives.
Its importance stems from its contribution to noise pollution reduction, enhanced driving comfort, and potential regulatory compliance. Benefits include a more pleasant auditory experience for both the vehicle occupants and the surrounding environment. Historically, improvements in these devices have mirrored advancements in engine technology and environmental awareness, leading to more efficient and effective designs over time. The evolution has focused on balancing noise reduction with minimal impact on engine performance and fuel efficiency.
The ensuing analysis will delve into various aspects related to this crucial vehicle component, including its construction materials, design variations, performance characteristics, and maintenance requirements. The subsequent sections will provide a detailed exploration of these elements, offering a comprehensive understanding of its role in modern automotive systems.
Guidance for Optimal Exhaust System Performance
The following recommendations are intended to maximize the lifespan and efficiency of exhaust systems, ensuring prolonged functionality and adherence to noise regulations.
Tip 1: Regular Inspections: Conduct routine visual examinations of the exhaust system. Look for signs of corrosion, physical damage (dents or punctures), and loose connections. Early detection of such issues prevents further degradation and costly repairs.
Tip 2: Prompt Repairs: Address any identified issues immediately. Delaying repairs can lead to more extensive damage, impacting engine performance and increasing noise levels. Welding or component replacement should be performed by qualified technicians.
Tip 3: Avoid Short Trips: Frequent short journeys can accelerate corrosion within the exhaust system. This is due to the incomplete evaporation of condensation, which contains corrosive byproducts of combustion. Opt for longer drives when possible to allow the system to reach optimal operating temperatures.
Tip 4: Use Quality Fuel: Employing high-quality fuel reduces the amount of contaminants entering the exhaust system. These contaminants can accelerate corrosion and damage catalytic converters, leading to increased noise and reduced efficiency.
Tip 5: Consider Protective Coatings: Applying heat-resistant coatings to the exhaust system can provide an additional layer of protection against corrosion and environmental damage. This is particularly beneficial in regions with harsh climates or salted roads.
Tip 6: Proper Installation: Ensure that all exhaust system components are correctly installed and aligned. Misalignment can cause stress on joints and connections, leading to premature failure and increased noise.
Tip 7: Monitor Exhaust Noise: Be attentive to any changes in exhaust noise. An increase in volume or the presence of unusual sounds may indicate a problem requiring professional attention.
Adherence to these guidelines contributes to a quieter, more efficient, and longer-lasting exhaust system, reducing environmental impact and maintaining vehicle performance.
The subsequent discussion will focus on specific techniques for diagnosing and resolving common exhaust system issues.
1. Superior Noise Reduction
Superior noise reduction constitutes a primary performance benchmark for a high-quality automotive exhaust component. This capability directly influences the acoustic environment, both within and surrounding the vehicle. The efficacy of such a device is measured by its ability to attenuate engine exhaust noise across a range of frequencies. Inferior noise reduction leads to increased noise pollution, affecting driver fatigue and potentially violating noise ordinances. For instance, vehicles operating in urban areas benefit significantly from enhanced noise reduction, minimizing disturbance to residents and pedestrians. The design and materials employed in the component’s construction dictate its noise-attenuating properties, with advanced designs incorporating multiple chambers and sound-absorbing materials to maximize effectiveness.
The practical significance of superior noise reduction extends beyond mere comfort. Reduced noise levels contribute to a more focused driving experience, potentially improving driver safety. Furthermore, adherence to noise regulations often necessitates the use of high-performance noise reduction components. Manufacturers frequently employ computational fluid dynamics (CFD) modeling to optimize designs for maximum noise attenuation while minimizing backpressure. Aftermarket performance upgrades often prioritize sound tuning, which is distinct from mere noise reduction, focusing instead on shaping the exhaust note to achieve a desired acoustic signature. However, even in performance applications, excessive noise can still be detrimental and may require the integration of additional sound-dampening technologies.
In summary, superior noise reduction represents a critical function of a high-performance exhaust component, influencing environmental impact, driver comfort, and regulatory compliance. While design and materials play a crucial role in achieving optimal noise attenuation, striking a balance between noise reduction and engine performance remains a significant engineering challenge. The ongoing development of advanced materials and designs promises continued improvements in exhaust noise reduction technology.
2. Durable Construction
Durable construction is a foundational characteristic of the specified exhaust component. The term “a 1 muffler,” implying top-tier quality, inherently necessitates robust materials and manufacturing processes to withstand the harsh operating environment of an exhaust system. This environment includes exposure to high temperatures, corrosive gases, road debris, and vibrational stress. The relationship is causal: inferior construction directly leads to premature failure, reduced noise reduction effectiveness, and increased maintenance costs. A component’s inability to resist these forces diminishes its value and compromises its intended function. For example, a stainless-steel exhaust component with welded seams is significantly more resistant to corrosion than a similar component constructed from mild steel with clamped connections.
The practical significance of durable construction is evident in the operational lifespan of the exhaust component. Systems crafted with high-grade materials and meticulous construction techniques require less frequent replacement and minimize the risk of catastrophic failure. This reduces both vehicle downtime and the overall cost of ownership. Furthermore, a structurally sound component maintains consistent noise reduction performance over time, ensuring continued compliance with noise regulations. Manufacturers often employ finite element analysis (FEA) during the design phase to optimize structural integrity and identify potential weak points. Surface treatments, such as ceramic coatings, can also enhance durability by providing an additional layer of protection against corrosion and heat damage. The adoption of advanced welding techniques, such as laser welding, further contributes to the creation of strong, leak-proof joints.
In conclusion, durable construction is an indispensable element of the referred exhaust system part. Its presence directly correlates with longevity, consistent performance, and reduced maintenance demands. The choice of materials, manufacturing processes, and protective treatments collectively determine the durability of the exhaust component, ultimately influencing its overall value and contributing to the reliable operation of the vehicle. Neglecting this aspect results in a compromised system that fails to meet the performance expectations implied by its designation.
3. Optimal Gas Flow
Optimal gas flow is a critical performance attribute inextricably linked to the quality and functionality of any high-performance exhaust component. A top-tier component, designated as “a 1 muffler,” must facilitate the efficient evacuation of exhaust gases from the engine. Restrictions in gas flow cause increased backpressure, resulting in reduced engine power, diminished fuel economy, and elevated operating temperatures. The relationship is fundamentally causal: impaired gas flow directly contributes to decreased engine performance. For instance, a poorly designed exhaust with constrictive bends or internal obstructions impedes gas velocity, negating any potential benefits of improved noise reduction or durable construction. The component’s internal geometry and the materials used in its construction dictate its capacity for facilitating optimal gas flow.
The practical significance of optimized gas flow is readily apparent in the performance characteristics of vehicles equipped with high-quality exhaust systems. Engines benefit from reduced pumping losses, allowing them to operate more efficiently and produce greater horsepower. In turbocharged engines, optimized exhaust flow is particularly crucial, as it minimizes turbine backpressure and allows the turbocharger to spool up more quickly. Manufacturers often employ computational fluid dynamics (CFD) to model and optimize exhaust system designs for minimal flow restriction. Aftermarket performance upgrades often prioritize gas flow optimization, utilizing larger diameter tubing, mandrel bends, and free-flowing mufflers to maximize engine output. However, striking a balance between gas flow, noise reduction, and regulatory compliance presents a significant engineering challenge. Excessive gas flow can lead to increased exhaust noise levels, potentially violating noise ordinances.
In summary, optimal gas flow represents an indispensable characteristic of a high-quality exhaust component. Its presence directly correlates with improved engine performance, enhanced fuel efficiency, and reduced operating temperatures. The design and construction of the exhaust component must prioritize the efficient evacuation of exhaust gases while simultaneously adhering to noise regulations. Compromising gas flow for the sake of noise reduction or cost savings ultimately diminishes the overall performance and value of the exhaust system. Continuing research and development efforts are focused on optimizing exhaust system designs to achieve the ideal balance between gas flow, noise attenuation, and environmental impact.
4. Corrosion Resistance
Corrosion resistance is a paramount attribute of any exhaust component aspiring to a high-quality designation. Exhaust systems are consistently exposed to a corrosive environment, making material selection and protective measures crucial for longevity and sustained performance.
- Material Composition and Selection
The choice of materials directly impacts the ability to resist corrosion. Stainless steel alloys, particularly grades 304 and 316, are commonly employed due to their inherent resistance to oxidation and chemical attack from exhaust gases. In contrast, mild steel, while more cost-effective, requires protective coatings to mitigate corrosion. The quality of the alloy, its chromium content, and the presence of other alloying elements significantly influence its corrosion resistance. Components designated “a 1 muffler” typically feature high-grade stainless steel or aluminized steel with robust protective coatings.
- Protective Coatings and Treatments
Protective coatings provide an additional barrier against corrosion. Aluminizing, ceramic coatings, and paint applications are common treatments. Aluminizing involves coating the steel with a layer of aluminum, which forms a protective oxide layer when exposed to air. Ceramic coatings offer exceptional heat resistance and corrosion protection, particularly in high-temperature areas of the exhaust system. The effectiveness of these coatings depends on their adherence to the substrate and their ability to withstand thermal cycling and mechanical abrasion. Premium exhaust components employ multi-layer coatings for enhanced durability.
- Welding Techniques and Seam Integrity
Welding is an integral part of exhaust system construction, and the quality of welds directly affects corrosion resistance. Poorly executed welds create points of weakness susceptible to corrosion, leading to premature failure. Gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW), also known as TIG welding, is often preferred for its precision and ability to create clean, corrosion-resistant welds. Proper seam preparation and the use of appropriate filler metals are essential for ensuring weld integrity. High-quality components undergo rigorous quality control inspections to verify weld soundness and corrosion resistance.
- Environmental Factors and Operational Conditions
The severity of the operating environment influences the rate of corrosion. Exposure to road salt, humidity, and extreme temperatures accelerates corrosion. Vehicles operating in coastal regions or areas with heavy snowfall are particularly susceptible. Furthermore, the type of fuel used and the engine’s operating conditions affect the composition of exhaust gases, influencing their corrosiveness. Components designed for severe operating conditions often incorporate additional corrosion-resistant features, such as thicker materials and more robust coatings.
The relationship between corrosion resistance and overall exhaust system performance is undeniable. An “a 1 muffler” designation implies a commitment to employing superior materials, protective treatments, and construction techniques to maximize resistance to corrosion. This, in turn, translates to extended lifespan, consistent performance, and reduced maintenance costs for the vehicle owner.
5. Precise Fitment
The concept of precise fitment is intrinsically linked to the definition of a high-quality automotive exhaust component. A device bearing the designation “a 1 muffler” implies adherence to exacting dimensional specifications, ensuring seamless integration with the vehicle’s existing exhaust system. This characteristic transcends mere convenience; it directly impacts performance, reliability, and safety.
- Dimensional Accuracy and Compatibility
Precise fitment begins with dimensional accuracy. A component intended as a direct replacement must conform to the original equipment manufacturer’s (OEM) specifications. Variations in length, diameter, or mounting point locations can lead to misalignment, exhaust leaks, and structural stress. Examples include flanges that fail to mate correctly, causing exhaust gas escape, or hangers that do not align with chassis mounting points, leading to premature system failure due to vibration. “A 1 muffler” demands strict adherence to dimensional tolerances.
- Ease of Installation and Reduced Labor Costs
A component designed for precise fitment streamlines the installation process. Reduced installation time translates directly to lower labor costs for the vehicle owner. Ill-fitting components necessitate modifications such as cutting, welding, or bending, adding to the complexity and expense of the repair. Such alterations can also compromise the structural integrity of the system. A component that aligns seamlessly with existing mounting points and requires no modification exemplifies precise fitment.
- Prevention of Exhaust Leaks and Safety Implications
Exhaust leaks pose significant safety risks. The escape of exhaust gases into the passenger compartment can lead to carbon monoxide poisoning, a potentially fatal hazard. Leaks also reduce engine performance and fuel efficiency. Precise fitment eliminates the gaps and misalignments that contribute to exhaust leaks. Components that seal properly at all connection points, without the need for excessive clamping force, demonstrate precise fitment and enhanced safety.
- Alignment with Existing Components and System Integrity
Precise fitment extends beyond individual components to encompass the entire exhaust system. A well-fitting component ensures proper alignment and support, minimizing stress on other parts of the system, such as catalytic converters and exhaust manifolds. Misalignment can cause premature wear, cracking, and failure of these components. A system where each component aligns and interfaces seamlessly contributes to overall system integrity and longevity, reflecting a high standard of engineering and manufacturing.
The commitment to precise fitment inherent in the designation “a 1 muffler” represents a dedication to quality, safety, and customer satisfaction. A component that installs easily, seals effectively, and aligns properly with existing components exemplifies the benefits of precise engineering and manufacturing. Conversely, a lack of precise fitment compromises performance, safety, and overall system integrity, undermining the value of the component.
6. Compliance Standards
Adherence to established compliance standards is intrinsically linked to the designation “a 1 muffler.” This designation signifies a product that not only meets but exceeds minimum performance and regulatory requirements. Therefore, understanding the relevant compliance standards is essential for assessing the quality and suitability of an exhaust component. This exploration delineates several facets of compliance standards and their implications for exhaust systems.
- Noise Emission Regulations
Noise emission regulations constitute a primary compliance area. Governmental bodies, such as the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in the United States and similar organizations globally, establish maximum permissible noise levels for vehicles. Exhaust components must be designed to attenuate engine noise to within these limits. Failure to comply can result in fines, vehicle recalls, and legal liabilities for manufacturers and owners. For example, some aftermarket exhaust systems, while enhancing engine performance, may exceed permissible noise levels, rendering them non-compliant in certain jurisdictions. “A 1 muffler” implies adherence to applicable noise emission standards.
- Emissions Control Compliance
Exhaust systems play a crucial role in emissions control. Components such as catalytic converters are designed to reduce harmful pollutants, including hydrocarbons, carbon monoxide, and nitrogen oxides. Compliance with emissions standards, such as those outlined in the Clean Air Act, is mandatory. Replacement exhaust components must not compromise the effectiveness of emissions control systems. Aftermarket components that remove or bypass catalytic converters are generally illegal and can result in severe penalties. “A 1 muffler” ensures compatibility with existing emissions control systems and adherence to relevant regulations.
- Safety Standards and Material Certification
Safety standards govern the structural integrity and fire resistance of exhaust components. Materials used in construction must meet specific requirements for heat resistance, corrosion resistance, and mechanical strength. Certifications, such as those provided by Underwriters Laboratories (UL), indicate that a component has been tested and meets established safety standards. Components that fail to meet safety standards can pose a fire hazard or compromise the structural integrity of the vehicle. “A 1 muffler” adheres to relevant safety standards and utilizes certified materials.
- International Standards and Harmonization
International standards, such as those developed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), promote harmonization and interoperability of exhaust components across different regions. Compliance with international standards facilitates trade and ensures that components meet minimum quality and performance requirements. These standards may cover aspects such as dimensions, materials, and testing procedures. “A 1 muffler” aligns with relevant international standards to ensure global compatibility and acceptance.
In conclusion, the designation “a 1 muffler” signifies more than just superior performance; it represents a commitment to meeting or exceeding applicable compliance standards. These standards encompass noise emissions, emissions control, safety, and international harmonization. Adherence to these standards is essential for ensuring the legality, safety, and environmental responsibility of exhaust systems. Choosing a component that meets these standards protects the vehicle owner from potential liabilities and contributes to a cleaner and safer environment.
7. Extended Lifespan
The characteristic of extended lifespan, when applied to a vehicle’s exhaust component, directly correlates with reduced maintenance costs, enhanced vehicle reliability, and minimized environmental impact. An exhaust system component designated as “a 1 muffler” inherently implies a design and construction intended to maximize its operational life. This expectation distinguishes it from lesser-quality alternatives with shorter service intervals.
- Material Selection and Degradation Rates
The choice of materials critically affects the degradation rate of an exhaust component. High-grade stainless steel, for example, exhibits superior resistance to corrosion and thermal fatigue compared to aluminized steel or mild steel. A component constructed from such materials will, under similar operating conditions, possess a significantly longer lifespan. Premature failure due to corrosion, cracking, or weld failure is less likely with high-quality materials.
- Design Optimization and Stress Reduction
The design of the exhaust component also influences its lifespan. Components with optimized flow paths and minimal stress concentrations are less susceptible to fatigue-related failures. Features such as reinforced welds, flexible couplings, and vibration dampers can mitigate stress caused by engine vibration and thermal expansion. A well-designed component distributes stress evenly, preventing localized failures and extending overall lifespan.
- Environmental Factors and Corrosion Protection
The operating environment significantly impacts exhaust system lifespan. Exposure to road salt, humidity, and extreme temperatures accelerates corrosion. Components with robust corrosion protection measures, such as multi-layer coatings and sacrificial anodes, exhibit greater longevity in harsh environments. A component designed for extended lifespan will incorporate these protective measures to minimize the effects of environmental factors.
- Manufacturing Precision and Quality Control
Precise manufacturing and rigorous quality control are essential for ensuring consistent component performance and extended lifespan. Components manufactured to tight tolerances are less likely to exhibit defects or premature failures. Quality control procedures, such as non-destructive testing and pressure testing, identify and eliminate substandard components before they reach the market. A component designated “a 1 muffler” undergoes stringent quality control to ensure reliable performance and extended lifespan.
In summary, extended lifespan in an exhaust component is not an isolated characteristic but rather the culmination of material selection, design optimization, corrosion protection, and manufacturing precision. An “a 1 muffler” embodies these principles, offering a durable and reliable solution that minimizes maintenance requirements, reduces environmental impact, and enhances the overall value proposition for the vehicle owner. The increased initial investment associated with such a component is typically offset by its longer service life and reduced risk of premature failure.
Frequently Asked Questions Regarding Premium Automotive Exhaust Components
This section addresses common inquiries concerning high-quality exhaust components, often referred to by a specific designation indicating superior performance and durability. The responses provided aim to clarify misconceptions and offer informed perspectives on the attributes and benefits associated with such products.
Question 1: What distinguishes a premium exhaust component from a standard alternative?
Premium exhaust components are characterized by superior materials, advanced design, stringent manufacturing processes, and rigorous quality control. These factors contribute to enhanced durability, optimized gas flow, reduced noise emissions, and extended lifespan compared to standard components.
Question 2: How does the material composition affect the performance and longevity of an exhaust system component?
Material composition is a critical determinant of performance and longevity. High-grade stainless steel offers superior resistance to corrosion and thermal fatigue compared to mild steel or aluminized steel. The choice of material directly impacts the component’s ability to withstand harsh operating conditions and maintain its structural integrity over time.
Question 3: What role does exhaust system design play in engine performance?
Exhaust system design significantly impacts engine performance by influencing gas flow and backpressure. Optimized designs minimize flow restrictions, reducing pumping losses and enhancing engine power output. Conversely, poorly designed systems can impede gas flow, leading to reduced performance and increased fuel consumption.
Question 4: Are aftermarket exhaust systems compliant with emissions regulations?
Compliance with emissions regulations varies depending on the specific component and jurisdiction. Aftermarket systems that remove or bypass catalytic converters are generally illegal and can result in significant penalties. Components designed as direct replacements for OEM parts are typically engineered to maintain compliance with emissions standards.
Question 5: How does noise reduction technology impact vehicle performance?
Noise reduction technology aims to minimize exhaust noise without compromising engine performance. Advanced designs incorporate multiple chambers, resonators, and sound-absorbing materials to attenuate noise while maintaining optimal gas flow. Poorly designed noise reduction systems can create excessive backpressure, reducing engine power.
Question 6: What maintenance practices can extend the lifespan of an exhaust component?
Regular inspections, prompt repairs, and the use of high-quality fuel can extend the lifespan of an exhaust component. Avoiding short trips, which promote condensation and corrosion, is also beneficial. Applying protective coatings can provide an additional barrier against environmental damage.
In summary, selecting a high-quality exhaust system component necessitates careful consideration of materials, design, compliance, and maintenance. Opting for a premium product ensures enhanced performance, extended lifespan, and adherence to regulatory requirements.
The subsequent section will explore specific techniques for diagnosing and resolving common exhaust system issues.
Concluding Remarks on Automotive Exhaust Excellence
The preceding analysis has underscored the multifaceted characteristics defining a high-caliber automotive exhaust component, often represented by the designation “a 1 muffler.” The exploration highlighted superior noise reduction, durable construction, optimal gas flow, corrosion resistance, precise fitment, compliance standards, and extended lifespan as crucial attributes. The integration of these elements contributes to enhanced vehicle performance, reduced environmental impact, and increased operational longevity.
The discerning vehicle owner or automotive professional must prioritize these factors when evaluating exhaust system components. The long-term benefits derived from selecting a component embodying these qualities extend beyond immediate performance gains, representing a prudent investment in vehicle reliability and environmental stewardship. Continued advancements in materials science and engineering promise further refinements in exhaust system technology, solidifying the importance of informed decision-making in this critical automotive domain. The selection of an appropriate exhaust system component thus remains a pivotal element in ensuring optimal vehicle operation and responsible environmental practices.