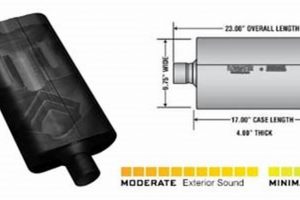
An automotive exhaust system component bearing a specific designation facilitates the reduction of engine noise and the channeling of exhaust gases away from the vehicle. These units are integral to maintaining acceptable noise levels and optimizing engine performance.
The importance of this component stems from its contribution to environmental regulations regarding noise pollution. Functionality includes reducing emissions and improving fuel efficiency through proper backpressure management, all of which contributes to the vehicle’s operational reliability and potentially extending its lifespan. Historically, designs have evolved to incorporate catalytic converters and other pollution control technologies.
The subsequent sections will delve into various aspects of aftermarket automotive exhaust systems, including factors to consider during purchase, installation procedures, and common maintenance practices to ensure optimal functionality and longevity. We’ll also consider key differentiators between standard and performance oriented designs.
Reyes Muffler
The following guidance assists in ensuring the longevity and optimal performance of exhaust system components.
Tip 1: Regular Inspection: Conduct routine visual inspections for signs of corrosion, rust, or physical damage. Early detection can prevent minor issues from escalating into major repairs.
Tip 2: Prompt Repair: Address any detected leaks or damage immediately. Exhaust leaks can impact fuel efficiency, engine performance, and pose safety risks.
Tip 3: Professional Installation: Ensure proper installation by a qualified technician. Incorrect installation can lead to premature failure and compromise performance.
Tip 4: Proper Mounting: Confirm all mounting points are secure and in good condition. Loose or damaged mounts can cause excessive vibration and stress on the system.
Tip 5: Material Selection: Consider the environmental conditions when selecting replacement components. Stainless steel offers superior corrosion resistance in harsh climates.
Tip 6: Avoid Short Trips: Minimize frequent short trips, as they contribute to moisture buildup in the exhaust system, accelerating corrosion.
Adhering to these recommendations contributes to the long-term reliability and effectiveness of exhaust systems, ensuring compliance and optimal vehicle operation.
The subsequent section will provide a summary of key considerations related to selection and maintenance of exhaust system components.
1. Noise Reduction
Attenuation of engine exhaust sound is a primary function accomplished through the implementation of carefully engineered internal structures. These structures manipulate sound waves to minimize the audible impact of engine operation.
- Internal Baffle Design
The arrangement of baffles within the housing dictates the degree of sound wave cancellation. Baffles redirect sound waves, causing them to collide and destructively interfere, thus reducing amplitude. An example involves a series of offset plates that force exhaust gases, and consequently sound waves, to traverse a tortuous path. This configuration leads to significant noise dampening. The configuration impacts both the intensity and frequency profile of the exhaust note.
- Resonator Chamber Volume
The size and shape of the resonator chamber are tuned to target specific frequencies prominent in engine exhaust noise. Resonator chambers act as Helmholtz resonators, canceling out certain frequencies. For instance, a resonator tuned to 120 Hz will effectively reduce the drone often associated with that frequency, commonly perceived during highway cruising. Mismatched volume leads to ineffective noise reduction or even amplification of undesired frequencies.
- Acoustic Absorption Materials
Utilization of materials engineered to absorb sound energy plays a critical role. These materials, often fiberglass or mineral wool, line the interior, converting sound energy into heat through friction. Example: Packing the internal chamber with densely packed fiberglass effectively dampens high-frequency sounds. Degradation or loss of these materials diminishes the component’s noise reduction effectiveness.
Collectively, the interplay of internal baffle design, resonator chamber volume, and acoustic absorption materials dictates the overall noise-reduction capability. Selection of components and design considerations are integral in achieving satisfactory acoustic performance, thereby balancing driver experience with regulatory compliance and public nuisance minimization. The aforementioned elements impact performance and require a well-thought strategy.
2. Exhaust Channeling
Effective exhaust channeling, the directed removal of combustion byproducts from the engine, directly relies on the design and integrity of exhaust system components. An improperly functioning component can impede optimal exhaust gas flow, leading to reduced engine performance and potential safety hazards. For instance, a damaged or corroded internal structure can create backpressure, hindering the engine’s ability to expel exhaust gases efficiently.
A properly designed unit facilitates laminar flow, optimizing engine efficiency and reducing harmful emissions. An integral component contributes to this functionality by providing a pathway for gases to travel away from the engine. The physical characteristics, such as pipe diameter, bend radius, and internal surface finish, influence the flow rate and pressure within the exhaust system. Selecting components with optimized channeling characteristics supports efficient combustion and emission control. A restriction can cause the engine to work harder, reduce fuel economy, and accelerate component wear.
The importance of exhaust channeling in overall vehicle performance cannot be overstated. A well-maintained and appropriately sized component ensures the efficient removal of exhaust gases, contributing to optimal engine operation, reduced emissions, and improved fuel economy. Conversely, a compromised component can lead to a cascade of problems, negatively impacting vehicle performance and potentially posing safety risks. Regular inspection and timely replacement of damaged parts are crucial for maintaining proper exhaust channeling and overall vehicle health.
3. Engine Performance
Engine performance, directly influenced by exhaust system efficiency, is intrinsically linked to the function of exhaust components. Optimizing exhaust flow is critical for maximizing power output, fuel economy, and minimizing harmful emissions. A properly functioning component contributes to this optimization; conversely, a restrictive or damaged unit can significantly impede engine operation.
- Backpressure Management
Exhaust systems create backpressure, a resistance to exhaust gas flow. A component designed to specific parameters manages this backpressure to optimize engine performance. Excessive backpressure reduces engine power and fuel efficiency; insufficient backpressure can lead to poor low-end torque. This balance is especially critical for turbocharged engines, where backpressure significantly impacts turbocharger performance. A properly selected unit will target backpressure characteristics that complement the engine’s design parameters.
- Exhaust Gas Scavenging
The design of the exhaust system, and specifically the component’s internal structure, can promote exhaust gas scavenging. Scavenging leverages pressure waves within the exhaust system to help draw exhaust gases out of the cylinders, improving combustion efficiency. Carefully tuned exhaust manifolds and the component can create a scavenging effect at specific engine speeds. This results in improved cylinder filling and enhanced power output. Poorly designed components impede this scavenging effect, diminishing overall engine performance.
- Catalytic Converter Efficiency
The placement and design of the exhaust component relative to the catalytic converter can affect its efficiency. Maintaining optimal operating temperatures for the catalytic converter is essential for proper emissions control. Exhaust components can contribute to this temperature management by influencing exhaust gas velocity and heat retention. A unit positioned too far from the engine can result in the catalytic converter not reaching its optimal operating temperature, leading to increased emissions. Proper placement and insulation are crucial for ensuring effective catalytic converter operation.
- Sound Wave Tuning
Performance-oriented exhaust components utilize sound wave tuning to enhance engine output. By carefully manipulating sound waves within the exhaust system, these units can create resonant effects that improve cylinder filling and exhaust gas scavenging. However, these effects are frequency-dependent and only beneficial within a specific engine speed range. Improper tuning can lead to detrimental effects on engine performance at other speeds. A well-tuned component enhances power output at a targeted RPM range, often at the expense of broader performance gains.
These elements exemplify the interplay between exhaust system design and engine performance. A carefully selected component, tailored to the engine’s specific needs, can optimize exhaust flow, improve combustion efficiency, and enhance overall power output. Conversely, a poorly chosen or damaged unit can significantly impede engine operation, reducing power, increasing emissions, and negatively impacting fuel economy.
4. Emission Control
The reduction of harmful pollutants released into the atmosphere is intrinsically linked to the design and functionality of exhaust systems. A component within this system plays a crucial role in minimizing emissions, often working in concert with catalytic converters and other pollution control devices. An improperly functioning unit can contribute to increased levels of carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons, and nitrogen oxides, exceeding regulatory limits and negatively impacting air quality. The effectiveness of emission control measures is directly influenced by the structural integrity and performance characteristics of exhaust components. For example, a compromised unit can disrupt the flow of exhaust gases, reducing the efficiency of the catalytic converter and leading to elevated pollutant levels.
Specific design features can enhance emission control performance. Internal baffling and resonance chambers are engineered to optimize exhaust gas flow and temperature, contributing to more efficient catalytic conversion. Furthermore, some component designs incorporate materials that promote the reduction of specific pollutants. For example, certain metal alloys exhibit catalytic properties, aiding in the conversion of harmful gases into less harmful substances. The selection of appropriate components and the maintenance of their operational integrity are essential for ensuring effective emission control. Aftermarket components are sometimes marketed as improving emissions, but their performance must be validated through independent testing to ensure compliance with regulatory standards.
In conclusion, the link between emission control and exhaust systems underscores the importance of proper component selection and maintenance. A functional component is crucial for minimizing harmful emissions and complying with environmental regulations. Challenges remain in optimizing exhaust system designs to balance emission control with engine performance and fuel efficiency. Further research and development in this area are necessary to address the evolving needs of the automotive industry and the growing concern for air quality. Continuous monitoring and adherence to emissions standards are critical for mitigating the environmental impact of vehicle operation.
5. Corrosion Resistance
Corrosion resistance is a critical performance attribute directly impacting the longevity and functionality of exhaust system components. Exposure to moisture, road salts, and high temperatures accelerates the degradation of metallic components, potentially leading to structural failure and compromised performance. Therefore, the selection of materials exhibiting superior resistance to corrosion is paramount in ensuring the long-term operational effectiveness of exhaust systems.
The operational lifespan of an exhaust system is significantly influenced by the material used in its construction. For example, stainless steel alloys offer enhanced protection against corrosion compared to traditional carbon steel. This increased resistance translates to extended service life, reduced maintenance requirements, and minimized risk of exhaust leaks or structural damage. In regions with harsh winter climates where road salts are heavily applied, the use of corrosion-resistant materials is especially crucial for preventing premature failure. The selection of materials and protective coatings represents a critical design consideration, balancing cost with long-term durability.
Understanding the mechanisms of corrosion and the properties of corrosion-resistant materials allows for informed decision-making regarding exhaust system maintenance and replacement. Regular inspection for signs of corrosion, such as rust or pitting, facilitates early detection of potential problems. Implementing preventative measures, such as applying protective coatings or selecting components constructed from corrosion-resistant alloys, contributes to the long-term reliability and performance of exhaust systems, thereby reducing maintenance costs and ensuring safe vehicle operation.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following addresses common inquiries regarding exhaust system components, their function, maintenance, and related concerns.
Question 1: What are the primary functions of exhaust systems?
Exhaust systems channel exhaust gases away from the engine, reduce noise levels, and convert harmful pollutants into less harmful substances through catalytic converters.
Question 2: How does a damaged exhaust system impact vehicle performance?
A damaged exhaust system reduces engine efficiency, diminishes fuel economy, and may lead to increased emissions. Leaks can create unsafe conditions within the vehicle cabin.
Question 3: What are common indicators of exhaust system problems?
Common indicators include unusual noises (e.g., rattling, hissing), decreased fuel efficiency, reduced engine power, and visible rust or damage to exhaust components.
Question 4: Is it possible to replace only a portion of the exhaust system?
Yes, individual components can be replaced. However, it is often advisable to replace multiple components simultaneously to ensure proper system integration and balanced performance.
Question 5: What factors should be considered when selecting replacement exhaust system components?
Material quality, compatibility with the vehicle’s make and model, and adherence to emissions regulations must be carefully considered. Certification documentation should be verified.
Question 6: How frequently should exhaust systems be inspected?
A comprehensive inspection is recommended annually or whenever unusual symptoms are observed. More frequent inspections may be necessary in harsh climates.
Maintaining a properly functioning exhaust system is crucial for ensuring optimal vehicle performance, environmental compliance, and occupant safety. Neglecting system maintenance can result in significant operational and financial consequences.
The subsequent section will focus on aftermarket performance enhancements to existing exhaust system components, as well as their potential impact on vehicle operations.
Concluding Remarks
This exploration has illuminated the role of automotive exhaust systems, especially regarding components contributing to noise reduction, exhaust channeling, engine performance, emission control, and corrosion resistance. The proper selection, maintenance, and functionality of these components are essential for achieving optimal vehicle operation, regulatory compliance, and environmental responsibility.
Recognizing the significance of exhaust system integrity, individuals and organizations should prioritize routine inspections and implement timely repairs. Commitment to these practices promotes not only vehicle longevity and performance but also supports broader efforts toward sustainable transportation and the reduction of harmful emissions. Continued vigilance and informed decision-making are crucial for upholding the standards of automotive engineering and environmental stewardship.