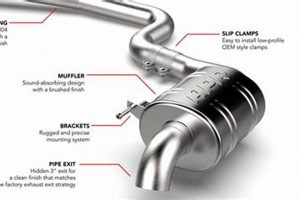
Repairing an exhaust silencing device typically involves addressing issues such as corrosion, holes, or loose connections that compromise its ability to reduce engine noise. This process may range from patching small perforations with specialized materials to replacing entire sections of the exhaust system when damage is extensive. An example would be welding a metal patch over a rusted-through area to restore the integrity of the component.
Maintaining the functionality of this component is important for several reasons. It contributes to noise pollution reduction, improves vehicle efficiency by ensuring proper exhaust flow, and helps a vehicle meet mandated emissions standards. Historically, effective silencing devices have been critical to balancing the performance of internal combustion engines with public health and environmental concerns.
The following sections will detail common failure points in exhaust silencing devices, explore temporary and permanent repair methods, and outline safety precautions to observe when performing such work. Furthermore, it will present alternatives to repair, such as component replacement, and touch upon preventative measures that can extend the lifespan of the exhaust system.
Tips for Addressing Exhaust Silencing Device Issues
The following are guidelines to consider when undertaking repairs to exhaust silencing components. These tips aim to improve the likelihood of a successful outcome and promote safety during the process.
Tip 1: Proper Assessment: Thoroughly inspect the entire exhaust system to determine the full extent of the damage. Corrosion often spreads beyond the immediately visible area.
Tip 2: Material Selection: Choose repair materials compatible with the existing metal of the exhaust system. Welding requires matching filler metals to prevent future corrosion issues.
Tip 3: Surface Preparation: Prior to any repair, thoroughly clean and prepare the affected area. Remove rust, dirt, and grease to ensure a strong bond for patches or welds.
Tip 4: Welding Proficiency: Welding requires skill and appropriate equipment. If unfamiliar with welding techniques, seek assistance from a qualified professional.
Tip 5: Exhaust Clamps: When joining exhaust pipes, use high-quality exhaust clamps designed for the specific pipe diameter. Ensure the clamps are properly tightened to prevent leaks.
Tip 6: Heat Shields: Replace or repair any damaged heat shields. These components protect surrounding parts from excessive heat and reduce the risk of fire.
Tip 7: Safety Precautions: Always work in a well-ventilated area and wear appropriate safety gear, including eye protection, gloves, and a respirator if dealing with rust or chemicals.
Proper application of these guidelines can increase the effectiveness of exhaust silencing device repair efforts and minimize potential complications. Addressing problems promptly and correctly is crucial to maintaining vehicle performance and safety.
The subsequent section will address alternative solutions and long-term preventative maintenance strategies for these systems.
1. Assessment
The initial stage in addressing a compromised exhaust silencing device involves a comprehensive assessment to determine the scope and nature of the damage. This evaluation is crucial for selecting the appropriate repair strategy and ensuring the longevity of the restoration.
- Visual Inspection
A detailed visual inspection forms the cornerstone of the assessment process. It entails a thorough examination of the silencing device’s exterior for signs of corrosion, perforations, or structural damage. Examples include noting the presence of rust scaling, observing cracks along welded seams, or identifying physical impact points. The implications of a visual inspection directly influence subsequent steps, determining whether a simple patch is sufficient or if a more extensive repair is necessary.
- Leak Detection
Leak detection methods are essential for identifying compromised areas within the exhaust system. Techniques include listening for unusual noises, such as hissing or sputtering, or utilizing smoke tests to pinpoint the source of exhaust gas escaping. For example, applying a soapy water solution to suspect areas and observing bubble formation indicates a leak. Early and accurate leak detection prevents further damage and ensures the exhaust system operates within acceptable performance parameters.
- Structural Integrity Evaluation
Assessing the structural integrity of the silencing device involves evaluating the overall stability of the component. This includes checking for loose connections, weakened mounting points, or deformation of the metal housing. For instance, a severely corroded mounting bracket may render the entire silencing device unstable, necessitating replacement rather than repair. This evaluation provides critical insights into the safety and reliability of the exhaust system after any repair efforts.
- Internal Condition Examination
In certain cases, examining the internal condition of the silencing device is necessary. This may involve using an inspection camera to assess the state of internal baffles and chambers, looking for signs of blockage or collapse. A collapsed baffle, for example, can significantly impede exhaust flow and degrade performance, requiring complete silencing device replacement. Understanding the internal condition enables a more accurate diagnosis and guides the selection of the most effective repair or replacement option.
These facets of assessment collectively contribute to a complete understanding of the problem, allowing for the selection of the most appropriate repair or replacement strategy. Neglecting thorough assessment increases the likelihood of ineffective repairs and premature failure of the exhaust silencing device.
2. Welding
Welding represents a crucial skill and technique when addressing damage to exhaust silencing devices. Its application allows for the structural re-integration of metal components, restoring integrity and functionality to compromised areas.
- Structural Reinforcement
Welding offers the capability to reinforce weakened sections of the silencing device, particularly areas prone to corrosion or stress fractures. An example includes welding a patch panel over a rusted-through area, adding a layer of durable metal to prevent further degradation. This reinforcement extends the operational lifespan of the device, mitigating the need for complete replacement.
- Seam Repair
Exhaust silencing devices often fail along welded seams due to thermal cycling and vibration. Welding provides a method for re-establishing these seams, creating a gas-tight seal and preventing exhaust leaks. The process involves cleaning the existing seam, applying a weld bead, and ensuring proper penetration for a robust connection. Failure to address seam failures promptly can lead to diminished engine performance and increased noise levels.
- Custom Fabrication
In instances where sections of the silencing device are severely damaged or missing, welding enables the custom fabrication of replacement components. This may involve creating a new inlet pipe, outlet pipe, or even an entire muffler body from raw materials. Custom fabrication requires precise measurements and skilled welding techniques to ensure proper fit and performance.
- Material Compatibility
Successful welding on exhaust silencing devices hinges on understanding material compatibility. Exhaust systems are typically constructed from mild steel, aluminized steel, or stainless steel. Selecting the appropriate welding process and filler metal is critical to avoid dissimilar metal corrosion. For example, welding stainless steel with mild steel filler can lead to premature failure due to galvanic corrosion.
The effective utilization of welding in this context depends on proficiency and careful attention to detail. Proper preparation, appropriate techniques, and material selection are paramount to achieving durable and long-lasting repairs. In cases where welding is not feasible or practical, alternative methods such as patching or component replacement may be considered.
3. Patching
Patching serves as a remedial technique employed in addressing localized damage to exhaust silencing devices, offering a cost-effective alternative to complete component replacement under specific circumstances. Its relevance lies in the ability to restore functionality and mitigate noise output when the damage is not extensive.
- Localized Damage Containment
Patching is primarily suited for addressing small perforations, rust holes, or minor cracks on the surface of the silencing device. For instance, a pinhole leak caused by corrosion can be effectively sealed with a patch, preventing exhaust gas leakage and restoring noise reduction capabilities. This approach avoids the cost and effort associated with replacing the entire muffler when the majority of the component remains structurally sound.
- Material Selection for Patching
The effectiveness of patching hinges on the selection of appropriate materials that are compatible with the existing metal of the exhaust system. Options include specialized exhaust patches, metal repair tapes, and welding patches fabricated from similar metals. For example, using a heat-resistant epoxy patch designed for exhaust systems ensures a durable seal that can withstand high temperatures and vibrations. Incompatibility can lead to premature failure of the patch and renewed exhaust leaks.
- Surface Preparation Prior to Application
Proper surface preparation is critical to ensure a strong and lasting bond between the patch and the silencing device. This involves removing rust, dirt, and grease from the affected area using wire brushes, sandpaper, or chemical cleaners. For example, thoroughly cleaning the area around a hole with a wire brush and applying a rust converter before applying the patch maximizes adhesion and prevents further corrosion. Neglecting this step can result in a weak bond and early patch failure.
- Limitations and Considerations
Patching is not a universal solution for all exhaust silencing device issues. It is generally unsuitable for addressing extensive damage, structural failures, or internal component degradation. For example, a muffler with severely corroded baffles or a large rupture should be replaced rather than patched. Attempting to patch such damage may provide a temporary fix but will likely result in premature failure and potential safety hazards. A thorough assessment of the damage is essential to determine the suitability of patching as a repair method.
In summary, patching offers a viable approach for addressing localized damage to exhaust silencing devices, provided that appropriate materials are used, proper surface preparation is performed, and the extent of the damage falls within acceptable limits. This technique, when applied correctly, can extend the life of the muffler and delay the need for costly replacement. It’s very important to assess the situation properly before trying to fix a muffler. If the damage is too big, replacing it is always a great option to think about.
4. Sealing
Sealing plays a crucial role in exhaust silencing device repair, directly influencing the effectiveness and longevity of any restoration effort. The purpose of the component is to prevent the escape of exhaust gases from unintended locations, maintaining optimal system performance and minimizing noise pollution. Incomplete or ineffective sealing compromises these objectives, rendering repair efforts largely futile. For instance, a weld repair to a rust hole will fail to deliver desired results if pinhole leaks persist along the weld bead due to inadequate sealing. This cause-and-effect relationship highlights the indivisible link between the two, when thinking of how to fix a muffler.
Practical applications of sealing techniques vary depending on the nature and location of the breach. High-temperature silicone sealants are often employed to close small gaps around joints or seams, providing a flexible and heat-resistant barrier. Exhaust wraps, impregnated with sealing compounds, can be used to cover larger areas of corrosion or damage, effectively encasing the affected region and preventing gas leakage. In more severe cases, the application of specialized exhaust putty, followed by heat curing, can provide a robust and durable seal capable of withstanding high temperatures and pressures. The practical significance of understanding these techniques lies in the ability to tailor the sealing solution to the specific problem, optimizing the repair outcome.
The challenge in sealing exhaust silencing devices lies in achieving a durable and gas-tight barrier that can withstand the harsh operating conditions, including high temperatures, vibrations, and exposure to corrosive elements. Improper sealing can lead to exhaust leaks, reduced engine efficiency, increased noise levels, and potential safety hazards. A comprehensive understanding of sealing materials and techniques, coupled with meticulous application, is essential to ensuring the success of any exhaust silencing device repair. Therefore, to achieve effective and long-lasting results when fixing a muffler, sealing is the key.
5. Replacement
Component replacement represents a decisive course of action when addressing the repair of exhaust silencing devices, particularly when the extent of damage precludes viable restoration through alternative methods. The decision to replace a muffler often involves careful consideration of factors such as cost, availability, and the overall condition of the exhaust system.
- Complete System Degradation
When an exhaust silencing device exhibits pervasive corrosion, structural fatigue, or internal component failure, complete replacement emerges as the most prudent solution. Attempting repairs on a fundamentally compromised component can lead to recurring issues, reduced performance, and potential safety hazards. Selecting a new, compatible silencing device restores optimal function and ensures long-term reliability. For example, after years of exposure to road salt and extreme temperatures, a muffler might exhibit widespread rust that extends to internal baffles, rendering patching or welding ineffective. This scenario calls for full replacement.
- Cost-Benefit Analysis
A critical aspect of deciding on replacement involves weighing the costs associated with repair against the cost of a new component. While patching or welding may appear more economical initially, these methods often provide only temporary solutions, necessitating further repairs in the near future. In contrast, replacing the entire silencing device offers a longer service life and reduces the likelihood of subsequent maintenance expenses. For instance, if the cost of labor and materials for extensive welding approaches the price of a new muffler, replacement becomes the financially sounder option.
- Performance Enhancement
Replacement provides an opportunity to upgrade to a higher-performing or more efficient exhaust silencing device. Options may include components designed to improve exhaust flow, reduce backpressure, or enhance the vehicle’s sound characteristics. This approach not only resolves existing issues but also offers the potential to optimize vehicle performance. For example, a driver seeking to improve fuel economy might opt for a replacement muffler with a less restrictive design, thereby minimizing engine strain and increasing efficiency.
- Regulatory Compliance
In certain jurisdictions, regulations mandate that exhaust systems meet specific noise and emissions standards. When a silencing device fails to comply with these requirements, replacement becomes necessary to ensure legal operation of the vehicle. This is particularly relevant in areas with strict noise ordinances or emissions testing programs. For example, replacing a damaged muffler with a compliant aftermarket option guarantees adherence to local laws and avoids potential fines or penalties.
The decision to replace an exhaust silencing device ultimately rests on a comprehensive evaluation of the component’s condition, the associated costs, potential performance benefits, and regulatory requirements. While repair may offer a short-term solution in some cases, replacement often represents the most effective and sustainable strategy for ensuring optimal vehicle performance and long-term reliability.
6. Safety
Ensuring personal safety when repairing exhaust silencing devices is paramount, directly influencing the well-being of the individual undertaking the task. The connection between safety protocols and exhaust system repair is evident in the potential hazards involved, ranging from burns and exposure to toxic fumes to the risk of physical injury. Failure to adhere to safety guidelines can result in adverse health effects and compromise the effectiveness of the repair itself. For instance, neglecting to wear eye protection while grinding rust from an exhaust pipe can lead to eye injury, while inadequate ventilation during welding can cause respiratory distress from inhaling metal fumes. Therefore, safety is not merely an adjunct but an integral component of any repair procedure.
Specific safety measures applicable to exhaust system repair include utilizing appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), such as gloves, eye protection, and respirators, to mitigate exposure to hazards. Proper ventilation is essential to minimize inhalation of exhaust fumes and welding gases. Furthermore, allowing the exhaust system to cool completely before commencing work reduces the risk of burns. Disconnecting the vehicle’s battery prevents accidental electrical shorts during welding. Employing jack stands to securely support the vehicle is necessary to prevent crushing injuries. The implementation of these measures transforms a potentially hazardous activity into a manageable task with minimized risks. It is more than a procedural checklist; it is necessary for self-preservation and the long-term success of any repair.
Ultimately, recognizing safety as an indispensable element of exhaust system repair is crucial. The potential consequences of neglecting safety protocols are significant, ranging from minor injuries to severe health complications. Adherence to established safety guidelines protects the individual performing the work and contributes to the overall quality and longevity of the repair. Safety consciousness, therefore, is not merely a recommendation but a fundamental prerequisite for any undertaking involving the repair or maintenance of exhaust silencing devices.
7. Prevention
The relationship between preventative maintenance and exhaust silencing device longevity is direct: proactive measures mitigate the factors that lead to component failure, thus reducing the necessity for repairs. Corrosion, a primary cause of exhaust system degradation, can be slowed significantly through regular applications of rust inhibitors. Similarly, ensuring proper engine tuning minimizes excessive heat generation, which strains the exhaust system and shortens its lifespan. Neglecting these measures increases the likelihood of encountering problems that demand corrective action. For example, a vehicle operated in a region with heavy road salt application, without regular undercarriage washes and rust inhibitor treatments, is significantly more prone to muffler damage than a vehicle receiving such care. This increased susceptibility illustrates the cause-and-effect dynamic: inaction precipitates damage, leading to the need for subsequent repair or replacement efforts. Considering this, you can avoid the problem of, how to fix a muffler.
Practical application of preventative strategies extends beyond merely applying protective coatings. Periodically inspecting exhaust system components for signs of wear or damage allows for early detection and resolution of minor issues before they escalate into major problems. For instance, identifying a loose exhaust hanger and promptly re-securing it prevents excessive vibration that could cause cracks or leaks in the muffler. Similarly, addressing engine misfires or other performance issues that cause increased exhaust temperatures can protect the silencing device from thermal stress. These proactive inspections and interventions demonstrate the practical significance of integrating preventative maintenance into vehicle ownership.
In summary, preventative maintenance forms a critical defense against premature failure of exhaust silencing devices. While repairs address existing damage, prevention focuses on mitigating the underlying causes of that damage, thereby reducing the frequency and severity of required interventions. Embracing a proactive approach to exhaust system care, through rust protection, regular inspections, and timely issue resolution, extends the lifespan of the component and minimizes the need for extensive or costly repairs. Integrating prevention into routine vehicle maintenance maximizes the return on investment and ensures long-term reliability of the exhaust system.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following addresses common inquiries regarding the assessment, repair, and maintenance of exhaust silencing devices. The information presented aims to provide clarity and guidance for individuals seeking to address issues affecting these components.
Question 1: What are the primary indicators that an exhaust silencing device requires attention?
Increased exhaust noise, a hissing or sputtering sound emanating from beneath the vehicle, decreased fuel efficiency, and the presence of visible rust or damage on the muffler’s exterior are all potential indicators.
Question 2: Is it possible to temporarily repair a muffler leak using household materials?
While certain household materials, such as exhaust tape, may provide a short-term solution for minor leaks, these are generally not durable and should be considered temporary measures until a proper repair can be performed.
Question 3: What tools are typically needed for exhaust silencing device repair?
Commonly required tools include wrenches, sockets, a hacksaw or pipe cutter, safety glasses, gloves, a wire brush, and potentially a welding machine, depending on the repair method.
Question 4: What are the safety precautions to consider during muffler repair?
It’s crucial to allow the exhaust system to cool completely before beginning work, wear eye protection and gloves, ensure adequate ventilation, and use jack stands to securely support the vehicle.
Question 5: When is replacement a more appropriate solution than repair?
Replacement is generally recommended when the muffler exhibits extensive corrosion, structural damage, or internal component failure, or when the cost of repair approaches or exceeds the cost of a new muffler.
Question 6: How can the lifespan of an exhaust silencing device be extended?
Regular vehicle maintenance, avoiding short trips that prevent the exhaust system from fully warming up, applying rust inhibitors, and promptly addressing any signs of corrosion or damage can help to extend the muffler’s lifespan.
In summary, effective diagnosis, appropriate repair techniques, and adherence to safety guidelines are essential for successfully addressing exhaust silencing device issues. Prioritizing preventative maintenance contributes significantly to the longevity and optimal performance of the component.
The subsequent section will provide a detailed conclusion, summarizing key takeaways from the entirety of the preceding document.
Conclusion
This document has explored various facets of exhaust silencing device repair, encompassing assessment methodologies, repair techniques such as welding and patching, considerations for sealing and component replacement, crucial safety precautions, and proactive preventative measures. Emphasis has been placed on the importance of accurate diagnosis, appropriate material selection, and adherence to established safety protocols throughout the repair process, which is necessary to any, how to fix a muffler.
The long-term functionality of exhaust systems is not solely dependent on effective repairs, but also on the consistent implementation of preventative maintenance practices. Owners are encouraged to prioritize regular inspections and timely interventions to maximize component lifespan and maintain optimal vehicle performance, adhering to regulatory compliance and minimizing environmental impact.