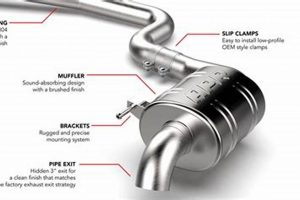
This automotive component is designed to reduce the noise emitted by an internal combustion engine. It achieves this through a series of chambers and baffles that attenuate sound waves generated during the exhaust process. An example of its application is in reducing noise pollution in residential areas caused by vehicular traffic.
The importance of this device lies in its contribution to environmental and auditory comfort. By minimizing exhaust noise, it helps to meet regulatory standards and improves the quality of life in urban environments. Historically, early iterations were relatively simple, but advancements in materials science and acoustic engineering have led to more sophisticated and efficient designs.
The following sections will delve further into the various aspects of exhaust systems, exploring their design, performance characteristics, and maintenance requirements, offering a comprehensive overview of relevant topics.
Maintenance and Optimization Strategies
The following guidelines outline best practices for ensuring optimal performance and longevity of the exhaust system. Adherence to these recommendations will contribute to reduced noise levels, improved engine efficiency, and compliance with environmental regulations.
Tip 1: Regular Inspection: Conduct routine visual inspections for signs of corrosion, damage, or leaks. Early detection of potential issues can prevent costly repairs.
Tip 2: Prompt Repair of Leaks: Address exhaust leaks immediately. Leaks not only increase noise pollution but can also compromise engine performance and potentially introduce harmful gases into the vehicle cabin.
Tip 3: Proper Mounting and Support: Ensure all hangers and supports are securely attached and in good condition. Damaged or missing supports can cause undue stress on the system, leading to premature failure.
Tip 4: Avoid Short Trips: Frequent short trips can lead to condensation buildup within the system, accelerating corrosion. Longer trips allow the exhaust to reach operating temperature, evaporating moisture.
Tip 5: Consider Material Upgrades: When replacement is necessary, consider upgrading to stainless steel or other corrosion-resistant materials for extended lifespan and improved durability.
Tip 6: Professional Installation: Engage qualified technicians for installation or replacement. Proper installation is critical for ensuring optimal performance and avoiding potential safety hazards.
Tip 7: Catalytic Converter Maintenance: Ensure the catalytic converter is functioning correctly. A faulty converter can significantly increase emissions and negatively impact engine performance.
By implementing these preventative measures and adhering to recommended maintenance schedules, the operational lifespan and overall effectiveness of the exhaust system can be significantly enhanced.
The subsequent sections will explore advanced diagnostic techniques and troubleshooting strategies for addressing complex exhaust system issues.
1. Sound attenuation
Sound attenuation is the primary function achieved by a muffler. This exhaust system component is specifically engineered to reduce the amplitude of sound waves generated by the internal combustion engine. The muffler achieves this through a combination of internal chambers, baffles, and sound-absorbing materials. The effect of this attenuation is a reduction in noise pollution, improving the acoustic environment surrounding the vehicle.
The design and effectiveness of the sound attenuation process are directly related to the internal structure of the muffler. For instance, reactive mufflers employ precisely sized chambers to create destructive interference, canceling out specific frequencies. Absorptive mufflers, on the other hand, utilize fiberglass or other materials to convert sound energy into heat. In applications like passenger vehicles, mufflers are crucial for meeting noise regulations and enhancing passenger comfort, while in industrial settings, effective attenuation is essential for worker safety and compliance with occupational health standards.
In summary, sound attenuation is an integral function and desired result of the muffler. Without effective attenuation, vehicles would generate excessive noise, leading to legal repercussions, reduced public acceptance, and potential health concerns. The understanding of this connection is, therefore, critical for engineers designing exhaust systems, manufacturers producing mufflers, and vehicle owners seeking to maintain a quieter, more environmentally friendly operation.
2. Engine efficiency
Engine efficiency, defined as the ratio of useful power output to the energy consumed, is intrinsically linked to the design and condition of the exhaust system. The role of the muffler, a key component within this system, directly influences the engine’s ability to operate at peak performance.
- Backpressure Considerations
Excessive backpressure within the exhaust system hinders the efficient expulsion of exhaust gases. This restriction increases pumping losses within the engine, requiring it to expend more energy to evacuate the cylinders. Consequently, fuel consumption increases, and power output diminishes. An improperly designed or obstructed muffler contributes to this negative effect. For instance, a clogged muffler, due to corrosion or carbon buildup, significantly increases backpressure, resulting in a noticeable reduction in horsepower and fuel economy.
- Flow Optimization
A well-designed muffler minimizes flow restriction while still effectively attenuating noise. This balance is crucial for maintaining optimal engine performance. Aftermarket mufflers designed for performance often prioritize flow, potentially reducing backpressure compared to factory-installed units. However, the trade-off may be an increase in exhaust noise levels. In applications such as high-performance vehicles or racing, specialized mufflers are used to achieve the desired balance between power output and noise regulations.
- Catalytic Converter Interaction
Although the muffler’s primary function is sound attenuation, it resides downstream of the catalytic converter. A malfunctioning converter can significantly increase backpressure, indirectly impacting engine efficiency. A choked catalytic converter, often caused by contamination or age, creates a bottleneck in the exhaust flow, similar to an obstructed muffler. Regular inspection and maintenance of the catalytic converter are, therefore, essential for sustaining engine performance.
- Exhaust Gas Scavenging
In certain high-performance engine designs, the exhaust system, including the muffler, can be tuned to promote exhaust gas scavenging. This phenomenon utilizes pressure waves within the exhaust system to create a vacuum that helps to draw exhaust gases from the cylinder during the overlap period between the exhaust and intake valve opening. A properly tuned muffler can contribute to this scavenging effect, improving cylinder filling and enhancing engine efficiency. However, achieving this requires careful design and matching of the exhaust system components to the specific engine characteristics.
The preceding facets underscore the complex interrelationship between engine efficiency and the exhaust system, emphasizing the critical role of the muffler. Its design, condition, and interaction with other components directly affect the engine’s ability to breathe freely and operate efficiently. Maintaining a properly functioning exhaust system, with a focus on minimizing backpressure and optimizing flow, is essential for maximizing fuel economy, power output, and overall engine performance.
3. Emissions control
The exhaust system, including the muffler, plays an indirect yet significant role in emissions control. While the primary responsibility for reducing harmful emissions rests with the catalytic converter, the mufflers functionality can influence the overall effectiveness of the emissions control system. A properly functioning muffler minimizes backpressure, which is crucial for optimal catalytic converter performance. Excessive backpressure, caused by a damaged or clogged muffler, can hinder the catalytic converters ability to efficiently convert pollutants like hydrocarbons, carbon monoxide, and nitrogen oxides into less harmful substances.
Consider the scenario of a vehicle with a corroded and partially obstructed muffler. This restriction increases backpressure, leading to elevated exhaust temperatures. These higher temperatures can, in turn, damage the catalytic converter, reducing its efficiency in emissions reduction. As a result, the vehicle emits higher levels of pollutants, potentially failing emissions inspections and contributing to air pollution. Conversely, a well-maintained muffler allows for smoother exhaust flow, enabling the catalytic converter to operate within its designed parameters, ensuring effective emissions control. Furthermore, some aftermarket mufflers are designed to optimize exhaust flow for specific engine types, indirectly enhancing the catalytic converter’s performance.
In summary, while the muffler itself does not directly control emissions, its structural integrity and operational efficiency are essential for supporting the catalytic converter’s function. Maintaining the muffler in good condition, including preventing blockages and addressing corrosion, contributes to the overall effectiveness of the vehicle’s emissions control system, helping to minimize its environmental impact. A compromised muffler can thus lead to a degradation in air quality through its indirect impact on the performance of the catalytic converter, the emissions control system’s cornerstone.
4. Corrosion resistance
Corrosion resistance is a critical attribute for an exhaust system component, directly impacting its lifespan and performance. Mufflers, particularly those exposed to harsh environmental conditions, are susceptible to corrosion from road salts, moisture, and acidic compounds present in exhaust gases. The degradation of materials through corrosion can lead to structural weakening, exhaust leaks, and increased noise emissions, thereby compromising the intended function of the muffler. Consider, for instance, a vehicle operated in a region with significant snowfall and frequent road salting. The accumulated salt spray on the undercarriage accelerates corrosion of the muffler, potentially resulting in premature failure and the need for replacement. This demonstrates the direct correlation between environmental exposure and the importance of corrosion-resistant materials.
The selection of appropriate materials is paramount in achieving adequate corrosion resistance. Aluminized steel, stainless steel, and specialized coatings are commonly employed in muffler construction to mitigate the effects of corrosion. Stainless steel, while more expensive, offers superior corrosion resistance compared to aluminized steel, making it a suitable choice for vehicles operating in harsh environments. Furthermore, the design of the muffler can influence its susceptibility to corrosion. Internal baffles and chambers can trap moisture and accelerate corrosion from within. Manufacturers often incorporate drainage holes and optimized geometries to minimize moisture accumulation and promote ventilation. The practical significance of understanding these factors lies in informed material selection and proactive maintenance strategies to extend the lifespan of the muffler.
In conclusion, corrosion resistance is an indispensable characteristic, contributing to the longevity, structural integrity, and operational effectiveness of the exhaust system. The use of corrosion-resistant materials and thoughtful design considerations are essential for mitigating the detrimental effects of environmental exposure and exhaust gas constituents. This understanding enables vehicle owners and maintenance professionals to make informed decisions regarding muffler selection, inspection, and preventative measures, ultimately reducing repair costs and minimizing environmental impact.
5. Material selection
Material selection significantly impacts the performance, longevity, and cost-effectiveness of an exhaust system component. The selection of appropriate materials influences the capacity to withstand high temperatures, corrosive exhaust gases, and external environmental factors such as road salts and moisture. Inadequate material selection leads to premature failure due to corrosion, cracking, or structural fatigue. For instance, using standard carbon steel in a muffler exposes it to rapid oxidation and degradation from the acidic compounds in exhaust gases, resulting in a shortened lifespan and increased exhaust noise as the muffler develops leaks.
Common materials employed in the manufacture of this exhaust component include aluminized steel, stainless steel, and titanium. Aluminized steel offers a balance between cost and corrosion resistance, making it a prevalent choice for original equipment manufacturers. Stainless steel provides superior corrosion resistance, extending the lifespan of the component, particularly in harsh environments. Titanium, while offering exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance, is generally reserved for high-performance applications due to its higher cost. The thickness of the material also contributes to its durability; a thicker gauge of steel will generally provide greater resistance to physical damage and corrosion. The practical implication is that selecting a higher-grade material, while initially more expensive, can yield significant cost savings over the lifespan of a vehicle by reducing the frequency of replacement.
Effective material selection is, therefore, essential to optimize the exhaust system component’s functionality, durability, and overall value. Understanding the properties of various materials, and the specific demands placed upon this component in different operating conditions, enables informed decisions that contribute to reduced noise emissions, improved engine performance, and decreased environmental impact. Ignoring these material considerations inevitably leads to compromised performance and accelerated wear, negating any initial cost savings and increasing the total cost of ownership.
6. Secure mounting
Secure mounting is paramount for the proper functioning and longevity of an exhaust system component. This mounting method refers to the secure attachment of the device to the vehicle’s undercarriage using hangers, brackets, and other support structures. Improper or inadequate securing techniques can lead to a cascade of adverse effects, directly compromising the functionality and lifespan. For instance, a disconnected or weakened hanger allows the component to vibrate excessively, increasing stress on the welds and joints. This elevated stress accelerates metal fatigue, leading to cracks, leaks, and ultimately, premature failure of the entire system.
The secure mounting method also plays a vital role in preventing damage to other vehicle components. If this device is improperly secured, it may come into contact with the vehicle’s frame, suspension components, or fuel lines. Such contact can cause chafing, wear, and potential damage to these parts, leading to costly repairs. Moreover, excessive vibration, resulting from inadequate securing techniques, amplifies noise levels. A loose system generates rattling and banging sounds, detracting from the driving experience and potentially violating noise regulations. A practical example is a scenario where a vehicle repeatedly traverses rough terrain; if the device is not securely mounted, the increased vibration and impacts from road debris will inevitably accelerate its degradation.
In summary, secure mounting is not merely a perfunctory step but a fundamental requirement for ensuring optimal performance, preventing collateral damage, and maintaining compliance with noise regulations. Proper installation, periodic inspections, and timely replacement of worn-out hangers and supports are essential for maintaining the structural integrity of the entire exhaust system. This proactive approach minimizes the risk of component failure, reduces noise pollution, and protects other vehicle components, thus extending the lifespan and reliability of the vehicle.
7. Leak prevention
Leak prevention is critical to the performance and longevity of an exhaust system component. Exhaust leaks compromise noise reduction capabilities, allowing excessive engine noise to escape into the environment. Furthermore, leaks diminish fuel efficiency, as the engine management system may compensate for lost backpressure, resulting in increased fuel consumption. Perhaps most importantly, exhaust leaks introduce harmful gases, such as carbon monoxide, into the vehicle cabin, posing a significant health hazard to occupants. A vehicle with a corroded or improperly installed system, exhibiting noticeable exhaust fumes inside the passenger compartment, serves as a clear example of the consequences of inadequate leak prevention.
Effective leak prevention relies on several factors, including proper installation techniques, the use of high-quality gaskets and seals, and regular inspection and maintenance. During installation, ensuring that all connections are properly aligned and tightened to the manufacturer’s specifications is paramount. Damaged or worn gaskets must be replaced to guarantee a tight seal between connecting components. Regular inspections can identify early signs of corrosion or damage, allowing for timely repairs before leaks develop. Employing specialized exhaust sealants can further enhance leak prevention, particularly in areas prone to corrosion or vibration. Commercial vehicles, often subjected to rigorous use and exposure to harsh conditions, benefit significantly from proactive leak prevention measures.
In summary, leak prevention is an essential aspect of exhaust system maintenance, directly influencing environmental noise levels, fuel economy, and occupant safety. Adhering to proper installation procedures, utilizing quality sealing components, and implementing a proactive inspection and maintenance program are crucial for minimizing the risk of exhaust leaks. By prioritizing leak prevention, vehicle owners and maintenance professionals can ensure optimal system performance, minimize health risks, and extend the lifespan of the exhaust system.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following addresses commonly encountered questions concerning exhaust system sound dampening devices, aiming to provide clarity on various aspects of their function, maintenance, and performance implications.
Question 1: What is the primary function?
The primary function is to attenuate noise generated by the internal combustion engine. This is achieved through internal chambers and baffling designed to reduce the amplitude of sound waves.
Question 2: How does a failing example impact engine performance?
A failing example, particularly if clogged or corroded, can increase backpressure, hindering the efficient expulsion of exhaust gases. This increased backpressure reduces engine power and fuel efficiency.
Question 3: What are the signs of a deteriorating one?
Common signs include excessive exhaust noise, a rattling or banging sound emanating from the undercarriage, reduced fuel economy, and a noticeable decrease in engine power.
Question 4: Can an aftermarket replacement improve performance?
Certain aftermarket replacements, designed for performance, optimize exhaust flow, potentially reducing backpressure and enhancing engine power. However, this may result in increased exhaust noise levels.
Question 5: How does corrosion affect its functionality?
Corrosion weakens the structural integrity, leading to exhaust leaks and increased noise emissions. Severe corrosion can cause internal components to break down, further restricting exhaust flow.
Question 6: Is maintenance required?
Regular inspection for corrosion, damage, and leaks is essential. Prompt repair of leaks and replacement of worn or damaged hangers and supports prolong the lifespan and ensure optimal performance.
Understanding these key aspects is crucial for ensuring the effective operation, preventing costly repairs, and mitigating the environmental impact of motor vehicle exhaust systems.
The subsequent section delves into advanced diagnostic techniques and troubleshooting strategies for resolving intricate exhaust system complications.
Concluding Remarks on Ira’s Muffler
The preceding analysis has detailed the multifaceted role of exhaust system components, specifically focusing on sound reduction devices. From sound attenuation to material selection and secure mounting, each aspect contributes to the overall efficiency, longevity, and environmental impact of a motor vehicle. The interconnectedness of these factors emphasizes the importance of proper maintenance, informed decision-making regarding replacement parts, and a thorough understanding of the system’s function.
Therefore, a continued commitment to upholding the integrity of vehicle exhaust systems remains crucial for minimizing noise pollution, optimizing engine performance, and adhering to regulatory standards. Emphasizing responsible vehicle ownership and promoting awareness of the critical role these components play contributes to a more sustainable and environmentally conscious transportation landscape.