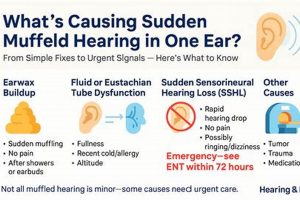
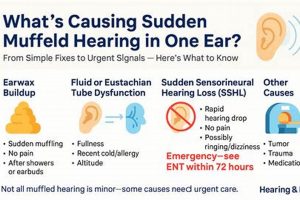
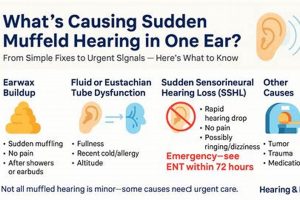
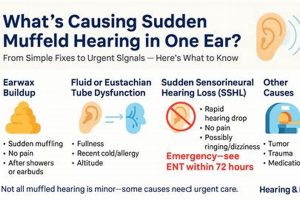
A sensation of reduced sound clarity and volume in one or both ears can manifest as if the auditory input is obstructed or distant. Individuals experiencing this may describe the surrounding sounds as dull, faint, or as if their ears are plugged. This altered perception of hearing can arise from various underlying causes, ranging from temporary conditions to more persistent issues. For example, the sensation can occur during air travel due to pressure changes affecting the middle ear.
Accurate diagnosis of compromised auditory perception is crucial because it directly impacts communication, spatial awareness, and overall quality of life. Early identification and treatment of the underlying cause can prevent potential long-term hearing impairments or other complications. Throughout history, advancements in audiology and otolaryngology have continually improved our understanding and management of such auditory disturbances, leading to more effective diagnostic and therapeutic approaches.
The subsequent sections will delve into the common etiologies responsible for this altered auditory experience. We will explore diagnostic methods employed to pinpoint the root cause and outline the range of treatment options available, from simple home remedies to more complex medical interventions.
Addressing Altered Auditory Perception
Experiencing a diminished or altered sense of hearing requires careful attention to potential causes and appropriate management strategies. The following points offer guidance on addressing this auditory concern.
Tip 1: Identify Potential Environmental Triggers: Consider recent exposures to loud noise, changes in altitude (e.g., air travel), or environments with poor air quality. Recognizing these factors may suggest a temporary cause that resolves spontaneously.
Tip 2: Manage Sinus Congestion: Nasal congestion, often due to allergies or upper respiratory infections, can impact ear pressure. Utilize saline nasal sprays or decongestants as directed to alleviate congestion and equalize pressure in the middle ear.
Tip 3: Practice Ear Hygiene Judiciously: Avoid inserting objects into the ear canal, as this can compact earwax or damage the delicate structures. If earwax buildup is suspected, consult a healthcare professional for safe removal.
Tip 4: Monitor for Associated Symptoms: Note the presence of additional symptoms, such as ear pain, drainage, dizziness, or tinnitus (ringing in the ears). These symptoms can provide crucial information for diagnosis.
Tip 5: Seek Professional Evaluation: If the sensation persists for more than a few days, is accompanied by pain or other concerning symptoms, or interferes with daily activities, a consultation with an audiologist or otolaryngologist is warranted. A hearing test can objectively assess the extent of any hearing loss.
Tip 6: Review Medications: Certain medications are known to have ototoxic (ear-damaging) effects. Discuss your current medications with your physician to determine if any could be contributing to the issue.
Tip 7: Ensure Adequate Hydration: Dehydration can sometimes contribute to ear discomfort or pressure imbalances. Maintaining sufficient fluid intake can support overall bodily function and potentially alleviate symptoms.
Addressing auditory changes promptly and methodically can lead to accurate diagnosis and effective management, preserving optimal hearing health.
The following sections will discuss potential treatments and further steps that could provide relief.
1. Etiology identification
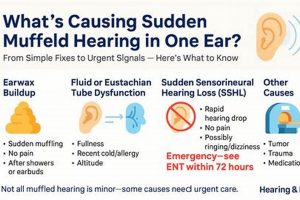
The sensation of altered auditory perception often necessitates a thorough investigation into its potential causes, a process known as etiology identification. The presence of diminished or distorted sound perception is not a disease in itself, but rather a symptom indicative of an underlying physiological or environmental factor. A systematic approach to pinpointing the precise cause is paramount, as the effectiveness of subsequent interventions hinges on an accurate diagnosis. For instance, a feeling of auditory occlusion due to cerumen impaction requires a fundamentally different management strategy compared to a similar sensation stemming from Eustachian tube dysfunction secondary to an upper respiratory infection.
The differential diagnosis for compromised auditory perception is extensive. It includes, but is not limited to, outer ear issues such as cerumen impaction or otitis externa, middle ear problems like otitis media or Eustachian tube dysfunction, inner ear conditions such as sensorineural hearing loss or Meniere’s disease, and even neurological conditions affecting the auditory pathways. Failure to accurately identify the etiology can lead to inappropriate treatment, potentially exacerbating the underlying condition or delaying necessary interventions. Consider, for example, the misdiagnosis of a middle ear effusion as simple congestion, potentially delaying antibiotic treatment in cases of bacterial infection and increasing the risk of complications such as mastoiditis.
In conclusion, meticulous etiology identification is a cornerstone in the management of altered auditory perception. The diagnostic process should encompass a comprehensive medical history, physical examination, and audiometric testing to differentiate between various potential causes. This targeted approach ensures that the therapeutic strategy is aligned with the specific underlying pathology, optimizing the likelihood of a successful outcome and minimizing the risk of further auditory complications. This careful determination of cause ensures the appropriate management and preserves auditory health.
2. Auditory evaluation
Auditory evaluation plays a crucial role in objectively assessing the nature and extent of altered auditory perception. When individuals report a sense of diminished or altered sound, a comprehensive assessment of hearing function becomes paramount to identify the underlying cause and guide appropriate management strategies.
- Pure-Tone Audiometry
Pure-tone audiometry is a fundamental component of auditory evaluation, measuring the softest sounds an individual can hear at various frequencies. This test helps to determine the degree and type of hearing loss, whether conductive (related to the outer or middle ear) or sensorineural (related to the inner ear or auditory nerve). For instance, if pure-tone audiometry reveals a conductive hearing loss, it suggests a potential issue in the transmission of sound to the inner ear, consistent with conditions such as cerumen impaction or middle ear effusion, often associated with a sensation of diminished sound quality.
- Tympanometry
Tympanometry assesses the function of the middle ear by measuring the movement of the eardrum in response to changes in air pressure. This test can identify middle ear pathologies such as fluid accumulation (otitis media), Eustachian tube dysfunction, or ossicular chain abnormalities. A flat tympanogram, for example, indicates restricted eardrum movement, suggesting middle ear involvement as a contributing factor to the reported altered auditory perception.
- Speech Audiometry
Speech audiometry evaluates an individual’s ability to understand spoken words at various intensity levels. This assessment provides valuable information about the impact of hearing loss on communication abilities. Speech discrimination scores, obtained through speech audiometry, can reveal difficulties in understanding speech even when sounds are audible, which may be indicative of sensorineural hearing loss or central auditory processing disorders potentially contributing to altered sound quality.
- Otoacoustic Emissions (OAEs)
Otoacoustic emissions (OAEs) are sounds produced by the outer hair cells in the cochlea. Measuring OAEs provides information about the integrity of the inner ear function. Absent or reduced OAEs suggest damage to the outer hair cells, commonly associated with sensorineural hearing loss. OAE testing is particularly useful in identifying cochlear dysfunction as a potential cause of altered auditory perception, especially in cases where pure-tone audiometry results are inconclusive.
These evaluations combine to offer a detailed overview, assisting the medical professional to find root causes for a patient’s subjective sense of auditory distortion. With clear and distinct parameters and findings, care and medical treatment may continue in a proper and relevant way.
3. Pressure equalization
The sensation of altered auditory perception can frequently be attributed to disparities in air pressure between the middle ear and the external environment. The middle ear, a small air-filled space behind the eardrum, is connected to the back of the nose and throat via the Eustachian tube. This tube’s primary function is to regulate and equalize pressure within the middle ear, ensuring optimal eardrum mobility and, consequently, clear sound transmission. When external air pressure changes rapidly, such as during airplane ascent or descent, scuba diving, or even rapid elevation changes in mountainous regions, the Eustachian tube may not adjust quickly enough. This pressure imbalance can create a feeling of fullness, blockage, or diminished sound clarity, often described as hearing sounds in a muted manner. An inability of the Eustachian tube to equilibrate this pressure results in a restriction of eardrum vibration, which is necessary for efficient sound conduction.
Active pressure equalization techniques, such as the Valsalva maneuver (gentle forced exhalation against a closed nose and mouth), yawning, or swallowing, can often alleviate these symptoms by forcing the Eustachian tube open and allowing air to flow into or out of the middle ear to match external pressure. Individuals with Eustachian tube dysfunction, whether due to allergies, upper respiratory infections, or anatomical abnormalities, are more susceptible to experiencing these auditory changes. For instance, a person with seasonal allergies may experience a blocked sensation in their ears during pollen season, which is exacerbated during air travel because of pre-existing Eustachian tube inflammation. Similarly, children are prone to middle ear issues as their Eustachian tubes are shorter and more horizontal, making them less effective at pressure regulation and more susceptible to infection. Untreated pressure imbalances can lead to barotrauma, potentially causing eardrum damage or middle ear fluid accumulation.
Therefore, understanding the mechanics of pressure equalization and actively employing strategies to facilitate this process is crucial for maintaining optimal hearing health. Proactive measures, especially during activities known to induce pressure changes, can significantly mitigate the sensation of altered auditory perception. Furthermore, if equalization proves consistently difficult or is accompanied by pain or other symptoms, a medical evaluation is warranted to identify any underlying issues affecting Eustachian tube function and to prevent potential complications.
4. Cerumen impaction
Cerumen, commonly known as earwax, is a naturally occurring substance produced within the ear canal to protect, lubricate, and cleanse the ear. However, an excessive accumulation of cerumen can lead to impaction, physically obstructing the ear canal and impeding the transmission of sound waves to the eardrum. This obstruction often results in a subjective experience of reduced sound clarity and volume, a condition frequently described as altered auditory perception.
- Physical Obstruction and Sound Attenuation
Cerumen impaction directly attenuates sound waves as they travel through the ear canal. The physical barrier created by the impacted cerumen reduces the amplitude of sound vibrations reaching the tympanic membrane, leading to a decrease in perceived loudness. An individual might notice that speech sounds distant or that they need to increase the volume of electronic devices to hear clearly. The degree of sound attenuation is directly correlated with the size and density of the impaction.
- Frequency-Dependent Hearing Loss
Cerumen impaction does not uniformly affect all sound frequencies. Lower frequencies are often less affected due to their longer wavelengths, which can partially diffract around the impaction. Higher frequencies, with shorter wavelengths, are more significantly attenuated. This frequency-dependent hearing loss can result in a distorted perception of sound, where certain sounds are muffled or less distinct than others. A musician, for example, might find it challenging to discern the high-pitched tones of a musical piece.
- Associated Symptoms and Inner Ear Effects
Beyond the primary effect of sound attenuation, cerumen impaction can induce secondary symptoms that further contribute to altered auditory perception. Pressure from the impaction can irritate the ear canal, leading to a sensation of fullness or discomfort. In some cases, impaction can trigger tinnitus (ringing in the ears) or vertigo (dizziness), which further compound the subjective experience of hearing sounds in a muffled state. A person might feel that their ear is blocked, experiencing intermittent popping or clicking sensations, as well as an overall decrease in their hearing acuity.
- Differential Diagnosis and Clinical Management
While cerumen impaction is a common cause of altered auditory perception, it is crucial to differentiate it from other potential etiologies, such as middle ear infections, Eustachian tube dysfunction, or sensorineural hearing loss. A thorough otoscopic examination by a healthcare professional can confirm the presence of cerumen impaction and rule out other conditions. Safe and effective cerumen removal methods, such as irrigation, manual extraction, or cerumenolytics, can restore normal sound conduction and resolve the altered auditory perception. Improper removal attempts, however, can lead to further impaction or damage to the ear canal and eardrum. A clear diagnosis is necessary for effective management of an impaction.
In summary, cerumen impaction directly interferes with the transmission of sound, resulting in reduced sound level, altered frequency perception, and other aural symptoms. Diagnosis and treatment require professional intervention to ensure the underlying reason is addressed.
5. Neural involvement
Altered auditory perception, characterized by a sensation of muffled sounds, may arise from disruptions within the neural pathways responsible for transmitting auditory information from the inner ear to the brain. Neural involvement signifies a malfunction or compromise within the auditory nerve (cranial nerve VIII) or the central auditory processing centers within the brainstem and auditory cortex. When these neural pathways are affected, the accurate transmission and processing of sound signals are compromised, leading to a subjective experience of diminished sound clarity or volume. Such disruptions can manifest from various etiologies, including acoustic neuromas (benign tumors on the auditory nerve), demyelinating diseases like multiple sclerosis, stroke affecting auditory processing regions, or even certain neurotoxic medications. For instance, an individual with an acoustic neuroma might report a gradual decline in hearing, accompanied by tinnitus and a sense of fullness, all stemming from compression of the auditory nerve.
The impact of neural involvement on auditory perception extends beyond simple sound attenuation. Damage to specific neural pathways can distort the frequency or temporal coding of auditory signals, resulting in altered pitch perception, difficulties in sound localization, or an inability to distinguish speech in noisy environments. Moreover, central auditory processing disorders, which involve disruptions in the brain’s ability to interpret auditory information, can manifest as a sensation of muffled sounds despite normal hearing thresholds on standard audiometric tests. A child with a central auditory processing disorder, for example, might struggle to understand instructions in a classroom setting, even though their hearing is technically normal. Consequently, evaluation for central auditory processing abnormalities is critical in individuals who report auditory processing challenges that are not explained by peripheral hearing loss alone.
In conclusion, neural involvement represents a complex etiological factor contributing to altered auditory perception. Accurate diagnosis requires a comprehensive neuro-audiological evaluation, including auditory brainstem response (ABR) testing, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain, and central auditory processing assessments. Appropriate management strategies may involve surgical intervention (e.g., acoustic neuroma resection), medical management (e.g., corticosteroids for demyelinating lesions), or rehabilitative therapies (e.g., auditory training for central auditory processing disorders). Early identification and targeted intervention are essential to mitigate the impact of neural involvement on auditory function and improve the overall quality of life for affected individuals.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following questions address common concerns regarding experiencing sounds as though they are muffled, providing clarification on possible causes, diagnostic procedures, and management strategies.
Question 1: What are the primary causes contributing to an altered auditory experience where sounds lack clarity?
Primary factors include cerumen impaction obstructing the ear canal, Eustachian tube dysfunction leading to pressure imbalances, middle ear infections causing fluid accumulation, sensorineural hearing loss affecting inner ear function, and, less commonly, neural involvement impacting the auditory pathways.
Question 2: How can a healthcare professional determine the reason when sounds are perceived with reduced clarity?
Diagnosis typically involves a comprehensive evaluation, including otoscopy to examine the ear canal and eardrum, audiometry to assess hearing thresholds, tympanometry to evaluate middle ear function, and, if necessary, advanced imaging (e.g., MRI) to rule out neural or structural abnormalities.
Question 3: Is it possible for earwax accumulation to suddenly affect hearing clarity?
Yes, while cerumen accumulation is typically a gradual process, certain events can precipitate a sudden sensation of reduced sound clarity. These include water entering the ear canal and causing the wax to swell, or the physical displacement of cerumen further into the canal, causing immediate obstruction.
Question 4: Is there a connection between nasal congestion and a decrease in auditory acuity?
Nasal congestion, often associated with allergies or upper respiratory infections, can lead to Eustachian tube dysfunction, which impairs pressure equalization in the middle ear. This pressure imbalance can result in diminished sound clarity and a sensation of fullness or blockage in the ears.
Question 5: What are the potential long-term consequences of disregarding altered auditory perception?
Ignoring persistent auditory changes can lead to delayed diagnosis of underlying conditions, potentially resulting in irreversible hearing loss, communication difficulties, social isolation, and impaired cognitive function. Early intervention is paramount to mitigate these risks.
Question 6: How is sensorineural hearing loss contributing to the feeling of ear muffle different from how earwax impaction does it?
Sensorineural hearing loss involves damage to the inner ear or auditory nerve, leading to a distortion or reduction in the intensity of sound signals transmitted to the brain. It may involve certain frequencies and certain distortions of sound quality. Earwax impaction creates a physical block of the ear canal, obstructing sound waves, leading to generalized decreased volume and muffled sound.
Addressing auditory issues promptly through accurate diagnosis and appropriate management is crucial for preserving hearing health and maintaining overall well-being.
The following sections will discuss potential treatments and further steps that could provide relief.
Conclusion
This exploration has elucidated that “ears sound muffled” describes a diminished or distorted auditory experience stemming from diverse etiologies. From simple cerumen impaction to complex neural involvement, accurate diagnosis is paramount. Auditory evaluations, including audiometry and tympanometry, are critical for identifying the underlying cause. Effective management strategies range from cerumen removal and pressure equalization techniques to medical or surgical interventions for more serious conditions.
The persistence of altered auditory perception warrants prompt medical attention. Early diagnosis and appropriate intervention are crucial to prevent long-term complications and preserve hearing health. Individuals experiencing compromised auditory acuity should seek professional assessment to ensure optimal management and mitigate the potential impact on communication, cognitive function, and overall quality of life.