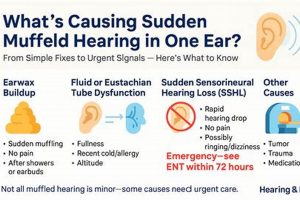
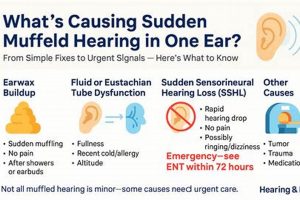
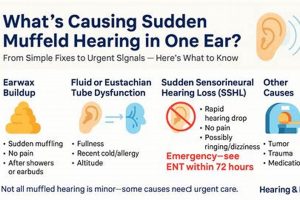
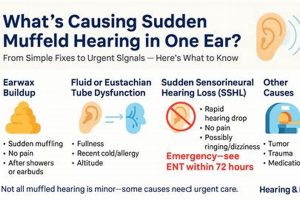
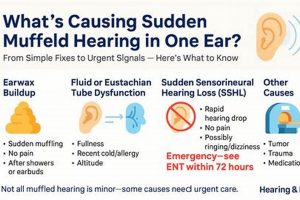
Perceived sound blockage or a sense of decreased sound clarity within the auditory canal is often characterized by a “muffled ear.” This sensation can manifest as a difficulty in discerning speech, a feeling of pressure, or a general reduction in the volume of environmental sounds reaching the eardrum. For example, an individual may experience a muffled ear after swimming, during air travel, or when experiencing an upper respiratory infection.
Addressing this auditory issue promptly is important for maintaining effective communication, ensuring safety through accurate environmental awareness, and preventing potential complications stemming from underlying medical conditions. Historically, various methods, ranging from simple home remedies to more complex medical interventions, have been employed to resolve the sensation of diminished auditory acuity. Understanding the underlying causes is crucial for effective resolution.
The following sections will detail common causes of reduced auditory clarity, explore potential remedies, and outline when seeking professional medical advice is warranted to restore normal hearing function.
Addressing Reduced Auditory Clarity
The following provides actionable steps to consider when experiencing diminished sound clarity in the ear. These suggestions aim to address common causes and offer potential solutions.
Tip 1: Equalize Pressure. Employ techniques such as yawning, swallowing, or performing the Valsalva maneuver (gently blowing air while pinching the nose and closing the mouth). These actions can help equalize pressure in the middle ear, particularly after altitude changes or underwater activities.
Tip 2: Clear Nasal Passages. Use a saline nasal spray or a neti pot to irrigate the nasal passages. This can help alleviate congestion that may be contributing to Eustachian tube dysfunction and reduced auditory clarity.
Tip 3: Manage Allergies. If allergies are suspected, consider using over-the-counter antihistamines or consulting with a physician for allergy testing and management. Allergic reactions can cause inflammation in the nasal passages and Eustachian tubes, affecting hearing.
Tip 4: Avoid Irritants. Refrain from smoking or being around smoke, as these can irritate the nasal passages and Eustachian tubes. Similarly, limit exposure to other environmental irritants like dust and strong odors.
Tip 5: Ensure Proper Hydration. Drinking sufficient fluids can help thin mucus secretions, making it easier for the Eustachian tube to function properly and clear any blockages.
Tip 6: Earwax Removal (with Caution). If earwax buildup is suspected, consider using over-the-counter earwax softening drops. However, exercise caution and avoid using cotton swabs, as these can push the wax further into the ear canal. If unsure, consult a healthcare professional for safe earwax removal.
Tip 7: Rest and Recovery. If experiencing a cold or upper respiratory infection, ensure adequate rest and hydration. Allow the body to recover fully, as these infections can often lead to temporary hearing issues.
Following these recommendations can often restore clarity to auditory perception by addressing common underlying causes. However, persistent or worsening symptoms necessitate professional medical evaluation.
The subsequent sections will explore scenarios where medical intervention is essential and provide guidance on seeking appropriate care.
1. Pressure Equalization Techniques
Pressure equalization techniques play a critical role in alleviating the sensation of a muffled ear, particularly when this symptom arises from barometric pressure imbalances affecting the middle ear. The middle ear, an air-filled cavity behind the eardrum, is connected to the back of the throat by the Eustachian tube. This tube normally equalizes pressure between the middle ear and the surrounding environment. When external air pressure changes rapidly, such as during air travel, scuba diving, or even swift elevator ascents, the Eustachian tube may not adjust quickly enough, leading to a pressure differential. This difference can cause the eardrum to retract or bulge, resulting in discomfort and a muffled or blocked sensation in the ear.
Techniques like yawning, swallowing, chewing gum, or performing the Valsalva maneuver (gently attempting to exhale while pinching the nose and closing the mouth) actively open the Eustachian tube, facilitating airflow and equalizing the pressure. For instance, a pilot executing frequent swallows during descent utilizes this principle to maintain ear comfort. Similarly, a diver employing the Valsalva maneuver prevents barotrauma by ensuring that middle ear pressure remains consistent with the increasing external pressure underwater. The effectiveness of these techniques hinges on the proper functioning of the Eustachian tube; in cases of congestion due to colds, allergies, or infections, these maneuvers may be less effective or require repeated attempts.
In summary, understanding and applying pressure equalization techniques is a fundamental step in addressing muffled ear sensations linked to pressure changes. While simple and often effective, these techniques rely on a healthy and functioning Eustachian tube. If muffled hearing persists despite repeated attempts at equalization, it may indicate an underlying issue requiring medical assessment to rule out infections, Eustachian tube dysfunction, or other ear-related problems. The practical significance of these techniques lies in their accessibility and ease of application, empowering individuals to proactively manage common causes of transient auditory discomfort.
2. Eustachian Tube Function
Eustachian tube function is intrinsically linked to the resolution of muffled auditory perception. This tube, connecting the middle ear to the nasopharynx, facilitates pressure regulation and drainage. A properly functioning Eustachian tube ensures that the air pressure within the middle ear equals the ambient atmospheric pressure. When this equilibrium is disrupted, the eardrum may retract or bulge, leading to a sensation of muffled hearing. Dysfunction can stem from inflammation caused by allergies, upper respiratory infections, or barometric pressure changes during activities such as air travel. Therefore, restoring Eustachian tube function is often paramount in addressing and eliminating muffled auditory experiences. A practical example involves individuals experiencing ear pressure and muffled hearing during airplane descent; active swallowing or yawning encourages Eustachian tube opening, equalizing pressure and alleviating the symptoms.
Impairment of Eustachian tube function may manifest in various ways, including persistent ear fullness, popping or clicking sounds, and varying degrees of hearing impairment. The medical management of Eustachian tube dysfunction aims to reduce inflammation, promote drainage, and prevent further complications. Decongestants, antihistamines, and nasal steroid sprays are frequently prescribed to address underlying causes such as allergies or infections. In more severe cases, surgical interventions, such as myringotomy with tympanostomy tube insertion, may be considered to facilitate pressure equalization and prevent chronic middle ear fluid accumulation. Furthermore, lifestyle adjustments, such as avoiding exposure to allergens and irritants, can play a significant role in managing Eustachian tube health.
In conclusion, understanding Eustachian tube function is essential for effectively addressing and mitigating muffled auditory perception. The ability to maintain pressure equalization and drainage through this tube is critical for optimal hearing. While simple maneuvers and conservative medical treatments are often sufficient, persistent or severe dysfunction may necessitate more aggressive interventions. The key to effective management lies in identifying the underlying cause of Eustachian tube impairment and tailoring treatment accordingly.
3. Wax Buildup Management
Cerumen, commonly known as earwax, is a naturally occurring substance produced within the ear canal to protect it from dust, debris, and microorganisms. However, excessive accumulation of cerumen can lead to impaction, physically obstructing the ear canal and impeding the transmission of sound waves to the eardrum. This obstruction frequently manifests as a sensation of muffled hearing. Effective wax buildup management is, therefore, a critical component in the process of restoring auditory clarity. An individual experiencing a gradual decline in hearing acuity may find that professional cerumen removal resolves the issue entirely, highlighting the direct correlation between wax buildup and auditory perception.
Management strategies range from home-based remedies to professional medical interventions. Over-the-counter cerumen softening drops, containing ingredients such as mineral oil or hydrogen peroxide, can help to loosen impacted wax, facilitating its natural expulsion from the ear canal. However, caution is advised when using these products, as improper use can potentially lead to irritation or infection of the ear canal. In cases of severe impaction or when home remedies prove ineffective, manual removal by a healthcare professional is necessary. This can be achieved through techniques such as irrigation, suction, or the use of specialized instruments like curettes. The choice of removal method depends on the severity and consistency of the wax buildup, as well as the individual’s medical history and anatomy.
Ultimately, understanding the impact of cerumen accumulation on auditory function is paramount. While cerumen serves a protective purpose, its overabundance can significantly impair hearing. Implementation of appropriate wax buildup management strategies, whether through diligent home care or professional intervention, is a fundamental aspect of maintaining optimal auditory health. Individuals experiencing persistent muffled hearing should consider cerumen impaction as a potential underlying cause and seek professional evaluation for appropriate diagnosis and treatment.
4. Infection Control Measures
Infection control measures are directly pertinent to resolving muffled auditory perception, especially when the underlying cause is middle ear infection (otitis media) or external ear infection (otitis externa). Infections induce inflammation and fluid accumulation within the ear, obstructing sound transmission and resulting in a muffled or distorted auditory experience. Effective infection control aims to eradicate the causative pathogens, reduce inflammation, and restore normal auditory function. For example, patients with otitis media often present with a complaint of muffled hearing alongside ear pain and fever. Timely administration of antibiotics, guided by a medical professional, addresses the infection and subsequently alleviates the auditory symptoms.
The implementation of infection control protocols extends beyond therapeutic interventions to preventative strategies. Maintaining good hygiene practices, such as thorough hand washing and avoiding sharing personal items like earphones, minimizes the risk of introducing infectious agents into the ear canal. In the context of swimming-related ear infections (swimmer’s ear), utilizing earplugs and drying the ear canal thoroughly after water exposure reduces the likelihood of bacterial or fungal proliferation. Moreover, avoiding the use of cotton swabs to clean the ear canal is crucial, as they can traumatize the skin and introduce pathogens, thereby increasing the susceptibility to infection. The practical application of these measures, consistently adhered to, significantly lowers the incidence of infection-related muffled hearing.
In summary, infection control measures form an integral component in addressing muffled auditory perception caused by ear infections. Prompt and appropriate treatment of existing infections, coupled with preventative hygiene practices, promotes auditory health and reduces the frequency of infection-related hearing impairment. The understanding and consistent application of these measures are essential for both individuals and healthcare professionals in effectively managing and mitigating this common auditory symptom. The efficacy of infection control underscores its significance as a cornerstone in the broader approach to auditory healthcare.
5. Allergy Symptom Relief
Allergy symptom relief is often an instrumental component in addressing muffled auditory perception, particularly when allergies contribute to Eustachian tube dysfunction and middle ear inflammation. Allergic reactions can trigger the release of histamine and other inflammatory mediators, leading to nasal congestion, increased mucus production, and swelling of the Eustachian tube lining. This inflammation impairs the tube’s ability to equalize pressure in the middle ear, resulting in a sensation of fullness, pressure, and diminished sound clarity. Therefore, effective management of allergy symptoms can directly alleviate these auditory symptoms. For instance, an individual experiencing seasonal allergies might notice improved hearing after taking antihistamines or using nasal corticosteroids to reduce inflammation in the nasal passages and Eustachian tube.
Practical application of allergy symptom relief involves several strategies, including allergen avoidance, pharmacotherapy, and immunotherapy. Identifying and minimizing exposure to specific allergens, such as pollen, dust mites, or pet dander, is a foundational step. Pharmacological interventions include antihistamines to block histamine receptors, decongestants to reduce nasal congestion, and nasal corticosteroids to suppress inflammation. In cases of severe or persistent allergies, immunotherapy, involving gradual exposure to increasing doses of allergens, may be considered to desensitize the immune system. The choice of treatment strategy depends on the severity and type of allergy, as well as individual patient factors. Successfully mitigating allergy symptoms frequently translates to improved Eustachian tube function and subsequent resolution of muffled hearing.
In conclusion, allergy symptom relief represents a crucial intervention in managing muffled auditory perception linked to allergic rhinitis and Eustachian tube dysfunction. Addressing underlying allergic inflammation restores normal Eustachian tube function, facilitating pressure equalization and improving sound transmission. While challenges may exist in accurately identifying allergens and optimizing treatment regimens, the connection between allergy control and auditory health underscores the importance of comprehensive allergy management. The practical significance lies in the potential to improve quality of life by addressing a common and often overlooked cause of hearing impairment.
Frequently Asked Questions Regarding Muffled Auditory Perception
The following provides answers to frequently asked questions concerning the sensation of diminished or unclear hearing, often described as a “muffled ear.” The information presented aims to clarify common misconceptions and provide guidance on appropriate management strategies.
Question 1: Is the sensation of a “muffled ear” always indicative of a serious medical condition?
The perception of muffled hearing can stem from various causes, some of which are transient and self-resolving, such as temporary Eustachian tube dysfunction due to altitude changes or mild congestion. However, persistent or recurrent muffled hearing may signify an underlying medical condition requiring professional evaluation, including ear infections, excessive earwax accumulation, or, in rare cases, more serious neurological issues.
Question 2: Can over-the-counter ear drops safely resolve the sensation of muffled hearing?
Over-the-counter ear drops designed to soften earwax can be effective for addressing muffled hearing caused by cerumen impaction. However, caution is advised. Individuals with a history of ear infections, perforated eardrums, or ear surgery should consult a healthcare professional before using such products. Improper use can potentially exacerbate existing conditions or introduce new complications.
Question 3: How does nasal congestion contribute to the sensation of a “muffled ear?”
Nasal congestion, often associated with colds, allergies, or sinus infections, can lead to Eustachian tube dysfunction. The Eustachian tube, connecting the middle ear to the nasopharynx, facilitates pressure equalization. When nasal congestion obstructs this tube, pressure imbalances in the middle ear can occur, resulting in a feeling of fullness, discomfort, and muffled hearing.
Question 4: Are there specific techniques to try at home to alleviate the sensation of a “muffled ear?”
Several techniques can be attempted to relieve the sensation. These include yawning, swallowing, chewing gum, or performing the Valsalva maneuver (gently blowing air while pinching the nose and closing the mouth). These actions can help to open the Eustachian tube and equalize pressure in the middle ear. However, if symptoms persist or worsen, professional medical attention is recommended.
Question 5: When should a medical professional be consulted for muffled hearing?
Medical evaluation is warranted if the sensation persists for more than a few days, is accompanied by ear pain, drainage, fever, dizziness, or sudden hearing loss. These symptoms may indicate a more serious underlying condition requiring prompt diagnosis and treatment. Delaying evaluation could potentially lead to complications or permanent hearing damage.
Question 6: Can chronic exposure to loud noise cause muffled hearing?
Chronic exposure to excessive noise levels can lead to noise-induced hearing loss, which may initially manifest as a temporary threshold shift, characterized by muffled hearing or tinnitus (ringing in the ears). Prolonged or repeated exposure can result in permanent hearing damage. Consistent use of appropriate hearing protection in noisy environments is essential to prevent noise-induced hearing loss.
In summary, while transient muffled hearing is often benign, persistent or concerning symptoms necessitate professional medical evaluation to identify the underlying cause and implement appropriate management strategies. Self-treatment should be approached with caution, and any doubts should be resolved through consultation with a qualified healthcare provider.
The following section will detail potential medical interventions and treatment options available for addressing persistent or complex cases of reduced auditory clarity.
Conclusion
This exploration of methods to resolve a diminished auditory perception has covered a range of approaches, from simple pressure equalization techniques and diligent wax management to infection control measures and allergy symptom relief. The effectiveness of each intervention is contingent upon identifying the precise underlying cause of the auditory reduction. Successful resolution often requires a combination of strategies tailored to the individual’s specific circumstances.
The sustained experience of reduced auditory clarity warrants professional medical assessment to preclude potential complications and ensure appropriate management. The information provided herein serves as a guide and should not substitute qualified medical advice. Prioritizing proactive healthcare management is essential for safeguarding long-term auditory well-being.