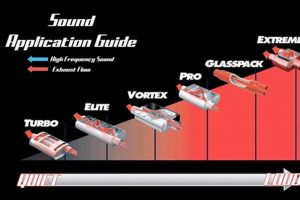
A vehicle component designed to reduce the noise emitted from the engine’s exhaust system. This specialized device utilizes a series of chambers and tubes to dampen sound waves, resulting in a quieter operating experience. For example, its effectiveness is often evaluated by measuring decibel levels before and after installation to quantify noise reduction.
The incorporation of this component into automotive design offers several advantages, including minimizing environmental noise pollution and enhancing the comfort of both vehicle occupants and surrounding communities. Historically, advancements in its design have focused on optimizing both sound dampening and exhaust flow efficiency, impacting fuel economy and overall engine performance. This has led to variations in design and materials, tailored to specific vehicle types and performance requirements.
The following sections will delve further into the intricacies of exhaust system components, exploring specific design principles, material considerations, and the impact of aftermarket modifications on vehicle performance and emissions compliance.
Maintenance and Longevity Guidance
The following recommendations are provided to ensure optimal performance and extended lifespan of the exhaust system noise reduction component.
Tip 1: Regular Inspection is Crucial. Conduct periodic visual inspections for signs of corrosion, rust, or physical damage. Early detection can prevent minor issues from escalating into costly repairs or component failure.
Tip 2: Promptly Address Unusual Noises. Be attentive to changes in exhaust sound. Rattling, hissing, or excessively loud noises may indicate a leak, a loose connection, or internal damage requiring immediate attention.
Tip 3: Ensure Proper Installation and Fitment. When replacing the component, verify compatibility with the vehicle’s make and model. Improper installation can lead to reduced effectiveness and potential damage to other exhaust system parts.
Tip 4: Avoid Exposure to Harsh Chemicals. Minimize contact with corrosive substances such as road salt or certain cleaning agents, as prolonged exposure can accelerate corrosion and reduce the component’s lifespan.
Tip 5: Maintain Proper Engine Function. Issues such as engine misfires or excessive fuel consumption can place undue stress on the exhaust system, potentially damaging the noise reduction component over time. Address engine problems promptly.
Tip 6: Consider Professional Inspection. Schedule routine inspections with a qualified mechanic, especially if experiencing performance issues or suspecting damage. Professional evaluation can identify potential problems that may not be readily apparent.
Adhering to these guidelines will contribute to the effective functioning and extended durability of the exhaust system noise reduction component, reducing the need for premature replacement.
The subsequent section will cover frequently asked questions regarding this component and its interaction within the broader automotive context.
1. Noise Reduction Efficiency
Noise reduction efficiency is a primary performance metric directly associated with an exhaust noise reduction component. It quantifies the device’s ability to attenuate engine exhaust noise, impacting both vehicle occupants and the surrounding environment. Effective noise reduction contributes to compliance with noise regulations and enhances overall driving comfort.
- Attenuation Mechanisms
The effectiveness of an exhaust noise reduction component relies on various attenuation mechanisms, including reactive and absorptive principles. Reactive muffling utilizes chambers and tubes to reflect and cancel out sound waves, while absorptive muffling employs sound-absorbing materials. The design of internal chambers and the type of absorptive material determine the frequency range targeted for noise reduction.
- Frequency Spectrum Targeting
Engine exhaust noise comprises a broad spectrum of frequencies. Effective components are designed to target specific frequency ranges known to contribute most to perceived noise levels. Manufacturers often employ computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulations to optimize internal geometry and material selection for targeted frequency attenuation. Components intended for diesel engines, for instance, may focus on lower frequencies.
- Backpressure Considerations
Noise reduction and exhaust flow are often competing objectives. Aggressive noise reduction designs can increase backpressure, negatively impacting engine performance and fuel efficiency. Optimal components strike a balance between noise attenuation and minimal backpressure. Designs incorporating perforated tubes and optimized chamber geometries can minimize backpressure while maintaining adequate noise reduction.
- Material Properties and Durability
The effectiveness of absorptive materials, such as fiberglass or steel wool, can degrade over time due to exposure to high temperatures, moisture, and exhaust byproducts. Material selection and construction techniques influence the component’s long-term noise reduction capabilities. Stainless steel construction and the use of high-temperature-resistant absorptive materials enhance durability and maintain performance over extended periods.
The interplay between attenuation mechanisms, frequency targeting, backpressure considerations, and material durability ultimately dictates the noise reduction efficiency of an exhaust system component. Continuous advancements in material science and design optimization are driving improvements in both noise reduction and overall exhaust system performance. The selection and maintenance of exhaust noise reduction components should consider these factors to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
2. Exhaust Flow Optimization
Exhaust flow optimization directly influences the performance and efficiency of an engine’s exhaust system. An integral element within this system is the component intended to reduce noise. Exhaust flow optimization entails minimizing backpressure and turbulence within the exhaust pathway, thereby facilitating efficient evacuation of exhaust gases from the engine’s cylinders. A poorly designed or restrictive component can impede this flow, leading to reduced engine power, increased fuel consumption, and elevated exhaust gas temperatures. Real-world examples demonstrate that engines equipped with optimized exhaust systems experience improved throttle response and enhanced horsepower output compared to those with highly restrictive systems. The practical significance of understanding this relationship lies in the ability to select, maintain, and modify exhaust components to achieve optimal engine performance.
The internal design of the noise-reducing component is critical to achieving exhaust flow optimization. Straight-through designs, perforated cores, and strategically placed baffles can minimize flow restriction while still providing adequate noise attenuation. Aftermarket components are often marketed with claims of improved flow rates, and independent testing is frequently performed to validate these assertions. For instance, testing a vehicle before and after installing a performance-oriented component can provide quantitative data regarding horsepower and torque gains. It is important to note that overly aggressive modifications to the exhaust system, such as removing components entirely, can have detrimental effects on emissions compliance and may negatively impact overall engine reliability.
In conclusion, exhaust flow optimization is inextricably linked to the design and performance of the noise-reducing component within the exhaust system. Balancing noise reduction with minimal flow restriction is a primary engineering challenge in exhaust system design. Understanding this relationship is essential for selecting appropriate components, maintaining system efficiency, and maximizing engine performance while adhering to regulatory requirements. Further research and development in materials science and internal component design hold the potential for further improvements in exhaust flow optimization and noise attenuation technologies.
3. Material Durability Factors
Material durability factors are fundamentally linked to the longevity and performance of an exhaust system noise reduction component. The component’s function necessitates exposure to high temperatures, corrosive exhaust gases, and potential physical impacts from road debris. Therefore, the selection of materials with inherent resistance to these conditions is paramount. Premature failure due to corrosion, cracking, or erosion compromises the effectiveness of the component in both noise reduction and exhaust flow, potentially leading to increased emissions and reduced engine efficiency. For example, a component constructed primarily of mild steel in a region with heavy road salting will exhibit significantly shorter lifespan compared to one fabricated from stainless steel.
The choice of material directly influences the component’s ability to withstand thermal stress. Repeated heating and cooling cycles induce expansion and contraction, potentially leading to fatigue and cracking. High-grade stainless steel alloys, such as 304 or 409, offer superior thermal fatigue resistance compared to lower-grade materials. Furthermore, the presence of moisture and acidic compounds in exhaust gases necessitates materials that are resistant to chemical attack. Galvanic corrosion, a phenomenon occurring when dissimilar metals are in contact in the presence of an electrolyte, can also accelerate degradation. Therefore, material selection must consider the compatibility of different components within the exhaust system to minimize this risk. The welding process used to join materials also impacts durability; proper welding techniques are crucial to ensure strong, corrosion-resistant joints.
In summary, material durability factors represent a critical consideration in the design and manufacture of exhaust system noise reduction components. Selection of appropriate materials based on the operating environment, exhaust gas composition, and thermal conditions is essential to ensure long-term reliability and optimal performance. Ongoing research and development efforts are focused on exploring advanced materials and coatings that offer enhanced resistance to corrosion, thermal stress, and erosion, contributing to increased component lifespan and reduced environmental impact. The understanding of material science principles is therefore integral to the field of exhaust system engineering.
4. Installation Compatibility
Installation compatibility constitutes a critical aspect of exhaust system components, directly influencing performance and longevity. Proper fitment ensures optimal function and prevents potential damage to the vehicle and the installed component. Selecting components designed for the specific vehicle make, model, and year is essential to achieving seamless integration and avoiding operational issues. The absence of correct installation can cause problems with engine operation, and cause the component to fail prematurely.
- Vehicle-Specific Design
Exhaust systems are often designed with vehicle-specific geometries and mounting points. A component not intended for a particular vehicle may require modifications to fit, potentially compromising its structural integrity or performance characteristics. Attempting to force-fit incompatible parts can damage both the component and the vehicle’s exhaust system. For example, the length of the pipe may not fit under the frame.
- Emissions System Integration
Modern vehicles often incorporate sophisticated emissions control systems. The component must be compatible with these systems to ensure compliance with emission regulations. An improperly installed or incompatible component can disrupt the operation of catalytic converters, oxygen sensors, and other emissions-related components, leading to increased pollutant emissions and potential diagnostic trouble codes.
- Mounting and Support Structures
The component is secured to the vehicle using various mounting brackets and hangers. These structures are designed to support the weight of the component and dampen vibrations. Incompatible components may lack the necessary mounting points or require alterations to the vehicle’s frame, compromising structural integrity and increasing the risk of component failure due to vibration or stress. A missing hanger is dangerous and needs to be addressed.
- Diameter and Connection Type Alignment
The diameter of the inlet and outlet pipes must match the vehicle’s existing exhaust system. Likewise, the type of connection (e.g., flange, slip-fit) must be compatible. Mismatched diameters or connection types require adapters or welding, increasing the complexity of the installation and potentially creating leaks. It may be safer to replace the whole assembly if there is no compatible installation.
In summary, installation compatibility is a key factor in ensuring the proper function and longevity of exhaust system components. Selecting components designed for the specific vehicle, paying attention to emissions system integration, and verifying proper mounting and connections are essential for a successful installation. Failure to address these considerations can lead to reduced performance, increased emissions, and potential damage to the vehicle. The component to be installed should be compatible so it could be installed properly.
5. Corrosion Resistance
Corrosion resistance is a critical attribute directly impacting the lifespan and performance of an exhaust system component. This component, designed to attenuate engine noise, operates in a harsh environment characterized by high temperatures, moisture, and corrosive exhaust gases. The degree to which the component resists degradation from these elements dictates its functional longevity. Insufficient corrosion resistance leads to structural weakening, exhaust leaks, increased noise emissions, and ultimately, component failure. For instance, in regions with heavy road salting, components constructed from materials lacking adequate corrosion protection will experience accelerated deterioration, requiring premature replacement.
The selection of appropriate materials and protective coatings is paramount in achieving optimal corrosion resistance. Stainless steel alloys, aluminized steel, and ceramic coatings represent common strategies employed to mitigate corrosion. These materials form a barrier against the corrosive effects of exhaust gases and environmental factors. The effectiveness of these measures can be quantified through standardized corrosion testing procedures, such as salt spray testing or electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Such testing simulates real-world conditions and allows for comparative evaluation of different materials and coatings. The practical application of this understanding is evident in the automotive industry’s ongoing efforts to develop more durable and corrosion-resistant exhaust system components, reducing warranty claims and minimizing environmental impact.
In conclusion, corrosion resistance is an indispensable characteristic of effective exhaust system components. The choice of materials, the application of protective coatings, and adherence to proper manufacturing techniques are all essential in ensuring long-term performance and reliability. Ongoing research and development in materials science continue to drive innovation in corrosion-resistant technologies, contributing to the creation of more durable and environmentally sustainable automotive components. A deeper knowledge of the effect corrosion has is important.
6. Backpressure Effects
The performance of an exhaust system noise reduction component, such as the specified brand, is inextricably linked to backpressure effects. Backpressure refers to the resistance encountered by exhaust gases as they flow through the exhaust system. A components design influences this resistance, impacting engine efficiency and power output. Excessive backpressure impedes the expulsion of exhaust gases from the engine cylinders, resulting in reduced volumetric efficiency, diminished horsepower, and increased fuel consumption. Conversely, insufficient backpressure can lead to poor scavenging of exhaust gases, potentially affecting combustion quality and emissions.
The internal design of an exhaust noise reduction component is crucial in managing backpressure. Chambers, baffles, and the diameter of internal passages dictate the flow characteristics. For example, a component with a complex internal structure and narrow passages will generate higher backpressure than one with a straight-through design and larger diameter. Real-world applications demonstrate that selecting an exhaust noise reduction component optimized for a particular engine type and performance requirements is essential. Aftermarket components often advertise reduced backpressure, claiming to improve engine performance. However, such claims must be evaluated critically, as excessive reduction in backpressure can have detrimental effects on engine operation, particularly in engines relying on a certain degree of exhaust restriction for proper cylinder scavenging.
In summary, backpressure effects represent a critical consideration when evaluating the performance characteristics of an exhaust system noise reduction component. Balancing noise reduction with minimal backpressure is a key engineering challenge. Understanding this relationship allows for informed component selection, ensuring optimal engine performance and minimizing potential negative impacts on fuel efficiency and emissions. This understanding also promotes a realistic evaluation of advertised performance enhancements associated with aftermarket exhaust system modifications.
7. Emissions Compliance Standards
The functionality of an exhaust system component, like an exhaust noise reduction component from any manufacturer, directly affects its adherence to emissions compliance standards. These standards, established by governmental regulatory bodies, mandate permissible levels of specific pollutants released into the atmosphere. The ability of a particular component to effectively manage and control exhaust gases determines its contribution to meeting these stringent requirements. Failure to comply with emissions standards results in legal penalties, vehicle recall campaigns, and reputational damage for the manufacturer. For example, a malfunctioning or improperly designed component can increase the concentration of regulated pollutants, such as nitrogen oxides (NOx) and particulate matter (PM), exceeding permissible thresholds.
The design and manufacturing of exhaust noise reduction components must consider their impact on emissions control systems. Components are often integrated with catalytic converters and oxygen sensors, which are crucial for reducing harmful emissions. An exhaust noise reduction component that generates excessive backpressure can impede the performance of these systems, leading to incomplete combustion and increased pollutant output. Conversely, a component that excessively reduces backpressure can disrupt the operation of engines designed to operate with a specific level of exhaust restriction. The interplay between exhaust system components and emissions control systems necessitates meticulous engineering and rigorous testing to ensure compliance.
In summary, a demonstrable link exists between the effectiveness of exhaust system components and adherence to emissions compliance standards. These components play a critical role in managing exhaust gases and supporting the operation of emissions control systems. Manufacturers must prioritize compliance with regulatory requirements through careful design, rigorous testing, and ongoing monitoring of component performance. The long-term success of these technologies depends on a continuous commitment to environmental responsibility and regulatory compliance. The failure is costly and creates a bad name.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries concerning the exhaust system noise reduction component, and aims to provide clarity on its function, maintenance, and impact on vehicle performance and regulatory compliance.
Question 1: What constitutes the primary function of an exhaust system noise reduction component?
The primary function is to attenuate noise generated by the engine’s exhaust gases. This is achieved through internal design features that dampen sound waves before they exit the exhaust system, reducing noise pollution.
Question 2: How does the selection of materials influence the longevity of an exhaust system noise reduction component?
Material selection directly impacts the component’s resistance to corrosion, thermal stress, and physical damage. Stainless steel and aluminized steel offer enhanced durability compared to mild steel, extending the component’s lifespan.
Question 3: What effect does an exhaust system noise reduction component have on engine backpressure?
The component inherently introduces some level of backpressure. A poorly designed component can excessively restrict exhaust flow, negatively affecting engine performance. Optimizing internal design minimizes backpressure while maintaining adequate noise reduction.
Question 4: What are the potential consequences of installing an incompatible exhaust system noise reduction component?
Installation of an incompatible component may lead to reduced performance, increased emissions, and potential damage to the vehicle’s exhaust system. Proper fitment is crucial for optimal function and compliance with emissions regulations.
Question 5: How frequently should an exhaust system noise reduction component be inspected for damage?
Regular visual inspections are recommended, particularly in regions with harsh environmental conditions. Inspections should focus on identifying signs of corrosion, rust, or physical damage that may compromise the component’s integrity.
Question 6: Does modifying or removing the exhaust system noise reduction component affect emissions compliance?
Modifying or removing the component can negatively impact emissions control and may violate local, state, or federal regulations. Such alterations can disrupt the operation of catalytic converters and increase pollutant emissions.
These FAQs highlight crucial aspects of exhaust system components, emphasizing the importance of proper selection, maintenance, and installation for optimal performance and regulatory compliance.
The subsequent section will address potential troubleshooting scenarios related to exhaust system components, offering guidance on identifying and resolving common issues.
Conclusion
This exploration has detailed the function, benefits, and complexities associated with exhaust system noise reduction components. The analyses have underscored the importance of material selection, design optimization, and installation compatibility in achieving optimal performance, longevity, and emissions compliance. The critical aspects of backpressure management and corrosion resistance have also been highlighted.
The continued development and refinement of exhaust system technologies remain essential for mitigating environmental noise pollution and ensuring compliance with evolving emissions regulations. Professionals in automotive engineering and vehicle maintenance must prioritize informed component selection and diligent system upkeep to uphold vehicle performance and environmental responsibility. The proper selection, operation, and maintainence of Meade’s Muffler is very important.