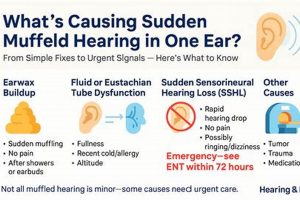
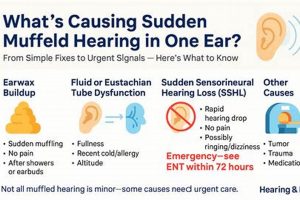
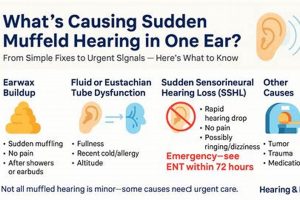
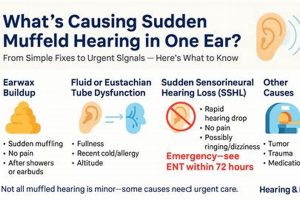
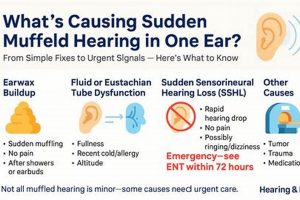
The sensation of reduced sound clarity or a feeling of blockage in the auditory canal can be unsettling. It presents as if external noises are faint or distant, even when they are not. Addressing this issue often involves identifying potential causes and implementing appropriate solutions to restore normal hearing function.
Relief from this auditory issue can significantly enhance the quality of life. Clearer auditory perception improves communication, safety awareness, and overall sensory experience. Historically, various methods have been employed to combat this sensation, ranging from folk treatments to contemporary medical interventions, reflecting the importance of auditory health throughout different eras.
The following sections will explore several approaches to alleviate the described auditory discomfort, examining methods which can be implemented in a domestic setting with readily available materials, alongside considerations regarding when professional medical evaluation is warranted.
Alleviating Auditory Muffling
The following outlines several methods that may offer relief from the sensation of muffled hearing. These techniques are generally considered safe for initial attempts at resolution, but persistent or worsening symptoms necessitate professional medical evaluation.
Tip 1: Warm Compress Application: Applying a warm, damp compress to the affected ear can help to loosen accumulated earwax and promote drainage. Ensure the compress is not excessively hot to avoid burns.
Tip 2: Steam Inhalation: Inhaling steam may assist in clearing congestion in the Eustachian tubes, which can contribute to muffled hearing. Exercise caution to prevent burns from hot steam. A bowl of hot water (not boiling) can be used, with a towel draped over the head to trap the steam.
Tip 3: Jaw Exercises: Specific jaw movements, such as gently yawning or chewing gum, can help to equalize pressure in the middle ear. Repeat these exercises several times a day.
Tip 4: Over-the-Counter Decongestants: If the muffling is suspected to be related to sinus congestion or a cold, over-the-counter decongestants may provide temporary relief. Follow dosage instructions carefully.
Tip 5: Hydrogen Peroxide Solution: A diluted solution of 3% hydrogen peroxide can be used to soften earwax. Tilt the head, instill a few drops into the ear canal, allow it to sit for a minute or two, then drain. This approach should be used sparingly and avoided if there is any suspicion of a perforated eardrum. Seek professional advice if unsure.
Tip 6: Olive Oil Application: Similar to hydrogen peroxide, a few drops of warmed (not hot) olive oil can soften earwax. Use the same instillation and drainage procedure as with hydrogen peroxide.
Tip 7: Maintaining Hydration: Adequate fluid intake helps to thin mucus and secretions, potentially alleviating Eustachian tube congestion. Aim for sufficient daily water consumption.
These methods focus on addressing common causes of the described hearing issue, such as wax buildup or congestion. Consistent and careful application may lead to improved auditory clarity.
While these techniques can be helpful for some individuals, they are not a substitute for professional medical advice. If the muffled hearing persists or is accompanied by pain, drainage, dizziness, or other concerning symptoms, a healthcare provider should be consulted to determine the underlying cause and appropriate treatment plan.
1. Earwax Management
The accumulation of cerumen, commonly known as earwax, is a physiological process intended to protect the ear canal. However, excessive buildup can impede sound transmission, leading to a sensation of muffled hearing. Addressing impacted earwax is a primary focus within the realm of auditory well-being, and several domestic strategies are employed for its management.
- Cerumenolytic Agents
Cerumenolytic agents, such as hydrogen peroxide or mineral oil, function to soften hardened earwax, facilitating its natural expulsion. These agents are instilled into the ear canal, allowing them to penetrate and loosen the wax impaction. While generally safe, overuse can cause irritation or, in rare cases, damage to the delicate tissues of the ear canal. Prior to use, it is imperative to confirm the absence of a perforated eardrum, as these agents can be ototoxic.
- Aural Irrigation Techniques
Following the softening of earwax with cerumenolytic agents, gentle aural irrigation may be employed to dislodge the softened wax. This involves using a bulb syringe or a specialized irrigation device to introduce lukewarm water into the ear canal. The water pressure should be low to avoid trauma to the eardrum. Irrigation should be performed carefully, and discontinued if pain or discomfort arises.
- Mechanical Removal Precautions
The use of cotton swabs or other instruments to manually remove earwax is generally discouraged. Such practices often push the wax further into the ear canal, exacerbating the impaction. Additionally, improper use of these instruments can cause trauma to the ear canal or eardrum. If manual removal is necessary, it should be performed by a qualified healthcare professional.
- Prevention Strategies
The best management strategy for earwax is often prevention. Avoid over-cleaning the ears, as this can stimulate cerumen production. Periodically applying a few drops of mineral oil can help to keep the earwax soft and prevent impaction. Individuals who are prone to excessive earwax buildup should consult with a healthcare provider regarding appropriate preventative measures.
Effective earwax management plays a crucial role in alleviating the subjective experience of muffled hearing. By understanding the physiological properties of earwax and employing safe and appropriate removal techniques, individuals can often restore normal auditory function. However, persistent or severe earwax impaction, or the presence of other ear-related symptoms, warrants prompt evaluation by a medical professional to rule out underlying pathology and receive appropriate care.
2. Eustachian Tube Function
The Eustachian tube plays a critical role in maintaining healthy auditory function. Dysfunction of this tube is a common contributor to the sensation of muffled hearing, prompting exploration of various strategies to restore its proper operation.
- Pressure Equalization
The Eustachian tube connects the middle ear to the nasopharynx, allowing for the equalization of pressure between the middle ear and the external environment. When this function is impaired, pressure imbalances can lead to fluid accumulation in the middle ear, resulting in muffled hearing. Yawning, swallowing, or performing the Valsalva maneuver (gentle blowing while pinching the nose and closing the mouth) are common methods employed to manually open the Eustachian tube and equalize pressure. Such techniques can be considered initial strategies for alleviating pressure-related auditory muffling.
- Drainage of Middle Ear Fluids
The Eustachian tube also facilitates the drainage of fluids from the middle ear. Infections or allergies can cause inflammation and swelling of the Eustachian tube lining, obstructing drainage. This leads to fluid buildup in the middle ear, contributing to muffled hearing and potentially increasing the risk of infection. Steam inhalation and nasal saline rinses aim to reduce congestion and promote drainage, thus addressing this specific cause of auditory muffling.
- Protection from Nasopharyngeal Secretions
The Eustachian tube acts as a barrier, preventing nasopharyngeal secretions from entering the middle ear. However, during upper respiratory infections or instances of significant nasal congestion, this protective function can be compromised. Pathogens can ascend into the middle ear, causing inflammation and fluid accumulation, leading to muffled hearing and potentially acute otitis media. Addressing underlying infections or allergies with appropriate medications or supportive therapies, as advised by a healthcare professional, is crucial for restoring normal Eustachian tube function.
- Muscle Function and Exercise
The tensor veli palatini and levator veli palatini muscles assist in opening the Eustachian tube. Exercises that strengthen these muscles, such as chewing gum or performing specific jaw movements, may improve Eustachian tube function. These exercises can be considered as a component of a comprehensive approach to alleviating muffled hearing resulting from Eustachian tube dysfunction, although their efficacy may vary among individuals.
The multifaceted roles of the Eustachian tube highlight its importance in auditory health. Strategies aimed at improving its function often address the underlying causes of muffled hearing, such as pressure imbalances, fluid accumulation, or infection. While several methods can be implemented in a domestic setting, persistent or severe symptoms warrant professional medical evaluation to identify and address any underlying pathology.
3. Congestion Reduction
Nasal and sinus congestion frequently contribute to the sensation of muffled hearing. The interconnectedness of the upper respiratory system means that inflammation and fluid buildup in the nasal passages and sinuses can directly impact the Eustachian tube, which is responsible for pressure equalization in the middle ear. Congestion obstructs the Eustachian tube, preventing proper ventilation and drainage of the middle ear cavity. This obstruction leads to negative pressure within the middle ear and the potential accumulation of fluid, thus impairing the transmission of sound waves and resulting in perceived auditory muffling. Therefore, congestion reduction becomes a critical component in alleviating this specific type of auditory distortion.
Practical approaches to congestion reduction, as part of managing muffled hearing, include nasal saline rinses. These rinses clear nasal passages of mucus and irritants, reducing inflammation and allowing the Eustachian tube to function more effectively. Similarly, steam inhalation helps to loosen mucus and promote drainage. Over-the-counter decongestants, used judiciously, can temporarily shrink swollen nasal tissues, relieving congestion and potentially improving Eustachian tube function. In instances of allergic rhinitis contributing to congestion, antihistamines can be implemented to manage allergic reactions and reduce inflammation. These remedies aim to restore normal Eustachian tube function, thus facilitating proper middle ear ventilation and reducing the sensation of muffled hearing. Consider the example of an individual experiencing muffled hearing alongside a common cold; utilizing nasal saline rinses regularly throughout the illness can help maintain Eustachian tube patency, reducing the severity and duration of auditory symptoms.
In summary, the link between congestion reduction and improved auditory perception is direct, particularly when muffled hearing arises from upper respiratory infections or allergies. Implementing strategies to alleviate nasal and sinus congestion can restore Eustachian tube function, thereby resolving the pressure imbalances and fluid accumulation that lead to auditory distortion. However, it is crucial to note that if muffled hearing persists despite these measures, or if it is accompanied by pain, fever, or other concerning symptoms, a medical evaluation is necessary to rule out more serious underlying conditions requiring specific medical intervention.
4. Inflammation Control
Inflammation within the auditory system is a significant factor contributing to the perception of muffled hearing. Controlling inflammatory processes, whether acute or chronic, is crucial when considering strategies aimed at restoring normal auditory function. Approaches targeting inflammation control may assist in reducing swelling, improving drainage, and ultimately alleviating the sensation of muffled hearing.
- Dietary Modifications
Certain foods can promote or exacerbate inflammation within the body. An anti-inflammatory diet, rich in omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and lean proteins, can contribute to overall inflammation control. Conversely, limiting processed foods, sugary beverages, and excessive amounts of saturated fats may help reduce inflammatory responses. For instance, increased consumption of fish oil supplements or incorporating foods like salmon and walnuts into the diet has been shown to reduce inflammatory markers in some individuals.
- Topical Warm Compress Application
Applying a warm compress to the external ear can reduce localized inflammation and promote blood flow, which aids in the natural healing processes. The warmth helps to relax muscles and open blood vessels, which can reduce swelling and discomfort. For instance, a warm compress applied for 15-20 minutes several times a day may provide relief from inflammation associated with minor ear irritations.
- Herbal Remedies (with caution)
Certain herbal remedies possess anti-inflammatory properties. Ginger, turmeric, and chamomile have demonstrated anti-inflammatory effects in various studies. However, the use of herbal remedies requires careful consideration, as some may interact with medications or have potential side effects. Consulting a healthcare professional before incorporating herbal remedies into a treatment plan is essential to ensure safety and efficacy.
- Avoiding Irritants and Allergens
Exposure to irritants or allergens can trigger inflammatory responses in the auditory system. Common irritants include cigarette smoke, loud noises, and certain chemicals. Identifying and avoiding these triggers can help prevent inflammatory reactions and reduce the likelihood of muffled hearing. For example, individuals with allergies should take steps to minimize exposure to allergens such as pollen or dust mites, and may consider using air purifiers in their homes.
The presented facets of inflammation control illustrate that a multi-pronged approach can be beneficial in managing inflammation-related auditory issues. Ranging from dietary adjustments to topical applications, each strategy contributes to creating an environment conducive to reducing inflammation and restoring normal auditory function. While these interventions can be a valuable part of domestic management, persistent or severe symptoms, such as muffled hearing accompanied by pain or drainage, should prompt evaluation by a healthcare provider to rule out underlying pathology and receive appropriate medical care.
5. Hydration Levels
Maintaining adequate hydration is a physiological necessity with ramifications extending beyond basic bodily functions. Sufficient fluid intake plays a crucial, albeit often overlooked, role in auditory health. Specifically, the sensation of muffled hearing can be influenced by hydration levels, impacting the viscosity of bodily fluids and the overall efficiency of various bodily processes. While not a direct remedy in isolation, proper hydration serves as a supporting element in maintaining optimal conditions for auditory function and can enhance the effectiveness of other interventions.
- Mucus Membrane Function
Dehydration can lead to thickened mucus secretions within the nasal passages and Eustachian tubes. This thickened mucus impedes normal drainage and ventilation within the middle ear, contributing to pressure imbalances and a sensation of muffled hearing. Adequate hydration thins these secretions, promoting proper drainage and potentially alleviating pressure-related auditory discomfort. For instance, during a sinus infection, increased fluid intake can help to clear congested nasal passages and Eustachian tubes, which may indirectly reduce the experience of muffled hearing.
- Circulatory Efficiency
Proper hydration supports optimal blood volume and circulatory efficiency. The inner ear relies on adequate blood flow for oxygen and nutrient delivery to the delicate sensory cells responsible for hearing. Dehydration can reduce blood volume, potentially impairing blood flow to the inner ear and affecting auditory function. Maintaining sufficient hydration ensures that the inner ear receives the necessary resources for optimal performance. Consider the individual who experiences temporary auditory disturbances during periods of intense physical activity without adequate fluid replacement; these disturbances may be related to decreased blood flow to the inner ear due to dehydration.
- Lymphatic Drainage
The lymphatic system plays a crucial role in removing waste products and maintaining fluid balance within the body. Dehydration can impair lymphatic drainage, potentially leading to fluid accumulation in various tissues, including those surrounding the ear. Optimal hydration supports efficient lymphatic function, reducing the likelihood of fluid buildup and associated auditory disturbances. For example, individuals prone to edema or fluid retention may find that adequate hydration assists in maintaining fluid balance and minimizing pressure around the middle ear.
- Cerebrospinal Fluid Volume
While the precise connection between cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and muffled hearing is complex and not fully understood, dehydration can affect overall CSF volume. Changes in CSF volume and pressure could theoretically impact inner ear function, although direct evidence supporting this connection is limited. Maintaining adequate hydration contributes to overall physiological homeostasis, which may indirectly support auditory health by optimizing the environment surrounding the inner ear.
While maintaining optimal hydration levels is not a standalone solution for muffled hearing, its role in supporting mucus membrane function, circulatory efficiency, lymphatic drainage, and potentially cerebrospinal fluid volume should not be discounted. Integrating adequate fluid intake into a comprehensive approach to managing muffled hearing can enhance the effectiveness of other strategies and contribute to overall auditory well-being. However, persistent or severe auditory symptoms necessitate professional medical evaluation to identify underlying pathology and implement appropriate medical interventions.
6. Cautious Application
The application of domestic strategies for addressing the sensation of muffled hearing necessitates a deliberate and cautious approach. While readily accessible and potentially effective for certain etiologies, the inappropriate or indiscriminate use of these techniques can lead to adverse effects or delay appropriate medical intervention. Thorough understanding and measured implementation are paramount.
- Differential Diagnosis Considerations
Prior to initiating any domestic treatment, a preliminary assessment of the potential underlying cause of the muffled hearing is critical. The sensation can arise from a variety of factors, including earwax impaction, Eustachian tube dysfunction, upper respiratory infections, or, less commonly, more serious conditions such as sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Employing a domestic technique intended for earwax removal in a case of sudden sensorineural hearing loss, for example, would be not only ineffective but could also delay critical medical intervention, potentially resulting in irreversible hearing damage. A cautious approach involves considering potential causes and limiting domestic interventions to scenarios where the likely etiology aligns with the intended treatment.
- Technique Specific Contraindications
Each domestic technique carries its own set of contraindications. The instillation of hydrogen peroxide into the ear canal, while often effective for earwax softening, is strictly contraindicated in individuals with a known or suspected perforated eardrum. Similarly, forceful aural irrigation can cause barotrauma to the eardrum, particularly in individuals with pre-existing ear conditions. A cautious approach entails a thorough understanding of the contraindications associated with each technique and a careful assessment of the individual’s ear health history before initiating any intervention.
- Monitoring for Adverse Reactions
Even when applied appropriately, domestic techniques can occasionally result in adverse reactions. Irritation of the ear canal, allergic reactions to topical agents, or exacerbation of existing symptoms are all possible. A cautious approach involves close monitoring for any signs of adverse reactions during and after the application of domestic techniques. If any concerning symptoms arise, such as increased pain, drainage, dizziness, or worsening hearing loss, the intervention should be immediately discontinued, and a healthcare professional should be consulted.
- Limitations of Domestic Interventions
Domestic techniques for muffled hearing are generally intended for mild or self-limiting conditions. Persistent or severe symptoms, particularly those accompanied by other concerning signs, warrant prompt medical evaluation. A cautious approach recognizes the limitations of domestic interventions and avoids relying on them as a substitute for professional medical care when more serious underlying conditions are suspected. Delaying appropriate medical intervention in favor of prolonged or inappropriate domestic treatment can have serious consequences, potentially leading to permanent hearing damage or other complications.
The principles of differential diagnosis, awareness of technique-specific contraindications, close monitoring for adverse reactions, and acknowledgment of the limitations inherent in domestic approaches are essential to ensuring the responsible application of these techniques. Instances of persistent auditory distortion warrant referral to an audiologist. Integrating these elements of cautious application into the use of domestic techniques can maximize their potential benefits while minimizing the risk of harm, thereby contributing to more effective management of certain types of muffled hearing.
Frequently Asked Questions About Addressing Muffled Hearing
The following addresses common inquiries regarding the application of home-based strategies intended to alleviate the sensation of muffled hearing. These responses are for informational purposes only and do not constitute medical advice.
Question 1: When is medical intervention necessary for muffled hearing, as opposed to attempting a home remedy?
Muffled hearing that persists for more than a few days, is accompanied by pain, drainage, dizziness, or sudden onset warrants immediate medical evaluation. These symptoms may indicate a more serious underlying condition requiring prompt professional intervention to prevent potential complications.
Question 2: Is the use of cotton swabs a safe and effective method for resolving muffled hearing caused by earwax?
The use of cotton swabs for earwax removal is generally discouraged. Swabs often push earwax further into the ear canal, exacerbating the impaction and potentially damaging the eardrum. Safer alternatives include cerumenolytic agents or professional ear cleaning.
Question 3: Can dietary changes directly impact muffled hearing?
While dietary changes may not directly resolve the primary cause of muffled hearing, an anti-inflammatory diet can support overall ear health and potentially reduce inflammation that contributes to auditory symptoms. Specific dietary modifications should be discussed with a healthcare provider or registered dietitian.
Question 4: How can one differentiate between muffled hearing caused by earwax impaction versus Eustachian tube dysfunction?
Muffled hearing caused by earwax impaction typically presents gradually and may be accompanied by a feeling of fullness in the ear. Eustachian tube dysfunction often manifests with pressure changes, popping sensations, or muffled hearing that fluctuates with swallowing or yawning. A healthcare professional can provide a definitive diagnosis.
Question 5: Are there specific over-the-counter medications that are recommended for alleviating muffled hearing?
Over-the-counter decongestants or antihistamines may provide temporary relief if muffled hearing is related to nasal congestion or allergies. However, these medications address the underlying cause of the congestion, not the hearing issue itself. These should be used according to package instructions and with consideration of potential side effects.
Question 6: How frequently should hydrogen peroxide be used to address earwax buildup and prevent muffled hearing?
Hydrogen peroxide should be used sparingly and only when necessary to soften earwax. Excessive use can irritate the ear canal and disrupt the natural protective mechanisms. A general recommendation is to use a diluted solution no more than once or twice a week, if needed, and to discontinue use if any irritation occurs. Professional ear cleaning is a safer alternative for frequent earwax management.
In summation, while select home-based strategies may offer relief from certain causes of muffled hearing, a thorough understanding of potential risks, contraindications, and limitations is essential. Persistent or concerning symptoms require professional medical evaluation.
The subsequent section will further explore advanced intervention strategies.
Muffled Ear Home Remedies
This exploration has detailed various “muffled ear home remedies,” outlining their potential benefits and inherent limitations. Techniques ranging from warm compresses to specific earwax management strategies have been presented. The importance of understanding the underlying cause of the auditory muffling, whether due to wax impaction, Eustachian tube dysfunction, or other etiologies, has been consistently emphasized.
The information provided serves to empower informed decision-making; however, it should not be interpreted as a substitute for professional medical advice. Any persistent or worsening auditory disturbance warrants prompt evaluation by a qualified healthcare provider. Prioritizing responsible application and recognizing the boundaries of “muffled ear home remedies” remains paramount for ensuring patient safety and optimal auditory outcomes.