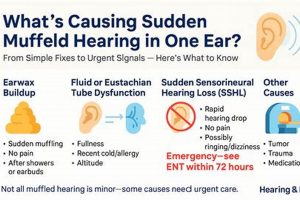
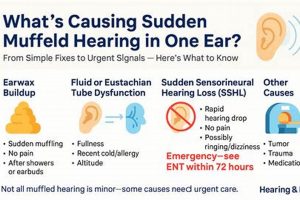
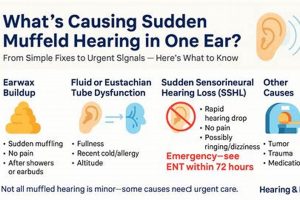
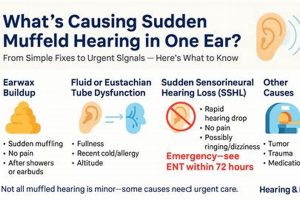
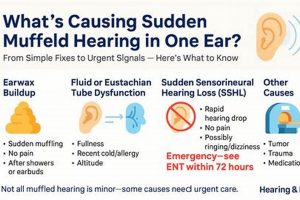
A solution targeting the sensation of reduced sound clarity and volume, often described as hearing through a barrier, is a common need. This condition can arise from various causes, including earwax buildup, sinus congestion, or exposure to loud noises, resulting in a diminished auditory experience. An example of such a solution might be using over-the-counter ear drops to soften impacted earwax.
Addressing this auditory issue is important for maintaining overall quality of life. Untreated, it can lead to communication difficulties, social isolation, and even exacerbate underlying medical conditions. Historically, remedies have ranged from simple home techniques to professional medical interventions, reflecting evolving understanding of ear anatomy and physiology.
The subsequent sections will delve into specific approaches for managing the described hearing problem, including preventive measures, at-home care, and when it is essential to seek professional medical advice.
Remediation Strategies for Muffled Hearing
The following guidelines outline potential actions to alleviate the sensation of reduced sound clarity, assuming the cause is not severe or indicative of a serious underlying condition.
Tip 1: Over-the-Counter Ear Drops: Consider using commercially available ear drops designed to soften and dissolve earwax. Follow product instructions carefully to prevent irritation or further impaction.
Tip 2: Steam Inhalation: Inhaling steam can help to alleviate sinus congestion, a potential cause of auditory blockage. Use a bowl of hot water (not boiling) or a warm shower for this purpose.
Tip 3: Valsalva Maneuver (with caution): Gently attempt to equalize pressure in the ears by pinching the nose, closing the mouth, and lightly blowing air. Avoid excessive force, as this can cause ear damage.
Tip 4: Hydration: Maintaining adequate hydration can help to thin mucus and alleviate congestion throughout the body, potentially improving ear drainage.
Tip 5: Avoid Irritants: Limit exposure to known irritants such as cigarette smoke, allergens, and pollutants, as these can exacerbate congestion and impact auditory clarity.
Tip 6: Nasal Irrigation: Employ a saline nasal rinse to clear nasal passages and reduce sinus pressure, which may contribute to the perceived hearing impediment.
Tip 7: Address Allergies: If allergies are suspected, consult with a medical professional regarding appropriate management strategies, including antihistamines or other allergy medications.
These strategies aim to address common, non-serious causes of diminished auditory perception. However, if the sensation persists, worsens, or is accompanied by pain, dizziness, or discharge, professional medical evaluation is imperative.
The subsequent section addresses circumstances under which seeking professional medical attention becomes necessary for the resolution of muffled hearing.
1. Earwax softening agents
Earwax, also known as cerumen, is a naturally occurring substance produced within the ear canal. Its primary function is to protect the ear by trapping dirt, dust, and other foreign particles, preventing them from reaching the delicate eardrum. While the ear typically self-cleans through natural jaw movements like chewing and talking, excessive earwax production or improper cleaning habits (such as using cotton swabs, which can push wax further into the ear canal) can lead to impaction. This impaction, in turn, is a frequent cause of diminished auditory clarity, a condition often described as muffled hearing. Earwax softening agents play a crucial role in resolving this issue by loosening and breaking down the impacted cerumen, facilitating its natural removal or allowing for easier extraction by a healthcare professional. The presence of impacted earwax physically obstructs sound waves from reaching the eardrum, thus attenuating the volume and clarity of perceived sounds.
Common earwax softening agents include over-the-counter ear drops containing ingredients like mineral oil, hydrogen peroxide, carbamide peroxide, or saline solutions. These agents work by penetrating the earwax and either lubricating it for easier removal or chemically breaking it down. For instance, carbamide peroxide releases oxygen upon contact with earwax, causing it to foam and disintegrate. The consistent and proper use of these agents, as directed by product instructions or healthcare provider recommendations, is often sufficient to resolve mild to moderate earwax impaction and restore normal hearing. However, it is important to note that self-treatment with earwax softening agents is not appropriate for all cases of diminished auditory clarity. Individuals with ear infections, perforated eardrums, or who have undergone recent ear surgery should consult a medical professional before using these products.
In summary, earwax softening agents constitute a significant component of addressing muffled hearing caused by cerumen impaction. They are a readily available and often effective first-line treatment option. However, it is imperative to discern the underlying cause of the hearing reduction and to exercise caution and seek professional guidance when dealing with pre-existing ear conditions or when symptoms persist despite treatment. Their effectiveness is predicated on correct usage and the absence of contraindicating factors. Failure to improve with appropriate use of these agents suggests a different etiology for the diminished hearing, warranting medical evaluation.
2. Sinus congestion relief
Sinus congestion frequently manifests as a sensation of diminished auditory clarity, creating a direct link to the necessity for effective resolution strategies. The anatomical proximity of the sinuses to the middle ear via the Eustachian tube underscores the relevance of addressing sinus issues when managing perceived hearing impediments.
- Eustachian Tube Dysfunction
The Eustachian tube, connecting the middle ear to the nasopharynx, regulates pressure equalization. Sinus congestion can lead to inflammation and obstruction of this tube, preventing proper pressure balance. This pressure differential can result in a feeling of fullness or blockage in the ear, directly contributing to a muffled hearing experience. For instance, during a sinus infection, the swollen nasal passages impede Eustachian tube function, creating pressure that distorts the eardrum’s ability to vibrate efficiently.
- Inflammatory Mediators
Sinus infections trigger the release of inflammatory mediators that can affect the inner ear. These substances can induce inflammation within the middle ear space, potentially leading to fluid accumulation or thickening of the tissues responsible for sound transmission. This inflammatory process can attenuate sound vibrations, resulting in the perception of muffled hearing. As an example, cytokines released during a sinus infection can cause swelling in the middle ear, impacting its mechanical function.
- Nasal Passage Obstruction
Severe sinus congestion causes significant nasal passage obstruction, impacting airflow and pressure dynamics within the upper respiratory system. The resulting pressure variations can affect the Eustachian tube’s ability to ventilate the middle ear. This obstruction can exacerbate existing middle ear conditions or create a vacuum effect, further contributing to muffled hearing. Nasal polyps obstructing sinus drainage, for example, can chronically impair Eustachian tube function.
- Treatment Overlap
Many strategies aimed at sinus congestion relief directly benefit the resolution of muffled hearing. Decongestants, nasal saline rinses, and steam inhalation work to reduce inflammation and clear nasal passages, thereby improving Eustachian tube function and restoring normal pressure within the middle ear. As sinus congestion improves, the associated muffled hearing often resolves concurrently, demonstrating a direct therapeutic link. For instance, using a neti pot to clear sinus passages can also improve Eustachian tube drainage, thereby alleviating related muffled hearing.
The multifaceted connection between sinus congestion and muffled hearing highlights the importance of considering sinus-related issues when addressing auditory disturbances. Effective management of sinus congestion frequently contributes to the amelioration of perceived auditory deficits, reinforcing the integrated nature of the respiratory and auditory systems. The resolution of sinus congestion allows for the physiological restoration of the auditory system.
3. Pressure Equalization Techniques
Pressure equalization techniques are relevant to addressing diminished auditory clarity, as pressure imbalances within the middle ear are a common source of this sensation. These techniques aim to normalize pressure differences between the middle ear and the external environment, thus restoring optimal eardrum function and improving auditory perception.
- Valsalva Maneuver
The Valsalva maneuver involves attempting to exhale against a closed airway. This increases pressure in the nasopharynx, forcing air through the Eustachian tube into the middle ear. While effective, it must be performed gently to avoid barotrauma. For example, during air travel, this maneuver can alleviate the sensation of ear blockage caused by changes in cabin pressure.
- Toynbee Maneuver
The Toynbee maneuver involves swallowing while the nostrils are pinched closed. Swallowing contracts muscles that open the Eustachian tube, allowing air to enter the middle ear and equalize pressure. This is a subtler technique suitable for situations with minor pressure imbalances. An instance is when descending from a high altitude, the frequent swallowing helps maintain pressure equilibrium.
- Frenzel Maneuver
The Frenzel maneuver is a more advanced technique used by divers and involves using the tongue as a piston to force air through the Eustachian tube. This method requires practice and coordination but can equalize pressure more effectively at greater depths. For instance, a scuba diver uses this technique to equalize pressure to prevent ear squeeze.
- Yawning and Chewing
Yawning and chewing stimulate the muscles surrounding the Eustachian tube, promoting its opening and facilitating pressure equalization. These are natural responses to pressure changes and can be consciously employed to mitigate ear discomfort. As an example, chewing gum during airplane descents helps prevent muffled hearing.
The successful application of pressure equalization techniques directly addresses instances of diminished auditory clarity stemming from barometric pressure differentials or Eustachian tube dysfunction. These methods can restore optimal eardrum mobility and auditory function, thus resolving the sensation of muffled hearing. The choice of technique depends on the situation and individual comfort level, but proper execution is crucial to avoid potential complications.
4. Hydration maintenance
Adequate hydration supports numerous physiological functions, including those pertinent to auditory health. The connection between maintaining sufficient fluid intake and alleviating muffled hearing centers on hydration’s role in regulating mucus viscosity, circulatory efficiency, and overall cellular function within the auditory system. Dehydration can lead to thickened mucus secretions within the sinuses and Eustachian tube, potentially impeding proper drainage and contributing to pressure imbalances in the middle ear. These imbalances can manifest as a feeling of fullness or reduced auditory clarity. A real-world example is the increased incidence of muffled hearing reported during periods of intense physical activity or in arid climates, where dehydration is more prevalent. Proper hydration, conversely, helps maintain the fluidity of these secretions, promoting normal Eustachian tube function and reducing the likelihood of pressure-related auditory symptoms. The practical significance lies in the accessibility and ease with which hydration can be managed as a preventative or supportive measure.
Furthermore, maintaining adequate hydration contributes to optimal circulatory function, ensuring efficient delivery of oxygen and nutrients to the delicate structures within the inner ear. The inner ear, responsible for converting sound vibrations into neural signals, is particularly sensitive to disruptions in blood flow. Dehydration can reduce blood volume and increase blood viscosity, potentially impairing microcirculation within the inner ear and affecting the function of hair cells responsible for sound transduction. In scenarios such as prolonged air travel, where cabin air tends to be dry and dehydrating, proactive hydration helps maintain inner ear function and mitigate potential auditory discomfort. This demonstrates the application of hydration as a means of ensuring the resilience of the auditory system to environmental stressors.
In summary, hydration maintenance presents a foundational and often overlooked component of strategies to address muffled hearing. While hydration alone may not resolve all causes of diminished auditory clarity, its impact on mucus viscosity, Eustachian tube function, and inner ear circulation makes it a relevant factor in promoting overall auditory health. Challenges may arise in consistently maintaining adequate fluid intake, particularly in individuals with limited access to clean water or those with underlying medical conditions that affect fluid balance. However, understanding the role of hydration underscores a readily implementable step in supporting auditory well-being.
5. Professional audiological assessment
A professional audiological assessment constitutes a critical step in addressing diminished auditory clarity. When self-remedies prove insufficient, a comprehensive evaluation by a qualified audiologist provides insights into the underlying cause of the auditory impediment and informs targeted intervention strategies. Such assessment moves beyond symptomatic relief, focusing instead on diagnostic precision.
- Differential Diagnosis
Audiological assessments employ a battery of tests designed to differentiate between various causes of muffled hearing. These tests can distinguish between conductive hearing loss (e.g., earwax impaction, middle ear infection), sensorineural hearing loss (e.g., noise-induced damage, age-related decline), and central auditory processing disorders. For example, audiometry can identify the specific frequencies at which hearing loss occurs, guiding subsequent management decisions. Improper self-treatment, without a confirmed diagnosis, could exacerbate underlying conditions.
- Severity Quantification
Professional assessment quantifies the degree of hearing loss, enabling appropriate intervention. The audiologist determines the extent to which the auditory system is affected, ranging from mild impairment to profound deafness. This information is crucial for selecting the most effective management options, such as hearing aids, assistive listening devices, or medical referrals. A quantifiable measure of hearing loss, expressed in decibels, provides a baseline for monitoring treatment efficacy.
- Etiological Determination
Audiological evaluations aim to identify the underlying etiology of diminished hearing clarity. While some causes, such as earwax, are readily apparent, others require specialized testing to uncover. For instance, tympanometry can reveal middle ear dysfunction, while otoacoustic emissions testing can assess the function of the inner ear. Accurate etiological determination is essential for directing targeted therapy, such as medical treatment for otitis media or counseling for noise-induced hearing loss.
- Management Recommendations
Based on the assessment findings, audiologists provide tailored management recommendations. These recommendations may include medical referrals, hearing aid fittings, aural rehabilitation, or counseling on hearing protection strategies. The audiologist guides patients towards evidence-based interventions to maximize auditory function and communication abilities. For example, a patient with noise-induced hearing loss may receive counseling on the use of earplugs and strategies for reducing noise exposure.
The insights gleaned from a professional audiological assessment enable informed decision-making regarding the most appropriate course of action for addressing muffled hearing. This proactive approach to auditory healthcare not only alleviates immediate symptoms but also addresses underlying causes and promotes long-term auditory well-being. The precision and individualization offered by professional assessment far surpass the limitations of generic self-remedies.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following questions address common concerns related to experiencing reduced auditory clarity, often described as muffled hearing. The information provided aims to offer clarity regarding potential causes, appropriate responses, and when professional medical advice is advisable.
Question 1: What are the most prevalent causes of a sensation of muffled hearing?
Common causes include earwax accumulation, Eustachian tube dysfunction resulting from allergies or upper respiratory infections, sinus congestion, exposure to loud noises, and, in some cases, age-related hearing loss. Less common causes may involve certain medications or underlying medical conditions. The specific etiology can vary significantly between individuals.
Question 2: When is it appropriate to attempt self-treatment for diminished auditory clarity?
Self-treatment may be considered for cases suspected to be caused by earwax buildup or mild sinus congestion. Over-the-counter ear drops designed to soften earwax can be utilized, and steam inhalation or saline nasal rinses may alleviate sinus-related symptoms. However, if the condition persists, worsens, or is accompanied by pain, drainage, or dizziness, medical evaluation is necessary.
Question 3: Are there potential risks associated with attempting to remove earwax at home?
Yes. Improper attempts to remove earwax can result in damage to the ear canal or eardrum. The use of cotton swabs is discouraged, as they often push the earwax further into the ear canal, exacerbating the problem. Individuals with a history of ear infections, eardrum perforation, or ear surgery should seek professional earwax removal.
Question 4: How do allergies contribute to a sensation of muffled hearing?
Allergic reactions can lead to inflammation and swelling of the nasal passages and Eustachian tube. This inflammation impairs the Eustachian tube’s ability to regulate pressure in the middle ear, resulting in a feeling of fullness or blockage, and consequently, diminished auditory clarity. The use of antihistamines or other allergy management strategies may alleviate these symptoms.
Question 5: Can prolonged exposure to loud noise result in permanent auditory damage?
Yes. Exposure to high decibel levels over extended periods can cause irreversible damage to the hair cells in the inner ear, leading to noise-induced hearing loss. This type of hearing loss often manifests as a gradual decline in auditory clarity, particularly at higher frequencies. Consistent use of hearing protection in noisy environments is essential for preventing this damage.
Question 6: What diagnostic procedures are typically involved in an audiological evaluation?
An audiological evaluation typically includes otoscopy (visual examination of the ear canal and eardrum), tympanometry (assessment of middle ear function), audiometry (measurement of hearing sensitivity at different frequencies), and speech audiometry (assessment of speech understanding). Additional tests may be performed depending on the individual’s specific symptoms and medical history. These procedures help determine the type, degree, and potential cause of hearing loss.
The preceding answers address several frequently encountered questions regarding diminished auditory clarity. Recognizing the potential causes, implementing appropriate initial steps, and seeking professional guidance when necessary are crucial for effective management and the preservation of auditory health.
The subsequent section explores advanced treatment options for muffled hearing.
Muffled Ear Remedy
This discussion has addressed the multifaceted nature of diminished auditory clarity and the interventions that can be employed to alleviate the sensation. From at-home approaches like earwax softening and sinus congestion relief to the critical importance of professional audiological assessments, various avenues exist to address this concern. It is crucial to recognize that the efficacy of any particular approach depends on the underlying cause and the individual’s unique circumstances.
The preservation of auditory health demands a proactive and informed approach. Persistent or worsening diminished auditory clarity necessitates prompt evaluation by a qualified healthcare professional. Early detection and appropriate management are paramount in mitigating potential long-term consequences and ensuring optimal communication abilities. Further research and technological advancements will continue to refine and expand the options available for addressing auditory impediments.