The replacement of a vehicle’s exhaust silencing component is a routine maintenance procedure. This component is responsible for minimizing noise generated by the engine’s combustion process. An example of when this procedure is necessary is when the original component exhibits signs of significant corrosion or physical damage, leading to increased exhaust noise levels.
This maintenance task contributes to overall vehicle operational efficiency by ensuring optimal backpressure within the exhaust system. It also plays a role in maintaining compliance with local noise regulations, preventing potential legal issues. Historically, maintaining this part was crucial for reducing noise pollution in urban environments and promoting quieter transportation. Timely servicing helps prevent further damage to other exhaust system components, potentially saving on more extensive repairs later.
The following sections will delve into the common causes necessitating this service, the tools and procedures involved, and the factors influencing the associated costs. Furthermore, considerations for selecting the appropriate replacement component and potential troubleshooting steps will be addressed.
Essential Considerations for Muffler Change
This section outlines crucial considerations to ensure a successful and efficient exhaust silencing component replacement process.
Tip 1: Proper Diagnosis: Before initiating the procedure, thoroughly inspect the existing system for leaks, corrosion, or damage beyond the component in question. Addressing underlying issues prevents premature failure of the new component.
Tip 2: Select the Correct Replacement: Ensure the replacement component matches the vehicle’s make, model, and year. Utilizing an incompatible component can lead to performance issues or damage to other exhaust system parts.
Tip 3: Use Appropriate Tools: Employ specialized tools such as exhaust hangers, penetrating oil, and oxygen sensor sockets to prevent damage during disassembly and reassembly.
Tip 4: Apply Anti-Seize Compound: When installing new fasteners, apply anti-seize compound to the threads to facilitate future removal and prevent corrosion.
Tip 5: Inspect Exhaust Hangers: Examine and replace worn or damaged exhaust hangers to properly support the exhaust system and prevent stress on the new component.
Tip 6: Torque to Specification: Tighten all fasteners to the manufacturer’s specified torque values. Over-tightening can damage components, while under-tightening can lead to leaks.
Tip 7: Post-Installation Inspection: After installation, start the vehicle and carefully inspect for exhaust leaks, unusual noises, or vibrations. Address any issues immediately.
Adhering to these guidelines will contribute to a longer lifespan for the replacement part and maintain optimal vehicle performance.
The subsequent section will provide guidance on selecting a qualified technician or repair facility for performing this maintenance task.
1. Component Degradation
Component degradation is a primary driver for exhaust silencing component replacement. The gradual deterioration of the part’s materials, due to various factors, ultimately compromises its functionality and necessitates its renewal. This deterioration impacts vehicle operation and requires attention to avoid further issues.
- Corrosion and Rust Formation
Exposure to road salts, moisture, and acidic exhaust gases accelerates corrosion on the component’s exterior and interior surfaces. This corrosion weakens the metal, leading to leaks, structural failure, and diminished noise reduction capabilities. An example is the formation of rust on the component’s welds, eventually causing separation and exhaust leaks.
- Internal Baffle Deterioration
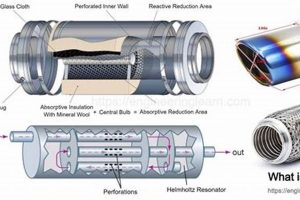
The internal baffles are designed to attenuate sound waves. Over time, these baffles can degrade due to thermal cycling, vibration, and the corrosive effects of exhaust gases. Deterioration reduces the component’s ability to effectively dampen exhaust noise. An instance of this is the disintegration of fiberglass packing within the component, leading to increased exhaust volume.
- Physical Damage from Road Debris
Impacts from road debris, such as rocks and other foreign objects, can cause dents, punctures, and structural damage. Physical damage compromises the integrity of the component, resulting in leaks and reduced effectiveness. For example, a large rock striking the component during operation can create a hole, leading to significant exhaust leaks and increased noise.
- Thermal Stress and Fatigue
Repeated heating and cooling cycles create thermal stress, leading to metal fatigue and cracking. The constant expansion and contraction weaken the component’s structure over time, contributing to its eventual failure. An example of this is the cracking of the component’s casing near the engine manifold due to extreme temperature fluctuations.
These facets of component degradation highlight the diverse mechanisms through which a vehicle’s exhaust silencing element fails. Each degradation pathway diminishes its ability to fulfill its intended function, underscoring the importance of regular inspection and timely replacement to maintain vehicle performance and compliance.
2. Noise Reduction
The exhaust silencing component replacement is intrinsically linked to noise reduction, serving as the primary means of mitigating engine exhaust noise. The original component’s degradation directly results in increased noise levels, prompting the need for replacement. The functionality of a new component is assessed by its capacity to reduce the engine’s exhaust noise output to within acceptable limits, frequently specified by local ordinances. For instance, a vehicle failing a noise inspection due to an ineffective component necessitates its replacement to achieve compliance.
Effective noise reduction relies on the component’s internal design, employing baffles and sound-absorbing materials to attenuate exhaust sound waves. Different component types, such as chambered or turbo components, offer varying degrees of noise reduction, affecting both sound level and tone. As an example, vehicles operating in residential zones typically require components with superior sound dampening characteristics to minimize disturbance. Conversely, performance-oriented vehicles might utilize components with less restrictive designs, trading some noise reduction for enhanced exhaust flow.
In summary, the efficacy of the exhaust silencing component replacement hinges upon its ability to achieve targeted noise reduction. The selection of the correct replacement, tailored to the vehicle’s application and local regulations, is crucial. Addressing component degradation maintains vehicle compliance, contributes to environmental noise control, and enhances the overall driving experience.
3. System Compatibility
System compatibility is paramount when undertaking an exhaust silencing component replacement. Ensuring the replacement part aligns with the vehicle’s specific make, model, year, and engine configuration is crucial for optimal performance, proper fitment, and the avoidance of potential operational issues. Incompatibility can lead to reduced efficiency, increased noise, and even damage to other exhaust system components.
- Dimensional Matching
The physical dimensions of the replacement must precisely match the original component. This includes overall length, inlet/outlet diameter, and mounting point locations. Dimensional discrepancies can prevent proper installation, leading to exhaust leaks, improper support, and potential damage to connecting components. For example, an incorrectly sized inlet diameter may require adapters or modifications, compromising the integrity of the exhaust system.
- Engine Configuration Alignment
Exhaust systems are often designed specifically for particular engine configurations (e.g., inline-four, V6, V8). Using a component designed for a different engine type can result in suboptimal performance and increased noise. This is because different engines produce varying exhaust gas volumes and flow characteristics. An example is installing a component designed for a high-performance V8 engine on a fuel-efficient inline-four, which could lead to reduced backpressure and compromised fuel economy.
- Emissions System Integration
Modern vehicles incorporate sophisticated emissions control systems, including catalytic converters and oxygen sensors. The replacement component must be compatible with these systems to ensure proper operation and compliance with emissions regulations. Incompatibility can trigger warning lights, reduce fuel efficiency, and potentially lead to failed emissions tests. An example is installing a component that interferes with the proper functioning of an oxygen sensor, leading to incorrect air-fuel mixture readings and reduced catalytic converter efficiency.
- Mounting Hardware and Support Structures
The replacement should utilize the same mounting points and support structures as the original, ensuring secure attachment and preventing undue stress on the exhaust system. Incorrect mounting can lead to vibration, premature failure, and potential damage to surrounding vehicle components. An example is using a component with incompatible hanger positions, requiring modifications to the vehicle’s chassis or the exhaust system itself, potentially compromising structural integrity.
The aspects of system compatibility highlight the importance of selecting a replacement part designed explicitly for the target vehicle. Failure to address these considerations can lead to a range of problems, compromising vehicle performance, emissions compliance, and overall reliability. Consulting vehicle manufacturer specifications or a qualified automotive technician is advisable when selecting a replacement to ensure proper fitment and functionality.
4. Regulatory Compliance
Regulatory compliance concerning exhaust silencing component replacement is a critical aspect of vehicle maintenance. Adherence to established noise level regulations and emissions standards is paramount. Ignoring these regulations can result in fines, failed inspections, and legal consequences. Ensuring the replacement adheres to these standards is a responsibility for both vehicle owners and service providers.
- Noise Emission Standards
Local, state, and federal regulations often impose specific decibel limits on vehicle exhaust noise. A degraded or improperly installed component can cause a vehicle to exceed these limits. Replacement necessitates selecting a component certified to meet the applicable noise standards. For example, many municipalities enforce noise ordinances, requiring vehicles to maintain exhaust noise below a specific threshold during operation; failure to comply results in a citation.
- Emissions Control Requirements
In regions with stringent emissions regulations, replacement components must not compromise the vehicle’s emissions control systems. Alterations to the exhaust system can affect the catalytic converter’s efficiency and increase harmful emissions. Replacement components must be designed to function in harmony with the existing emissions control devices. As an example, installing an aftermarket component that reduces backpressure beyond specified limits can negatively impact the catalytic converter’s ability to reduce pollutants, potentially causing the vehicle to fail an emissions test.
- Inspection and Testing Protocols
Periodic vehicle inspections frequently include evaluations of the exhaust system, including noise levels and emissions outputs. Replacement components must facilitate compliance with these inspection protocols. Non-compliant components necessitate rectification to pass inspection and maintain vehicle registration. As an example, vehicles in some states are subject to annual or biennial safety and emissions inspections. If the exhaust system fails to meet the prescribed standards, the vehicle owner must undertake repairs or replacements to rectify the issues.
- Aftermarket Component Certification
To ensure regulatory compliance, many aftermarket components undergo certification processes to verify their adherence to noise and emissions standards. These certifications, often denoted by labels or documentation, provide assurance that the component meets the necessary criteria. Purchasing certified components mitigates the risk of non-compliance. For instance, some regions require aftermarket components to be certified by specific agencies or organizations. These certifications confirm that the components have undergone testing and meet the required performance benchmarks.
The multifaceted nature of regulatory compliance underscores the importance of diligence when undertaking exhaust silencing component replacement. Selecting certified components, adhering to installation guidelines, and undergoing post-installation inspections are vital steps in ensuring that vehicles meet the necessary standards, thereby avoiding penalties and promoting environmental responsibility. Furthermore, understanding local regulations and inspection protocols is paramount for both vehicle owners and automotive technicians.
5. Performance Impact
The replacement of an exhaust silencing component significantly affects vehicle performance characteristics. The choice of component influences engine output, fuel efficiency, and overall driving dynamics. Therefore, a thorough understanding of performance implications is crucial when selecting a replacement.
- Exhaust Backpressure Modulation
The internal design of the exhaust silencing component directly impacts exhaust backpressure. Excessive backpressure restricts exhaust flow, reducing engine power, particularly at higher RPMs. Conversely, insufficient backpressure can negatively affect low-end torque and fuel economy. Replacement with a component offering similar backpressure characteristics to the original typically maintains factory performance. However, performance-oriented components designed to reduce backpressure are available, requiring careful consideration of potential trade-offs.
- Engine Tuning Considerations
Altering the exhaust system, including the component, can necessitate adjustments to the engine’s air-fuel ratio. A less restrictive exhaust system might require recalibration to prevent a lean condition, which can damage the engine. Some vehicles’ engine control units (ECUs) can automatically compensate for minor changes in exhaust flow. However, significant alterations often necessitate professional tuning to optimize performance and prevent engine damage.
- Sound Characteristics and Perceived Performance
While not directly affecting quantifiable performance metrics, the sound produced by the exhaust system influences the driver’s perception of performance. A more aggressive-sounding component may subjectively enhance the driving experience, even if actual performance gains are minimal. However, excessive noise can also be detrimental, leading to driver fatigue and potential violations of noise regulations.
- Impact on Fuel Efficiency
The selection of an exhaust silencing component can indirectly influence fuel efficiency. Components that significantly alter exhaust backpressure can affect engine efficiency, either positively or negatively. Maintaining similar backpressure characteristics to the original component generally preserves factory fuel economy. However, performance-oriented components that reduce backpressure might improve fuel economy under specific operating conditions, particularly at higher speeds and loads.
The interplay between component selection and vehicle performance underscores the need for informed decision-making. Considering the specific requirements of the vehicle and the desired performance characteristics ensures that the exhaust silencing component replacement enhances, rather than detracts from, the overall driving experience.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding exhaust silencing component replacement, providing clear and concise information to enhance understanding of this maintenance procedure.
Question 1: What constitutes a valid reason for exhaust silencing component replacement?
Substantial rust, physical damage causing exhaust leaks, and internal baffle deterioration leading to excessive noise are all valid reasons. A compromised component diminishes performance and potentially violates noise regulations.
Question 2: How frequently should exhaust silencing components be inspected?
Annual inspections are recommended, or more frequently in regions with harsh road conditions or frequent exposure to corrosive substances. Early detection of degradation prevents further complications.
Question 3: Does replacing the exhaust silencing component impact vehicle emissions?
If the replacement is non-compliant or alters the exhaust system’s design, it can affect emissions. Ensure the replacement meets or exceeds original equipment manufacturer (OEM) specifications to maintain emissions compliance.
Question 4: What are the consequences of neglecting a damaged exhaust silencing component?
Neglecting a damaged component can lead to increased exhaust noise, reduced fuel efficiency, potential damage to other exhaust system components, and possible fines for violating noise regulations.
Question 5: Can an exhaust silencing component replacement improve vehicle performance?
While the primary function is noise reduction, certain performance-oriented components can slightly improve exhaust flow, potentially leading to modest gains in horsepower and torque. However, significant performance enhancements are unlikely.
Question 6: Is exhaust silencing component replacement a do-it-yourself (DIY) project?
While mechanically inclined individuals may undertake this task, it often requires specialized tools, expertise in exhaust system mechanics, and attention to safety precautions. Professional installation is generally recommended to ensure proper fitment and avoid complications.
In summary, exhaust silencing component replacement is an essential maintenance task that should not be overlooked. Regular inspections and timely replacements are key to maintaining vehicle performance, regulatory compliance, and a comfortable driving experience.
The subsequent section will delve into troubleshooting common issues encountered after exhaust silencing component replacement.
Muffler Change
The preceding exposition detailed the nuances of exhaust silencing component replacement. Key areas encompassed included diagnostics, compatible replacement part selection, essential installation techniques, regulatory considerations, and potential performance implications. Addressing component degradation proactively remains critical for maintaining vehicle performance and compliance with applicable standards. Timely intervention mitigates further systemic damage and prevents regulatory infractions.
Therefore, diligent monitoring of the exhaust system’s integrity is paramount. Vehicle owners and maintenance personnel should prioritize regular inspections and prompt execution of necessary repairs. Prioritizing this maintenance aspect ensures continued compliance, optimizes operational efficiency, and preserves the overall longevity of the vehicle. Failure to address potential issues can lead to more complex and costly repairs in the future.