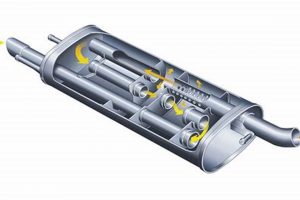
This refers to a component designed to reduce the noise emitted from internal combustion engines, specifically those used in vehicles operating in or around the Sioux region. It’s a type of exhaust system part crucial for compliance with noise regulations and enhancing the overall driving experience by minimizing disruptive sounds. For example, a vehicle operating near a residential area might require a high-quality version of this part to maintain a quiet environment.
The use of such a component is important for environmental considerations, promoting quieter communities and reducing noise pollution. Historically, efforts to control vehicle noise have led to advancements in design and materials, resulting in more effective sound dampening and improved vehicle performance. Its benefits extend to improved driver comfort and reduced disturbance to wildlife and local populations.
The following sections will delve into specific design features, material considerations, and maintenance practices relevant to ensuring the optimal functionality and longevity of exhaust noise reduction systems. Furthermore, an examination of current regulations related to vehicle sound emissions will be provided, highlighting the ongoing importance of effective sound mitigation technologies.
Maintenance and Longevity
The following tips are intended to provide guidance on maintaining and maximizing the lifespan of components designed to reduce exhaust noise, ensuring optimal performance and regulatory compliance.
Tip 1: Regular Inspection: Conduct routine visual inspections of the system. Look for signs of rust, corrosion, or physical damage. Address any issues promptly to prevent escalation.
Tip 2: Proper Installation: Ensure correct installation according to manufacturer specifications. Improper installation can lead to premature wear and reduced efficiency.
Tip 3: Address Leaks Immediately: Exhaust leaks not only increase noise levels but also pose potential safety hazards. Repair any leaks as soon as they are detected.
Tip 4: Use Quality Replacement Parts: When replacement is necessary, opt for high-quality components that meet or exceed original equipment manufacturer (OEM) standards. Inferior parts may offer short-term savings but ultimately compromise performance and longevity.
Tip 5: Avoid Harsh Chemicals: Refrain from using harsh chemicals or abrasive cleaners on the exhaust system. These can damage protective coatings and accelerate corrosion.
Tip 6: Monitor Engine Performance: Maintain optimal engine performance. Engine misfires or improper fuel combustion can increase exhaust temperatures and stress the sound-dampening components.
Tip 7: Consider Climate Factors: In regions with harsh winters and salted roads, consider applying rust-inhibiting coatings to protect the system from corrosion.
Implementing these maintenance practices will contribute to the extended operational life and consistent performance of the exhaust noise reduction system, ultimately ensuring both regulatory compliance and a more pleasant driving experience.
The subsequent sections will offer an overview of prevailing regulations concerning vehicle sound levels and explore the ongoing advancements in sound suppression technology.
1. Noise Level Reduction
Noise level reduction is a primary function, a critical performance characteristic, and a key design driver in the engineering and application of vehicular exhaust systems. Its effectiveness directly impacts regulatory compliance, environmental impact, and the quality of life within communities where vehicles operate.
- Acoustic Dampening Mechanisms
Internal baffling and sound-absorbing materials within the device are engineered to attenuate sound waves generated by the engine’s exhaust. These mechanisms convert acoustic energy into heat through friction and reflection, thereby reducing the intensity of the emitted sound. Inefficient acoustic dampening results in elevated noise levels, potentially exceeding legal limits and causing disturbance.
- Material Selection and Design
The choice of materials and the overall structural design significantly influence the component’s ability to reduce noise. Certain metals and composite materials exhibit superior sound-absorbing properties. Additionally, strategically designed chambers and passages within the component can optimize sound wave cancellation and minimize noise propagation. Poor material selection or suboptimal design compromises performance, leading to increased noise emissions.
- Impact on Environmental Regulations
Stringent noise pollution regulations are enforced in many jurisdictions to protect public health and environmental quality. Effective exhaust noise reduction is essential for vehicles to comply with these regulations. Failure to meet noise emission standards can result in fines, penalties, and restrictions on vehicle operation. Effective sound suppression is therefore a fundamental requirement for legal and responsible vehicle operation.
- Community Well-being and Quality of Life
Excessive vehicle noise contributes to noise pollution, which negatively impacts human health and well-being. Prolonged exposure to high noise levels can lead to stress, sleep disturbances, and other health problems. The effective reduction of exhaust noise improves the quality of life for residents living near roadways and contributes to quieter, more peaceful communities. The benefit of quiet is immeasurable, from public satisfaction to public health.
The combined effect of these facets illustrates the essential role of noise level reduction as a critical element in overall performance. In essence, the efficacy of any design is directly tied to its ability to minimize unwanted sound, emphasizing its role in achieving a balance between functionality, compliance, and societal well-being.
2. Material Durability
Material durability is a paramount consideration in the design and functionality of exhaust noise reduction systems. The exhaust system, including the sound reduction component, is exposed to extreme conditions. These conditions include high temperatures, corrosive exhaust gases, road salts, and physical impacts from debris. The chosen materials directly dictate the system’s lifespan, performance, and overall reliability. Consequently, selecting appropriate materials with high durability is crucial for minimizing maintenance costs and ensuring consistent operation.
The degradation of materials due to corrosion, thermal fatigue, or physical damage directly affects the performance. For instance, a rusted-through system component loses its structural integrity, causing exhaust leaks and increased noise levels. The use of high-grade stainless steel or aluminized steel is often preferred for their resistance to corrosion and high-temperature oxidation. Consider the practical example of vehicles operating in regions with harsh winter conditions. Road salts accelerate corrosion, requiring even more robust materials to withstand the environmental assault. Premature failure of the system noise reducer can lead to increased noise pollution, vehicle performance degradation, and the need for costly replacements.
In conclusion, the link between material durability and system noise reducers is undeniable. Selecting materials that withstand the rigors of the operating environment is essential for ensuring long-term performance, regulatory compliance, and minimizing environmental impact. The investment in high-quality, durable materials translates to reduced maintenance, increased reliability, and a sustained reduction in vehicle noise pollution. The pursuit of materials with enhanced durability remains a critical area of focus in the ongoing development and refinement of exhaust system technology.
3. Exhaust Flow Efficiency
Exhaust flow efficiency, or the ease with which exhaust gases are expelled from an engine, is inextricably linked to the functionality and performance characteristics of exhaust noise reduction devices. An exhaust system’s noise reducer serves a dual purpose: to diminish sound levels and to channel exhaust gases away from the engine. Compromising the system design such that it significantly impedes exhaust flow results in reduced engine performance, decreased fuel efficiency, and elevated engine temperatures. This is because the engine must work harder to expel the exhaust gases, leading to parasitic power loss and potential damage to engine components. Therefore, an effective exhaust noise reduction component requires a design that balances noise reduction with the need to maintain a relatively unrestricted flow path for exhaust gases. For instance, an ill-designed noise reducer with excessive baffling or restrictive passages creates backpressure, counteracting the engine’s natural aspiration process and negatively impacting volumetric efficiency.
The design directly impacts fuel consumption and emissions output. A noise reduction component with a high-flow design minimizes backpressure, enabling the engine to operate more efficiently, thus reducing fuel consumption and lowering emissions. Conversely, a restrictive device increases backpressure, resulting in increased fuel consumption and higher emissions levels. The selection of materials also influences exhaust flow efficiency. Smooth interior surfaces minimize turbulence, thereby reducing flow restriction. In contrast, rough or corroded surfaces increase turbulence, impeding exhaust flow and diminishing efficiency. A practical example of the consequence of neglecting flow efficiency is the experience of motorists who have replaced their factory-installed sound suppression device with an aftermarket part that, while effective at reducing noise, creates excessive backpressure, leading to noticeable degradation in vehicle performance.
In summary, the significance of exhaust flow efficiency in exhaust noise reduction devices cannot be overstated. An optimally designed system strikes a balance between noise reduction and flow efficiency, ensuring that the engine can operate at its peak performance while meeting noise emission standards. Neglecting flow efficiency leads to compromised engine performance, increased fuel consumption, and higher emissions. The pursuit of designs and materials that minimize flow restriction while maximizing sound attenuation remains a central focus in the ongoing evolution of exhaust system technology, reflecting a commitment to both environmental responsibility and optimal vehicle performance.
4. Regulatory Compliance
Adherence to noise emission standards is a fundamental requirement for vehicular operation, thereby establishing a direct and critical link to exhaust sound reduction components. These devices must effectively mitigate exhaust noise to comply with legally mandated decibel limits established by federal, state, and local regulatory bodies. Non-compliance results in penalties, potentially including fines, vehicle impoundment, or restrictions on operation. Consequently, the selection, installation, and maintenance of an effective exhaust noise reduction component are not merely matters of personal preference but legally mandated obligations.
Various regulatory frameworks govern vehicular noise emissions. Federal regulations, such as those enforced by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), set baseline standards for vehicle noise. Individual states and municipalities frequently impose more stringent regulations tailored to address specific local concerns, such as residential area proximity or noise-sensitive environments. The component must meet or exceed the requirements of all applicable jurisdictions to ensure legal and responsible vehicle operation. For example, a vehicle operating near a school zone may be subject to stricter noise limits than a vehicle operating in a less populated area, necessitating a higher-performing exhaust noise reduction system.
Therefore, regulatory compliance serves as a primary driver in the design, manufacturing, and application of exhaust noise reduction components. The ability to meet or exceed established noise emission standards is an indispensable criterion for the component’s effectiveness and suitability. The practical significance of this understanding is underscored by the legal and financial consequences of non-compliance, as well as the broader implications for public health and environmental well-being. A commitment to regulatory compliance ensures responsible vehicular operation and contributes to a quieter, more sustainable transportation landscape.
5. Installation Integrity
The operational effectiveness and longevity of exhaust noise reduction devices are contingent upon proper installation. Installation integrity, referring to the correct and secure fitting of the device within the vehicle’s exhaust system, directly affects its ability to attenuate noise and efficiently channel exhaust gases. Improper installation introduces vulnerabilities, compromising performance and potentially leading to premature component failure. A loosely fitted system, for instance, permits exhaust leaks, negating noise reduction efforts and presenting safety hazards due to the escape of harmful gases. This is particularly pertinent in enclosed environments. The causal relationship between correct installation and optimal performance is, therefore, a fundamental consideration.
The exhaust noise reduction system’s design and materials are relevant factors to achieve design installation. The process necessitates adherence to manufacturer specifications, using appropriate tools and techniques to ensure secure connections and prevent damage to the system components. Failure to properly align and secure the components creates stress points, accelerating wear and increasing the risk of leaks or disconnections. The integrity of the installation extends to the use of appropriate hardware, such as gaskets and clamps, to create airtight seals and withstand the vibrational forces generated by the engine. An example of the practical consequences of installation oversight is the increased prevalence of exhaust leaks in vehicles where the system components were hastily or improperly fitted during aftermarket modifications.
In summary, installation integrity is a foundational element for achieving desired performance. Neglecting this aspect undermines the design and material quality, leading to reduced noise attenuation, compromised exhaust flow, and increased risk of component failure. The practical significance of proper installation lies in the prevention of costly repairs, the maintenance of regulatory compliance, and the assurance of a quieter, more environmentally responsible vehicle operation. Continued emphasis on correct installation procedures is, therefore, essential for maximizing the value and effectiveness of exhaust noise reduction technologies.
6. Maintenance Schedule
Adherence to a well-defined maintenance schedule is paramount to sustaining the operational effectiveness and extending the lifespan of exhaust noise reduction devices. A failure to conduct routine inspections and address minor issues proactively invariably leads to accelerated wear, diminished performance, and potential regulatory non-compliance. The degradation of exhaust components is often gradual and, if undetected, culminates in significant functional compromise. The practical significance lies in the fact that a small investment in preventative maintenance often mitigates the need for costly repairs or premature replacement of the system component. A maintenance schedule should incorporate visual inspections for rust, corrosion, or physical damage; periodic tightening of clamps and fasteners; and prompt attention to any detected exhaust leaks. The correlation between a consistent maintenance schedule and prolonged functional reliability is statistically significant.
Neglecting maintenance has cascading consequences. For example, a small exhaust leak, if left unaddressed, escalates into a larger breach, reducing the muffler’s ability to attenuate noise. Moreover, the escaping hot exhaust gases accelerate corrosion in surrounding components. Internal corrosion or material failure compromises its sound-dampening capacity, resulting in increased noise emissions. The effectiveness in mitigating engine noise is contingent not only on its initial design and material composition but also on the consistent implementation of preventative maintenance. Routine maintenance practices, such as flushing corrosive road salts in winter, contribute directly to extending the lifespan and maintaining optimal performance.
A commitment to a structured maintenance schedule ensures consistent adherence to regulatory noise emission standards, reduces the likelihood of unexpected repairs, and maximizes the return on investment in exhaust noise reduction technology. Moreover, it contributes to a safer and more environmentally responsible vehicle operation. Therefore, the creation and diligent execution of a comprehensive maintenance schedule are essential for preserving the functionality, and regulatory compliance of this system component and the long term satisfaction from those served by this tool.
7. Regional Adaptation
The concept of regional adaptation, in the context of vehicle components, pertains to tailoring the design and materials of said components to withstand the specific environmental conditions prevalent in a given geographic area. For exhaust sound reduction devices operating in the Sioux region, this adaptation is not merely a cosmetic consideration but a practical imperative dictated by the region’s climate, terrain, and road maintenance practices.
- Corrosion Resistance Strategies
The Sioux region experiences harsh winters characterized by the extensive use of road salts for de-icing. These salts, primarily sodium chloride and calcium chloride, are highly corrosive to ferrous metals. Therefore, exhaust sound reduction devices intended for use in this region must incorporate advanced corrosion resistance strategies. This may involve the use of higher grades of stainless steel, aluminized coatings, or specialized polymer barriers to mitigate the accelerated corrosion caused by prolonged exposure to road salts. A practical example is the implementation of a multi-layered coating system on the external surfaces of the muffler to provide a robust barrier against salt penetration and electrochemical corrosion.
- Thermal Stress Management
Significant temperature fluctuations are common in the Sioux region, ranging from sub-zero winter temperatures to high summer heat. These fluctuations induce thermal stress in exhaust system components, potentially leading to fatigue cracking and premature failure. Regional adaptation in this context necessitates the selection of materials with high thermal fatigue resistance and the implementation of design features that minimize stress concentrations. The use of expansion joints or flexible couplings in the exhaust system can accommodate thermal expansion and contraction, reducing the strain on critical welds and joints. An example of thermal stress mitigation is the incorporation of strategically placed gussets or reinforcing ribs to enhance the structural integrity of the sound reduction device under extreme temperature variations.
- Terrain and Road Condition Adaptation
The Sioux region encompasses diverse terrain, including prairie landscapes, hilly regions, and areas with unpaved or poorly maintained roads. Vehicles operating in these environments are subjected to increased mechanical stress and impact from road debris. Regional adaptation involves reinforcing the structural integrity of the exhaust system to withstand these challenges. This may include increasing the thickness of the metal casing, reinforcing welds, and providing additional shielding to protect against impacts. An example would be the addition of a skid plate or rock guard to the underside of the vehicle to shield the exhaust from damage during off-road driving or on rough terrain.
- Air Quality Considerations
While not directly related to physical durability, regional air quality regulations may influence design choices. Stringent emissions standards may necessitate the integration of advanced catalytic converters within the exhaust system, impacting its overall size, weight, and backpressure characteristics. Regional adaptation, in this context, involves optimizing the design of the sound reduction device to accommodate these emissions control components while maintaining acceptable levels of noise reduction and exhaust flow efficiency. The adoption of low-restriction, high-efficiency catalytic converters minimizes the impact on engine performance and fuel economy while ensuring compliance with regional air quality regulations.
In summation, the concept of regional adaptation for exhaust sound reduction devices used in the Sioux region encompasses a multifaceted approach involving material selection, design optimization, and consideration of local regulatory requirements. By addressing the specific environmental challenges and regulatory constraints of the region, manufacturers can ensure the long-term durability, performance, and compliance of these critical vehicle components.
Frequently Asked Questions About Sioux Muffler Systems
This section addresses common inquiries concerning exhaust noise reduction devices, particularly those designed for vehicles operating in regions with conditions similar to those found in the Sioux area.
Question 1: What constitutes a Sioux Muffler?
This refers to a device engineered to attenuate exhaust noise emanating from internal combustion engines, with a design ideally suited for vehicles operating in the specific environmental conditions prevalent in the Sioux region. These conditions include cold winters with road salt usage, temperature fluctuations, and diverse terrain.
Question 2: How does road salt impact the lifespan of a Sioux Muffler?
Road salt, commonly used for de-icing in regions like the Sioux area, accelerates corrosion of metallic exhaust components. This necessitates the use of corrosion-resistant materials, such as high-grade stainless steel or aluminized steel, and protective coatings to prolong the component’s lifespan.
Question 3: Does Sioux Muffler impede engine performance?
A properly designed component should minimize backpressure to avoid negatively impacting engine performance and fuel efficiency. Efficient designs balance noise reduction with the need for unrestricted exhaust flow, optimizing overall vehicle operation.
Question 4: What are the legal implications of using a damaged noise reduction device?
Operating a vehicle with a damaged exhaust noise reducer that exceeds legal noise emission limits can result in fines, penalties, or vehicle restrictions. Adherence to local and federal noise regulations is a legal requirement.
Question 5: How often should exhaust noise reduction components be inspected?
Regular visual inspections should be conducted to identify signs of rust, corrosion, or physical damage. Annual professional inspections are advisable to ensure optimal performance and compliance with noise regulations.
Question 6: What are the key considerations when replacing a noise reduction device?
When replacing the component, opt for high-quality parts that meet or exceed OEM standards. Consider the material durability, exhaust flow efficiency, and regional environmental factors to ensure long-term performance and reliability.
Consistent adherence to these considerations ensures a quieter, more environmentally responsible vehicle operation.
Subsequent sections will delve into advanced strategies for maintaining and optimizing exhaust noise reduction systems in challenging environments.
Conclusion
The preceding exploration of “Sioux Muffler” clarifies its crucial role in maintaining vehicle performance, ensuring regulatory compliance, and mitigating noise pollution within the specified region. The analysis underscores the interplay of material durability, exhaust flow efficiency, regulatory mandates, proper installation, and consistent maintenance in achieving optimal noise reduction.
The continued development and implementation of advanced exhaust noise reduction technologies remain vital for fostering quieter, more sustainable communities. Prioritizing the considerations outlined in this document will lead to increased vehicle longevity, reduced environmental impact, and improved quality of life for residents throughout the region. Diligence in this area is not merely a matter of compliance but a responsibility to contribute to a more peaceful and sustainable future.