The subject in question refers to a specific vehicle exhaust component, presumably belonging to an individual named Tim. This component is designed to reduce the noise emitted by the engine’s combustion process as exhaust gases are expelled. For example, if Tim’s vehicle is noticeably quieter than other vehicles of similar make and model, the component is likely functioning as intended.
Effective reduction of exhaust noise contributes to a more pleasant driving experience for the operator and reduces noise pollution in the surrounding environment. Historically, such components have evolved significantly, from simple baffles to more complex designs incorporating resonance chambers and sound-absorbing materials, reflecting increasing concern for noise abatement.
Further discussion will delve into the specific aspects of vehicle exhaust systems, examining the principles of noise reduction and the various technologies employed to achieve quieter operation. Analysis will also consider the maintenance and potential issues associated with such components, ensuring optimal vehicle performance and compliance with noise regulations.
Maintenance and Longevity Insights
The following recommendations are designed to ensure optimal performance and extend the service life of a vehicle’s exhaust noise reduction system.
Tip 1: Routine Inspection: Conduct periodic visual inspections for signs of corrosion, physical damage, or leaks. Early detection allows for proactive repairs, preventing further deterioration.
Tip 2: Prompt Repair of Leaks: Address any detected exhaust leaks immediately. Leaks can compromise the system’s noise reduction capabilities and lead to increased fuel consumption and potential safety hazards.
Tip 3: Avoid Short Trips: Frequent short trips can cause condensation to accumulate within the system, accelerating corrosion. Longer trips allow the system to reach optimal operating temperature, evaporating moisture.
Tip 4: Use Quality Replacement Parts: When replacement is necessary, opt for components manufactured to original equipment specifications or higher. Inferior parts may exhibit reduced performance and durability.
Tip 5: Regular Cleaning: Periodically clean the exterior of the exhaust system to remove road salt and debris, particularly in regions with harsh winter conditions. This can help to minimize corrosion.
Tip 6: Engine Maintenance: Maintain the vehicle’s engine in good working order. A properly functioning engine reduces stress on the exhaust system, prolonging its lifespan.
Tip 7: Consider Professional Inspection: Schedule a professional inspection by a qualified mechanic at regular intervals. This allows for a comprehensive assessment of the system’s condition and can identify potential issues not readily apparent during a visual inspection.
Adherence to these recommendations can significantly improve the lifespan and effectiveness of a vehicle’s exhaust noise reduction system, ensuring continued compliance with noise regulations and a more comfortable driving experience.
The subsequent sections will elaborate on the legal regulations governing vehicle noise emissions and the impact of these regulations on vehicle design and maintenance practices.
1. Noise Reduction
Effective noise reduction is the fundamental purpose of the component in question, significantly impacting vehicle operation and environmental considerations. Its design and functionality directly correlate with the attenuation of engine exhaust noise, influencing both driver comfort and adherence to noise pollution regulations.
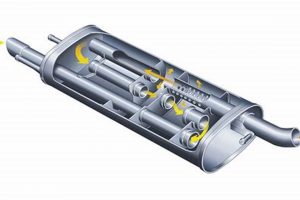
- Internal Baffle Design
The internal architecture, comprised of baffles and chambers, strategically redirects and dampens sound waves. Variation in the design impacts the frequency and intensity of the emitted noise. For instance, complex chamber designs can target specific frequencies, further reducing audible sound levels. Failure to maintain the integrity of these internal structures compromises their sound-dampening capabilities.
- Sound-Absorbing Materials
Certain materials, such as fiberglass or specialized acoustic packing, are employed to absorb sound energy within the component. Degradation of these materials over time reduces their effectiveness, leading to increased noise emissions. The type and density of these materials are crucial factors in determining the overall noise reduction performance. Over time, heat and condensation can degrade these materials.
- Resonance and Interference
Engineered resonance chambers within the component create destructive interference patterns, canceling out specific frequencies generated by the engine. The effectiveness of this technique is dependent on precise design and manufacturing tolerances. Damage or modification to these chambers disrupts the interference patterns, diminishing noise reduction capabilities. The effect is most pronounced at frequencies matched to the chamber design.
- Flow Restriction Considerations
While optimizing for noise reduction, the design must also minimize backpressure on the engine. Excessive flow restriction can negatively impact fuel efficiency and engine performance. The balance between noise reduction and exhaust flow is a critical design consideration. Modifications aimed at maximizing noise reduction at the expense of flow can have adverse consequences.
The interplay of these facets directly determines the effectiveness of a vehicle’s exhaust noise reduction system. Compromising any one of these elements, through damage, degradation, or improper modification, can lead to increased noise emissions and potential non-compliance with legal standards. Consistent maintenance and adherence to manufacturer specifications are essential for maintaining optimal noise reduction performance.
2. Material Integrity
Material integrity is paramount to the functional lifespan and effectiveness of a vehicle’s exhaust noise reduction system. The composition and condition of the materials directly influence the system’s ability to withstand the rigors of its operating environment and maintain optimal performance.
- Corrosion Resistance
The materials used in constructing the exhaust component must exhibit high resistance to corrosion from exhaust gases, road salts, and environmental moisture. Insufficient corrosion resistance leads to structural weakening, leaks, and reduced noise reduction capabilities. For example, untreated steel rapidly degrades in environments with high salt concentrations, necessitating the use of stainless steel or aluminized coatings.
- Thermal Stability
The exhaust system experiences significant temperature fluctuations. Materials must maintain their structural integrity and mechanical properties across a wide temperature range to prevent cracking, warping, and premature failure. Materials exhibiting poor thermal stability may experience accelerated degradation and reduced service life.
- Weld Integrity
The quality of the welds used to join the various components of the exhaust system is critical. Weak or poorly executed welds are prone to failure, leading to leaks and structural instability. Welding processes must be carefully controlled to ensure proper penetration and fusion of the materials, maintaining the overall strength and integrity of the assembly.
- Resistance to Mechanical Stress
The exhaust system is subject to vibration and mechanical stress from engine operation and road conditions. Materials must possess sufficient strength and fatigue resistance to withstand these stresses without cracking or fracturing. Inadequate resistance to mechanical stress can lead to premature failure, particularly at points of high stress concentration, such as welds and mounting points.
Maintaining the material integrity of a vehicle’s exhaust noise reduction system is essential for ensuring its long-term performance, reliability, and compliance with noise regulations. Regular inspections and prompt repair of any detected damage are crucial for preventing premature failure and maintaining optimal vehicle operation.
3. Exhaust Flow
Exhaust flow is intricately linked to the performance and longevity of a vehicle’s exhaust noise reduction component. The design of this component, including internal baffling and chamber configurations, directly influences the passage of exhaust gases. Inefficient exhaust flow caused by a clogged or poorly designed noise reduction component can result in increased backpressure on the engine. Elevated backpressure reduces engine efficiency, leading to decreased fuel economy and potentially diminishing power output. For example, a severely corroded muffler exhibiting significant internal blockage will impede exhaust gas flow, negatively impacting engine performance. Therefore, exhaust flow is an inseparable characteristic of a fully functional component.
Conversely, modifications aimed at maximizing exhaust flow, such as removing or altering internal baffles, can compromise the component’s primary function: noise reduction. This can lead to non-compliance with noise emission regulations. Certain high-performance vehicles utilize exhaust systems designed to optimize both flow and noise reduction, often employing complex chamber designs and advanced sound-absorbing materials to achieve the desired balance. Consider an instance where an individual replaces a stock muffler with an aftermarket component boasting “increased flow.” If that replacement fails to adequately suppress exhaust noise, the vehicle could face legal repercussions and reduced driver comfort.
In summary, exhaust flow is a critical parameter influencing the effectiveness and overall performance of any exhaust system. Impediments to flow can degrade engine efficiency, while modifications prioritizing flow at the expense of noise reduction can result in noise pollution and legal issues. Careful consideration of exhaust flow characteristics is essential when evaluating the condition, maintenance, or modification of “Tim’s Muffler” to ensure the desired balance between performance and compliance is achieved.
4. Legal Compliance
Adherence to noise emission standards is a critical aspect of vehicle operation, directly impacting the acceptability and legality of exhaust systems. The component under consideration, specifically, must conform to both federal and local regulations governing maximum permissible noise levels. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in fines, vehicle impoundment, and mandatory corrective actions. The precise noise level limits vary depending on jurisdiction, vehicle type, and date of manufacture, necessitating careful attention to the applicable standards. Tampering with or modifying exhaust components in a manner that increases noise emissions is a violation of these laws. A real-life example includes aftermarket modifications intended to enhance exhaust sound that, exceeding legal decibel limits, expose the vehicle owner to substantial penalties.
The regulatory framework governing vehicle noise is designed to mitigate noise pollution and ensure public health and safety. Enforcement of these regulations often involves roadside inspections, where vehicles are subjected to noise level testing using calibrated sound meters. Vehicles failing to meet the specified limits are issued notices of violation, requiring the owner to restore the exhaust system to a compliant configuration. Furthermore, regular vehicle inspections may include an assessment of the exhaust system’s condition, ensuring that it is functioning correctly and has not been subject to unauthorized modifications. The type of noise emitted is also under scrutiny, considering factors like pitch and frequency that could be considered disruptive or problematic in certain contexts.
In summary, legal compliance is an indispensable attribute of vehicle exhaust systems, including “Tim’s Muffler.” This compliance ensures responsible vehicle operation, protects public health, and avoids potential legal penalties. Understanding the applicable noise emission standards and maintaining the exhaust system in a compliant condition are essential for all vehicle owners. Failure to uphold these standards can lead to significant consequences, underscoring the importance of vigilance and adherence to regulatory guidelines.
5. Vehicle Performance
The condition and functionality of a vehicle’s exhaust noise reduction component directly influence overall vehicle performance. A properly functioning component optimizes exhaust flow, minimizing backpressure on the engine. Conversely, a damaged, corroded, or improperly modified component can impede exhaust flow, leading to increased backpressure, reduced engine efficiency, and diminished power output. For example, a clogged exhaust noise reduction component significantly restricts the expulsion of exhaust gases, placing undue strain on the engine and resulting in noticeable performance degradation. This illustrates the critical cause-and-effect relationship between the component’s condition and the vehicle’s operational capabilities. The ability of the exhaust system, specifically “Tim’s muffler”, to efficiently expel exhaust gases is vital for maintaining optimal engine performance. As such, it is an important component of the exhaust systems.
Understanding this connection has practical significance for vehicle maintenance and diagnostics. Changes in vehicle performance, such as reduced acceleration or fuel economy, can indicate underlying issues with the exhaust noise reduction component. Mechanics often use exhaust backpressure testing as a diagnostic tool to assess the component’s condition and identify potential flow restrictions. Replacing a malfunctioning component with a new one that meets or exceeds original equipment specifications can restore the vehicle’s performance to its intended level. For example, a vehicle experiencing sluggish acceleration and poor fuel economy may exhibit a significant improvement in both areas after the exhaust noise reduction component is replaced, restoring proper exhaust flow. Some individuals chose aftermarket mufflers and this might have unintended consequence, such as voiding the legal compliance.
In conclusion, the relationship between the exhaust noise reduction component, such as Tim’s muffler, and vehicle performance is direct and consequential. Maintaining this component in good working order is essential for preserving engine efficiency, power output, and overall vehicle drivability. Recognizing the symptoms of a malfunctioning component and addressing the issue promptly ensures that the vehicle operates at its optimal performance level. Challenges may arise from the long-term effects of weather and rust to the material of “Tim’s Muffler.”
6. Periodic Inspections
Regular evaluation of a vehicle’s exhaust noise reduction component, commonly referred to as “Tim’s Muffler,” is crucial for maintaining its functionality, ensuring legal compliance, and optimizing vehicle performance. Consistent observation enables the identification of potential issues before they escalate into significant problems, leading to more costly repairs or potential safety hazards.
- Corrosion Detection
Routine inspections provide an opportunity to identify corrosion, a common issue affecting exhaust components. Early detection allows for preventative measures, such as rust inhibitors or localized repairs, to be implemented. Undetected corrosion can weaken the metal structure, leading to exhaust leaks, reduced noise reduction efficiency, and potential structural failure. This is especially true in regions with elevated road salting during winter months, accelerating corrosion processes.
- Structural Integrity Assessment
Visual examination can reveal physical damage, such as dents, cracks, or broken hangers, which can compromise the component’s structural integrity and functionality. Damaged components may exhibit reduced noise reduction capabilities and may pose safety risks due to potential detachment from the vehicle. Early identification of structural issues allows for timely repairs or replacements, preventing further damage and ensuring continued safe operation.
- Leak Identification
Exhaust leaks not only increase noise emissions but can also pose health hazards due to the potential for carbon monoxide poisoning. Inspections can identify leaks through visual observation of soot deposits or by listening for unusual noises emanating from the exhaust system. Prompt repair of exhaust leaks is essential for maintaining safe vehicle operation and preventing environmental contamination.
- Mounting Security Verification
The mounting hardware securing the exhaust component to the vehicle is subject to wear and tear. Inspections should verify that all mounting brackets, bolts, and hangers are in good condition and properly secured. Loose or damaged mounting hardware can lead to excessive vibration, stress on the exhaust component, and potential detachment, posing safety risks. For example, failing to maintain mounting security can result in excessive stress on Tim’s Muffler, leading to the complete tear of the vehicle exhaust system.
In summary, periodic inspections are an essential element of responsible vehicle ownership. These assessments enable the proactive identification and resolution of issues affecting the exhaust noise reduction component, ensuring continued compliance with noise regulations, optimizing vehicle performance, and promoting safe and reliable operation. Consistent execution of the periodic inspections will benefit on safety and legal compliance issues.
Frequently Asked Questions Regarding Vehicle Exhaust Noise Reduction Components (e.g., “Tim’s Muffler”)
This section addresses common inquiries and clarifies misconceptions surrounding vehicle exhaust noise reduction components, ensuring informed decision-making regarding maintenance and regulatory compliance.
Question 1: What constitutes a “Tim’s Muffler” and what is its primary function?
The term refers to a specific vehicle exhaust noise reduction component, likely belonging to an individual named Tim. Its primary function is to attenuate engine exhaust noise, contributing to reduced noise pollution and enhanced vehicle operator comfort.
Question 2: What are the potential consequences of a damaged or malfunctioning exhaust noise reduction component?
A damaged or malfunctioning component can lead to increased noise emissions, reduced engine performance, decreased fuel efficiency, and potential violations of noise emission regulations. Structural failures can also pose safety hazards.
Question 3: How frequently should a vehicle exhaust noise reduction component be inspected?
Regular inspections are recommended at intervals of at least every six months or during routine vehicle maintenance. More frequent inspections may be necessary in regions with harsh winter conditions or where road salts are heavily used.
Question 4: Are aftermarket modifications to exhaust noise reduction components permissible?
Aftermarket modifications are permissible only if they comply with all applicable noise emission regulations. Modifications that increase noise levels beyond legal limits are prohibited and can result in fines and mandatory corrective actions.
Question 5: What factors contribute to the deterioration of an exhaust noise reduction component?
Factors contributing to deterioration include corrosion from exhaust gases and road salts, thermal stress from temperature fluctuations, mechanical stress from vibration and road conditions, and degradation of sound-absorbing materials.
Question 6: How can the lifespan of an exhaust noise reduction component be extended?
The lifespan can be extended through regular inspections, prompt repair of leaks, avoidance of short trips (which promote condensation), use of quality replacement parts, and periodic cleaning to remove road salts and debris.
In summary, understanding the function, potential issues, and maintenance requirements of vehicle exhaust noise reduction components is crucial for ensuring responsible vehicle operation, legal compliance, and optimal performance.
The following sections will provide practical guidance on selecting appropriate replacement components and performing basic maintenance procedures.
Concluding Remarks on Vehicle Exhaust System Components
This exploration of vehicle exhaust noise reduction components, exemplified by “Tim’s Muffler,” has underscored the multifaceted nature of their role. The analysis encompassed fundamental functionality, maintenance imperatives, regulatory mandates, and performance implications. Understanding these facets enables informed decisions regarding vehicle care and compliance. The component is subject to the elements and requires ongoing maintenance. The benefits of doing so will provide value into the future.
Continued attention to exhaust system integrity is paramount, ensuring adherence to evolving environmental standards and promoting responsible vehicle operation. Investment in preventative maintenance and timely repairs not only safeguards vehicle performance but also contributes to a quieter, more sustainable environment, protecting both the vehicle owner and the broader community. Long-term planning is recommended for maintaining vehicle exhaust system components to maximize the intended benefits.