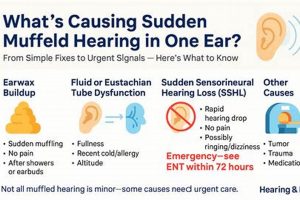
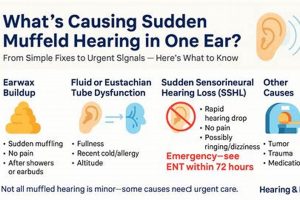
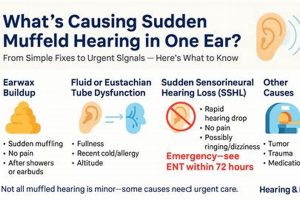
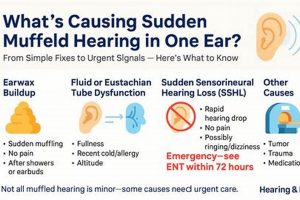
Auditory experiences characterized by perceived sounds in the absence of external stimuli, frequently accompanied by a sensation of reduced sound clarity, can indicate underlying issues within the auditory system. Individuals may describe these phantom sounds as ringing, buzzing, hissing, or other noises. The simultaneous presence of diminished sound perception suggests a blockage or interference within the ear canal or middle ear, or potentially a disruption within the auditory nerve’s transmission of signals to the brain.
The significance of addressing these combined symptoms lies in the potential for early detection of conditions impacting hearing health. While transient occurrences may resolve spontaneously, persistent or recurring episodes warrant investigation. Timely intervention can mitigate the progression of hearing loss, manage underlying medical conditions contributing to these auditory disturbances, and improve overall quality of life. Historically, such complaints have been dismissed as minor annoyances, but modern audiological practices emphasize the importance of thorough evaluation.
The following sections will delve into the potential causes of these auditory symptoms, diagnostic procedures employed to identify the underlying factors, and various treatment strategies available to alleviate discomfort and restore normal hearing function. Understanding these aspects is crucial for effective management and prevention of long-term auditory complications.
This section provides practical guidance for individuals experiencing compromised auditory perception, including phantom sounds and diminished sound clarity. Adherence to these recommendations can assist in minimizing discomfort and promoting proactive hearing health management.
Tip 1: Minimize Exposure to Loud Noises: Prolonged or intense noise exposure is a leading contributor to auditory damage. Employ ear protection, such as earplugs or earmuffs, in noisy environments, including concerts, construction sites, and during the operation of loud machinery. Monitor sound levels and limit exposure duration.
Tip 2: Avoid Ototoxic Substances: Certain medications and chemicals possess the potential to harm the auditory system. Consult with a physician or pharmacist regarding the ototoxic risks associated with prescribed or over-the-counter medications. Be mindful of environmental chemical exposures and implement appropriate safety measures.
Tip 3: Manage Cerumen Accumulation: Excessive earwax can obstruct the ear canal, leading to diminished sound clarity and potentially exacerbating perceived phantom sounds. Refrain from using cotton swabs, as they can push wax further into the ear. Seek professional cerumen removal from a qualified audiologist or healthcare provider.
Tip 4: Monitor Blood Pressure: Elevated blood pressure can contribute to vascular changes within the inner ear, potentially affecting auditory function. Maintain a healthy lifestyle through regular exercise, a balanced diet, and stress management techniques to promote optimal blood pressure levels.
Tip 5: Reduce Stress and Anxiety: Psychological stress and anxiety can exacerbate the perception of phantom sounds and diminish sound clarity. Implement relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, or yoga, to manage stress levels and promote overall well-being.
Tip 6: Seek Prompt Medical Evaluation: Persistent or recurring auditory symptoms warrant immediate medical attention. Schedule an appointment with an audiologist or otolaryngologist for a comprehensive hearing evaluation and to identify any underlying medical conditions.
Tip 7: Maintain Hydration: Adequate hydration is crucial for optimal bodily functions, including maintaining the fluid balance within the inner ear. Ensure sufficient fluid intake throughout the day, particularly during periods of physical activity or in hot weather.
Adherence to these guidelines promotes proactive auditory health management. Early intervention and consistent monitoring can significantly mitigate the impact of auditory symptoms and contribute to long-term hearing preservation.
The following section will address potential treatment options, and emphasize the importance of collaborating with healthcare professionals to determine the most appropriate course of action based on individual circumstances.
1. Etiology
The etiology, or the study of the causes of disease, is paramount in understanding instances of tinnitus accompanied by a sensation of muffled hearing. Determining the underlying cause is the initial and arguably most critical step in effectively managing and treating these concurrent symptoms. Without identifying the precise etiology, interventions risk being ineffective or, in some cases, detrimental.
Numerous factors can contribute to this combined auditory presentation. For instance, exposure to excessive noise, particularly chronic exposure, can damage the delicate hair cells within the cochlea, leading to both tinnitus and a perceived reduction in sound clarity. Ototoxic medications, which possess the potential to harm the inner ear, represent another significant etiological factor. Certain antibiotics, chemotherapy drugs, and even high doses of aspirin can induce these auditory disturbances as a side effect. Infections of the middle or inner ear can also disrupt normal auditory function, causing inflammation and fluid accumulation that result in both tinnitus and muffled hearing. Furthermore, Meniere’s disease, a disorder affecting the inner ear’s fluid balance, is characterized by episodes of vertigo, tinnitus, and fluctuating hearing loss, often presenting with a sensation of fullness or muffled sound. In rarer instances, acoustic neuromas, benign tumors on the auditory nerve, can gradually compress the nerve, leading to progressive hearing loss and tinnitus.
In conclusion, establishing the etiology is indispensable for guiding appropriate diagnostic procedures and treatment strategies. Understanding the specific cause, whether it be noise-induced damage, medication side effects, infection, or an underlying medical condition, allows for targeted interventions aimed at alleviating symptoms, preventing further auditory damage, and improving the patient’s overall quality of life. Failure to consider the etiological factors risks misdiagnosis and ineffective management, potentially leading to chronic auditory problems and reduced well-being.
2. Auditory Nerve
The auditory nerve, also known as the vestibulocochlear nerve or cranial nerve VIII, serves as the critical neural pathway transmitting auditory information from the inner ear to the brain. Damage or dysfunction of this nerve frequently manifests as both tinnitus and a sensation of muffled hearing. The precise nature of the auditory signals transmitted along this nerve is essential for accurate sound perception. Disruptions to this signaling process, whether due to nerve compression, inflammation, or demyelination, can lead to aberrant neural activity perceived as ringing or other phantom sounds. Simultaneously, the nerve’s compromised ability to efficiently transmit sound information results in reduced clarity and a muffled quality to external auditory stimuli. Acoustic neuroma, a benign tumor that grows on the auditory nerve, exemplifies this connection. As the tumor expands, it compresses the nerve, causing a gradual onset of tinnitus and progressive hearing loss characterized by muffled sound perception.
Further illustrating the auditory nerve’s role is its susceptibility to damage from viral infections. Certain viruses, such as those responsible for herpes zoster (shingles), can inflame the auditory nerve, resulting in sensorineural hearing loss and tinnitus. This condition, often referred to as Ramsay Hunt syndrome when accompanied by facial paralysis, underscores the direct causal link between nerve inflammation and the combined symptoms of muffled hearing and phantom sounds. Moreover, autoimmune disorders that target the myelin sheath surrounding the auditory nerve can disrupt nerve signal transmission, leading to similar auditory manifestations. Multiple sclerosis, for instance, can affect the auditory nerve, causing fluctuating hearing loss, tinnitus, and a distorted or muffled perception of sounds. Understanding the specific location and nature of auditory nerve involvement is paramount for accurate diagnosis and targeted treatment.
In summary, the auditory nerve’s integrity is indispensable for accurate sound perception. Insults to this nerve, whether from tumors, infections, autoimmune disorders, or other causes, frequently result in the combined auditory symptoms of tinnitus and muffled hearing. Recognizing the direct connection between auditory nerve dysfunction and these perceived auditory disturbances is critical for proper diagnosis, management, and rehabilitation strategies aimed at mitigating the impact on the individual’s auditory experience and overall quality of life.
3. Fluid Dynamics
Fluid dynamics within the inner ear, specifically concerning the endolymph and perilymph, exerts a significant influence on auditory function. Imbalances or disruptions in these fluids can manifest as both tinnitus and a sensation of muffled hearing. The delicate balance of pressure and composition within these fluids is crucial for the proper functioning of the cochlea and its ability to transduce sound vibrations into neural signals.
- Endolymphatic Hydrops
Endolymphatic hydrops, a condition characterized by excessive endolymph fluid within the inner ear, is a primary example of how fluid dynamics can impact hearing. The increased pressure distorts the membranes and sensory cells within the cochlea, leading to fluctuating hearing loss, tinnitus, and a sensation of aural fullness often described as muffled hearing. Meniere’s disease is a well-known manifestation of endolymphatic hydrops.
- Cochlear Microcirculation
The microcirculation within the cochlea provides essential nutrients and oxygen to the sensory cells and maintains the delicate fluid balance. Impaired microcirculation, due to conditions like diabetes or vascular disease, can disrupt the fluid dynamics within the cochlea, leading to ischemia and damage to the sensory cells. This damage can result in both tinnitus and a reduction in sound clarity, giving a muffled sensation.
- Perilymph Fistula
A perilymph fistula, a tear or rupture in one of the membranes separating the middle ear from the inner ear, allows perilymph fluid to leak into the middle ear space. This loss of fluid can disrupt the pressure equilibrium within the inner ear, leading to a sensation of imbalance, dizziness, tinnitus, and fluctuating hearing loss often described as muffled. Trauma, barotrauma, or even chronic ear infections can cause perilymph fistulas.
- Inflammation and Fluid Accumulation
Infections or inflammatory processes within the middle or inner ear can lead to fluid accumulation, altering the normal fluid dynamics. Otitis media with effusion, for example, results in fluid buildup in the middle ear, hindering the transmission of sound to the inner ear. This conductive hearing loss often presents as muffled hearing and can be accompanied by tinnitus due to the disruption of normal cochlear function.
In conclusion, disruptions in fluid dynamics within the inner and middle ear can significantly impact auditory function, frequently resulting in the concurrent symptoms of tinnitus and muffled hearing. Understanding the specific fluid-related mechanisms underlying these symptoms is crucial for accurate diagnosis and targeted therapeutic interventions aimed at restoring proper auditory function and alleviating patient distress.
4. Cerumen Occlusion
Cerumen occlusion, the impaction of earwax within the ear canal, represents a prevalent and readily addressed cause of diminished auditory acuity and the perception of phantom sounds. The physical presence of impacted cerumen obstructs the transmission of sound waves to the tympanic membrane, directly influencing auditory sensitivity and potentially triggering or exacerbating tinnitus.
- Physical Obstruction and Attenuation
Impacted cerumen acts as a physical barrier, impeding the efficient passage of sound waves through the external auditory canal. This attenuation primarily affects higher frequencies, resulting in a sensation of muffled hearing, particularly for speech comprehension. The degree of hearing loss is directly proportional to the extent of the occlusion. Furthermore, complete blockage of the ear canal can create a pressure differential, further altering sound conduction.
- Resonance and Acoustic Feedback
The presence of cerumen can alter the resonant frequencies within the ear canal. This alteration can lead to acoustic feedback, generating internal sound sensations perceived as ringing or buzzing. The shape and density of the impacted cerumen influence the specific frequencies amplified, resulting in varying tinnitus characteristics.
- Tympanic Membrane Irritation
In instances of severe impaction, cerumen can directly contact and irritate the tympanic membrane. This irritation can stimulate the auditory nerve, leading to the perception of tinnitus. The proximity of the cerumen to the sensitive structures of the middle ear makes this a potentially significant factor in the genesis of phantom sounds.
- Differential Pressure and Vestibular Effects
Cerumen occlusion can create differential pressure within the ear canal, potentially affecting the vestibular system located in the inner ear. This pressure imbalance can lead to dizziness, vertigo, and exacerbate the perception of tinnitus. The close anatomical relationship between the auditory and vestibular systems explains this interconnectedness.
The presented facets underscore the multifaceted impact of cerumen occlusion on auditory perception. The physical obstruction, altered resonance, tympanic membrane irritation, and potential vestibular effects collectively contribute to the concurrent experience of diminished hearing and phantom auditory sensations. Simple cerumen management techniques, performed by qualified healthcare providers, often provide immediate relief from these symptoms.
5. Vascular Compromise
Vascular compromise, referring to impaired blood flow to the inner ear, represents a significant factor in the development of both tinnitus and a sensation of muffled hearing. The delicate structures within the inner ear, including the cochlea and auditory nerve, rely on a consistent and adequate blood supply for proper function. Disruptions to this vascular supply can lead to ischemia, cellular damage, and ultimately, auditory dysfunction.
- Reduced Cochlear Perfusion
The cochlea, responsible for converting sound vibrations into neural signals, is highly sensitive to fluctuations in blood flow. Conditions such as atherosclerosis, hypertension, and diabetes can compromise the microvasculature supplying the cochlea, leading to reduced perfusion. This ischemia can damage the hair cells within the cochlea, resulting in both tinnitus and sensorineural hearing loss, often perceived as muffled hearing.
- Auditory Nerve Ischemia
The auditory nerve, which transmits auditory information from the cochlea to the brain, also relies on adequate blood flow. Vascular compromise affecting the vessels supplying the auditory nerve can lead to nerve ischemia and subsequent dysfunction. This can manifest as tinnitus, due to aberrant neural activity, and reduced clarity of sound perception, resulting in a muffled auditory experience.
- Vasospasm and Transient Ischemic Attacks
Vasospasm, the sudden constriction of blood vessels, can temporarily reduce blood flow to the inner ear. Similarly, transient ischemic attacks (TIAs) affecting the vertebrobasilar system, which supplies blood to the brainstem and inner ear, can cause brief episodes of ischemia. These transient vascular events can trigger sudden onset of tinnitus and a sensation of muffled hearing, which may resolve as blood flow is restored, or potentially lead to permanent damage.
- Inner Ear Hemorrhage
Although less common, hemorrhage within the inner ear can also occur due to vascular compromise. Rupture of small blood vessels within the cochlea or auditory nerve can lead to bleeding and subsequent damage to the surrounding structures. This can result in sudden hearing loss, often described as muffled, and tinnitus due to the disruption of normal auditory function and irritation of the auditory nerve.
The relationship between vascular compromise and auditory symptoms highlights the importance of maintaining cardiovascular health for preserving auditory function. Conditions that impair blood flow to the inner ear can significantly impact hearing and quality of life, underscoring the need for early detection, management of underlying vascular risk factors, and prompt medical evaluation for individuals experiencing combined tinnitus and muffled hearing.
6. Neurological Factors
Neurological factors represent a complex and often overlooked dimension in the genesis of concurrent tinnitus and diminished auditory clarity. The brain plays a crucial role in processing auditory information, and disruptions within neurological pathways or structures can manifest as both phantom sounds and impaired sound perception. Understanding these neurological contributions is essential for comprehensive assessment and targeted intervention strategies.
- Central Auditory Processing Disorder (CAPD)
CAPD involves deficits in the brain’s ability to process auditory information, despite normal peripheral hearing function. Individuals with CAPD may experience difficulty discriminating sounds, understanding speech in noisy environments, and localizing sound sources. This can manifest as a sensation of muffled hearing or distorted sound perception, often accompanied by tinnitus. The precise mechanisms underlying CAPD-related tinnitus are not fully understood but likely involve aberrant neural activity in the auditory cortex.
- Auditory Cortex Dysfunction
The auditory cortex, located in the temporal lobe of the brain, is responsible for processing and interpreting auditory signals. Damage or dysfunction within the auditory cortex, due to stroke, traumatic brain injury, or neurodegenerative diseases, can disrupt normal auditory processing. This can result in tinnitus, often described as complex or musical tinnitus, and a distorted or muffled perception of sound. The severity of the auditory symptoms depends on the extent and location of the cortical damage.
- Neural Plasticity and Maladaptive Changes
Following peripheral hearing loss or auditory nerve damage, the brain undergoes neural plasticity, reorganizing its neural connections to compensate for the reduced auditory input. In some cases, this plasticity can be maladaptive, leading to the development of tinnitus. The brain attempts to compensate for the lack of external sound input by generating its own internal signals, perceived as ringing or other phantom sounds. This maladaptive plasticity can also alter the processing of sound, resulting in a distorted or muffled perception.
- Neuromodulation and Neurotransmitter Imbalances
Neurotransmitters, such as glutamate and GABA, play a critical role in regulating neural activity within the auditory system. Imbalances in these neurotransmitters, due to various neurological conditions or medications, can disrupt the normal balance of excitation and inhibition in the auditory pathways. This imbalance can lead to hyperactivity in the auditory cortex, resulting in tinnitus, and altered sound processing, contributing to a sensation of muffled hearing. Neuromodulation techniques, such as transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS), aim to restore this balance and alleviate auditory symptoms.
In summary, neurological factors play a significant role in the complex interplay of mechanisms contributing to tinnitus and muffled hearing. From central auditory processing deficits to cortical dysfunction and maladaptive plasticity, neurological abnormalities can significantly impact auditory perception. A comprehensive understanding of these neurological contributions is essential for accurate diagnosis, personalized treatment strategies, and improved outcomes for individuals experiencing these challenging auditory symptoms. Further research is needed to fully elucidate the underlying neurological mechanisms and develop more effective interventions.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following addresses common inquiries regarding the combined auditory symptoms of perceived phantom sounds and a sensation of reduced clarity in hearing. This information aims to clarify potential causes and appropriate courses of action.
Question 1: What are the most common causes of simultaneous ringing and muffled hearing?
Common causes include noise-induced hearing damage, earwax impaction, middle ear infections, certain medications (ototoxic drugs), Meniere’s disease, and acoustic neuroma. Vascular disorders and neurological conditions can also contribute.
Question 2: Is the occurrence of phantom sounds and muffled hearing always indicative of permanent hearing damage?
Not necessarily. Transient occurrences may be due to temporary factors like congestion or short-term noise exposure. However, persistent or recurring symptoms warrant prompt audiological evaluation to rule out permanent damage or underlying medical conditions.
Question 3: Can stress and anxiety contribute to the perception of ringing and muffled hearing?
Yes. While stress and anxiety are not direct causes of hearing loss, they can exacerbate pre-existing auditory symptoms or amplify the perception of phantom sounds. Stress management techniques can be beneficial.
Question 4: What diagnostic procedures are typically employed to evaluate these combined symptoms?
Audiological evaluations typically involve pure-tone audiometry, tympanometry, acoustic reflex testing, and otoacoustic emissions testing. In some cases, imaging studies like MRI may be necessary to rule out structural abnormalities.
Question 5: What treatment options are available for addressing both ringing and muffled hearing?
Treatment depends on the underlying cause. Options may include earwax removal, antibiotics for infections, hearing aids for hearing loss, tinnitus retraining therapy, medication adjustments, and, in rare cases, surgical intervention.
Question 6: When should one seek professional medical attention for these auditory symptoms?
Medical attention is warranted if the symptoms are sudden in onset, persistent (lasting more than a few days), accompanied by dizziness or vertigo, associated with pain or drainage from the ear, or significantly impacting daily functioning. Early intervention improves the likelihood of successful management.
In summation, prompt evaluation and appropriate management of combined phantom sounds and reduced hearing clarity are crucial for preserving auditory health. Individual experiences may vary, necessitating personalized treatment plans.
The subsequent section provides additional resources and guidance for managing auditory health and accessing professional audiological services.
Concluding Remarks
The convergence of phantom auditory sensations and diminished sound clarity, represented by the condition of “my ear is ringing and muffled,” signifies a potential disruption within the intricate auditory system. This exploration has highlighted various etiological factors, ranging from physical obstructions and inner ear fluid imbalances to neurological and vascular compromises. Recognition of these diverse underlying causes is paramount for accurate diagnosis and effective management strategies.
Persistent or recurring episodes warrant comprehensive audiological evaluation to ascertain the root cause and implement appropriate interventions. Proactive management, including minimizing noise exposure, addressing underlying medical conditions, and adhering to professional guidance, contributes to preserving auditory function and mitigating the impact on overall quality of life. Continued research and advancements in audiological care offer ongoing hope for improved diagnostic tools and therapeutic approaches.