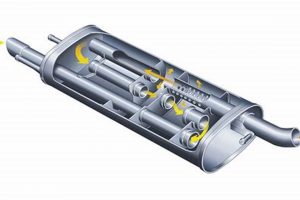
An exhaust component designed to minimize the sound output of all-terrain vehicles is a critical element for noise reduction. A practical example would be a spark arrestor fitted with advanced baffling and sound-dampening materials specifically engineered to reduce decibel levels during operation. This device effectively mitigates noise pollution emanating from the vehicle’s engine.
The advantages of employing such a system extend beyond mere compliance with noise regulations. Reduced auditory impact benefits the environment by minimizing disturbance to wildlife and improving the recreational experience for riders and those nearby. Historically, the development of these systems has been driven by increasing awareness of the detrimental effects of excessive noise and subsequent legislation aimed at controlling it.
The following sections will explore specific technologies used in these sound-reducing devices, compare various models available on the market, and provide guidance on selecting the most suitable option based on individual needs and intended riding environment.
Selecting an ATV Exhaust System for Minimal Noise
Optimizing an all-terrain vehicle’s exhaust system for reduced sound emissions requires careful consideration. The following tips provide guidance on identifying and installing effective noise-reduction solutions.
Tip 1: Evaluate Decibel Ratings: Prioritize models that publish standardized decibel ratings. These ratings offer a quantifiable measure of noise output, facilitating comparisons between different exhaust systems. Lower decibel values generally indicate quieter operation.
Tip 2: Investigate Construction Materials: Exhaust systems constructed from materials such as stainless steel or aluminum often offer enhanced sound absorption properties compared to those made from less dense materials. Evaluate the material composition when selecting a system.
Tip 3: Consider Baffle Design: Internal baffle designs play a crucial role in sound attenuation. Look for systems that incorporate multi-stage baffling or advanced sound-dampening materials within the muffler to maximize noise reduction effectiveness.
Tip 4: Research Spark Arrestor Compatibility: Ensure the selected exhaust system is compatible with a US Forest Service-approved spark arrestor. This is not only crucial for fire safety in certain riding areas but can also contribute to overall noise reduction.
Tip 5: Review Product Testing Data: Seek out independent testing data or user reviews that specifically address noise levels. Real-world feedback can provide valuable insights beyond manufacturer specifications.
Tip 6: Professional Installation: The installation process can impact the system’s performance. Professional installation ensures proper sealing and alignment, maximizing its noise-reduction capabilities.
Tip 7: Regular Maintenance: Periodic inspection and maintenance of the exhaust system, including cleaning and replacement of worn components, are crucial for maintaining optimal sound reduction over time.
Adhering to these recommendations will enhance the likelihood of selecting and maintaining an effective noise-reducing exhaust system. This will ensure compliance with noise regulations and mitigate disturbances to the surrounding environment.
The subsequent sections will delve into specific product recommendations and further considerations for optimizing ATV exhaust systems.
1. Sound Absorption
Sound absorption plays a pivotal role in minimizing the auditory impact of all-terrain vehicles. Efficient sound absorption within the exhaust system directly contributes to achieving the goal of a significantly quieter machine, mitigating noise pollution and enhancing the overall riding experience.
- Acoustic Material Integration
The inclusion of specific materials engineered for their sound-absorbing properties is fundamental. Fiberglass packing, steel wool, or specialized ceramic composites are strategically placed within the muffler to capture and dissipate sound waves. For instance, densely packed fiberglass absorbs a broader spectrum of frequencies, reducing the overall noise level emanating from the exhaust. Insufficient acoustic material leads to increased noise transmission, thereby compromising the effectiveness.
- Surface Area Maximization
The effectiveness of sound absorption is directly proportional to the surface area available for interaction with sound waves. Internal muffler designs often incorporate perforated tubes or baffles to increase the surface area. This expanded surface facilitates greater interaction between the sound waves and the absorptive material, amplifying the reduction in noise. A smaller surface area provides less opportunity for sound absorption.
- Frequency-Specific Absorption
Different materials exhibit varying degrees of effectiveness at absorbing different frequencies. Exhaust system designs may incorporate multiple materials to target a broader range of frequencies, resulting in a more balanced reduction in noise across the spectrum. For example, a combination of fiberglass and a high-density composite material can effectively address both high-frequency and low-frequency noise components. Without targeted frequency management, certain noise levels may remain unaddressed.
- Material Degradation and Maintenance
The sound-absorbing capabilities of materials within the exhaust system diminish over time due to heat, vibration, and exposure to exhaust gases. Regular maintenance, including repacking or replacing the absorptive materials, is crucial to sustain optimal noise reduction. Neglecting maintenance leads to increased noise emissions and reduced overall performance of the “quietest atv muffler.”
Effectively integrating sound-absorbing materials within the exhaust system is not merely an add-on; it is a core design principle in achieving a “quietest atv muffler.” The careful selection, strategic placement, and ongoing maintenance of these materials are essential for minimizing auditory impact and enhancing the recreational experience.
2. Baffle Design
Baffle design within an all-terrain vehicle’s exhaust system is paramount to achieving significant noise reduction. The configuration and materials used in these internal structures directly influence the sound wave propagation and dissipation, ultimately determining the operational sound level of the vehicle.
- Sound Wave Redirection
Baffles are strategically placed obstructions within the muffler designed to redirect sound waves, causing them to collide with each other. This interference leads to a reduction in amplitude, effectively lowering the overall noise output. For example, a series of staggered, perforated plates forces sound waves to travel a longer, more convoluted path, promoting greater interference and sound attenuation. Improper baffle placement may result in minimal sound wave disruption, limiting the muffler’s effectiveness.
- Frequency Attenuation
Different baffle designs can be optimized to attenuate specific frequencies. Certain configurations may be more effective at reducing high-frequency noise, while others target lower frequencies. Resonance chambers, for instance, are designed to cancel out specific frequencies, thereby producing a more balanced and less intrusive sound profile. A poorly designed baffle system may exacerbate certain frequencies, creating a harsh or irritating exhaust note.
- Backpressure Management
While noise reduction is a primary goal, baffle design must also consider backpressure. Excessive backpressure can negatively impact engine performance, reducing horsepower and fuel efficiency. Therefore, an effective design seeks a balance between noise attenuation and minimizing restrictions on exhaust flow. For example, a multi-core baffle system can provide adequate sound reduction while maintaining acceptable backpressure levels. A design that prioritizes noise reduction at the expense of engine performance is generally considered undesirable.
- Material Properties and Construction
The materials used in baffle construction significantly impact their ability to absorb and dissipate sound energy. Dense, heat-resistant materials such as stainless steel are commonly used to withstand the harsh conditions within the exhaust system. The precision and quality of the welds and construction also contribute to the overall durability and effectiveness of the baffle system. Inferior materials or poor construction can lead to premature failure and increased noise levels.
In conclusion, baffle design is not merely an afterthought but a critical engineering consideration in developing a “quietest atv muffler”. The strategic placement, frequency-specific optimization, backpressure management, and material properties of baffles collectively determine the effectiveness of the exhaust system in minimizing noise output while maintaining optimal engine performance. The trade-offs and balance in these design elements is the major consideration for atv muffler manufacturers.
3. Material Density
Material density is a critical parameter in the design and performance of an all-terrain vehicle exhaust system intended for minimal noise output. The inherent properties of the materials employed directly influence their ability to attenuate sound waves, thereby contributing to the overall effectiveness of the system.
- Sound Wave Absorption Capacity
Denser materials generally exhibit a greater capacity for absorbing sound energy. The increased mass impedes the transmission of sound waves, converting a portion of their energy into heat through internal friction. For example, a muffler constructed with a thick-walled steel casing will typically provide superior sound damping compared to one made from thin-gauge aluminum. The effectiveness of the sound absorption directly correlates with the density.
- Vibration Dampening Characteristics
High-density materials possess enhanced vibration dampening characteristics. They are less prone to resonating at frequencies generated by the engine, thereby reducing the amplification of sound waves. Mufflers constructed from materials with a high modulus of elasticity, such as certain grades of stainless steel, effectively minimize vibration and the associated noise. Lower density materials can act as resonators, amplifying undesirable frequencies.
- Acoustic Impedance Matching
Optimizing the acoustic impedance matching between different components within the exhaust system, including the muffler casing and internal baffling, requires careful consideration of material densities. Mismatched impedances can lead to sound wave reflections and increased noise levels. Employing materials with similar densities can minimize these reflections and promote more efficient sound absorption. Complex exhaust systems often incorporate multiple layers of materials with varying densities to manage impedance effectively.
- Durability and Longevity
While density contributes to sound attenuation, it also influences the overall durability and longevity of the exhaust system. Denser materials are generally more resistant to corrosion, heat stress, and physical damage, ensuring consistent performance over an extended lifespan. Selecting a material with an appropriate density provides a balance between sound reduction, structural integrity, and thermal resistance. Premature degradation of the material can diminish sound dampening capabilities.
The selection of materials with appropriate densities is therefore not merely a superficial consideration, but a fundamental engineering aspect of achieving a “quietest atv muffler”. Balancing sound absorption, vibration dampening, acoustic impedance, and durability requires a comprehensive understanding of material properties and their interaction within the complex environment of an exhaust system.
4. Spark Arrestor
The inclusion of a spark arrestor significantly impacts the overall noise profile of an all-terrain vehicle exhaust system. Although primarily designed to prevent the emission of flammable particles, thereby reducing the risk of wildfires, the presence and design of a spark arrestor inherently influence sound wave propagation. An effectively designed spark arrestor can contribute to noise reduction by disrupting the direct flow of exhaust gases, creating turbulence that attenuates certain frequencies. Conversely, a poorly designed or damaged spark arrestor can generate additional noise due to increased turbulence or flow restrictions. For instance, a US Forest Service-approved spark arrestor, when integrated within a muffler designed for low noise emissions, provides a dual benefit: fire safety and improved sound dampening.
Beyond the basic functionality of preventing spark emission, the physical structure of a spark arrestor its shape, size, and perforation pattern can be optimized to further reduce noise. Some spark arrestors incorporate intricate designs that act as additional baffles, forcing exhaust gases to follow a more tortuous path. This increased path length and internal reflection contribute to sound attenuation. A common example is a conical spark arrestor with a series of strategically placed perforations that disrupt the direct line of sight through the exhaust system, thereby reducing noise levels. The materials used in the spark arrestor’s construction also play a role. Denser materials can provide greater sound dampening than lighter, less rigid alternatives.
In summary, while the primary purpose of a spark arrestor is fire prevention, its design and integration within the exhaust system have a direct impact on noise levels. A well-designed spark arrestor, working in concert with other noise-reducing components, contributes significantly to the objective of achieving a “quietest atv muffler.” Therefore, selection should consider not only fire safety compliance but also its contribution to overall sound reduction. Failure to do so can result in a system that meets legal requirements for spark arrestors but fails to achieve optimal noise levels.
5. Decibel Rating
The decibel rating serves as a quantifiable metric for assessing the sound output of all-terrain vehicle exhaust systems, directly correlating with the objective of identifying or engineering the “quietest atv muffler.” This measurement provides a standardized unit for comparing the noise levels produced by different systems, allowing consumers and manufacturers to evaluate performance objectively.
- Standardized Measurement Protocols
Decibel ratings are derived from standardized testing procedures, ensuring a degree of consistency across different manufacturers and products. Organizations such as the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) establish protocols for measuring exhaust noise under specific operating conditions. These protocols typically involve measuring sound levels at a predetermined distance and angle from the exhaust outlet while the engine is operating at a specified RPM. Adherence to these protocols is crucial for obtaining reliable and comparable decibel ratings, enabling consumers to accurately assess the relative quietness of different exhaust systems. Non-standardized tests lack the consistency to deliver meaningful comparisons.
- Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Many jurisdictions impose noise restrictions on all-terrain vehicles, often expressed in decibel limits. A low decibel rating is essential for ensuring compliance with these regulations, allowing riders to operate their vehicles legally in designated areas. Exceeding these limits can result in fines or restrictions on vehicle use. The “quietest atv muffler,” therefore, not only enhances the riding experience but also facilitates compliance with applicable noise ordinances. Legal limitations create a framework for the design, sale and operation of these vehicles.
- Impact on Rider and Environmental Wellbeing
Excessive noise exposure can have detrimental effects on both the rider and the surrounding environment. Prolonged exposure to high decibel levels can lead to hearing damage, increased stress levels, and disruption of wildlife. A “quietest atv muffler,” characterized by a low decibel rating, minimizes these negative impacts, promoting a more enjoyable and responsible riding experience. Noise reduction becomes a primary aspect of the overall operator and environmental experience.
- Trade-offs with Performance
Achieving a low decibel rating often involves trade-offs with engine performance. Restricting exhaust flow to reduce noise can potentially decrease horsepower and torque. Therefore, the design of the “quietest atv muffler” requires a careful balance between noise attenuation and maintaining acceptable performance levels. Advanced technologies, such as variable exhaust valves and tuned resonators, are employed to optimize both noise reduction and engine efficiency. Exhaust system design requires addressing these competing considerations.
In conclusion, the decibel rating provides a crucial benchmark for evaluating the effectiveness of noise reduction measures in all-terrain vehicle exhaust systems. Its significance extends beyond mere compliance with regulations, influencing rider comfort, environmental impact, and overall vehicle performance. Balancing the decibel rating with other performance characteristics remains a primary consideration in the development and selection of the “quietest atv muffler.”
6. Exhaust Leaks
Exhaust leaks compromise the effectiveness of any system designed to achieve minimal noise output in all-terrain vehicles. The design and engineering of a “quietest atv muffler” hinges on directing exhaust gases through specific pathways and sound-dampening materials. When leaks occur, these gases bypass the intended sound attenuation mechanisms, resulting in elevated noise levels. The location and size of the leak directly correlate with the magnitude of the noise increase. For instance, a leak near the engine manifold can generate a high-pitched hissing sound, while a larger leak further downstream may produce a louder, more disruptive rumble.
The causes of exhaust leaks are varied, ranging from corrosion and gasket failure to physical damage resulting from impacts or stress. Over time, exposure to heat, moisture, and vibrations can degrade exhaust system components, leading to the formation of cracks or perforations. Improper installation or maintenance practices, such as overtightening fasteners or neglecting regular inspections, can also contribute to leaks. Addressing exhaust leaks is therefore not merely a matter of repairing a localized problem but requires a comprehensive assessment of the entire system to identify and rectify underlying causes. Neglecting regular inspections and maintenance results in a degradation of performance.
Effective mitigation of exhaust leaks is essential for realizing the full potential of a “quietest atv muffler.” Regular inspections, proper maintenance procedures, and the use of high-quality replacement parts are crucial for preventing and addressing leaks promptly. Furthermore, proper installation techniques, including the use of appropriate sealants and torque specifications, are vital for ensuring a leak-free system. Minimizing exhaust leaks requires careful attention to detail throughout the life cycle of the exhaust system, contributing significantly to achieving the desired low-noise performance. A proactive maintenance plan is crucial for consistent operations.
7. Installation Quality
The achieved sound reduction of any all-terrain vehicle exhaust system, regardless of its design, hinges critically on the quality of its installation. The term “quietest atv muffler” describes an ideal state that can only be realized with proper installation practices. A system meticulously engineered for noise attenuation can fail to meet its intended performance if improperly installed. Exhaust leaks, misaligned components, and loose connections are all direct consequences of poor installation practices, circumventing the muffler’s designed noise reduction capabilities. For instance, if the exhaust manifold is not correctly sealed to the engine, high-pressure exhaust gases escape before reaching the muffler, negating its intended function. Such instances highlight the crucial cause-and-effect relationship between installation quality and actual noise levels.
Proper installation extends beyond merely attaching the muffler to the vehicle. It involves careful attention to detail, including the use of correct mounting hardware, appropriate torque specifications, and proper alignment of all exhaust system components. Gasket selection and sealing techniques are also important considerations. For example, using the wrong type of gasket or failing to apply sealant correctly can create pathways for exhaust gases to escape, even if the connections appear tight. Furthermore, ensuring that the muffler is securely mounted to the vehicle’s frame is essential to prevent vibrations that can loosen connections over time. These vibrations can lead to eventual failures, and increased noise emissions as a result.
In conclusion, the inherent design of a sound-reducing ATV muffler constitutes only one aspect of noise mitigation. Installation quality serves as an equally crucial factor, determining whether the design’s potential is fully realized. Addressing “installation quality” is crucial for maximizing the actual noise reduction achieved, supporting the claim of a “quietest atv muffler.” A focus on the quality of installation, therefore, should be emphasized.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding the implementation of low-noise exhaust systems for all-terrain vehicles. The information provided aims to clarify prevalent concerns and misconceptions.
Question 1: What constitutes a “quietest atv muffler,” and how is it measured?
A “quietest atv muffler” refers to an exhaust system component engineered to minimize sound output during vehicle operation. Its effectiveness is typically quantified using decibel (dB) ratings obtained through standardized testing protocols.
Question 2: Are there legal restrictions on ATV exhaust noise levels?
Many jurisdictions impose noise restrictions on all-terrain vehicles. These regulations often specify maximum allowable decibel levels and may vary depending on the location and time of day. Exceeding these limits can result in penalties.
Question 3: Do noise-reducing mufflers compromise engine performance?
Some noise-reducing mufflers may slightly impact engine performance by increasing backpressure. However, advanced designs strive to balance noise attenuation with maintaining optimal horsepower and torque.
Question 4: What materials are most effective in minimizing exhaust noise?
Dense materials, such as stainless steel and specialized sound-absorbing composites, are commonly used in constructing low-noise mufflers. These materials effectively dampen sound waves and reduce vibration.
Question 5: How does a spark arrestor contribute to noise reduction?
While primarily designed to prevent spark emission, the physical structure of a spark arrestor can disrupt the flow of exhaust gases, resulting in some sound attenuation. Properly designed spark arrestors can thus contribute to a quieter exhaust system.
Question 6: Is professional installation necessary for optimal noise reduction?
Professional installation is highly recommended to ensure proper sealing and alignment of all exhaust system components. Improper installation can lead to exhaust leaks and diminished noise reduction performance.
Selecting and maintaining a low-noise exhaust system requires careful consideration of various factors, including decibel ratings, material properties, and installation quality.
The subsequent section will provide specific recommendations for aftermarket products.
Realizing the “Quietest ATV Muffler”
The preceding discussion has detailed the multifaceted considerations necessary to achieve minimal noise output from all-terrain vehicle exhaust systems. It underscores that the “quietest atv muffler” is not merely a product but the culmination of engineering design, material selection, installation precision, and ongoing maintenance. Legal compliance, rider well-being, and environmental stewardship are all fundamentally linked to effective noise reduction.
Therefore, a conscientious approach is required. Consumers must prioritize informed decision-making, considering decibel ratings, material composition, and expert installation. Manufacturers bear the responsibility of developing systems that optimally balance noise attenuation with performance. With persistent focus, minimizing the auditory impact of all-terrain vehicles through the pursuit of truly achieving a “quietest atv muffler,” can continue advancing.