An exhaust component designed for single-cylinder, air-cooled engines manufactured by a well-known engine company reduces noise generated during engine operation. This component is typically constructed of steel and designed to withstand high temperatures and pressures associated with exhaust gases. Its function is to direct these gases away from the engine operator, minimizing sound pollution and promoting safer operation.
Effective management of engine exhaust offers several benefits. A primary advantage is noise reduction, creating a more pleasant operating environment and complying with noise regulations in certain areas. Furthermore, a properly functioning exhaust system can contribute to improved engine performance by optimizing backpressure. Historically, advancements in exhaust technology have focused on increasing efficiency and reducing emissions from small engines.
The following discussion will delve into the construction, maintenance, and troubleshooting of these exhaust components, along with an examination of factors influencing their performance and longevity, and available replacement options when servicing small engines.
Maintenance and Longevity Tips
Proper care and maintenance extend the lifespan and ensure optimal performance of the engine exhaust component. Adhering to these guidelines minimizes the need for premature replacement and sustains efficient engine operation.
Tip 1: Regular Inspection: Conduct routine visual inspections for signs of rust, cracks, or physical damage. Early detection of these issues prevents further deterioration and potential exhaust leaks.
Tip 2: Proper Cleaning: Remove accumulated debris, such as grass clippings or dirt, from the exterior surface. This prevents overheating and reduces the risk of corrosion.
Tip 3: Tighten Connections: Periodically check and tighten all bolts and fasteners securing the exhaust component to the engine. Loose connections lead to exhaust leaks and reduced performance.
Tip 4: Avoid Physical Impact: Protect the exhaust component from impacts with solid objects, as dents and deformation compromise its structural integrity and effectiveness.
Tip 5: Engine Tuning: Ensure the engine is properly tuned and operating within its specified parameters. An improperly tuned engine produces excessive heat and exhaust, shortening the lifespan of exhaust components.
Tip 6: Storage Considerations: When storing the equipment for extended periods, apply a rust inhibitor to the exterior surface of the exhaust component to prevent corrosion during storage.
Implementing these maintenance practices prolongs the service life of the exhaust component, contributing to reliable engine operation and minimizing potential repair costs.
The following sections will detail troubleshooting common exhaust problems and identifying appropriate replacement options when necessary.
1. Steel Construction
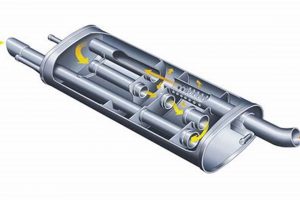
The utilization of steel in the construction of this exhaust component is fundamental to its functionality and durability. The high temperatures generated during engine operation necessitate a material capable of withstanding extreme heat and pressure without deforming or failing. Steel’s inherent strength and thermal resistance make it a suitable choice for this application. For instance, a stainless-steel variant may be used in certain models to further enhance corrosion resistance, especially in environments where the equipment is exposed to moisture or chemicals. The gauge, or thickness, of the steel also plays a critical role, ensuring structural integrity against the pulsating forces of exhaust gases. A thinner gauge may reduce weight but could compromise longevity, whereas a thicker gauge adds weight but increases resistance to physical damage and thermal stress.
The method of steel construction also influences the overall performance. Welded seams, for example, must be robust to prevent leaks that would diminish the component’s sound-dampening capabilities and potentially expose the operator to harmful exhaust fumes. Furthermore, the internal baffles and chambers within the component, which are critical for sound wave attenuation, are typically formed from steel and precisely positioned to optimize noise reduction. The manufacturing process involves stamping, forming, and welding steel components to create a complex internal structure that maximizes sound absorption while minimizing backpressure on the engine. Examples include the use of aluminized steel, which provides a protective layer against corrosion, or the implementation of double-walled construction for improved heat shielding.
In summary, steel construction provides the necessary robustness for enduring the harsh operating conditions encountered by this engine exhaust part. The choice of steel alloy, gauge, and fabrication techniques directly impact the component’s longevity, efficiency, and safety. Understanding the material properties and construction methods is crucial for proper maintenance, troubleshooting, and selecting suitable replacement options, ensuring optimal performance and minimizing potential hazards.
2. Exhaust Efficiency
Exhaust efficiency, in the context of the component designed for engines from a particular manufacturer, pertains to its ability to effectively expel combustion gases while minimizing backpressure. Backpressure, or resistance to flow, can negatively impact engine performance, reducing power output and fuel efficiency. The component’s internal design directly influences exhaust efficiency. For example, improperly sized or obstructed internal passages impede gas flow, increasing backpressure and diminishing engine performance. A well-designed component ensures smooth and unimpeded flow of exhaust gases, leading to improved engine responsiveness and fuel economy. Cause and effect are evident: efficient exhaust expulsion results in enhanced engine operation, while restricted flow creates performance deficits.
The geometry and volume of the internal chambers within the component are critical factors determining its effect on engine operation. Larger chambers generally reduce backpressure, but excessively large chambers may diminish the scavenging effect, where exhaust pulses help draw fresh intake charge into the cylinder. The optimal design balances backpressure reduction with efficient scavenging. Field testing demonstrates that modifications to the internal baffle design can measurably alter engine torque and horsepower. For instance, removing restrictive baffles might increase top-end power, but at the expense of low-end torque, illustrating the trade-offs involved in optimizing exhaust efficiency. Furthermore, the material and surface finish of the internal passages influence gas flow; smoother surfaces reduce friction and promote more efficient exhaust expulsion.
In conclusion, exhaust efficiency is an integral component of the overall engine performance equation. A component that effectively manages exhaust gases not only reduces noise but also contributes to enhanced power, improved fuel economy, and reduced emissions. Understanding the relationship between internal design and exhaust efficiency allows for informed selection, maintenance, and modification, ultimately ensuring the engine operates at its optimal potential. Challenges in optimizing exhaust efficiency include balancing conflicting design goals and adapting to the specific characteristics of different engine models.
3. Engine Compatibility
Engine compatibility is a critical parameter when selecting a component designed for engines manufactured by Briggs & Stratton. The design and specifications are engine-specific, ensuring proper fit, function, and performance. A mismatch can lead to reduced exhaust efficiency, increased noise levels, or even engine damage. This component is not a universal part; its dimensions, mounting points, and internal flow characteristics are tailored to specific engine models or series. For example, a component designed for a small, horizontal-shaft engine will not properly fit or function on a larger, vertical-shaft engine. Using an incompatible component will impair exhaust flow, potentially causing the engine to overheat or lose power.
The cause-and-effect relationship between engine compatibility and performance is direct. A correctly matched component ensures optimal backpressure, which is essential for efficient combustion and power generation. Conversely, an incorrect component can create excessive backpressure, hindering the engine’s ability to expel exhaust gases effectively. The consequences range from reduced fuel efficiency and increased emissions to catastrophic engine failure. For example, if the exhaust outlet diameter of the component is significantly smaller than the engine’s exhaust port, the resulting backpressure can damage exhaust valves and pistons over time. Real-world examples include homeowners experiencing reduced lawnmower performance after installing a non-OEM exhaust part or commercial landscapers facing equipment downtime due to engine damage caused by incompatible components.
Therefore, verifying engine compatibility before installation is paramount. This involves checking the engine model number against the component’s specifications, often listed in parts catalogs or online databases. Understanding the practical significance of engine compatibility prevents costly repairs, extends engine life, and ensures optimal equipment performance. Challenges in achieving compatibility arise from the proliferation of aftermarket parts, some of which may claim universal compatibility but fail to meet the specific requirements of engines manufactured by Briggs & Stratton. Adhering to manufacturer recommendations and verifying part numbers ensures the correct match and avoids potential problems.
4. Sound Attenuation
Sound attenuation is a primary functional characteristic of the specified engine exhaust component. Its importance derives from the need to mitigate noise pollution generated during engine operation. The component’s design incorporates elements specifically engineered to reduce the amplitude of sound waves produced by the combustion process. This noise reduction is achieved through a combination of mechanisms, including sound wave reflection, absorption, and destructive interference. Ineffective sound attenuation results in elevated noise levels, which can violate noise regulations and create discomfort for equipment operators and surrounding communities. The relationship between the component’s internal structure and its sound attenuation capabilities is a direct cause-and-effect relationship; design flaws or damage compromise its ability to reduce noise effectively. An example of this is a crack in the component that allows exhaust gases, and therefore sound waves, to escape without being properly attenuated, leading to a noticeable increase in engine noise.
Further, sound attenuation is not merely about reducing the overall decibel level; it’s also about altering the frequency characteristics of the sound. The component is engineered to suppress certain frequencies that are particularly irritating or harmful to human hearing. This frequency shaping is accomplished through the strategic placement of baffles and resonators within the component’s internal structure. Real-world scenarios illustrate the significance of effective sound attenuation. For instance, construction sites utilizing equipment powered by small engines must comply with noise ordinances to minimize disruption to nearby residents. Similarly, lawn care professionals operating in residential areas rely on equipment with effective sound attenuation to maintain customer satisfaction and avoid noise complaints. The benefits of enhanced sound attenuation extend beyond regulatory compliance; it contributes to a more comfortable and productive working environment, reducing operator fatigue and improving overall quality of life.
In summary, sound attenuation is an indispensable attribute of the exhaust component. Its effectiveness is contingent upon the integrity of the design and materials used in its construction. Understanding the principles of sound attenuation and the mechanisms by which this component reduces noise is crucial for proper maintenance, troubleshooting, and component selection. While challenges exist in balancing sound attenuation with exhaust efficiency and engine performance, the benefits of noise reduction far outweigh the complexities. Future advancements in engine exhaust technology continue to focus on optimizing sound attenuation while simultaneously minimizing backpressure and emissions, ensuring quieter and more environmentally friendly engine operation.
5. Replacement Parts
The availability and quality of replacement components are critical to maintaining the functionality and extending the lifespan of engine exhaust systems. The necessity for exchanging worn or damaged components arises from the continuous exposure to high temperatures, corrosive gases, and physical stress that characterizes engine operation. Selecting appropriate replacement components requires careful consideration to ensure compatibility, performance, and safety.
- OEM vs. Aftermarket Components
Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) parts, sourced directly from the engine manufacturer, guarantee exact fit and adherence to original design specifications. Aftermarket components offer alternative options, often at a lower cost, but may vary in quality and performance. Selecting OEM replacement components ensures optimal engine performance and reliability, while aftermarket options require careful evaluation to assess compatibility and durability.
- Material Composition and Durability
The material composition directly impacts the component’s resistance to corrosion and thermal stress. Replacement components should be constructed from materials equivalent to or exceeding the original specifications. Stainless steel or aluminized steel are often preferred for enhanced durability in harsh operating conditions. The gauge, or thickness, of the steel also affects longevity, with thicker gauges providing greater resistance to physical damage and thermal fatigue.
- Compatibility Verification
Ensuring compatibility with the specific engine model is paramount. Incompatible replacement components can lead to reduced engine performance, increased noise levels, or even engine damage. Verifying the part number against the engine manufacturer’s specifications is crucial to avoid compatibility issues. Failure to verify compatibility can result in improper fitment, reduced exhaust efficiency, and potential safety hazards.
- Installation Procedures and Safety
Proper installation is essential for ensuring the replacement component functions as intended. Adhering to the engine manufacturer’s recommended installation procedures minimizes the risk of damage or injury. Using appropriate tools and safety precautions, such as wearing gloves and eye protection, is crucial when handling exhaust components. Incorrect installation can lead to exhaust leaks, overheating, and potential exposure to harmful gases.
The selection and installation of appropriate replacement components directly influence the overall performance, longevity, and safety of engines and engine-powered equipment. Regular inspection, timely replacement of worn components, and adherence to manufacturer recommendations are vital for maintaining optimal engine operation and minimizing potential risks.
6. Operator Safety
The integrity of the engine exhaust system is paramount to ensure operator safety during the use of equipment powered by engines from a particular manufacturer. A properly functioning exhaust component mitigates several hazards associated with engine operation, directly safeguarding the individual using the equipment.
- Exhaust Gas Exposure
The primary function is to direct harmful exhaust gases away from the operator. These gases contain carbon monoxide, a colorless, odorless, and potentially lethal substance. A compromised exhaust system, such as one with leaks or damage, can allow these gases to accumulate in the operator’s vicinity, leading to carbon monoxide poisoning. The symptoms of carbon monoxide poisoning range from mild headaches and dizziness to loss of consciousness and death. Properly installed and maintained exhaust components effectively channel these gases away from the operator, significantly reducing the risk of exposure. Consider the example of a leaf blower used in an enclosed space; a faulty exhaust system can quickly create a hazardous environment.
- Burn Prevention
The surface of the exhaust component becomes extremely hot during engine operation. Direct contact with the hot surface can result in severe burns. The positioning and shielding of the exhaust system are designed to minimize the likelihood of accidental contact. Heat shields or guards integrated into the design provide a barrier between the hot surface and the operator. Furthermore, the routing of the exhaust pipe away from common operator touchpoints reduces the risk of burns. For instance, a lawnmower with an improperly shielded exhaust system poses a significant burn hazard, particularly to operators wearing shorts or open-toed shoes.
- Noise Reduction and Hearing Protection
Prolonged exposure to high levels of engine noise can lead to hearing damage. The component contributes to noise reduction by muffling the sound of the engine. While the exhaust component alone does not eliminate all engine noise, it plays a crucial role in lowering the overall sound level. Operators should still wear appropriate hearing protection, especially when using equipment for extended periods, but the exhaust component’s noise reduction capabilities reduce the strain on hearing protection and prolong the operator’s auditory health. The decibel reduction provided by a functional component is crucial for ensuring a safer operating environment.
- Fire Hazard Mitigation
A malfunctioning or improperly maintained system can increase the risk of fire. Leaks in the exhaust system can allow hot exhaust gases to come into contact with flammable materials, such as dry grass or fuel spills. The exhaust system’s design and integrity prevent this scenario by containing and directing the exhaust gases safely away from potential ignition sources. Moreover, a properly functioning spark arrestor, often integrated into the component, prevents the emission of hot sparks that could ignite nearby flammable materials. This is particularly important in dry or wooded environments, where the risk of wildfire is elevated.
In conclusion, the integrity of the exhaust component directly influences operator safety by mitigating the risks of exhaust gas exposure, burns, hearing damage, and fire. Regular inspection, proper maintenance, and the use of compatible replacement parts are crucial to ensuring the continued effectiveness of the exhaust system and safeguarding the well-being of the operator.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding the engine exhaust component, offering concise and informative responses to ensure proper understanding and maintenance.
Question 1: What are the primary functions of the engine exhaust component?
The exhaust component serves primarily to reduce engine noise, direct exhaust gases away from the operator, and minimize backpressure to maintain optimal engine performance.
Question 2: How frequently should the engine exhaust component be inspected?
The exhaust component should be visually inspected prior to each use and more thoroughly inspected after every 25 hours of operation or annually, whichever occurs first. This ensures early detection of damage or corrosion.
Question 3: What are the signs of a failing engine exhaust component?
Indications of a failing component include increased engine noise, visible rust or cracks, exhaust leaks, reduced engine performance, and physical damage to the component.
Question 4: Is it safe to operate an engine with a damaged exhaust component?
Operating an engine with a damaged component is not recommended. A compromised exhaust system can expose the operator to harmful exhaust gases, increase the risk of burns, and create a fire hazard.
Question 5: Can any exhaust component be used as a replacement?
No, exhaust components are engine-specific. Replacement requires the use of a component that is compatible with the engine model, either an OEM part or a verified aftermarket equivalent. Incompatible components can impair engine performance and pose safety risks.
Question 6: What safety precautions should be observed when replacing the exhaust component?
Allow the engine to cool completely before commencing any work. Disconnect the spark plug wire to prevent accidental engine start. Wear gloves and eye protection. Ensure proper ventilation. Consult the engine manufacturer’s service manual for detailed instructions.
Proper maintenance and timely replacement of the engine exhaust component are essential for ensuring safe and efficient engine operation.
The following section will provide resources for locating replacement components and accessing additional information on engine maintenance.
Conclusion
This exploration has detailed various aspects of the Briggs & Stratton muffler, encompassing its construction, maintenance, and significance for engine operation. Key considerations include material composition, engine compatibility, sound attenuation, and adherence to safety protocols. Understanding these facets is critical for ensuring both the longevity of the engine and the safety of the operator.
Continued adherence to best practices for maintenance and component selection remains vital. Prioritizing genuine or certified replacement parts and conducting regular inspections can mitigate risks associated with compromised exhaust systems. Responsible ownership and operation of equipment powered by Briggs & Stratton engines necessitates a commitment to these standards.