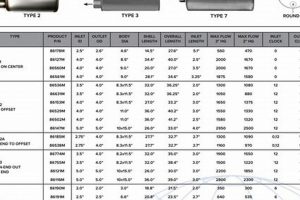
A component designed to reduce the noise output of an internal combustion engine is under consideration. This device, often associated with automotive exhaust systems, serves to minimize the acoustic impact of engine operation on the surrounding environment. For example, the effectiveness of a particular unit can be measured by the decibel reduction achieved during standardized testing procedures.
The importance of effective sound dampening systems stems from both regulatory requirements and consumer demand for quieter vehicles. These systems contribute to noise pollution reduction and improve the overall driving experience. Historically, advancements in materials science and engineering have led to more efficient and durable designs, enhancing both performance and longevity.
Further examination will delve into the specific attributes of this noise reduction component, including its construction, performance characteristics, and suitability for various applications. This investigation will encompass aspects such as material composition, internal baffling design, and compatibility with different engine types and vehicle models.
Maintenance and Optimization Guidelines
The following guidelines offer insight into maximizing the lifespan and performance of automotive sound reduction systems. Adhering to these points can contribute to enhanced vehicle operation and reduced maintenance costs.
Tip 1: Routine Inspection: Regular visual examination of the unit is essential. Look for signs of corrosion, physical damage, or leaks. Early detection of these issues can prevent more extensive and costly repairs.
Tip 2: Address Unusual Noises Promptly: Changes in exhaust sound, such as rattling or excessive loudness, often indicate internal damage or component failure. Ignoring these signals can lead to further deterioration.
Tip 3: Ensure Proper Installation: Precise mounting and secure connections are crucial for optimal performance and longevity. Improper installation can result in premature wear and reduced effectiveness.
Tip 4: Consider Material Composition: When replacing the unit, consider the material used in its construction. Stainless steel offers superior resistance to corrosion compared to aluminized steel, although it may have a higher initial cost.
Tip 5: Monitor Fuel Efficiency: A degraded or damaged unit can impact engine efficiency. Reduced fuel economy may indicate a problem requiring immediate attention.
Tip 6: Professional Assessment: Periodic evaluation by a qualified mechanic can identify subtle issues not readily apparent through visual inspection. Professional diagnostics can ensure continued optimal operation.
By implementing these guidelines, owners can proactively maintain the sound reduction system, ensuring optimal performance, extending its service life, and minimizing the risk of costly repairs. These actions contribute to a more reliable and environmentally responsible vehicle operation.
Subsequent sections will address the environmental impact of these components and advancements in noise reduction technology.
1. Sound Dampening
Sound dampening is a primary function of this automotive exhaust component, serving to mitigate the acoustic energy produced by the engine. Effective sound dampening is essential for compliance with noise regulations and enhancing vehicle comfort.
- Internal Baffle Design
Internal baffles within the unit serve to redirect and dissipate sound waves. The complexity and configuration of these baffles significantly influence the frequency and amplitude of sound reduction. Varied baffle designs are employed to target specific noise frequencies, optimizing overall dampening performance.
- Acoustic Absorption Materials
Certain designs incorporate sound-absorbing materials within the unit’s structure. These materials, often composed of fiberglass or specialized composites, convert acoustic energy into heat, further reducing noise levels. The type and quantity of absorption material impact the overall effectiveness of sound dampening.
- Resonator Chambers
Resonator chambers are tuned volumes designed to cancel out specific frequencies of sound. These chambers operate by creating destructive interference, effectively neutralizing targeted noise components. The dimensions and placement of resonator chambers are critical for achieving optimal sound dampening.
- Shell Construction and Material
The shell construction, including its thickness and material composition, contributes to sound dampening. Denser materials and multi-layered designs offer enhanced noise reduction capabilities. The shell also plays a role in containing and directing sound waves within the internal components.
The integration of internal baffle designs, acoustic absorption materials, resonator chambers, and shell construction are all interconnected and essential for effective sound dampening in these units. Optimization of these features leads to superior noise reduction performance and contributes to compliance with increasingly stringent noise regulations.
2. Exhaust Flow
Exhaust flow, the movement of combustion gases through the exhaust system, is intrinsically linked to the design and performance of this automotive component. The internal structure directly influences the rate and efficiency with which these gases are expelled from the engine. Restriction of exhaust flow can negatively impact engine performance, leading to reduced power output and decreased fuel economy. Conversely, a design that facilitates optimal exhaust flow can enhance engine efficiency and improve overall vehicle performance.
For instance, a system with excessively convoluted internal baffling or a small outlet diameter will create backpressure, hindering the engine’s ability to efficiently expel exhaust gases. This backpressure forces the engine to work harder, resulting in increased fuel consumption and reduced horsepower. In contrast, designs incorporating smoother internal surfaces and larger diameter passages promote a more laminar flow, minimizing backpressure and maximizing engine efficiency. Examples of this can be seen in aftermarket high-performance systems, where modifications focus on optimizing internal flow paths to reduce resistance.
Therefore, the balance between sound dampening and exhaust flow is a critical design consideration. Effective noise reduction must be achieved without unduly restricting the passage of exhaust gases. Challenges arise in developing systems that meet stringent noise regulations while simultaneously preserving optimal engine performance. Advancements in computational fluid dynamics and material science are continually contributing to innovations that address this trade-off, leading to systems that offer both effective sound dampening and efficient exhaust flow.
3. Material Durability
Material durability is a critical factor in determining the lifespan and overall performance of automotive exhaust system components. The capacity of a unit to withstand the harsh conditions within an exhaust system directly influences its ability to effectively reduce noise and maintain optimal exhaust flow over time. Selection of appropriate materials is therefore paramount in ensuring longevity and reliability.
- Corrosion Resistance
The exhaust system is subjected to corrosive elements, including moisture, road salt, and acidic combustion byproducts. Materials lacking sufficient corrosion resistance are prone to degradation, leading to structural failure and reduced effectiveness. Stainless steel, with its high chromium content, offers superior corrosion resistance compared to aluminized steel or mild steel. The choice of material impacts the longevity of the component in corrosive environments.
- Thermal Stability
Exhaust gases can reach extremely high temperatures, especially during periods of high engine load. Materials must possess adequate thermal stability to withstand these temperatures without undergoing deformation, cracking, or other forms of thermal degradation. The thermal properties of the selected material directly influence the component’s ability to maintain its structural integrity and functional performance under extreme operating conditions.
- Mechanical Strength
The exhaust system is subjected to vibrations and mechanical stresses arising from engine operation and vehicle movement. Materials must exhibit sufficient mechanical strength to resist these forces without cracking, fracturing, or experiencing fatigue failure. The mechanical properties of the material, including its tensile strength and yield strength, determine its ability to withstand these mechanical stresses and maintain structural integrity.
- Abrasion Resistance
Road debris, such as rocks and gravel, can impact the exhaust system, causing abrasion and surface damage. Materials with higher abrasion resistance are better able to withstand this type of wear and maintain their structural integrity. The abrasive properties of the material contribute to its ability to resist damage from external impacts and maintain its functional performance over time.
The interplay of corrosion resistance, thermal stability, mechanical strength, and abrasion resistance determines the overall material durability of a sound dampening system. Careful consideration of these factors during material selection is essential for ensuring a long service life and consistent performance, ultimately contributing to reduced maintenance costs and enhanced vehicle reliability.
4. Corrosion Resistance
The longevity and operational effectiveness of exhaust components are intrinsically linked to their inherent corrosion resistance. Exhaust systems are exposed to a confluence of corrosive elements, including moisture, road salts, and acidic byproducts of combustion. These elements can induce rapid degradation of materials lacking sufficient resistance, leading to structural compromise and diminished sound dampening capabilities. The selection of materials with high corrosion resistance is, therefore, a critical factor in ensuring the extended service life of such components. The failure to adequately address corrosion can manifest as premature rust, perforation of the system, and ultimately, a reduction in the component’s capacity to effectively control noise emissions. For instance, systems constructed primarily of mild steel are particularly susceptible to corrosion in regions with heavy winter road salting, requiring more frequent replacement.
Stainless steel, due to its chromium content, exhibits superior resistance to corrosion compared to other common materials like aluminized steel. The chromium forms a passive oxide layer on the surface, preventing further oxidation and significantly extending the component’s lifespan. This enhanced resistance translates directly into reduced maintenance costs and a more reliable, long-term solution for noise abatement. In marine environments, or areas with high humidity, the benefits of utilizing corrosion-resistant materials are even more pronounced. The use of less corrosion-resistant materials will lead to early failures, necessitating frequent maintenance and compromising vehicle performance.
In summary, the selection of appropriate materials exhibiting high corrosion resistance is not merely a design consideration but a critical requirement for ensuring the durability, performance, and longevity of automotive sound control systems. While initial costs may be higher for certain materials, the long-term benefits of reduced maintenance, extended service life, and consistent performance far outweigh the initial investment. Addressing corrosion proactively ensures adherence to noise regulations and enhances the overall reliability of the vehicle.
5. Engine Compatibility
Engine compatibility, in relation to automotive sound reduction components, is a critical determinant of optimal performance and engine health. The design of these components must align precisely with the specifications of the engine for which it is intended. Mismatched components can lead to increased backpressure, reduced power output, and potential damage to the engine itself. The underlying principle is that the exhaust system must efficiently expel combustion gases without impeding the engine’s operational cycle. A correctly matched component facilitates this process, while an incompatible one introduces inefficiencies.
One example highlighting the significance of engine compatibility involves instances where a system designed for a smaller displacement engine is installed on a larger, more powerful engine. The restricted flow capacity of the mismatched system creates excessive backpressure, hindering the engine’s ability to breathe effectively. This can result in a noticeable reduction in horsepower and torque, as well as increased fuel consumption. Furthermore, the increased backpressure can accelerate wear on engine components such as exhaust valves. Conversely, a system designed for a larger engine installed on a smaller engine might result in insufficient backpressure, impacting low-end torque and potentially leading to inefficient combustion. Specific cases where aftermarket modifications disregard engine compatibility often illustrate these negative consequences.
In conclusion, engine compatibility is not merely a desirable attribute but a fundamental requirement for the proper functioning of automotive sound reduction components. The ramifications of incompatibility extend beyond mere performance degradation, potentially leading to engine damage and increased maintenance costs. Thorough consideration of engine specifications and component compatibility is therefore essential for ensuring optimal performance, longevity, and overall vehicle health.
6. Regulatory Compliance
Automotive sound reduction components are subject to stringent noise emission regulations imposed by various governing bodies worldwide. These regulations, often expressed as decibel limits at specified distances and engine operating conditions, necessitate that manufacturers design and produce components that meet these standards. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in significant penalties, including fines, product recalls, and restrictions on sales. Therefore, adherence to regulatory compliance is not merely a matter of ethical practice but a critical business imperative for manufacturers of these systems.
For example, the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) sets noise emission standards for vehicles and aftermarket exhaust systems. Similar regulations exist in the European Union, Japan, and other countries. Components intended for sale in these regions must undergo rigorous testing to demonstrate compliance with the applicable standards. This testing typically involves measuring noise levels under various operating conditions and certifying that the component meets the specified limits. The design of the component, including internal baffling and materials, directly influences its ability to meet these regulatory requirements. Manufacturers must also maintain detailed records of testing and certification to demonstrate compliance to regulatory agencies. Furthermore, regulations often specify requirements for labeling and marking components to ensure that consumers are aware of their compliance status.
In summary, regulatory compliance is a fundamental aspect of the design, manufacturing, and distribution of automotive sound reduction systems. The complex interplay between design considerations, testing procedures, and regulatory requirements underscores the importance of a comprehensive approach to compliance. By prioritizing regulatory compliance, manufacturers can ensure that their products meet legal standards, minimize the risk of penalties, and contribute to a quieter and more sustainable environment. Challenges remain in adapting to evolving regulations and developing innovative technologies that meet both noise reduction and performance requirements.
Frequently Asked Questions About Automotive Sound Reduction Systems
The following section addresses common inquiries regarding the function, maintenance, and performance characteristics of automotive sound reduction systems.
Question 1: What is the primary function of a muffler?
The primary function of a muffler is to reduce the noise produced by an internal combustion engine as exhaust gases are expelled. It achieves this through a combination of internal baffling, resonance chambers, and sound-absorbing materials.
Question 2: How does a faulty muffler affect vehicle performance?
A degraded or damaged muffler can lead to increased backpressure in the exhaust system. This backpressure can reduce engine efficiency, resulting in diminished power output and decreased fuel economy.
Question 3: What are the common signs of muffler failure?
Common indicators of muffler failure include excessive exhaust noise, rattling sounds emanating from the exhaust system, visible corrosion or damage, and reduced fuel efficiency.
Question 4: What materials are commonly used in muffler construction?
Mufflers are typically constructed from steel, aluminized steel, or stainless steel. Stainless steel offers superior corrosion resistance and a longer lifespan compared to the other materials.
Question 5: How often should a muffler be inspected?
A muffler should be visually inspected during routine vehicle maintenance, typically every six months or 6,000 miles. More frequent inspections may be necessary in regions with harsh environmental conditions.
Question 6: Does muffler replacement require specialized tools or expertise?
Muffler replacement often involves specialized tools and a working knowledge of automotive exhaust systems. It is generally recommended that replacement be performed by a qualified mechanic.
In summary, maintaining a properly functioning muffler is essential for noise reduction, optimal engine performance, and regulatory compliance.
The subsequent section will explore the environmental considerations associated with these components.
Concluding Remarks
This exploration has underscored the multifaceted importance of the automotive sound reduction component. From mitigating noise pollution to ensuring optimal engine performance and adhering to regulatory mandates, the system’s role within the vehicle ecosystem is significant. Factors such as material durability, engine compatibility, and internal design characteristics each contribute to the component’s overall effectiveness and longevity.
Continued advancements in materials science and engineering promise further innovations in noise reduction technology. A focus on enhanced durability, improved flow dynamics, and sustainable manufacturing practices will likely define the future of these systems. Prioritizing responsible design and maintenance ensures both regulatory compliance and a quieter, more environmentally conscious automotive landscape.