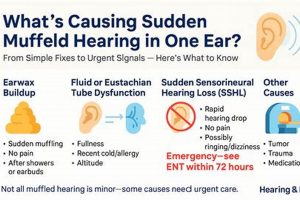
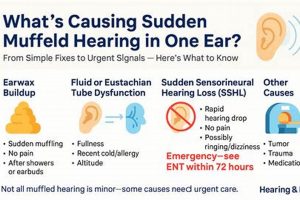
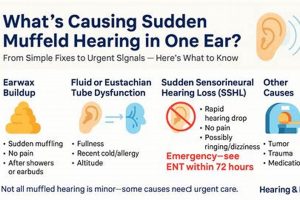
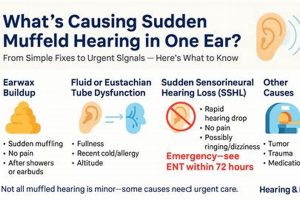
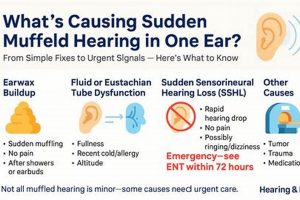
The experience of diminished sound clarity, often described as hearing as if through a barrier, can be unsettling and disruptive. This sensation may arise from various causes affecting the ear canal, middle ear, or even auditory processing within the brain. For example, a buildup of cerumen (earwax) can physically obstruct the passage of sound waves, resulting in reduced auditory acuity. Similarly, inflammation or fluid accumulation in the middle ear, frequently associated with infections, can impede the proper functioning of the ossicles, the tiny bones responsible for transmitting sound.
Addressing diminished auditory perception is crucial not only for maintaining effective communication and engagement with the surrounding environment, but also for preserving overall well-being. Untreated, persistent auditory impairment can lead to social isolation, anxiety, and potentially cognitive decline. Throughout history, various methods have been employed to alleviate this condition, ranging from simple home remedies aimed at wax removal to advanced medical interventions targeting underlying pathological processes. The emphasis on restoring clear auditory perception highlights its fundamental role in human interaction and quality of life.
The following sections will delve into the common causes of this auditory disturbance, effective strategies for self-care and prevention, and instances when seeking professional medical evaluation becomes necessary. Furthermore, the role of specific medical treatments, including pharmaceutical interventions and surgical options, will be examined in detail. The ultimate goal is to provide comprehensive information to facilitate informed decision-making and promote optimal auditory health.
Strategies for Addressing Diminished Auditory Perception
The following guidelines offer practical strategies for mitigating the sensation of reduced sound clarity. Implementing these suggestions may provide symptomatic improvement and promote better auditory well-being. Adherence to these recommendations does not substitute for professional medical advice, particularly if symptoms are persistent or severe.
Tip 1: Cerumen Management: Excessive earwax accumulation is a common cause of auditory obstruction. Employ over-the-counter cerumenolytic agents (earwax softeners) according to product instructions. If self-administration is unsuccessful or concerns exist, consult a healthcare professional for manual removal.
Tip 2: Sinus Pressure Mitigation: Sinus congestion can indirectly affect middle ear pressure. Utilize saline nasal sprays or irrigations to alleviate nasal congestion and promote sinus drainage. Steam inhalation may also provide symptomatic relief.
Tip 3: Eustachian Tube Function Enhancement: The Eustachian tube equalizes pressure between the middle ear and the nasopharynx. Perform gentle Valsalva maneuvers (pinching the nose and gently blowing) to promote Eustachian tube opening. Caution is advised to avoid forceful maneuvers, which can cause barotrauma.
Tip 4: Environmental Noise Reduction: Minimize exposure to excessive noise levels. Employ earplugs or noise-canceling headphones in loud environments to protect auditory structures from damage and reduce auditory fatigue.
Tip 5: Hydration Maintenance: Adequate hydration supports overall bodily functions, including maintaining optimal fluid balance within the middle ear. Ensure sufficient fluid intake throughout the day.
Tip 6: Monitor Allergens: Allergies can cause inflammation and fluid buildup in the ears. Take antihistamines or allergy medications as directed. Minimize exposure to allergens when possible.
Tip 7: Positional Changes: Change positions frequently throughout the day, especially if related to a cold or sinus congestion, to promote natural drainage. Lying down for extended periods can exacerbate fluid buildup.
These strategies aim to address common underlying factors that contribute to diminished auditory perception. Implementing these measures may help restore clearer auditory input and enhance overall sensory experience.
The subsequent sections will provide insights into diagnostic procedures, medical treatments, and preventative measures for maintaining long-term auditory health.
1. Cerumen Impaction Resolution
Cerumen impaction, the excessive buildup and compaction of earwax within the ear canal, stands as a primary and readily addressable cause of diminished auditory perception. Effective resolution of cerumen impaction is frequently a direct pathway to the restoration of normal hearing acuity, thus underscoring its critical role in achieving auditory clarity.
- Physical Obstruction Clearance
Cerumen impaction physically blocks the transmission of sound waves to the tympanic membrane (eardrum). Removing the impacted cerumen creates an unobstructed channel, allowing sound waves to reach the eardrum and initiate the normal hearing process. For instance, a patient experiencing progressively diminished hearing discovers upon examination that the ear canal is completely occluded by a dense plug of earwax; removal immediately restores normal hearing thresholds.
- Improved Sound Conduction
Even partial cerumen impaction can attenuate specific sound frequencies, leading to a distorted or muffled auditory experience. Clearing the ear canal of cerumen optimizes the transmission of the full spectrum of sound frequencies, ensuring a more accurate and complete auditory input. Consider a scenario where an individual struggles to hear higher-pitched sounds; removal of even a small amount of impacted cerumen from the ear canal leads to a noticeable improvement in high-frequency sound perception.
- Enhanced Diagnostic Accuracy
The presence of impacted cerumen can obscure the tympanic membrane, hindering accurate otoscopic examination and preventing the identification of other potential underlying causes of hearing loss or ear discomfort. Resolution of the impaction facilitates a clear view of the tympanic membrane, enabling the detection of infections, perforations, or other abnormalities that may contribute to auditory disturbances. An audiologist cannot accurately assess a patient’s middle ear function if the ear canal is blocked with earwax.
In summary, the resolution of cerumen impaction is often a straightforward and effective means of addressing diminished auditory perception. By removing the physical obstruction, improving sound conduction, and enabling accurate diagnostic assessment, cerumen impaction resolution serves as a crucial first step in restoring normal hearing and enhancing overall auditory well-being. Timely identification and management of cerumen impaction can prevent unnecessary auditory impairment and improve quality of life.
2. Eustachian Tube Function
Eustachian tube function plays a pivotal role in auditory perception. This tube, connecting the middle ear to the nasopharynx, is essential for pressure regulation and fluid drainage, factors directly influencing sound transmission. Dysfunction of the Eustachian tube frequently manifests as a sensation of diminished auditory clarity.
- Pressure Equalization Dynamics
The Eustachian tube’s primary function is to equalize pressure between the middle ear and the external environment. When atmospheric pressure changes, such as during altitude variations or rapid ascents/descents, the Eustachian tube opens to equilibrate pressure. If the Eustachian tube fails to open, a pressure differential develops, leading to a feeling of fullness or diminished hearing. For example, individuals experiencing barotrauma during air travel often report this sensation until the pressure equalizes. Such imbalances directly contribute to reduced auditory acuity.
- Fluid Drainage Mechanisms
The Eustachian tube also facilitates drainage of fluid from the middle ear. In cases of infection or inflammation, fluid accumulation in the middle ear cavity can impede the movement of the ossicles, the tiny bones responsible for transmitting sound vibrations. Impaired drainage, resulting from Eustachian tube dysfunction, leads to a conductive hearing loss, perceived as reduced sound clarity. Chronic middle ear effusions illustrate this principle, where persistent fluid buildup obstructs sound transmission, affecting hearing sensitivity.
- Ventilation and Mucosal Health
Adequate ventilation through the Eustachian tube is crucial for maintaining the health of the middle ear mucosa. Poor ventilation can create a negative pressure environment, predisposing the middle ear to infection and inflammation. Furthermore, chronic inflammation can lead to mucosal thickening and scarring, further impairing Eustachian tube function and contributing to persistent auditory disturbances. A history of recurrent ear infections, often associated with Eustachian tube dysfunction, increases the risk of long-term auditory deficits.
- Impact of External Factors
Various external factors, such as allergies, upper respiratory infections, and environmental irritants, can influence Eustachian tube function. Allergic reactions can cause inflammation and swelling of the nasal passages, indirectly affecting the Eustachian tube’s ability to open and close properly. Similarly, viral or bacterial infections can lead to congestion and obstruction of the Eustachian tube. Exposure to cigarette smoke and other environmental irritants can also exacerbate Eustachian tube dysfunction. Addressing these external factors can mitigate the impact on auditory perception.
In conclusion, Eustachian tube function is integral to maintaining optimal auditory acuity. Dysfunction of this tube leads to pressure imbalances, impaired fluid drainage, and mucosal inflammation, all of which contribute to the sensation of diminished sound clarity. Understanding the dynamics of Eustachian tube function is essential for developing targeted strategies to address and alleviate auditory disturbances.
3. Middle Ear Pressure Equalization
Middle ear pressure equalization represents a critical physiological process directly linked to auditory clarity. A pressure differential between the middle ear and the external environment impedes the tympanic membrane’s ability to vibrate optimally, resulting in the perception of muffled sounds. This imbalance disrupts the efficient transmission of sound waves through the ossicular chain, leading to a diminished auditory experience. Instances such as rapid altitude changes during air travel exemplify this effect; the inability of the Eustachian tube to quickly equalize pressure results in temporary auditory dulling, a common complaint among passengers. Proper middle ear pressure equalization, therefore, is a prerequisite for unimpeded sound transduction and subsequent clarity.
The Eustachian tube serves as the primary mechanism for achieving middle ear pressure equalization. This tube connects the middle ear to the nasopharynx, facilitating the passage of air to regulate pressure. Various factors can impair Eustachian tube function, including infections, allergies, and anatomical abnormalities. When the Eustachian tube is compromised, the middle ear becomes a sealed space, susceptible to pressure fluctuations relative to the external environment. Individuals with chronic Eustachian tube dysfunction often report persistent auditory distortion and a sense of fullness, even in the absence of external pressure variations. Active measures to promote Eustachian tube patency, such as Valsalva maneuvers or medical interventions, address the root cause of the auditory impairment.
Effective middle ear pressure equalization is not merely a passive physiological process but an active mechanism essential for maintaining auditory acuity. Failure to address pressure imbalances leads to persistent auditory distortion and potential complications, such as middle ear effusions or infections. Therefore, strategies targeting Eustachian tube function and promoting pressure regulation are integral to alleviating the sensation of muffled hearing and ensuring optimal auditory health. The understanding of this connection allows for informed interventions aimed at restoring normal middle ear pressure and improving the overall auditory experience.
4. Infection Management Protocols
The presence of infection within the auditory system, particularly in the middle ear, frequently manifests as diminished auditory perception. Infection management protocols directly address this cause of muffled hearing. The inflammation and fluid accumulation associated with otitis media, for example, impede the normal vibration of the tympanic membrane and ossicular chain, resulting in reduced sound transmission. Infection management protocols, encompassing diagnostic procedures and therapeutic interventions, aim to eradicate the infectious agent and resolve the inflammatory response, thereby restoring clear auditory acuity. Without appropriate intervention, persistent infection can lead to chronic middle ear pathology and permanent hearing damage. A child experiencing recurring ear infections, if left untreated, may develop long-term auditory processing difficulties.
Specific infection management protocols involve the administration of antibiotics to combat bacterial infections, decongestants to reduce inflammation, and analgesics to alleviate pain. In severe cases, surgical intervention, such as myringotomy with tympanostomy tube placement, may be necessary to drain fluid from the middle ear and prevent recurrent infections. Accurate diagnosis is paramount; otoscopy, tympanometry, and audiometry assist in identifying the causative agent and assessing the extent of auditory involvement. The effectiveness of infection management protocols is contingent upon timely and accurate diagnosis, adherence to prescribed treatment regimens, and monitoring for potential complications. Post-treatment audiometric testing confirms the restoration of auditory function and detects any residual hearing loss. A patient presenting with acute otitis media undergoes antibiotic therapy and experiences complete resolution of symptoms, with audiometric testing confirming normal hearing thresholds.
In conclusion, infection management protocols represent a crucial component in addressing diminished auditory perception arising from infections within the auditory system. Prompt and appropriate intervention prevents the progression of infection, reduces inflammation, and restores normal auditory function. While effective infection management protocols significantly improve auditory outcomes, challenges remain in addressing antibiotic resistance and preventing recurrent infections. Continued research and adherence to evidence-based guidelines are essential to optimizing infection management and ensuring long-term auditory health. By effectively managing infections, audiologists/ENTs address a significant causative factor, contributing to sustained auditory clarity and overall well-being.
5. Auditory Pathway Decongestion
The sensation of diminished auditory clarity often stems from congestion within the auditory pathway, encompassing the ear canal, middle ear, and inner ear structures. Addressing this congestion is frequently critical to restoring optimal auditory perception and ameliorating the subjective experience of muffled hearing. Specific facets of this process warrant detailed examination.
- Cerumen and Debris Clearance
The accumulation of cerumen (earwax) or other debris within the ear canal represents a common cause of auditory obstruction. Physical removal of impacted cerumen, either manually or through irrigation, directly clears the sound pathway, allowing unimpeded transmission of sound waves to the tympanic membrane. Failure to address cerumen impaction can result in significant attenuation of sound, particularly at higher frequencies, leading to a perceived muffling effect. The complete restoration of auditory acuity following cerumen removal underscores the significance of this aspect of auditory pathway decongestion.
- Middle Ear Fluid Drainage
Fluid accumulation within the middle ear, frequently associated with infections or Eustachian tube dysfunction, impedes the movement of the ossicular chain and dampens sound vibrations. Promoting drainage of this fluid, either through medical management (e.g., antibiotics, decongestants) or surgical intervention (e.g., myringotomy), is essential for restoring efficient sound transmission. Persistent middle ear effusion significantly contributes to conductive hearing loss, characterized by a perceived muffling or reduction in sound volume. Effective drainage alleviates this conductive component, facilitating clearer auditory perception. In example, tympanostomy tube placement allows pressure equalization/fluid drainage.
- Inflammatory Response Mitigation
Inflammation within the auditory pathway, whether stemming from infection, allergy, or other irritants, can compromise the function of auditory structures. Reducing inflammation through appropriate medical management is integral to improving auditory clarity. Inflammatory processes can lead to swelling of the Eustachian tube, impeding pressure equalization, or edema within the inner ear, affecting sensorineural function. Strategies aimed at mitigating the inflammatory response contribute to overall auditory pathway decongestion and improved auditory perception. For example, antihistamines to control allergen-induced inflammatory process.
- Eustachian Tube Patency Restoration
The Eustachian tubes function is to equalize air pressure between the middle ear and the outside environment, which is crucial to hearing. Impaired Eustachian tube function often results in negative pressure in the middle ear, which can impede the movement of tympanic membrane. Restoring normal air pressure can provide a measure of “muffled ear relief”. Strategies include medication to reduce inflammation and/or decongestants to open the tube.
Collectively, these facets of auditory pathway decongestion underscore the multifactorial nature of diminished auditory clarity. Addressing these components, through targeted medical or surgical interventions, contributes to improved auditory perception and alleviation of the subjective experience of muffled hearing. The successful decongestion of the auditory pathway is often a prerequisite for achieving optimal auditory function.
Frequently Asked Questions About Muffled Ear Relief
The following questions address common inquiries regarding the sensation of diminished auditory clarity and strategies for alleviation.
Question 1: What are the primary causes of diminished auditory perception, often described as muffled hearing?
Diminished auditory perception may arise from various factors, including cerumen impaction (earwax buildup), middle ear infections (otitis media), Eustachian tube dysfunction, exposure to loud noise, and, in some cases, sensorineural hearing loss. Each of these conditions affects the transmission or processing of sound, resulting in a subjective experience of muffled or unclear auditory input.
Question 2: When is seeking professional medical evaluation necessary for persistent muffled hearing?
Professional medical evaluation is indicated if muffled hearing persists for more than a few days, is accompanied by pain, drainage from the ear, dizziness, or sudden hearing loss, or if self-care measures prove ineffective. These symptoms may indicate an underlying medical condition requiring specific diagnosis and treatment.
Question 3: What are the potential long-term consequences of untreated muffled hearing?
Untreated muffled hearing can lead to social isolation, communication difficulties, reduced quality of life, and potentially cognitive decline. In some cases, underlying medical conditions causing the muffled hearing may worsen if left unaddressed, leading to permanent hearing loss or other complications.
Question 4: What role does the Eustachian tube play in auditory clarity, and how can its function be optimized?
The Eustachian tube connects the middle ear to the nasopharynx and is responsible for equalizing pressure and draining fluid from the middle ear. Optimizing Eustachian tube function can be achieved through maneuvers such as gentle Valsalva maneuvers (with caution), nasal decongestants (when appropriate), and management of underlying allergies or sinus conditions.
Question 5: Are over-the-counter earwax removal products safe and effective for addressing muffled hearing caused by cerumen impaction?
Over-the-counter earwax removal products can be safe and effective for some individuals with mild cerumen impaction. However, these products should be used with caution and according to product instructions. If symptoms persist or worsen, or if there is a history of ear surgery or eardrum perforation, professional medical evaluation and removal of earwax are recommended.
Question 6: Can exposure to loud noise contribute to muffled hearing, and what preventative measures can be taken?
Exposure to loud noise can indeed cause temporary or permanent muffled hearing due to damage to the delicate hair cells in the inner ear. Preventative measures include wearing earplugs or noise-canceling headphones in loud environments, limiting exposure time to loud noise sources, and maintaining a safe listening volume when using personal audio devices.
The information provided in these FAQs is intended for general knowledge and informational purposes only, and does not constitute medical advice. Consult with a qualified healthcare professional for any health concerns or before making any decisions related to healthcare.
The subsequent section will elaborate on specific medical treatments and preventative strategies for managing various causes of diminished auditory clarity.
Conclusion
The preceding sections have explored various facets of diminished auditory perception and potential strategies for “muffled ear relief.” The discussion encompassed common etiologies such as cerumen impaction and Eustachian tube dysfunction, alongside effective self-care measures and medical interventions. Emphasis was placed on accurate diagnosis, timely intervention, and the importance of professional medical consultation when symptoms persist or worsen.
Sustained attention to auditory health, including proactive management of underlying conditions and adherence to preventative strategies, remains paramount. Individuals experiencing persistent diminished auditory perception are strongly encouraged to seek professional evaluation to ensure appropriate diagnosis and management, thereby mitigating potential long-term consequences and promoting optimal auditory well-being. The preservation of auditory function is essential for effective communication, social engagement, and overall quality of life.