Reduced clarity during telephone conversations is a common issue characterized by speech that is difficult to understand. This degradation in audio quality can manifest as a lack of high-frequency sounds, making words seem indistinct and distant. For instance, a speaker might sound as if they are talking through a barrier, hindering effective communication.
Audio clarity is essential for effective communication in both personal and professional contexts. Its degradation can lead to misunderstandings, frustration, and reduced productivity. Historically, this issue has been addressed through improvements in telephone technology, including better microphones, noise cancellation techniques, and enhanced network infrastructure.
Several factors contribute to diminished audio quality during phone calls. These can range from physical obstructions and hardware malfunctions to network congestion and software glitches. Understanding the root causes is the first step in troubleshooting and resolving the problem. The subsequent sections will delve into these potential causes and provide practical solutions for improving the audio experience.
Troubleshooting Audio Clarity Issues During Phone Calls
The following are recommended steps to address reduced audio clarity experienced during phone conversations. Employing these strategies can enhance communication effectiveness and minimize potential misunderstandings.
Tip 1: Evaluate Device Obstructions: Examine the phones microphone and speaker for any physical impediments. Cases, debris, or even fingers can inadvertently cover these crucial components, diminishing sound quality. Clean the affected areas with a soft, dry cloth.
Tip 2: Assess Network Connectivity: A weak or unstable network connection significantly impacts call quality. Observe the signal strength indicator on the phone. Switching to a stronger Wi-Fi network or relocating to an area with better cellular reception may improve clarity. Consider restarting the modem and router to refresh the network connection.
Tip 3: Investigate Software Glitches: Software malfunctions can disrupt normal phone functionality. Restarting the device clears temporary system errors. Ensure the phone’s operating system and related applications are updated to the latest versions, as these updates often include bug fixes and performance enhancements.
Tip 4: Manage Bluetooth Interference: When using Bluetooth headsets or speakers, potential interference from other electronic devices can degrade audio quality. Move away from sources of interference, such as microwaves or other Bluetooth devices. Attempt using a wired headset for comparison.
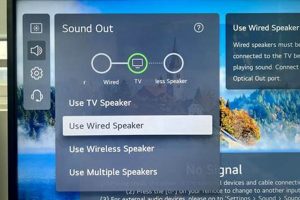
Tip 5: Examine Volume and Audio Settings: Confirm that the phones volume is appropriately adjusted. Navigate to the devices audio settings to ensure that noise cancellation or other audio enhancement features are properly configured. Experiment with different settings to optimize audio output.
Tip 6: Test Alternative Devices: If the issue persists, attempt making calls using a different phone or headset. This can help isolate whether the problem is specific to the original device or a more widespread issue, such as a network problem on the other end of the call.
Tip 7: Contact Service Provider: If the aforementioned steps do not resolve the issue, contact the phone service provider or mobile carrier. There might be underlying network problems or account-specific settings that need adjustment.
Successfully resolving audio clarity problems during phone calls requires a systematic approach. Addressing potential physical, network, software, and hardware-related causes is crucial for enhanced communication.
By methodically applying these strategies, users can diagnose and mitigate audio issues, ensuring a more effective and productive communication experience. The subsequent article sections may detail further advanced solutions and preventative measures.
1. Obstructions
Physical obstructions represent a primary cause of degraded audio quality in telephone communications. These impediments, whether intentional or accidental, directly interfere with the sound waves reaching the device’s microphone, thereby contributing to the phenomenon of indistinct or reduced audio. Identifying and removing these obstructions is often the initial and most straightforward solution to address clarity concerns.
- Dust and Debris Accumulation
Over time, dust, lint, and other small particles can accumulate within the microphone port of a mobile phone. This buildup physically dampens the sound waves, reducing the microphone’s sensitivity and resulting in quieter, less distinct audio transmission. Regular cleaning using compressed air or a soft brush can mitigate this issue.
- Protective Cases and Screen Protectors
Ill-fitting or poorly designed phone cases can partially or completely cover the microphone port. Even seemingly small amounts of blockage can significantly reduce audio clarity. Similarly, screen protectors that extend too far can interfere with the earpiece speaker. Ensuring that cases and protectors are appropriately sized and positioned is crucial.
- Finger Placement and Hand Position
During a phone call, the user’s hand or fingers may inadvertently cover the microphone, particularly on smaller devices. This unintentional blockage directly attenuates the speaker’s voice, resulting in unclear or inaudible transmission to the recipient. Adjusting hand position and grip can prevent this occurrence.
- Presence of Physical Barriers
Environmental factors, such as thick fabrics, surfaces, or positioning the phone near walls, can act as barriers that absorb or deflect sound waves. For example, holding a phone too close to the cheek or shoulder can result in muffled audio. Maintaining a clear line of sight between the speaker’s mouth and the microphone is essential for optimal audio transmission.
In conclusion, physical obstructions represent a tangible and readily addressable cause of diminished phone audio. Consistent maintenance, careful selection of accessories, and conscious awareness of hand and device positioning are practical strategies to minimize these impediments and enhance the clarity of phone conversations.
2. Connectivity
Unreliable network connectivity is a significant contributor to diminished audio clarity during telephone conversations. The quality of the transmitted audio is directly contingent upon the stability and bandwidth of the network connection. Insufficient signal strength, whether from a cellular network or Wi-Fi, results in data packet loss, a fragmented audio stream, and the perception of unclear speech. For example, an individual attempting to participate in a conference call while traveling through an area with intermittent cellular service may experience frequent audio disruptions and difficulty understanding other participants.
The practical implications of connectivity issues extend beyond mere inconvenience. In professional settings, unreliable audio can lead to miscommunication, errors, and reduced productivity. Emergency calls relying on cellular connectivity may experience critical delays in transmission, potentially impacting response times. Furthermore, voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) calls, dependent on stable internet connections, are particularly susceptible to connectivity-related audio degradation. Ensuring a robust and consistent network connection is, therefore, essential for reliable telephone communication.
In summary, stable connectivity is the bedrock of clear audio transmission during phone calls. Understanding the direct correlation between network strength and audio quality allows individuals to take proactive measures, such as relocating to areas with stronger signals or optimizing Wi-Fi configurations, to mitigate potential disruptions. Addressing connectivity limitations is a crucial step in ensuring effective and reliable telephone communication across various contexts.
3. Software
Software plays a critical role in the processing and transmission of audio during phone calls. The performance of audio codecs, operating system functions, and third-party applications directly influences the clarity and quality of the transmitted sound. Software malfunctions, outdated versions, or compatibility issues can introduce distortions and degrade audio, contributing to reduced sound fidelity.
- Codec Inefficiencies
Audio codecs compress and decompress voice data for efficient transmission. Inefficient or outdated codecs can introduce artifacts, reduce the dynamic range, or compromise the overall fidelity of the audio signal. For example, a phone using an older codec over a modern network might transmit audio that sounds compressed and lacking in detail, regardless of network strength.
- Operating System Bugs
The operating system manages the phone’s hardware and software resources, including audio processing. Bugs within the OS can interfere with microphone input, speaker output, or audio routing, leading to distorted or muffled sound. A software update containing a sound driver issue could cause previously clear audio to become distorted.
- Third-Party Application Conflicts
Applications that access the microphone or audio output can sometimes conflict with the phone’s native calling functions. Conflicting apps may monopolize audio resources or introduce unwanted sound processing, resulting in decreased clarity during calls. For instance, a voice recording app running in the background could interfere with a phone call’s audio pathway.
- Outdated Firmware
Phone firmware manages low-level hardware operations. Outdated firmware might lack optimizations or bug fixes necessary for clear audio transmission. Neglecting to update firmware can leave a device vulnerable to audio processing errors, making sound reproduction unclear. A user who postpones a necessary firmware update might notice a gradual decrease in clarity during phone calls.
These software-related factors highlight the importance of maintaining updated software, resolving application conflicts, and ensuring compatibility between codecs and hardware. Systematically addressing these factors is critical for preserving optimal audio clarity and mitigating the phenomenon of muffled phone sounds.
4. Hardware
The physical components of a telephone, collectively referred to as hardware, are foundational to audio quality. Malfunctions or degradation within these components directly impact the clarity of transmitted and received sound. Hardware limitations or failures manifest as distorted, weakened, or altogether absent audio, contributing significantly to the issue of reduced clarity during phone conversations.
- Microphone Malfunctions
The microphone’s primary function is to capture sound waves and convert them into electrical signals for transmission. Degradation, damage, or manufacturing defects within the microphone can impair its ability to accurately capture sound, resulting in weak, distorted, or muffled audio. A common example is a microphone diaphragm that has become stiff or damaged, leading to a reduced sensitivity and an inability to capture quieter sounds effectively. This directly affects the clarity of the speaker’s voice as perceived by the recipient.
- Speaker Degradation
The speaker is responsible for converting electrical signals back into audible sound waves. Over time, speakers can degrade due to physical stress, exposure to moisture, or damage to the speaker cone. This degradation manifests as distorted audio, reduced volume, or a lack of clarity, particularly in the higher frequencies. Consequently, the recipient may struggle to understand the speaker’s message due to the compromised audio output.
- Damaged Audio Jack
When using wired headphones or headsets, the audio jack serves as the connection point for transmitting audio signals. A damaged, corroded, or improperly seated audio jack can introduce interference, resulting in static, crackling sounds, or complete audio loss. This directly affects the listener’s ability to clearly hear the speaker’s voice, contributing to the perception of reduced audio clarity during the call.
- Internal Circuitry Problems
Phone handsets contain complex internal circuitry to route and process audio signals. Problems like loose connections, damaged components or shorts can disrupt the flow and processing of audio signals, leading to distorted or muffled sounds. A break in a circuit could cause improper amplification or filtering, resulting in low volume or distorted output.
Hardware integrity is essential for maintaining optimal audio clarity during phone calls. From the microphone capturing sound to the speaker reproducing it, each component plays a critical role. Addressing hardware issues, such as replacing damaged components or repairing faulty connections, is often necessary to resolve diminished clarity issues and restore effective communication.
5. Interference
External interference represents a significant source of diminished audio clarity during telephone conversations. Electromagnetic radiation and physical obstructions disrupt audio signal integrity, leading to the perception of muffled sound.
- Electromagnetic Interference (EMI)
EMI originates from various electronic devices emitting electromagnetic radiation, which can interfere with telephone signals. Common sources include microwaves, computers, and other wireless devices. When telephone equipment is situated near these sources, the EMI can introduce noise, distortion, or signal degradation. The consequences of EMI include reduced audio quality, crackling sounds, or complete signal loss during calls. Mitigating EMI often requires physical separation of telephone equipment from potential sources of electromagnetic radiation.
- Radio Frequency Interference (RFI)
RFI, a subset of EMI, specifically refers to interference from radio waves. RFI can originate from radio transmitters, broadcast towers, or amateur radio equipment. These radio waves can contaminate telephone signals, resulting in audible noise or distortion. RFI is particularly problematic in areas with high densities of radio transmitters. Shielding cables and equipment, as well as relocating telephone devices away from suspected RFI sources, are common mitigation strategies.
- Physical Obstructions and Signal Attenuation
Physical barriers can obstruct or weaken telephone signals, particularly wireless signals. Walls, buildings, and terrain can attenuate signal strength, leading to reduced audio quality. This is particularly relevant for cellular phone calls in areas with poor signal coverage. Relocating to an area with a stronger signal or utilizing signal boosters can alleviate signal attenuation issues. Dense foliage and metallic materials can further exacerbate signal attenuation.
- Bluetooth Interference
Bluetooth devices operating in close proximity to telephone equipment can also cause interference. Bluetooth signals, used for wireless headphones, speakers, and other accessories, operate in the same frequency range as some telephone systems, leading to potential conflicts. Interference from Bluetooth devices can result in audio distortion, signal dropouts, or reduced range. Maintaining adequate separation between Bluetooth devices and telephone equipment, or switching to a wired connection, is often necessary to mitigate Bluetooth interference.
These interference factors highlight the vulnerability of telephone audio signals to external influences. Recognizing and addressing these sources of interference is crucial for maintaining optimal audio clarity and minimizing disruptions during communication. Shielding, physical separation, and utilizing alternative communication methods when interference is unavoidable are key strategies for ensuring reliable audio quality.
6. Settings
Phone audio clarity is significantly influenced by device configuration. Incorrect or suboptimal configuration settings directly contribute to diminished audio quality, often perceived as muffled sound. A methodical examination and adjustment of these settings can significantly improve auditory performance.
- Volume Levels
Inadequate volume levels, whether for the earpiece, speakerphone, or microphone, are a common cause of perceived audio muffling. If the earpiece volume is set too low, incoming audio becomes difficult to hear clearly. Conversely, if the microphone volume is too low, the outgoing audio may be weak and indistinct. Adjusting these volume levels, typically through the devices settings menu, is a primary step in troubleshooting audio clarity problems. For example, during a conference call, a participant may report that a speaker sounds muffled solely due to the speaker’s microphone volume being set too low.
- Noise Cancellation Features
Modern phones often incorporate noise cancellation features intended to reduce background noise and improve call clarity. However, misconfigured or faulty noise cancellation settings can paradoxically degrade audio quality. Overly aggressive noise cancellation can suppress desired sounds, making the speaker’s voice sound distorted or muffled. Disabling or adjusting noise cancellation settings can sometimes resolve clarity problems. In a noisy environment, an inappropriately configured noise cancellation system may remove speech elements along with the background noise, leading to reduced speech intelligibility.
- Equalizer Settings
Some devices offer equalizer settings, allowing users to adjust the frequency response of audio output. Incorrect equalizer configurations can emphasize certain frequencies while suppressing others, resulting in an unbalanced and unnatural sound. A setting that excessively boosts low frequencies can make speech sound boomy and indistinct, while over-emphasizing high frequencies can create a harsh or tinny sound. Returning the equalizer to its default settings or experimenting with different profiles can often improve audio clarity. A user who has inadvertently set the equalizer to a bass-heavy configuration may experience muffled voices until the settings are adjusted.
- Audio Codec Preferences
Advanced users may have the option to select different audio codecs for voice communication. Certain codecs prioritize bandwidth efficiency over audio quality, potentially resulting in reduced fidelity. Selecting a higher-quality codec, if available, can improve audio clarity. The device must support the chosen codec, and both parties involved in the call must use compatible settings for the changes to be effective. An inappropriate codec choice can cause reduced bandwidth, resulting in robotic or choppy audio for both parties.
A systematic approach to configuring settings related to volume, noise cancellation, equalization, and audio codecs is crucial for optimizing audio quality. Addressing these software-related aspects is often necessary for resolving perceived muffling issues and ensuring clear communication during phone calls. Users should consult device manuals or online resources for specific instructions on adjusting these settings.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following addresses common inquiries regarding diminished audio clarity experienced during telephone communications. These questions aim to provide comprehensive insights into potential causes and remedial measures.
Question 1: What are the most prevalent causes of muffled phone audio?
Physical obstructions blocking the microphone or speaker, weak network connectivity (cellular or Wi-Fi), software glitches, and hardware malfunctions (e.g., a damaged microphone or speaker) constitute the most frequently encountered causes.
Question 2: How does network connectivity influence phone audio quality?
Network connectivity plays a vital role. An unstable or weak connection results in packet loss, leading to distorted or incomplete audio transmission. A stronger signal typically translates to improved audio clarity.
Question 3: Can software settings impact phone audio?
Software settings, particularly volume levels, noise cancellation, and equalizer configurations, significantly affect perceived audio quality. Incorrect settings can inadvertently diminish clarity or distort the audio signal.
Question 4: How can hardware problems contribute to diminished audio clarity?
Damaged microphones, speakers, or audio jacks introduce distortions or complete audio loss. A faulty microphone fails to accurately capture sound, while a degraded speaker cannot faithfully reproduce audio signals.
Question 5: Is electromagnetic interference a common cause of muffled phone audio?
Electromagnetic interference (EMI) from nearby electronic devices can indeed disrupt telephone signals, leading to noise, distortion, or complete signal loss. Separation from EMI sources is often necessary.
Question 6: What steps can be taken to troubleshoot and resolve muffled phone audio?
Begin by inspecting the phone for physical obstructions. Ensure a strong network connection. Check and adjust software settings. Test alternative devices (headsets). As needed, contact the service provider for assistance.
Effective diagnosis and resolution of audio clarity issues often necessitate a systematic approach, addressing potential physical, network, software, and hardware-related factors. Prioritizing optimal communication is the central objective.
The next article sections will delve into advanced solutions and preventative measures designed to ensure consistently high-quality audio experiences.
Concluding Remarks
The preceding analysis has illuminated various factors contributing to reduced audio clarity during phone calls. Physical obstructions, network instabilities, software misconfigurations, hardware malfunctions, and electromagnetic interference are all potential sources of this pervasive issue. Effective resolution necessitates a methodical approach, addressing each of these factors systematically.
Maintaining clear communication channels is crucial in both personal and professional spheres. Vigilance in identifying and rectifying the causes that lead to phone sounds muffled is vital to ensuring reliable and effective communication. Continued advancements in telecommunications technology offer the prospect of mitigating these challenges, but proactive user engagement remains fundamental in securing optimal audio performance. Prioritizing signal clarity is essential for effective information exchange.




![Fix: Why Does One of My AirPods Sound Muffled? [SOLVED] Best Mufflers for Cars & Trucks | Performance, Sound & Durability Upgrades Fix: Why Does One of My AirPods Sound Muffled? [SOLVED] | Best Mufflers for Cars & Trucks | Performance, Sound & Durability Upgrades](https://dnamufflers.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/02/th-396-300x200.jpg)